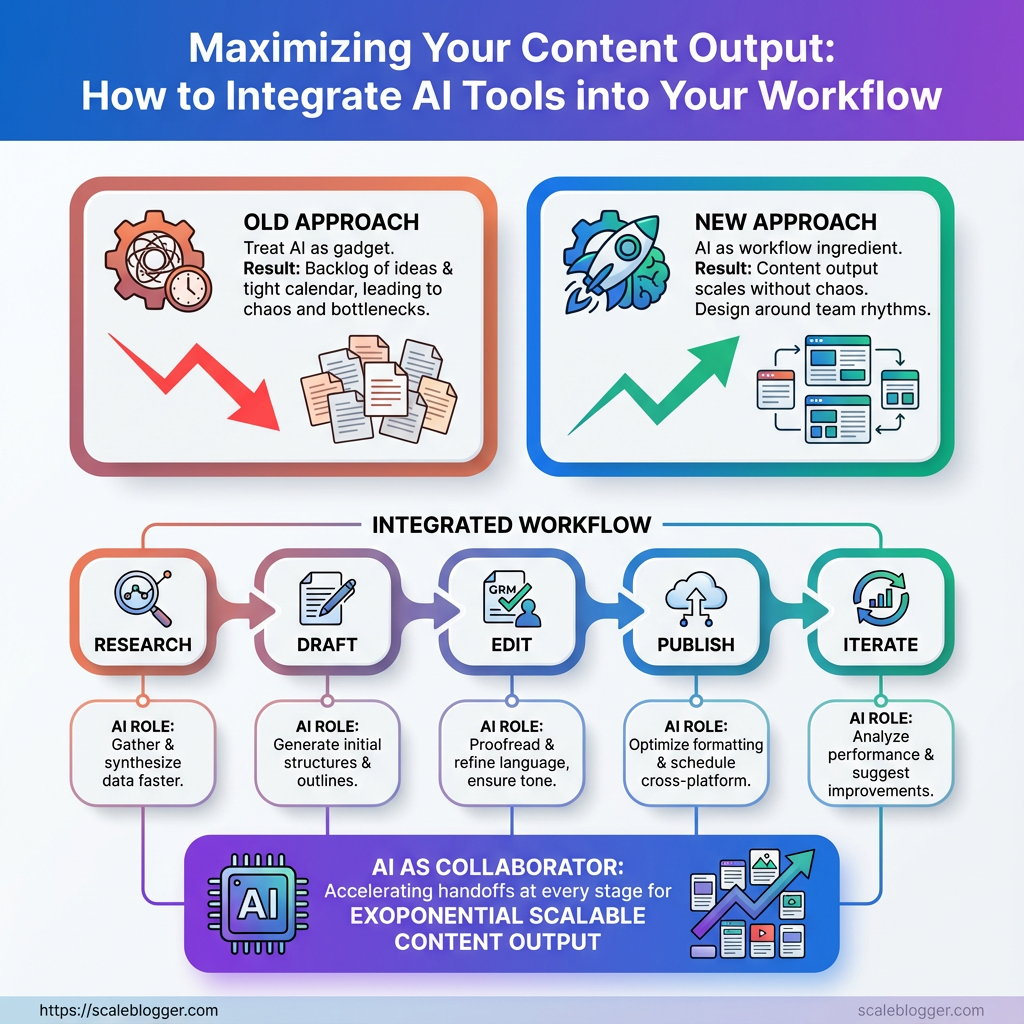
You know the feeling: a backlog of ideas, a tight calendar, and the same two writers stretched thin waiting on research or edits. The gap between having ideas and publishing consistently is often a systems problem, not a talent problem — and that’s where AI tools stop being a novelty and start being leverage.
