Publish deadlines keep moving while teams scramble to stitch together calendars, briefs, and last-minute edits, and inboxes fill with one-off requests that never scale. The pressure comes from two converging forces: the rapid rise of content automation tools and the expanding role of emerging technologies that reshape how audiences discover work. Understanding which shifts actually reduce churn, rather than add another dashboard, is the practical problem every content leader faces.
Practical clarity starts with separating automation that saves time from automation that creates technical debt, and with aligning any new workflow to measurable audience signals. Explore Scaleblogger’s AI content automation solutions — a hands-on way to test integrations and measure impact quickly. See how Scaleblogger can accelerate your content pilots by turning experiments into repeatable pipelines that inform decisions about the future of digital content.
What Is Content Automation?
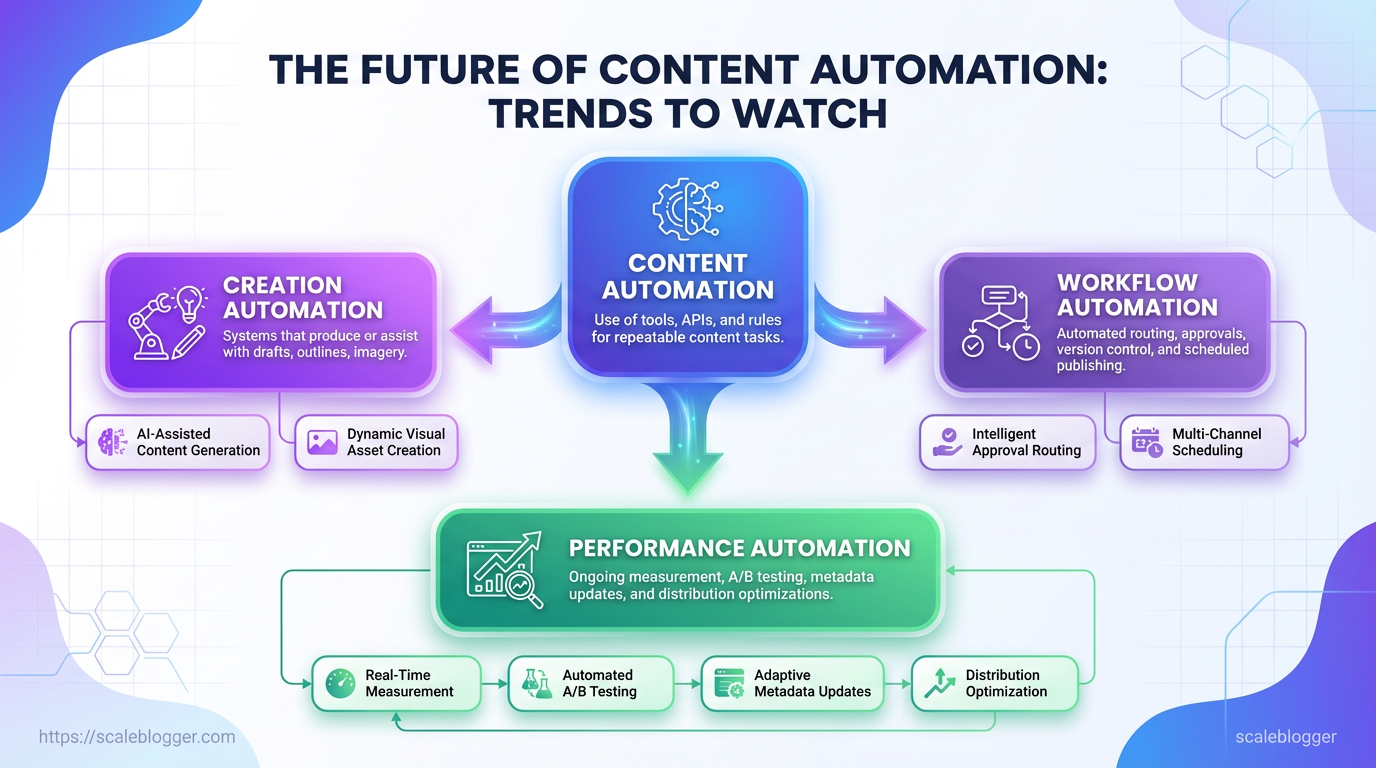
Content automation is the practice of using software and programmable workflows to handle repetitive, rule-based parts of the content lifecycle so teams focus on strategy and creativity. This covers everything from generating first drafts with models to routing articles through approval workflows and automatically updating SEO metadata based on performance signals.
