Your content sounds different depending on the channel: upbeat on social, formal in emails, and flat on the blog. That jarring inconsistency costs attention, trust, and conversions the moment a reader moves between touchpoints. Recognizing which words, rhythms, and visuals break continuity is the first step toward fixing it.
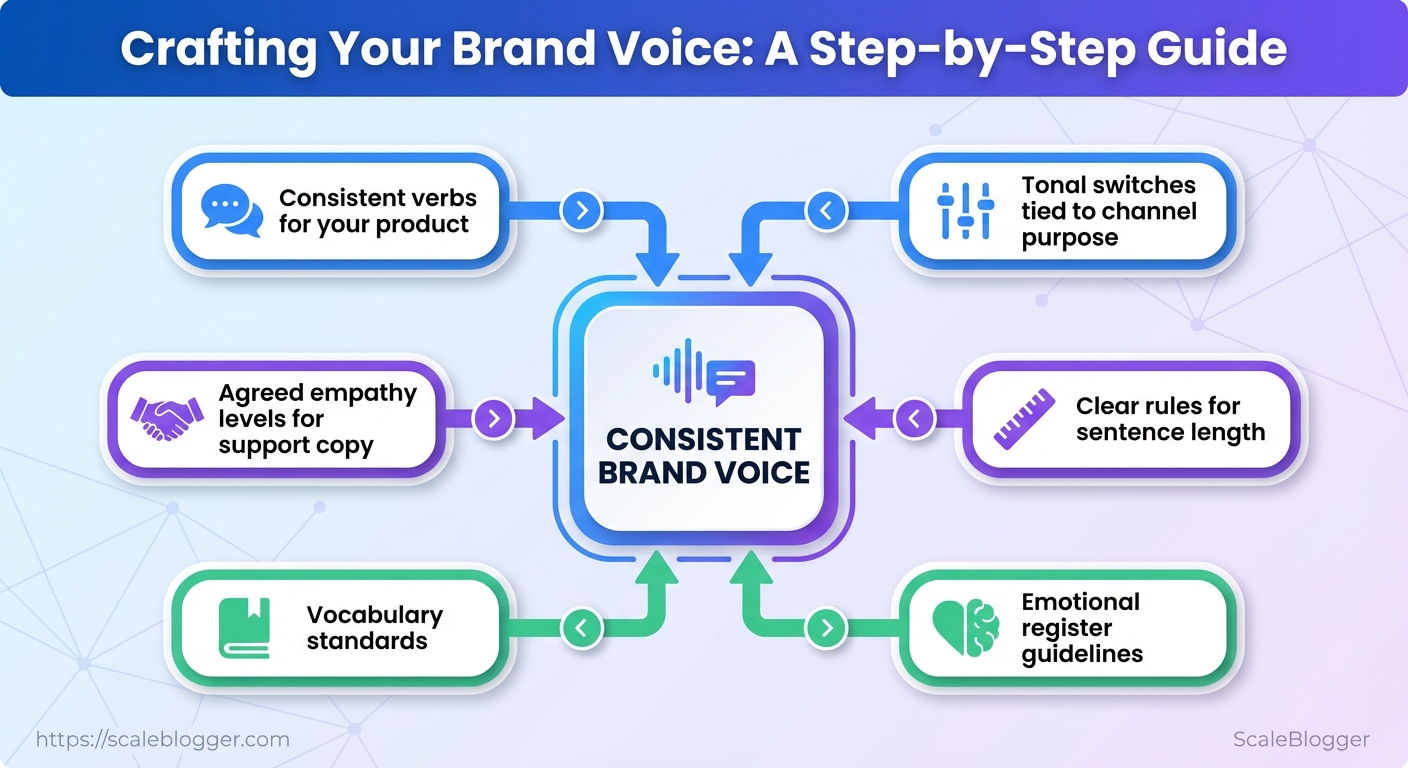
Most teams treat brand voice as an afterthought—a vague note in a deck rather than a living system. Without clear rules for sentence length, vocabulary, and emotional register, creators default to their personal habits, and the resulting noise confuses customers more than it clarifies. The practical challenge is not inventing a voice but operationalizing it so every writer, campaign, and tool produces coherent output.
Stabilize those decisions by aligning editorial rules to measurable outputs: consistent verbs for your product, agreed empathy levels for support copy, and a small set of tonal switches tied to channel purpose. Try Scaleblogger to automate brand voice rollouts.