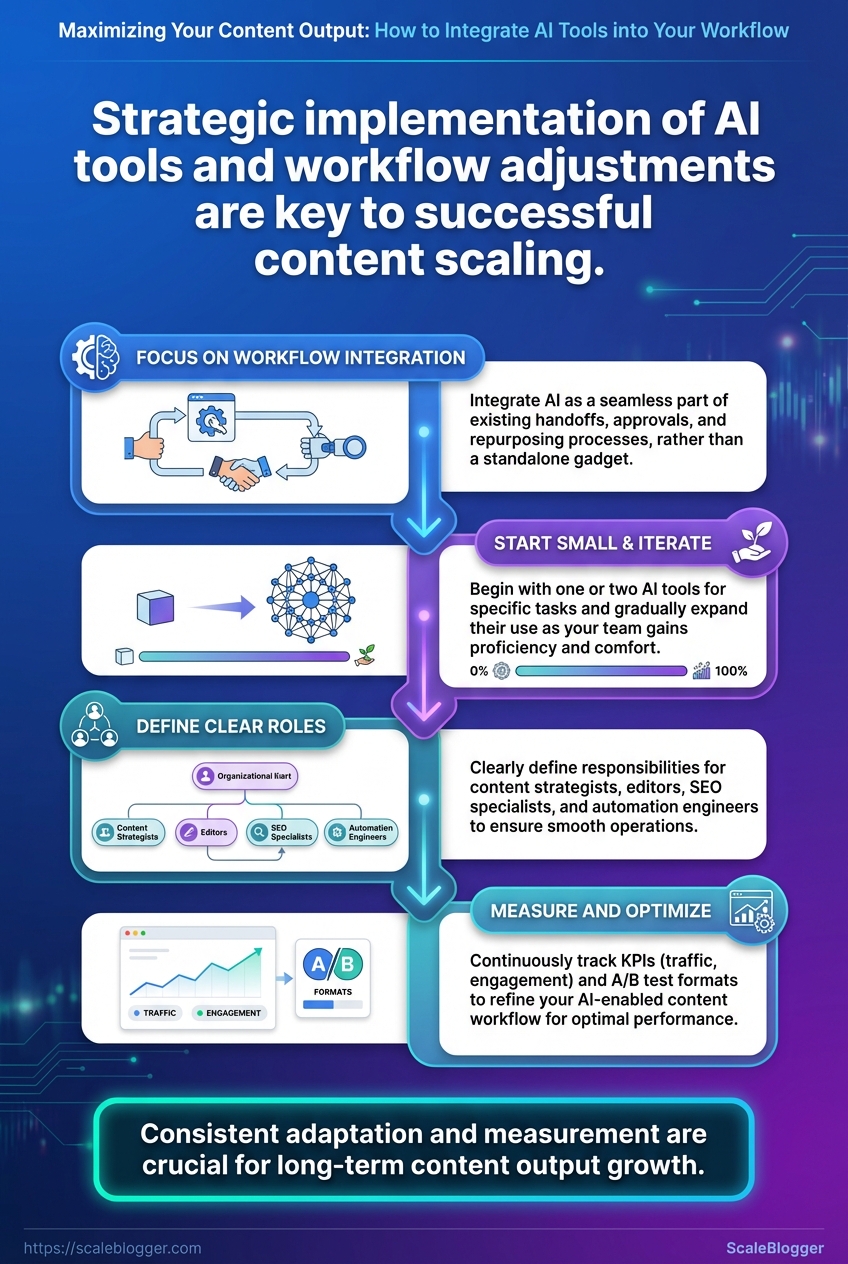
Most teams treat automation like a gadget instead of a workflow ingredient, so outputs stay inconsistent and quality dips when volume rises. Shift the focus to how those tools plug into handoffs, approvals, and repurposing, and content output scales without turning into chaos.