Content automation: The use of tools, APIs, and rules to perform repeatable content tasks without manual intervention.
Creation automation: Systems that produce or assist with drafts, outlines, imagery, or repurposed assets.
Workflow automation: Automated routing, approvals, version control, and scheduled publishing inside a CMS.
Performance automation: Ongoing measurement, A/B testing, metadata updates, and distribution optimizations based on analytics.
Practical examples make the difference. A marketing team might use an NLP model to generate a 700-word draft, a workflow engine to assign the draft to an editor, and a scheduler to publish at the optimal time. Where simple scheduling merely posts at a set time, content automation ties that schedule to triggers such as content score thresholds, audience signals, or calendar events.
Common components and capabilities Draft generation: Create outlines, headlines, and first drafts with AI-assisted tools. Editorial routing: Automatically assign reviews and approvals based on role, SLA, or content type. Metadata updates: Sync SEO tags, canonical URLs, and schema based on templates or performance. A/B testing: Rotate headlines or intros automatically and route winning variants to full publication. * Distribution: Push content to social, newsletters, or syndication channels when KPI triggers are met.
Analogy for accessibility: think of content automation like a modern bakery line. Machines mix dough and shape loaves to a spec, bakers add the signature finish, and conveyors move products to packaging—automation raises throughput while artisans preserve craft.
Quickly show which tasks fall under creation, workflow, and performance automation
| Task | Automation domain | Typical tools | Impact (time saved) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Draft generation | Creation | ChatGPT, Jasper, Claude — outline & draft | 2–6 hours per article |
| Editorial approvals | Workflow | Asana, Trello, Zapier, Workflows in CMS |
1–3 days per article |
| Scheduled publishing | Workflow | WordPress scheduler, Contentful, Git CI |
30–60 minutes weekly |
| SEO metadata updates | Performance | Surfer SEO, Clearscope, custom scripts | 15–45 minutes per page |
| A/B headline testing | Performance | Optimizely, VWO, native CMS tests | Decision in 24–72 hours |
Key insight: The table separates where automation yields the most leverage—creation slashes drafting time, workflow automation shortens review cycles, and performance automation tightens relevance and ranking.
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, automation reduces repetitive overhead and frees creators to focus on storytelling and strategy.
How Content Automation Works
Content automation stitches together data, AI, and operational glue so a team can produce more relevant content with fewer manual bottlenecks. At its core it’s an end-to-end pipeline: ideas and briefs flow in, machine intelligence drafts and enriches, automation executes routine publishing tasks, and humans validate quality at key checkpoints. When designed correctly, the system makes routine decisions automatically while reserving judgement calls for human reviewers.
Core mechanisms and architecture
- Ingest and discovery: collect keywords, analytics, and brief inputs from CMS, analytics, and keyword tools.
- Content generation and enrichment: call
LLMmodels for outlines, drafts, and summaries; run SEO optimizers and entity extractors. - Workflow orchestration: use orchestration tools and
APIsto route drafts into review, scheduling, and publishing queues. - Execution and publishing: automate CMS actions (create post, set metadata, schedule) via
RPAbots or native CMS APIs. - Monitoring and feedback: collect performance metrics, feed back into topic selection and model prompts.
Human-in-loop: Maintain review gates at draft, SEO-check, and pre-publish stages to catch hallucinations, brand voice drift, and factual errors.
Key enabling technologies
- Large Language Models (LLMs): generation, summarization, and intent-matching via prompt engineering.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): automating repetitive CMS tasks like uploading assets or tagging posts.
- APIs and webhooks: glue systems together—analytics, editorial calendars, and publishing platforms sync in real time.
- Rule-based engines: enforce business logic, content scoring thresholds, and approval rules.
Quality control checkpoint: Every automated draft should pass an ML-based content-quality score and then a human review before publishing.
Practical example
* Scenario: A weekly topical cluster pipeline. Automated steps generate topic ideas from search trends, create 800–1,200 word drafts with LLM, push drafts into editorial queue, then schedule publication via CMS API after human approval.