What You’ll Need (Prerequisites)
Start with access to the systems and artifacts that let you measure, iterate, and make decisions quickly. Without analytics, a living content inventory, a clear owner, and basic copy skills, any content automation or AI pipeline becomes guesswork. The practical prerequisites below ensure the team can evaluate performance, enforce brand voice, and act on data.
Analytics access: Full read (and ideally edit) access to Google Analytics/GA4 or an equivalent analytics platform so traffic, events, and conversion funnels can be queried.
Content inventory spreadsheet: A centralized inventory (CSV or Airtable) listing URLs, publish date, topic cluster, traffic, conversions, and content score.
Stakeholder list: Contact details and roles for the editorial lead, a primary decision-maker, and technical owner (CMS/devops) so approvals and fixes move quickly.
Examples of existing content: Copies (links or exports) of 5–10 top-performing and 5–10 low-performing posts to use as calibration examples for voice, structure, and gaps.
Basic copywriting knowledge: Familiarity with headline frameworks, UX copy patterns, and brand voice/tone guidelines so automated suggestions remain on-brand.
Tools & quick setup actions
- Grant analytics access: Give the editorial lead
vieweroranalystpermissions in GA4 and Search Console. - Export a content inventory: Run a crawl and export URLs, titles, meta, and traffic into a single sheet within one day.
- Assign a decision-maker: Name one person who can sign off on style and publishing changes.
- Collect representative examples: Pull 10 definite examples of high/low performers into a shared folder.
- Ensure GA4 and Search Console are linked and data collection is verified.
- Create a canonical content inventory template in Google Sheets or Airtable.
- Assign the primary decision-maker and add them to the inventory and analytics access lists.
Quick reference of required tools, why they’re needed, and free vs paid alternatives
| Tool/Resource | Purpose | Free Option | Paid Option |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analytics | Traffic, funnels, event tracking | Google Analytics / GA4 (Free) | Adobe Analytics (custom pricing) |
| Content Inventory | Centralized URL + metrics | Google Sheets (Free) | Airtable ($10+/user/mo) |
| Style Guide Template | Brand voice, dos/don’ts | Google Docs template (Free) | Frontify (starts ~$19/mo/user) |
| Collaboration | Approvals, notifications | Slack (Free tier) | Microsoft Teams / Slack Standard ($6-12/user/mo) |
| Tone Testing | Readability & tone checks | Hemingway App (Free web) | Grammarly Premium ($12/mo) |
Key insight: The table highlights low-friction free options for immediate setup and paid tools for scaling governance and automation; begin with the free stack, then add paid tools where governance or volume requires it.