Start small and design around the team’s natural rhythms: research, draft, edit, publish, iterate. Treat the tools as collaborators that accelerate specific handoffs in your content workflow, not as substitutes for judgment. Scale your AI-enabled content workflow with Scaleblogger
What You’ll Need (Prerequisites)
Start with the right mix of tools, people, and a short learning plan. For a modern AI-driven content workflow that actually scales, expect a handful of platform subscriptions, clear role definitions, and a 30/60/90 ramp that turns capability into repeatable output. Below are the concrete tools, platform choices, and team roles that make the difference between a chaotic content pile and a smooth, automated pipeline.
Tools, Platforms and Licenses
- Content ideation: AI topic generators and trend monitors to seed high-value ideas.
- Drafting: A large-language-model writing assistant for first drafts and variations.
- Optimization: AI SEO tools for on-page suggestions, keyword clustering, and content scoring.
- Automation: Workflow orchestration (Zapier, Make) to move assets between tools and trigger publishing.
- Collaboration: Editorial calendar and shared docs with version control and approvals.
Recommended tool categories and example options to help readers choose the right tool for their budget and needs
| Tool Category | Example Tools | Minimum Plan Recommended | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content Ideation | BuzzSumo, AnswerThePublic, Scaleblogger.com | Free tier / $99/mo for advanced trends | Topic discovery, question mining, content gap analysis |
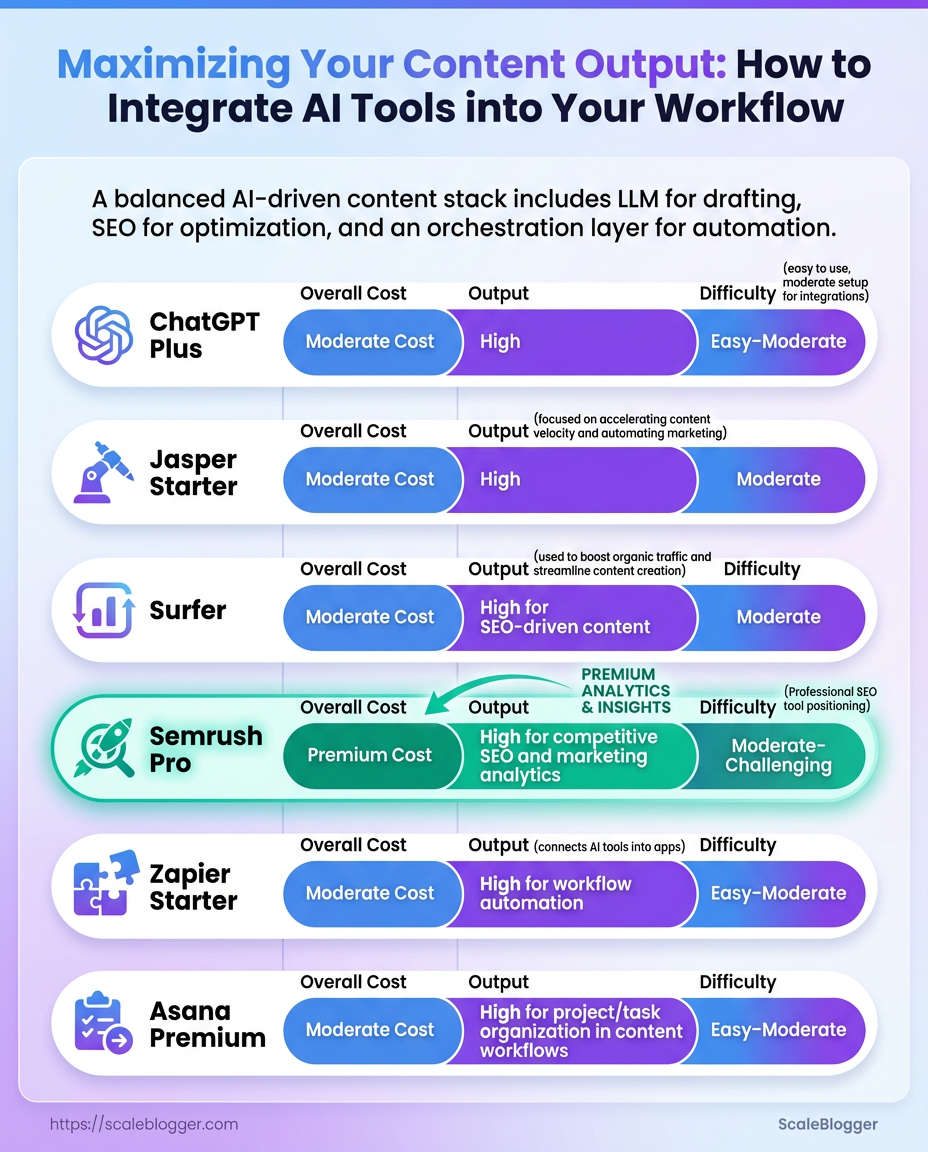
| Drafting / LLM Assistant | ChatGPT (Plus), Claude, Jasper | ChatGPT Plus $20/mo or Jasper Starter $39/mo | First drafts, tone variants, rapid iteration |
| SEO Optimization | Surfer, Clearscope, Semrush, MarketMuse | Surfer $59/mo, Semrush Pro $119.95/mo | On-page optimization, keyword clustering, content scoring |
| Automation / Orchestration | Zapier, Make (Integromat), n8n | Zapier Starter $19.99/mo | Triggered workflows, publish pipelines, cross-tool syncing |
| Editorial Calendar / Collaboration | Notion, Asana, Trello, Google Workspace | Notion Free / Asana Premium $10.99/mo | Editorial schedules, asset management, approvals |