AI, RPA, and traditional rule-based automation on strengths and ideal use cases
| Technology | Best for | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Language Models (LLMs) | Drafting, summaries, ideation | Natural prose, semantic understanding, scalable | Inconsistent facts, prompt sensitivity |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Repetitive UI tasks in legacy systems | Works without APIs, reliable for clicks/forms | Fragile to UI changes, scale limits |
| Rule-based engines | Enforcing policies, routing | Deterministic, transparent decisions | Poor at nuance, labor-intensive rule maintenance |
Key insight: LLMs handle creative and semantic tasks while RPA handles mechanical actions; rule engines enforce deterministic business rules—combining all three yields a resilient pipeline.
Integrating these components with well-placed human checks prevents quality erosion while accelerating output. Scale your content workflow by mapping which tasks must be human versus automated and building the API/RPA glue accordingly. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Trends to Watch: Near-Term (1–2 years)
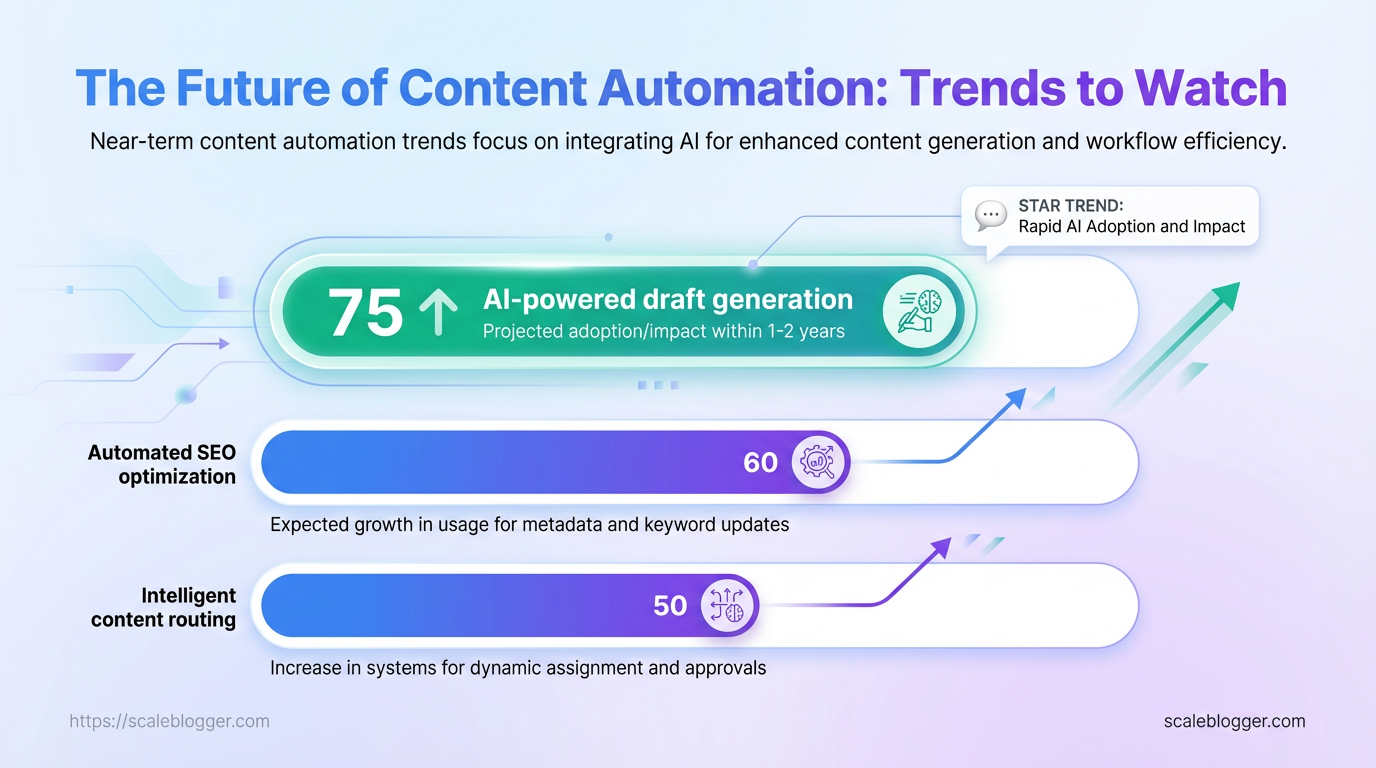
Expect rapid consolidation of three practical trends that directly change how teams produce, personalize, and optimize content: AI-assisted content workflows, personalized content at scale, and automated SEO and optimization. These are not theoretical — they solve throughput, relevance, and discoverability problems simultaneously, and the implementation details determine whether they become productivity multipliers or sources of technical debt.