Understanding these prerequisites removes friction during implementation and keeps iterative work focused on measurable outcomes. When teams bring these elements together, content automation projects move from experiments to predictable systems. For a practical automation partner that helps wire these pieces together, consider Scaleblogger.com.
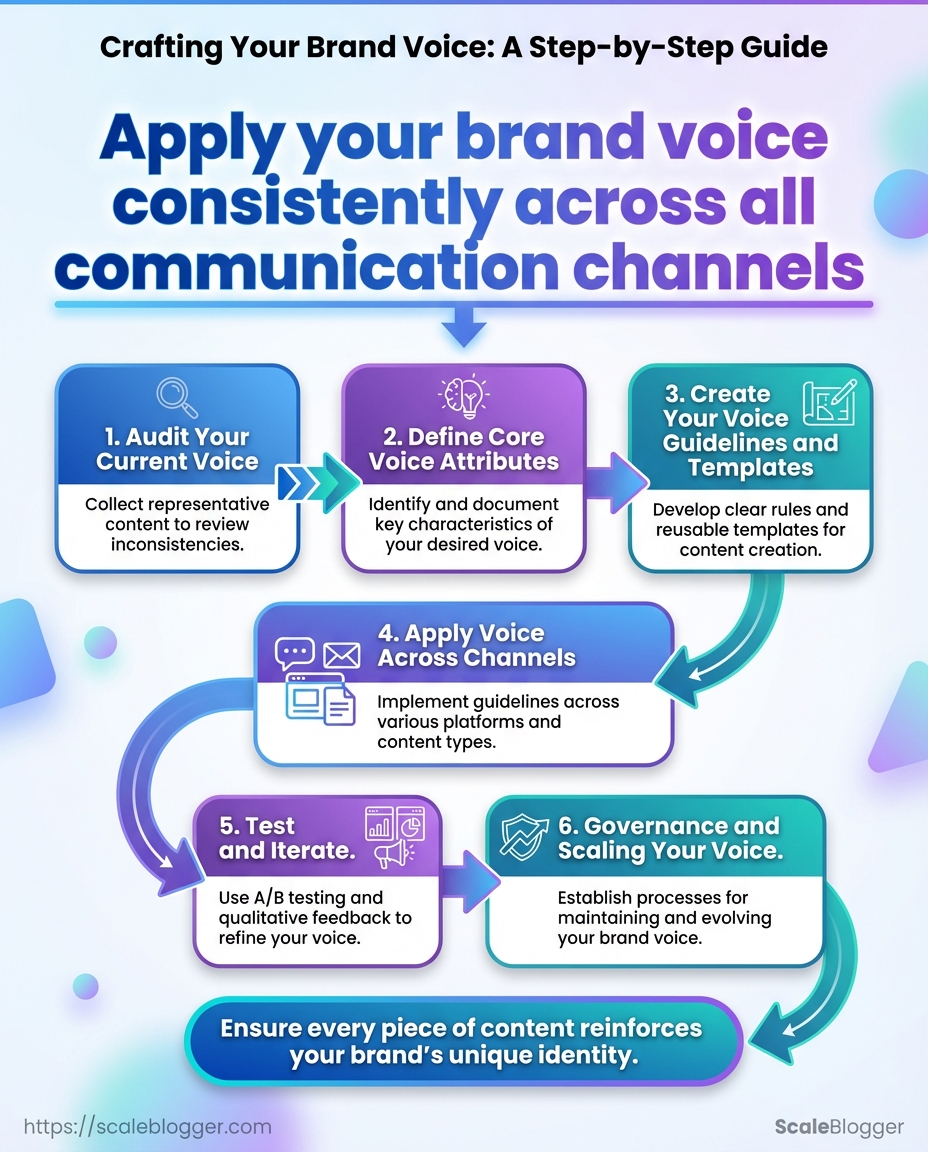
Audit Your Current Voice
Start by treating the audit like a forensic review of everything your brand says. Collect representative samples across channels, score them against a simple rubric, and produce an audited spreadsheet plus a one-paragraph synthesis that drives decisions. This makes subjective judgments repeatable and surfaces where automation or editorial guidelines will have the biggest impact.
Collect Samples and Scope What to collect: homepage headline, pricing page copy, onboarding email, Twitter thread, support FAQ, two high-traffic blog posts, product release note, and a customer success case. How much: 12–20 samples gives statistical signal without becoming unwieldy; prioritize high-traffic and high-conversion content. * Sampling tip: Pull the top-performing pages from analytics, the last 10 customer emails, and the most-shared social posts.
Scoring Rubric (3–5 dimensions) Clarity: Does the text communicate the idea in one scan? (1–5)
Personality: How distinct and on-brand is the voice? (1–5)
Formality: Is the register appropriate for the audience? (1–5)
Consistency: Does the piece match brand guidelines and other samples? (1–5)
Actionability: Does the text compel the desired next step? (optional) (1–5)
How to compute an overall consistency score 1. Average the four core dimensions (Clarity, Personality, Formality, Consistency) for each item. 2. Weight samples by impact: multiply each item’s average by a traffic/importance factor (e.g., homepage = 3, blog post = 1). 3. Sum weighted scores and divide by total weight to get a 0–5 consistency index. 4. Flag anything under 3.0 for immediate rewrite and anything 3.0–4.0 for guidelines + microtests.
Provide a sample scoring rubric with example entries to copy into the reader’s audit spreadsheet
| Content Item | Channel | Clarity (1-5) | Personality (1-5) | Formality (1-5) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homepage headline | Website | 5 | 4 | 3 | Clear value proposition; slightly formal |
| Pricing page copy | Website | 4 | 3 | 4 | Technical terms could be simplified |
| Onboarding email | 4 | 5 | 3 | Friendly, strong CTA | |
| Twitter thread | Social | 3 | 5 | 2 | High personality, inconsistent terminology |
| Support FAQ | Help Center | 5 | 2 | 5 | Clear and formal; lacks brand voice |
| Blog post — SEO guide | Blog | 4 | 3 | 3 | Helpful but variable headings |
| Product release note | Blog/Email | 3 | 3 | 4 | Jargon-heavy |
| Case study | Website | 4 | 4 | 4 | Good storytelling; tone varies by author |
Key insight: The table shows that owned channels (homepage, FAQ) tend to score higher on clarity and formality, while fast-publish channels (social, release notes) drop in consistency and require templating or editorial guards.