Key insight: The right stack mixes an LLM for drafting, an SEO tool for optimization, and an orchestration layer to automate repetitive handoffs. Budget options exist at every level; invest more in whichever area is currently your bottleneck.
Skills and Team Roles
Content Strategist: Defines topics, intent, and performance metrics.
Editor / UX Writer: Shapes drafts, enforces voice, and handles final QA.
SEO Specialist: Handles keyword strategy, on-page signals, and brief refinement.
Automation Engineer / Ops: Builds and maintains Zapier/Make workflows and CMS integrations.
Analytics Lead: Tracks KPIs and runs A/B tests on formats.
Freelancers/Agencies: Use for scalable drafting, specialized SEO audits, or temporary capacity when launching new verticals.
30/60/90 Day Skill Ramp
1. Day 1–30: Learn platform basics, write 5 drafts with the LLM, and publish one optimized post.
2. Day 31–60: Build 2 automation flows, implement SEO tool recommendations, and standardize a content brief template.
3. Day 61–90: Optimize workflows for scale, measure traffic/engagement, and iterate on brief + automation.
For teams without full-time hires, freelancers fill drafting and editing gaps while an agency or a service like Scaleblogger.com can build the automation and content pipeline quickly. These prerequisites set the stage for predictable, repeatable content output that grows organic visibility without burning the team out.
Step-by-Step: Audit Your Current Content Workflow
Start by treating the audit like a mini-investigation: map every repeatable action, measure how long it takes, and flag what feels manual or error-prone. Capturing that detail makes the next step — choosing which automations actually move the needle — unambiguous and fast.
- Map Every Content Task
- Inventory tasks comprehensively. Walk through a single piece of content from idea to archive and list every discrete task.
- Capture time and frequency. Use
time_trackingdata where available; otherwise run short interviews and use team estimates for average minutes per task. - Identify manual, repetitive tasks first. Look for copy-paste work, repeated file handling, manual QA checks, and recurring decision points.
- Map scope: Document one content type first (e.g., long-form blog) before expanding to others.
- Who owns what: Note task owners and backups to spot bottlenecks.
- Failure modes: Record where errors commonly occur (metadata, broken links, images).