AI-assisted content workflows AI moves from single-task helpers to orchestration layers that stitch brief generation, outlines, drafts, and revision cycles into a repeatable pipeline. Typical use cases include: Brief generation: create data-backed article briefs from search intent and competitor signals. Outline synthesis: assemble multi-section outlines with suggested headings and examples. * Draft expansion: convert outlines into first drafts optimized for readability and tone.
Pilot approach 1. Select two to three focused use cases that unblock content velocity (e.g., briefs + outline + QA prompts).
- Run an A/B pilot on 30–50 pieces, comparing traditional briefs to AI-assisted briefs.
- Iterate on prompts, editorial guardrails, and acceptance criteria.
Quality metric suggestions Readability score: target grade-level band and paragraph-length distribution. Editorial rejection rate: percent of AI drafts requiring heavy rewrites. * Time-to-publish: hours reduced from brief to published draft. Implement content scoring to quantify draft quality before human pass.
Personalized content at scale Personalization will leverage first-party signals and lightweight orchestration to increase conversion without exploding combinatorics. Data sources: CRM behavioral events, CMS analytics, email engagement, and product usage logs. Privacy and consent: respect user-level consent, store minimal identifiers, and prefer aggregated signals for A/B tests. * Measurement: run conversion lift tests with holdout groups and measure incremental revenue per visitor segment.
Automated SEO and content optimization Automation moves beyond recommendations into editorial actions: topic clustering, meta updates, internal linking, and content scoring can be surfaced and sometimes executed automatically. Auto topic clustering: group content by semantic intent for hub-and-spoke strategies. SEO workflow integration: push recommendations directly into CMS editorial tasks. * Testing and iteration: schedule iterative rewrites via short cycles and measure ranking and behavioral lifts.
Types of SEO automation features and the editorial benefits they deliver
| Feature | Function | When to use | Expected ROI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topic clustering | Groups pages by semantic intent, suggests hubs | Launching content silos or scaling categories | 20–50% faster topical coverage; improved SERP relevance |
| Meta tag generation | Auto-creates titles/descriptions with intent signals | Large catalogs or frequent updates | Saves manual time; click-through lift 5–15% typical |
| Content scoring | Evaluates on-page quality vs. peers (content scoring) |
Prioritizing rewrites and pruning | Focuses efforts; higher per-article traffic gains |
| Automated internal linking | Suggests or inserts contextual links | New content rollouts and evergreen updates | Improved crawlability; session duration and depth lift |
Key insight: Automating these features shifts editorial effort from discovery to creative advantage, letting teams deploy more strategic content instead of repeating manual tasks.
For teams ready to scale, adopt small pilots, measure conservative quality metrics, and integrate automation into editorial workflows. AI content automation can be the orchestration layer that reduces busywork while preserving editorial judgment. When executed carefully, these trends accelerate output and make every piece of content work harder.
Trends to Watch: Mid/Long-Term (3–5+ years)
Autonomous content systems will shift from assisted workflows to systems that ideate, produce, optimize, and publish with minimal human intervention, while multimodal automation will turn single assets into integrated text, audio, and video experiences at scale. Expect strategies to evolve from manual repurposing to orchestration layers that manage quality, brand voice, and distribution automatically.
Autonomous content systems
Autonomous systems combine NLP, editorial rules, user signals, and performance loops to produce and iterate content without manual drafting every step.
- What it does: Automatically generate topic clusters, draft posts, create meta elements, and push optimized versions based on performance.
- Risk: Drift in brand voice or factual errors from unchecked generation.
- Mitigation: Implement gated automation with staged human review, automated fact-checking pipelines, and A/B control groups.
- Governance recommendation: Create a content policy matrix that maps risk level to required approvals, and log model provenance for each asset (model version, prompt, temperature).
Multimodal content automation (text, audio, video)
Multimodal workflows turn a single canonical asset into a suite of formats, increasing reach and reuse without multiplying production cost.
- Benefits: Higher engagement across platforms, improved SEO through diverse indexing signals, and extended content lifespan.
- Toolchain considerations: Choose
TTSengines with natural voices, video templating platforms, and transcription + semantic tagging to enable dynamic repurposing. - Distribution automation: Use scheduling APIs to tailor formats per channel (short-form video for social, podcasts for audio platforms, long-form on-site articles), and connect analytics to close the loop on format performance.