Deliverables 1. Audited spreadsheet with sample rows, dimension columns, raw scores, weights, and overall index. 2. One-paragraph summary that states the consistency index, top 3 gaps, and recommended first actions.
Practical next action: run this audit, then convert recurring weaknesses into templates and content scoring automations—Scaleblogger.com can automate the scoring pipeline and push results into your editorial workflow. Understanding the current voice lets teams move faster while keeping every piece recognizably yours.
Define Core Voice Attributes
Start by picking 3–5 voice attributes that will consistently shape every headline, paragraph, and CTA. Choose attributes that reflect the brand’s audience expectations and business goals, then phrase each attribute in actionable language so writers can use them without guessing.
Clarity Definition: Communicate ideas directly and unambiguously. Do: Use short sentences and concrete nouns. Don’t: Lean on jargon or ambiguous phrases. Correct: “Install the plugin and connect your analytics account.” Incorrect: “Leverage integrations to streamline analytics.”
Warmth Definition: Create approachable, human-first copy that builds rapport. Do: Use conversational wording and inclusive language. Don’t: Sound too familiar or use gimmicky slang. Correct: “We’ll walk you through the setup step‑by‑step.” Incorrect: “Get this done, bro—fast and easy.”
Authority Definition: Present confident, evidence-based guidance. Do: Cite specifics, use decisive verbs. Don’t: Hedge with weak qualifiers (maybe, possibly). Correct: “Use monthly cohorts to track retention.” Incorrect: “You might want to try cohorts to see what happens.”
Simplicity Definition: Strip unnecessary complexity; make the next action obvious. Do: Favor one idea per paragraph and clear CTAs. Don’t: Cramp multiple calls-to-action into the same section. Correct: “Download the checklist.” Incorrect: “Learn more, sign up, and download—pick your path.”
Technicality Definition: Calibrate technical depth to audience expertise. Do: Provide code examples or config snippets for technical readers. Don’t: Dump raw specs without explanation for non-technical audiences. Correct: “Add X-Header: true to enable the webhook.” Incorrect: “Adjust headers to ensure webhook activation.”
Choose and Phrase Your Voice Attributes
| Attribute | Definition | Do (Example) | Don’t (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clarity | Communicate directly with concrete language | Use short sentences; concrete nouns | Use vague marketing jargon |
| Warmth | Friendly, human tone that builds rapport | Conversational phrasing; inclusive words | Overfamiliar slang or memes |
| Authority | Confident, evidence-led guidance | Cite specifics; decisive verbs | Hedging and weak qualifiers |
| Simplicity | Minimal cognitive load; clear next steps | One idea per paragraph; clear CTA | Multiple CTAs; dense blocks |
| Technicality | Appropriate depth for reader skill level | Provide code snippets for devs |
Dump specs without context |
Key insight: Defining these attributes reduces revision cycles and produces copy that performs predictably across formats. When onboarding writers, use the table above as a quick-reference voice matrix and pair it with sample copy tests.
- Draft 3 attribute-focused style examples per content type (blog, landing, email).
- Run a small A/B read with stakeholders and two target readers.
- Capture feedback, revise phrasing, and lock the final attribute set.
Validation: Obtain stakeholder sign-off via a short checklist indicating each attribute is understood and actionable. Integrate the final phrasing into the content brief and the voice matrix used by the editorial team or automation platform like Scaleblogger.com. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, the voice becomes a tool for scaling consistent, high-performing content.
Create Your Voice Guidelines and Templates
Start by defining a compact, practical voice guide that writers can open and use in minutes. The aim is not academic completeness but operational clarity: what to say, how to say it, and quick templates that remove friction. Build the guide so a contractor, junior writer, or automation script can produce on-brand content reliably.
Essential style guide sections
Purpose: Short mission statement for the brand voice (1–2 sentences).
Audience: Primary reader archetype and secondary segments.
Voice pillars: Three core attributes (e.g., confident, approachable, data-driven) with 1-sentence behavior rules.
Tone variants: How tone shifts by content type — blog, landing page, email, social.
Grammar and punctuation: Firm rules on contractions, Oxford comma, numbers, abbreviations.
Forbidden language: Words/phrases to avoid and acceptable alternatives.
Boilerplate snippets for quick start
- Brand opening: Two sentence company intro usable at top of posts.
- Author bio: One-line and full bio templates.
- CTA family: Three CTAs by intensity — informational, conversion, high-urgency.