Provide a spreadsheet template example showing how to capture task name, owner, frequency, time_spent, tool_used, and automation_opportunity
| Task Name | Owner | Frequency | Average Time (min) | Current Tool | Automation Opportunity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topic ideation | Content Lead | Weekly | 90 | Google Docs | AI-assisted topic suggestions |
| Brief creation | Writer | Per article | 30 | Notion | Template-based auto-fill |
| Draft writing | Writer | Per article | 240 | Google Docs | AI first-draft generation |
| SEO optimization | SEO Specialist | Per article | 60 | Ahrefs + Sheets | Automated on-page checklist |
| Publishing & distribution | Ops | Per article | 45 | WordPress, Buffer | Scheduled publish + syndication |
Key insight: The table exposes where most minutes accumulate (draft writing) and where small automations (briefs, SEO checks) can reduce friction quickly. That mix — a few high-effort tasks and several small-repeatable tasks — is typical in content ops.
- Prioritize High-Impact Automations
Score each candidate using two simple axes: impact (1–5) and effort (1–5). Multiply for a prioritization score where higher = better.
- Scoring rule: Impact × (6 − Effort) gives preference to high-impact, low-effort wins.
- Selection criteria: Quick wins are tasks with high frequency, low complexity, and clear success metrics (time saved, fewer errors).
- Example high-impact automations:
- Auto-generate briefs: fills outlines and research links — quick win.
- Automated SEO checks: runs before publish to catch missing meta and headings.
- Scheduled publishing + syndication: removes manual cross-posting.
- Analytics reporting: daily performance summary emailed to stakeholders.
- Internal linking suggestions: reduces manual link audits.
Pick 2–3 pilots: one low-effort quick win and one higher-impact system (like draft-assist) to validate ROI before scaling. If automation fits, consider bringing in an AI content pipeline like Scale your content workflow to accelerate pilots.
Running this audit turns fuzzy complaints into measurable opportunities and gives a clear roadmap for automations that actually free up creative time and improve consistency. Take the pilot data and let it drive the next round of automations — that’s how the workflow stops being a grind and starts producing predictable output.
Step-by-Step: Build an AI-Enabled Content Pipeline
Start by centralizing assets, then turn repeatable creative work into template-driven automation while keeping humans in the loop for judgment calls. The aim is a reliable, auditable flow where idea → draft → QA → publish runs on autopilot for routine pieces and surfaces exceptions for higher-value review.
Set Up a Centralized Content Repository
Choose a repository option that fits team size and integrations: CMS (WordPress, Contentful), cloud drive (Google Drive, OneDrive), or a headless repo (Git + Markdown for developer-heavy teams).
- Decide structure and templates.
- Create folder and naming conventions.
- Configure basic integrations.
Repository options: CMS, cloud drive, headless repo.
Essential metadata fields: Content Type: Article, Pillar, Update. Author: Assigned author name. Status: Idea / Draft / In Review / Scheduled / Published. SEO Keywords: Primary and secondary. Publish Date: Scheduled timestamp. Target Persona: Short tag.
Integrations to configure: webhook from idea tool → repo, CMS API keys, and Zapier/Make connectors for automations. For scale, include a content.json manifest or frontmatter in Markdown that maps metadata to downstream systems.
Create High-Quality Prompts and Prompt Templates
Prompt templates should have a clear purpose, placeholders for inputs, and an expected output shape.
Three prompt templates with expected inputs and outputs so writers can copy and paste
| Use Case | Prompt Template (short) | Required Inputs | Expected Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topic Ideation | “Generate 10 blog topics about {topic} targeting {persona} with keyword {keyword} and search intent {intent}.” | Topic; Persona; Keyword; Intent | 10 headline-quality topics with short angle notes |
| First Draft Generation | “Write a ~{length} word blog post on {topic} with headings: {h1,h2}, include intro, 3 examples, and CTA.” | Topic; Word count; Headings; Tone | Draft with structure, intro, subheads, and CTA |
| On-Page SEO Optimization | “Optimize the following draft for {keyword} and readability; suggest meta title and 3 alt tags.” | Draft text; Keyword; Readability target | Optimized draft, meta title, 3 image alt texts |
Key insight: These templates separate inputs from structure so non-technical writers can iterate quickly. Version prompts in a simple git-like log or a shared prompts.md file to track performance.