A mapping of source content types to automated output formats and typical tools used
| Source content | Automated outputs | Tools/tech | Use case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long-form article | Short clips, podcast episode, social threads | Descript, Repurpose.io, TTS engines |
SEO-to-social pipeline |
| Webinar transcript | Highlight reels, blog post, Q&A thread | Descript, Otter.ai, Kapwing | Lead-nurture snippets |
| Product documentation | How-to video, FAQ article, chatbot answers | GitBook, Scribe, Synthesia | Self-service support |
| User-generated content | Testimonial video, microblogs, review snippets | Lumen5, Gling, Brandwatch | Trust signals for acquisition |
Key insight: The most efficient pipelines use a canonical source of truth (long-form asset) plus semantic tagging to generate and distribute channel-optimized formats automatically; selecting interoperable tools and clear governance prevents quality decay.
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making format decisions programmatic and measurable.
Why It Matters: Business Impact and Use Cases
Adopting content automation changes the economics of content production: teams publish more, iterate faster, and shift effort from production to strategy. Automation reduces repetitive work—research aggregation, first-draft generation, metadata tagging, and scheduling—so specialists can focus on differentiation, testing, and amplification. The measurable business outcomes are higher output, improved SEO velocity, lower per-piece cost, and faster time-to-insight.
Real business impacts
- Higher output: Automated pipelines raise monthly article throughput without linear headcount increases.
- Faster time-to-publish: Integrations with
CMSand editorial workflows cut handoffs and idle time. - Lower cost per asset: Repetitive tasks shift to automation, reducing freelance and editor hours.
- Improved discoverability: Consistent optimization for intent and structure raises organic traffic over time.
- Better decisioning: Automated performance benchmarking surfaces what to scale and what to pause.
Practical limitations to watch
- Quality floor: Automation needs guardrails—style guides, quality checks, and human review—to avoid off-brand or shallow content.
- SEO risk: Blind automation can produce keyword-stuffed or duplicate-like pages unless semantic optimization is enforced.
- Operational debt: Poorly documented pipelines create brittle systems; invest in monitoring and retraining.
Real-world examples (hypothetical but realistic)
SaaS: Problem — slow release of feature guides. Automated solution — templated drafts plus API-driven screenshots. Result — monthly guide output up 3× in 6 months; free-trial signups +12%.
E‑commerce: Problem — catalog pages low on long-tail traffic. Automated solution — programmatic product descriptions with structured metadata. Result — organic sessions +25% in 4 months; returns unchanged.
Publisher: Problem — resource-heavy beats. Automated solution — AI-assisted summaries and tagging. Result — article-per-reporter +40%; page RPM increased.
> Industry analysis shows teams that combine automation with solid editorial governance scale content volume while preserving brand voice.
Summarize example use cases with KPIs before/after automation
| Industry | Use case | Metric before | Metric after | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SaaS | Feature docs + tutorials | 6 articles/mo | 18 articles/mo | 6 months |
| E-commerce | Product page descriptions | 1,200 monthly visits | 1,500 monthly visits | 4 months |
| Publisher | Topic coverage + tagging | 10 articles/week | 14 articles/week | 3 months |
| Agency | Client content production | 30 assets/mo | 55 assets/mo | 5 months |
| B2B enterprise | Whitepapers + sales enablement | 4 assets/quarter | 9 assets/quarter | 6 months |
Key insight: Volume gains translate to measurable traffic and lead improvements when paired with editorial controls and measurement.
Integrating a proven pipeline—template rules, CMS hooks, and performance benchmarking—avoids the usual pitfalls. For teams ready to scale, combining automation with governance tools like an AI content automation partner streamlines the transition while protecting brand quality. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Common Misconceptions and Risks
Automation doesn’t replace writers; it amplifies what skilled writers do best. Treat automation as a force multiplier: machines handle repetitive structure, data retrieval, and surface-level drafting while humans supply judgment, storytelling, and audience empathy. When teams incorrectly assume writers are expendable, quality and brand voice erode quickly — not because the tools are weak, but because oversight and editorial craft are missing.
Human-in-loop: A workflow where humans validate, edit, or extend automated outputs before publication.
This is how augmentation looks in practice: Draft acceleration: Automated outlines and first drafts cut research time, letting writers iterate faster. Data enrichment: Tools pull up-to-date figures and citations so writers focus on interpretation. * Scale with control: Templates ensure consistency while editors tune tone and factual accuracy.