- SEO meta template:
Title: [Primary keyword] — [Benefit] | BrandandMeta: [Hook] • [What reader learns] • [CTA]
- Create a
voice.json(or a markdown single-file) that lists voice pillars, tone rules, and boilerplate snippets. - Store canonical assets in a single source of truth (see next section), and link templates to content briefs so automation can fetch them.
- Convert 4–6 high-frequency templates into content blocks for reuse in CMS or automation pipelines (intro, conclusion, section opener, quote frame).
Recommended storage and versioning
- Primary storage: Single-source repository — a Git repo or shared drive with
voice.mdandvoice.json. - Versioning practice: Tag releases for major updates and use PRs for proposed changes.
- Access: Role-based editing so editors and engineers can update different parts safely.
Onboarding exercise to validate the guide usability
- Give a new writer a 300-word brief and the guide.
- Ask for a draft within 48 hours using only the guide and templates.
- Review against a 5-point rubric (voice match, tone accuracy, CTA usage, SEO meta, boilerplate compliance).
- Iterate the guide based on failure modes found in two trials.
Include the guide in automation workflows so templates feed drafts automatically; tools like Scaleblogger.com can integrate voice assets into AI pipelines and content scoring. Understanding these principles helps teams produce consistent content faster while keeping creative decisions at the team level.

Apply Voice Across Channels (Numbered Steps)
Apply the brand voice deliberately and sequentially so each channel feels like the same author writing in different formats. Start with the highest-impact touchpoints (homepage, emails) and progress to channels that amplify and reinforce the voice (social, docs, ads). The steps below are actionable and time-boxed so teams can roll this out in two weeks with clear owners, immediate QA checks, and lightweight A/B testing guidance.
- Align the homepage copy to the voice
- Owner: Content Lead / Product PM
- Time estimate: 6–8 hours (rewrite + staging)
- QA checks: tone match to style guide; headline clarity;
H1voice parity; conversion flows intact - Success criteria: bounce rate stable or improved; +5–10% click-to-signup after 7 days
- Update core email templates
- Owner: Email Specialist
- Time estimate: 4–6 hours (3 templates: welcome, activation, nurture)
- QA checks: subject-line voice alignment;
preheaderreadability; mobile preview - Success criteria: open rate lift or stable with higher reply/CTA clicks
- Refresh social profiles and pinned posts
- Owner: Social Manager
- Time estimate: 3–5 hours (profiles, 6 posts)
- QA checks: bio voice consistency; visual/caption tone match; pinned post that models voice
- Success criteria: engagement rate steady or higher; new follower sentiment aligned
- Publish docs, FAQ, and help center content
- Owner: Documentation Owner / Support Lead
- Time estimate: 6–10 hours (top 10 articles)
- QA checks: answer tone consistent; searchability (
keywordspresent); readability score - Success criteria: reduced support tickets for covered topics; helpfulness rating positive
- Launch ads and campaign copy
- Owner: Growth Marketer
- Time estimate: 4–8 hours (ad sets + landing variants)
- QA checks: headline/CTA voice match; compliance with ad platform policies; tracking tags set
- Success criteria: CTR within expected range; CPC stable or better; positive ad feedback
- Run lightweight A/B tests (parallel)
- Owner: CRO / Data Analyst
- Time estimate: setup 2–4 hours; run 7–14 days
- QA checks:
UTMaccuracy; randomization validation; enough sample size forconversion_ratecomparison - Guidance: test one variable at a time (headline OR CTA OR image), run on small traffic slices, and promote winning voice variants into canonical templates
- Post-rollout QA sweep and playbook update
- Owner: Content Ops
- Time estimate: 4 hours
- QA checks: checklist completion; stakeholder sign-off; update voice snippets library
- Success criteria: team can deploy consistent voice without ad-hoc approvals
Key features of a successful rollout:
- Ownership clarity: Single owner per channel with backups.
- Time-boxed edits: Short windows reduce drift and rework.
- Immediate QA: Quick checks catch glaring mismatches early.
- Data-driven validation: Use simple metrics before making global changes.
Two-week rollout timeline with owners, time estimates, and QA checks for each channel action
| Day/Week | Action | Owner | Time Estimate | QA Check |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Homepage rewrite & staging | Content Lead / Product PM | 6–8 hours | Headline voice match; H1 parity; conversion flows tested |
| Day 3 | Email templates (welcome, activation, nurture) | Email Specialist | 4–6 hours | Subject tone; preheader clarity; mobile preview |
| Day 5 | Social profiles + 6 posts | Social Manager | 3–5 hours | Bio consistency; caption tone; pinned post live | | Week 2 | Docs & FAQ (top 10 articles) | Documentation Owner / Support Lead | 6–10 hours | Tone in answers; search keywords; readability check | | Week 2 | Ads & campaign copy + landing variants | Growth Marketer | 4–8 hours | Headline/CTA match; policy compliance; UTM tags set |
Key insight: The timeline front-loads high-impact channels (homepage, email) so voice changes influence downstream assets, while week-two work builds support and amplification. Use one controlled A/B test per channel to validate changes before scaling.