Automate Repetitive Hand-offs and Publishing
- Define triggers: new draft saved → send to reviewer; status changes to
Scheduled→ publish job. - Build recipes in Zapier/Make: webhook payload with
title,slug,publish_date,content_html. - Add QA gates: automation pauses if
legal_flag= true or ifscore< threshold.
Sample payload snippet (JSON field names): {"title":"...","author":"...","publish_date":"2025-01-15T10:00Z","content_html":"
...
"}.
Integrate Human-in-the-Loop QA
Quick QA: Surface-level check for factual errors, tone, basic formatting. Full Editorial QA: Deep edit for structure, narrative, accuracy, and voice. SEO QA: Keyword placement, meta, schema checks. Legal/Compliance Review: Policy, claims, citations. Localization Review: Language and cultural accuracy.
Quick QA vs full editorial QA tasks and expected time budgets to set realistic SLAs
| QA Type | Scope | Typical Time | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quick QA | Grammar, basic facts, tone | 15–30 min | Short-form, updates, low-risk posts |
| Full Editorial QA | Structural edit, depth, citations | 2–4 hours | Flagged long-forms, flagship content |
| SEO QA | Keyword density, meta, internal links | 30–60 min | All published posts |
| Legal/Compliance Review | Claims, licensing, policies | 1–3 days | Regulated content, partnerships |
| Localization Review | Translation accuracy, cultural fit | 1–2 days | Market-specific launches |
Key insight: SLAs should be tiered—quick QA within 24 hours, full editorial within 72 hours for planned content. Automations can enforce these SLAs by escalating overdue items.
Measure and Iterate the Pipeline
KPIs to track: Time-to-publish, content velocity, draft-to-publish conversion rate, organic traffic per piece, AI-assist reduction in writer hours. Dashboard setup: Pull metrics into a BI tool; track A/B tests for AI vs human-first drafts. Iteration cadence: Run a 2-week sprint to collect data, then a monthly review to change prompts, templates, and thresholds.
Using templates, automations, and clear SLAs keeps the system predictable and improvable. Over time, the pipeline becomes the team’s most valuable productivity lever—freeing creative energy for high-impact work while the mundane runs itself.
Step-by-Step: Scale Content Output Without Sacrificing Quality
Batching content production, reusing AI outputs, and putting tight versioning and governance in place let teams publish more without letting quality slip. The practical approach below turns those principles into repeatable steps: schedule focused sprints, route AI drafts through repurposing flows, and lock changes behind clear version control and sign-offs. This keeps momentum, preserves brand voice, and reduces firefighting.
- Plan a 1-week batching sprint with clear owners and time estimates.
- Run focused production blocks: research → draft → edit → asset creation → QA → publish.
- Repurpose AI outputs into prioritized formats using simple prompts and templates.
- Enforce version control and governance rules with sign-offs and rollback paths.
Batch Content Production
- Sprint structure: Reserve two full days for drafting, one for editing, one for assets, one for scheduling.
- Throughput gain: Writing in batches reduces context-switching and typically doubles output per writer-day.
- Time-savings example: A 5-article weekly goal becomes realistic by concentrating research into one block, shaving ~30–40% off per-article time.
A sample 1-week batching sprint timeline with tasks, owners, and time estimates
| Day | Task | Owner | Time Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Topic research & outlines | Content Strategist | 4 hours |
| Day 2 | Drafting (batch writes) | 2 Writers | 6 hours |
| Day 3 | Editing & SEO pass | Senior Editor | 4 hours |
| Day 4 | Visual assets & CTAs | Designer | 3 hours |
| Day 5 | QA, scheduling, publish | Ops/Publish Lead | 2 hours |
Key insight: Concentrating related tasks into dedicated days reduces overhead from handoffs and context-switching, making a 5-piece weekly pipeline achievable with a small team.