New skill sets that matter now: Editorial engineering: Designing prompts, templates, and guardrails for predictable outputs. Quality assurance: Spot-checking facts, adjusting nuance, and preserving legal/compliance needs. * Analytics literacy: Interpreting content performance metrics to close the automation feedback loop.
Human-in-loop checklist Editorial owner assigned: One person accountable for final voice and accuracy. Source verification step: Every automated fact has a human-checked source. Tone calibration: Samples reviewed to align with brand guidelines. Rollback plan: Immediate unpublishing process for content with errors. * Performance review schedule: Weekly sample audits to catch drift.
Another prevalent myth is that automation guarantees better SEO. Tools can optimize for structure and identify keywords, but search performance depends on strategy, testing, and context. Blindly publishing AI-generated posts often produces thin, repetitive, or misaligned content that search algorithms penalize.
Testing approach for SEO-driven automation 1. Create control posts published under current manual process.
- Publish experiment posts created using automation with identical topical scope.
- Measure ranking, clicks, and engagement over 30–90 days.
- Iterate templates and prompts based on performance gaps.
Common pitfalls include over-optimization for keywords, lack of topical depth, and failure to monitor semantic intent. Use automation to surface opportunities — then apply editorial judgment and iterative A/B testing to validate impact. Tools like Scaleblogger.com can automate pipelines and provide content scoring frameworks, but they only deliver value when paired with disciplined oversight. Understanding these boundaries lets teams move faster without sacrificing credibility or long-term visibility.
📥 Download: Content Automation Implementation Checklist (PDF)
How to Start: Practical Roadmap for Adoption
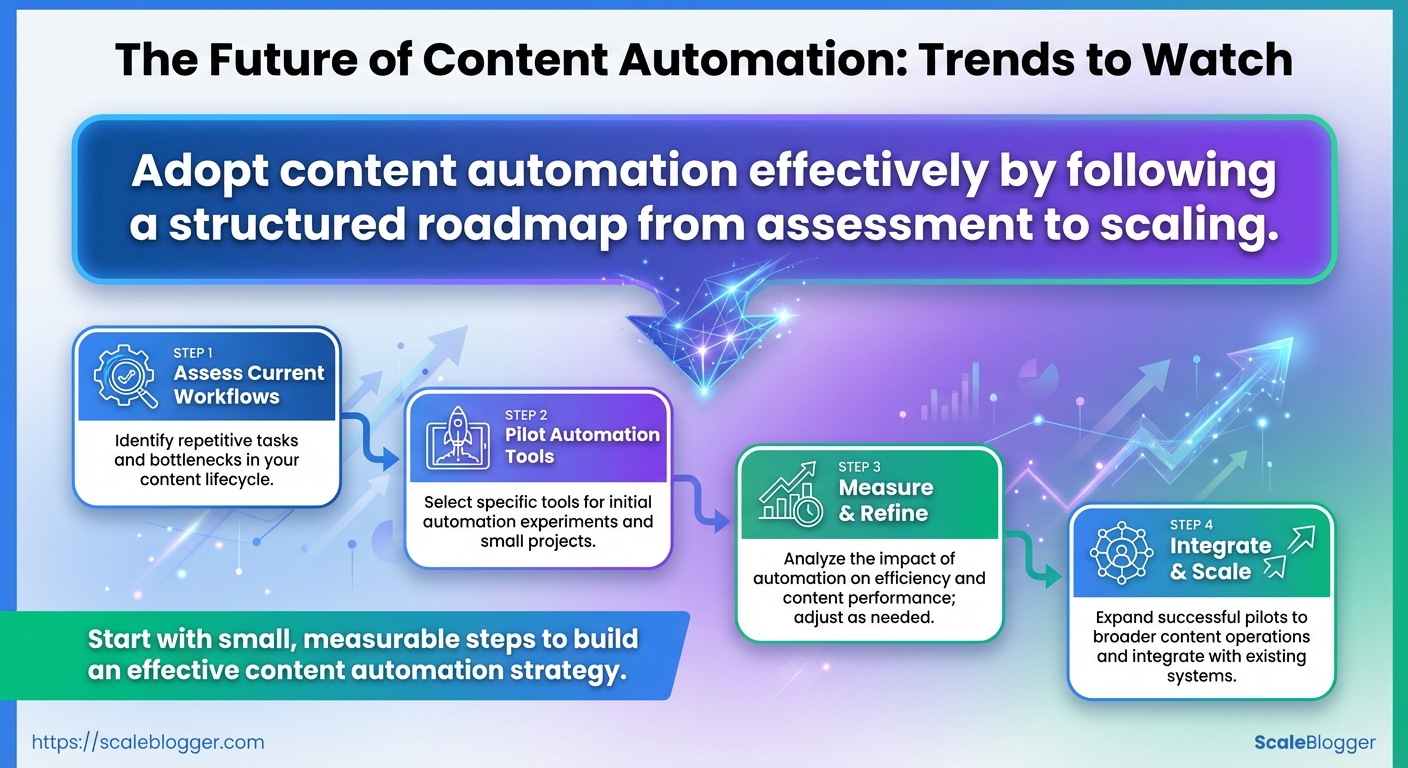
Begin by treating adoption as a product launch: define a narrow, measurable pilot, align the right stakeholders, and iterate fast. Successful rollouts prioritize clear owners, short feedback loops, and KPIs that measure both efficiency and impact on traffic/engagement. The six-step roadmap below turns an abstract strategy into concrete actions, with owners and KPIs suitable for a content organization moving toward automation.