Use a short playbook with example snippets and voice tokens for each channel so future contributors match the same language without repeated reviews. Consider AI content automation for templating voice variants and accelerating rollout across many assets. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
Test and Iterate (A/B and Qualitative Testing)
Start with a clear, falsifiable hypothesis and treat each test as an experiment whose outcome informs the next decision. A/B testing answers “which variant performs better on a specific metric,” while qualitative testing explains why users behave that way. Combine both to move from intuition to repeatable results.
- Define the hypothesis and primary metric.
- Define the hypothesis in one sentence (e.g., “Changing H1 from benefit-led to feature-led will increase organic CTR by 8%”).
- Choose a single primary metric and one secondary metric to avoid shifting goals (
CTR,time on page,bounce rate, orscroll depth). - Segment the audience and determine sample size.
- Split by meaningful segments (new vs returning, desktop vs mobile).
- Estimate sample size using baseline conversion and desired detectable effect; run long enough to cover traffic cycles (typically 1–4 weeks).
- Implement the test and monitor for validity.
- Use a reliable A/B platform or CMS with staged rollouts and
feature flagsto prevent leakage. - Stop tests only after statistical significance and practical significance align.
Qualitative research protocol
Interview script: Start with a neutral opening, then ask: “What did you expect to find here?” “What stopped you from taking the next step?” “Which part felt most useful or confusing?” Close with a quick ranking task.
Sample size guidance: 5–8 interviews per user segment reveal most usability patterns; 12–20 uncover rarer issues.
Practical logging and action workflow
- Collect: Use analytics to capture test IDs and user segments in each event.
- Centralize: Log results in a shared spreadsheet or dashboard with test hypothesis, sample size, start/end dates, and p-value.
- Annotate: Attach representative session recordings or quotes to each result row.
- Decide: If results are positive and durable, roll out; if mixed, run a follow-up test; if negative, document learnings and revert.
Key metrics to track
- Primary metric: CTR or conversion rate.
- Engagement metric: Time on page or scroll depth.
- Experience metric: NPS or qualitative sentiment for tone of voice.
- Quality metric: Content scoring framework or estimated organic traffic impact.
Pairing disciplined A/B setups with tightly scoped qualitative interviews transforms guesses into reliable decisions. When iteration is routine, teams move faster and make fewer costly rewrites.
Governance and Scaling Your Voice
Scaling a consistent brand voice requires rules, clear ownership, and automation that enforces standards without slowing creators. Define policy guardrails, assign roles with crisp responsibilities, and automate repeatable checks (SEO, factuality, legal) so teams can publish confidently. When approval paths are precise and reviews happen on a cadence, voice drift disappears and iteration accelerates.
Policies: Create a concise policy bundle that covers voice, tone, factual accuracy, source attribution, and sensitive-topic escalation. Roles: Assign an editor-in-chief, section editors, content owners, and an automation steward; each role has explicit decision boundaries. Automations: Implement automated checks for readability, SEO signals, duplicate content, and legal keywords to catch issues before human review. Quarterly governance review: Schedule a cross-functional review to update policies, evaluate automation rules, and rebalance workloads.
- Define role responsibilities and escalation paths.
- Build approval workflows in the CMS with conditional steps (e.g., legal review only for regulated topics).
- Configure automations to run pre-submit checks and notify owners on failures.
- Run a quarterly audit: policy compliance, metric drift, and automation performance; adjust SLAs.
Typical automations to keep voice consistent:
- Automated SEO checks: Title length, target keyword presence, and meta descriptions.
- Readability validators: Grade-level checks and passive-voice flags.
- Fact-check triggers: Keyword-based prompts for source citation when claims contain numbers.
- Tone classifiers: ML model that flags deviations from brand tone profiles.
- Duplicate-content detector: Scans internal corpus for overlap before publishing.