Reuse and Repurpose AI Outputs
Priority pathway: Long-form blog → LinkedIn post → newsletter excerpt → short video script. Sample prompt (repurpose to LinkedIn): Rewrite this 600-word section into a 150-word LinkedIn post, keep the brand voice concise, add one hook and one CTA. Sample prompt (repurpose to script): Turn this article intro and three bullets into a 60-second video script with spoken lines and suggested on-screen text. Checklist to maintain voice: Brand tone: Keep vocabulary consistent. Terminology: Preserve product names and claims exactly. CTA alignment: Same conversion goal across formats. Formatting: Use brand-approved headers and link patterns.
Implement Versioning and Content Governance
- Version control best practices: Use clear filenames
YYYYMMDD_title_v#, commit changes with notes, and store master in a single CMS branch. - Governance rules and sign-off: Author drafts → Editor approves content → Legal reviews claims (if required) → Publish lead schedules live date and confirms metadata.
- Archival and rollback: Archive every published version; keep a rollback window (30–90 days) with immediate restore process and a changelog for audit.
Using these steps keeps output high while protecting voice and accuracy, so scaling content becomes predictable rather than chaotic. Investing a bit of upfront discipline around batching, repurposing, and governance pays back in steady, reliable content velocity.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Low-quality or off-brand outputs usually come from weak prompts, missing guardrails, or noisy training data. Fixes start with diagnosing where the drift occurs — prompt, model, or post-process — then apply layered controls: stronger prompts, stricter QA rules, and automated rejection. Expect small iterative gains early; consistent guardrails prevent large-scale brand damage.
Diagnose poor outputs quickly Prompt mismatch: Model follows instructions literally; check whether the brief contains voice, audience, and forbidden phrases. Model limitation: Some models hallucinate on factual claims; mark requires_fact_check for those outputs. * Data noise: Old or off-brand examples in your fine-tune set skew tone.
Prompt fixes and guardrails 1. Use a compact style guide at the top of every prompt. 2. Add explicit negative examples and do_not_do bullets. 3. Automate a brand_score that rejects content below a threshold.
QA and rejection rules Automated checks: Run readability, brand_tone, and factuality checks against every draft. Human spot-checks: Sample 5–10% weekly; escalate recurring failures. * Rejection flow: Send failed items back to a small, dedicated rewrite queue.
Automation breaks or flaky integrations demand systematic debugging and safe rollback paths. Begin with an integration checklist and instrumented error handling so failures are visible before they reach production.
Common integration failure modes and corresponding fixes for quick diagnosis
| Failure Mode | Symptoms | Immediate Fix | Preventative Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auth token expired | 401s, sudden service denial | Refresh token; rotate keys | Short-lived tokens + automated rotation |
| Payload schema mismatch | 400s, missing fields | Validate and transform payload | Schema validation at ingress |
| Rate limits hit | 429 responses, throttled calls | Backoff and retry with jitter | Client-side rate limiting |
| Partial publish failures | Some posts live, others not | Retry failed items; reconcile state | Idempotent publish endpoints |
| Webhook delivery issues | Missed events, retries piling | Inspect delivery logs; resend | Durable queues + backpressure control |
Key insight: the table groups fast fixes and long-term prevention so you stop outages quickly and avoid repeats by design.
Compliance and copyright concerns require a defensible sourcing workflow and clear contract language with vendors. Build citation steps into the pipeline: require source_urls for facts, flag unattributed content, and run similarity checks against in-house IP.
When to consult legal: Complex licensing, syndicated content deals, or high-risk claims.
Vendor contract considerations: Explicit IP ownership, indemnities, and data-retention limits.