- Assess
- Pilot
- Integrate
- Train
- Measure
- Scale
A phased timeline for pilot → integrate → scale with suggested durations and owner roles
| Phase | Duration | Owners | Key deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assess | 2–4 weeks | Product Lead, Head of Content, SEO Lead | Inventory of content assets; workflow gap map; priority use cases |
| Pilot | 4–8 weeks | Cross-functional team (Content PM, 1–2 Writers, Data Analyst) | 3–5 automated workflows; sample posts published; pilot KPI dashboard |
| Integrate | 2–6 weeks | Engineering, CMS Admin, Content Ops | CMS connectors, editorial templates, API keys configured |
| Train | 2–3 weeks (ongoing) | Content Trainer, Writers, Editors | Playbook for prompts, editorial QA checklist, role-based training sessions |
| Measure | 4–12 weeks | Data Analyst, SEO Lead, Content PM | A/B test results, traffic and engagement metrics, efficiency metrics |
| Scale | 2–6 months | Head of Content, Operations, Product | Automation rollout plan, SLA for content ops, ROI report |
Key insight: This timeline balances speed with governance—short pilots reduce risk while clear owners prevent diffusion of responsibility.
Stakeholders to involve Business sponsor: secures budget and sets strategic priorities. Content owners: define editorial standards and acceptance criteria. Data/analytics: builds KPI tracking and experiments. Engineering/CMS: implements integrations and automations. * Legal/compliance: reviews sensitive content and brand safety.
Suggested pilot KPIs Speed: Time-to-publish reduction (target 30–50%). Quality: Content score via editorial rubric; maintain baseline or improve. SEO impact: Organic sessions and rankings for targeted topics. Efficiency: number of articles per editor per month. * User engagement: average time on page and scroll depth.
Practical tips: start with formats that map easily to automation (listicles, how-tos, data-driven summaries). Use API-first connectors for the CMS to avoid manual uploads. Consider Scaleblogger.com for automating pipelines and benchmarking pilot performance against industry patterns.
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When teams adopt this roadmap, decision-making shifts closer to creators and the organization gains predictable content velocity and measurable SEO upside.
Conclusion
Teams that move from ad-hoc publishing to systematic automation free capacity for strategy, not just faster output. The article showed how content automation reduces repetitive work, how orchestration layers connect briefs to distribution, and why near-term advances in AI-driven templates and mid-term platform consolidation matter for scalability. Practical roadmaps and the B2B marketing example illustrated that small pilot projects — one reusable template, one automated review loop — deliver measurable time savings and cleaner analytics. Common questions about quality and governance are answered by pairing human oversight with guardrails: set review thresholds, monitor performance signals, and iterate on content models rather than abandoning editorial standards.
For immediate next steps, pick one workflow to automate this quarter, measure baseline KPIs, and build a two-sprint pilot that includes templates, approval steps, and analytics. Start small, measure outcomes, and codify what works. For teams looking to streamline these processes at scale, platforms that combine AI-driven drafting, automation rules, and analytics accelerate adoption. To explore how those capabilities map to your roadmap, consider this practical option: Explore Scaleblogger’s AI content automation solutions. It’s one straightforward way to test the content automation trends shaping the future of digital content and to get a controlled, measurable pilot running.