Governance options: manual review vs lightweight automation vs full editorial pipeline
| Approach | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual review | High-quality nuance | Slow; scales poorly | Small teams; high-stakes content |
| Lightweight automation | Faster reviews; consistent checks | May miss nuanced errors | Growing teams; high throughput |
| Editorial workflow (SaaS) | Integrated tooling; analytics | Subscription cost; setup time | Mid-large teams; centralized ops |
| Hybrid | Balance of speed and judgment | Requires orchestration | Enterprise-scale content programs |
Key insight: Manual review yields the best nuance but is costly at scale; lightweight automation buys speed and consistency; SaaS editorial pipelines add analytics and integrations; a hybrid model is often the fastest path to scale while preserving quality.
Practical governance examples include routing any piece with legal keywords to legal, auto-failing posts missing attributions, and having editors approve only content flagged by tone classifiers. Scale your content workflow by combining clear role definitions with targeted automation, and schedule the quarterly review to refine policies based on measurable outcomes. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When a content pipeline stalls, the fastest path to recovery is a clear diagnostic sequence followed by immediate containment and a sustained remediation plan. Start by isolating the failure mode, then run quick validation checks to confirm the fix — this prevents wasteful rollbacks and repeated errors.
Fast diagnostics for common failures
- Check recent changes and deployments.
- Verify data flows: confirm the CMS received the publish request and the scheduler logged the job.
- Inspect logs for errors containing
500,timeout, orrate limit. - Reproduce the failure in a staging environment using the same inputs.
- Immediate fix: Re-run the failed job after clearing transient states like caches or queues.
- Containment: Disable automatic retries or webhooks that could amplify the problem.
- Communication: Notify stakeholders with status, impact, and ETA for the fix.
Stepwise remediation (immediate and long-term)
- Revert or hotfix the most recent change if diagnostics point to deployment.
- Restart the affected service or queue worker to clear stuck processes.
- Patch input validation or rate-limit handling that allowed malformed requests.
- Implement monitoring and alerting for the specific failure signature.
- Post-mortem: document cause, fix, and prevention steps; update runbooks.
- Short-term: Restore throughput and confirm content delivery paths are healthy.
- Long-term: Add automated tests and stage gating to prevent recurrence.
Validation checks after fixes
- Smoke test: Publish a small test article and confirm front-end rendering within 5 minutes.
- Integration check: Verify analytics ingestion and social-sharing metadata correctness.
- Performance check: Confirm average publish latency returned to baseline using recent job logs.
Content scoring framework: Use automated checks that validate title length, canonical tags, and schema before publish.
Rollback window: Define a 15–30 minute rollback period for automated deployments to allow safe recovery.
Common failure: rate limits from third-party APIs — reduce concurrency, add exponential backoff, and cache responses.
When a system works again, run the validation checks and capture the timeline. Applying both immediate containment and preventive automation reduces firefighting and lets teams focus on creating high-impact content. This is why automation and clear runbooks pay off: they keep releases predictable and free creators to iterate faster.
📥 Download: Brand Voice Crafting Checklist (PDF)
Tips for Success and Pro Tips
Start by focusing effort where it moves the needle: prioritize high-impact pages, protect brand voice, and treat automation as an amplifier—not a replacement—of editorial judgment. These practical habits shorten feedback loops, reduce rework, and keep content aligned with measurable business goals.
- Prioritize high-impact pages: Audit traffic, conversions, and topical authority to identify the top 10–20% of pages that drive 80% of outcomes.
- Test before rolling out broadly: Run A/B or incremental canary releases on small segments to validate automation prompts and templates.
- Use templates and pre-approved phrases: Build modular blocks for headlines, CTAs, and metadata to speed production while enforcing brand voice.
- Monitor tonal drift with automation: Track changes in
sentiment,readability, andbrand-voice scoreto catch divergence early. - Keep humans in the loop: Assign final reviews to editors trained in brand voice rather than relying on pass/fail automation gates.
Quick win sequence for rapid improvements
- Run a 30-day content triage to tag pages by impact and freshness.
- Create 3 reusable templates: title + meta, intro (50–70 words), and closing CTA.
- Deploy automated rewrites on the top 5% of pages, then measure engagement for 14 days.
- Lock successful templates into the pipeline and scale to the next batch.
Tonal drift: A measurable divergence between automated output and established brand voice; monitor with small validation sets and rollback thresholds.
Pre-approved phrases: Short, tested copy blocks editors can drop into content to ensure compliance and speed.
Practical examples that work
- Editorial checklist: One-sentence brand voice reminder + three tone checks (formal/informal balance, jargon, empathy).
- Performance baseline: Capture CTR and session duration before automation; use percentage deltas to evaluate impact.
- Canary releases: Update 5–10 pages, run for two weeks, then either roll forward or iterate on prompts.
Integrate tooling thoughtfully—link automated scoring to content ops and let product metrics guide prioritization. Where relevant, pipeline automation can be implemented via platforms that offer AI content automation; for teams scaling fast, AI content automation can reduce manual toil while preserving editorial control.
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level and keeping the brand voice consistent across scale.
Resources and Templates (Appendix)
This appendix collects the exact templates and downloadable assets needed to move from audit to launch without reinventing the wheel. Use these files to standardize decisions, speed reviews, and give contributors a single source of truth that scales across multiple authors and campaigns.
What’s included and when to use each file
- Audit Spreadsheet: Master CSV/Google Sheet to capture URL, traffic, intent, ranking keywords, and recommended action.
- Attribute Matrix: Document mapping content attributes (format, persona, funnel stage, CTA) to existing pages for gap analysis.
- Style Guide Template: Google Doc + Markdown-ready
style_guide.mdcovering brand voice, tone of voice, formatting rules, and snippet examples. - Interview Script: Reusable Google Doc for stakeholder and subject-matter interviews with prompts, time estimates, and recording checklist.
- Rollout Timeline: CSV/Google Sheet with columns for task owner, start/end dates, dependencies, and status for editorial and technical rollout.
Audit Spreadsheet: A single source to triage content by impact and effort. Attribute Matrix: Use this to assign consistent metadata and prevent duplicated topics. Style Guide Template: Drop into new projects to enforce brand voice and tone of voice across authors. Interview Script: Keeps conversations focused and captures quotable material. Rollout Timeline: Tracks delivery and handoffs so nothing slips.
How to use the assets (quick process)
- Export current site pages to
audit.csvand import into the Audit Spreadsheet. - Populate the Attribute Matrix by reviewing the top 150 pages and tagging format, persona, and funnel stage.
- Share the Style Guide Template with writers and paste the
style_guide.mdinto the repo. - Run stakeholder interviews using the Interview Script and attach transcripts to the related Audit Spreadsheet rows.
- Convert findings into tasks in the Rollout Timeline and assign owners with realistic lead times.
Quick inventory of templates, file formats, and ideal usage point in the workflow
| Resource | Format | When to Use | Quick Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audit Spreadsheet | CSV / Google Sheet | Post crawl, pre-prioritization | Tracks traffic, intent, action, owner |
| Attribute Matrix | Google Doc / Markdown | After audit, during mapping | Maps persona, funnel, format tags |
| Style Guide Template | Google Doc / style_guide.md |
Before writing, onboarding writers | Includes voice, tone, examples, snippets |
| Interview Script | Google Doc | Research phase | Prompts, time slots, consent checklist |
| Rollout Timeline | CSV / Google Sheet | Pre-launch and execution | Task owners, dependencies, status |
Key insight: The collection above turns ad-hoc content work into repeatable workflows; use the Audit Spreadsheet to prioritize, the Attribute Matrix to standardize metadata, the Style Guide to keep voice consistent, the Interview Script to source original material, and the Rollout Timeline to coordinate delivery.
For teams that need tighter automation, integrate these templates with an AI-powered pipeline to populate fields and score pages automatically — Scale your content workflow provides that capability. When these assets are adopted consistently, revisions become faster and content quality becomes predictable. This is why modern editorial operations favor reusable templates and clear handoffs.
Conclusion
Consistent brand voice and a clear tone of voice stop readers from getting whiplashed between channels and turn scattered content into a reliable signal that builds trust. Audit what’s live, lock down the core voice attributes you’ll reuse across formats, and deploy templates so teams don’t reinvent phrasing every time—those steps accelerate rollout and reduce revision cycles. Practical testing (A/B and qualitative interviews) and a lightweight governance model answer the two big questions most teams ask: how will we measure success, and who signs off on exceptions?
- Start with an audit: map where voice is inconsistent and prioritize high-impact channels.
- Standardize templates and examples: speed content production without losing nuance.
- Measure and iterate: combine engagement metrics with qualitative feedback to refine tone.
For teams ready to automate these workflows and scale voice rollouts across content calendars, editorial teams, and localization, platforms like Try Scaleblogger to automate brand voice rollouts can streamline template distribution, enforce guidelines, and track adoption. For further practical steps, see this related piece: undefined. Implement the core actions above this week, run a small pilot, and use the resulting learnings to expand governance across the full content stack.