For persistent problems, consider an external audit or partnering with a specialist. For teams ready to scale safely, integrating an AI content automation platform like Scaleblogger.com can standardize prompt templates, QA pipelines, and publishing controls while preserving brand voice. Keep monitoring and iterate — small safeguards save big headaches down the line.
Tips for Success (Pro Tips)
Start by fixing the low-effort wins, then make measurement and repeatability non-negotiable. These pro tips prioritize impact first: quick wins you can deploy in a day, then systems that compound results over months.
- Quick win — prioritize headlines: A/B test three headline variants for each post; swap in the best-performing title within 48 hours.
- Quick win — refresh evergreen content: Update stats, links, and a new intro for your top 10 posts every quarter to regain traffic quickly.
- Instrument for measurement: Add
UTMtags, page-level event tracking, and a simple dashboard so you know which posts drive leads and which only attract clicks. - Maintain a prompt/version library: Save every prompt, prompt variation, and the resulting output with version notes; refer back when a style or angle performs well.
- Use content scoring: Score drafts for intent match, readability, and keyword coverage before publishing to reduce guesswork.
- Build a reusable template system: Create templates for listicles, how-tos, and long-form that include required SEO fields and internal link slots.
- Automate mundane publishing tasks: Schedule social posts, canonical tags, and metadata updates through an automation tool to prevent human lag.
- Prioritize cluster strategy over isolated posts: Group content into topic clusters so authority and internal linking grow together.
- Set cadence with guardrails: Plan frequency (e.g., 2 long-forms + 4 updates per month) and enforce minimum quality checks for each publish.
- Run monthly performance reviews: Focus on velocity (publishing), traction (engagement), and conversion (leads) — then iterate.
- Add tracking: create
UTM-tagged campaign links for distribution. - Measure: check CTR, time-on-page, and conversion uplift after 30 days.
- Iterate: update poorly performing posts or repurpose high-engagement sections into short-form.
Prompt library: Store prompts, example outputs, and a short note about when to reuse each entry.
Common pitfalls to dodge: chasing every new tool without measurement, treating AI output as final copy, and skipping version control for prompts. Market leaders and experienced teams rely on repeatable processes, not one-off hacks. If you want a faster way to wire these systems together, platforms that automate pipelines and benchmarking can shave weeks off setup — consider solutions that integrate tracking, publishing, and content scoring like Scaleblogger.com.
Treat these tips as the operational rules that let good ideas scale into predictable results — implement the first three this week and measure the difference by month-end.
📥 Download: AI Integration Workflow Checklist (PDF)
Appendix: Templates, Prompts and Resources
This section collects ready-to-use prompts, downloadable templates, and a straightforward automation recipe so work moves from idea to publishable content with minimal friction. The templates are designed to slot into existing content workflows, speed audits and QA, and automate repetitive steps in a content pipeline.
- Prompt Templates: Copy/paste-ready prompts for ideation, outlines, and SEO optimization.
- Audit & QA Templates: Spreadsheets and checklists that surface structural SEO issues and editorial gaps.
- Automation Recipe: A step-by-step Zapier-style flow that connects content creation, review, and publishing.
Downloadable resources and what each contains so readers can grab assets quickly
| Resource | Format | Purpose | Estimated Customization Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content Audit Spreadsheet | Google Sheets | Crawl-based structure + editorial scorecards, keyword coverage matrix | 30–60 minutes |
| Prompt Template Pack | Markdown / DOCX | 30+ prompts: ideation, outline, draft expansion, meta tags, CTAs | 15–30 minutes |
| QA Checklist | PDF / Checklist | Editorial checks, SEO checks, accessibility items, publish checklist | 10–20 minutes |
| Zapier Recipe Example | JSON export / text | Trigger: Approved draft → actions: publish draft, notify slack, update sheet | 20–45 minutes |
| Governance Policy Template | Google Docs | Roles, versioning, AI usage policy, approval SLAs | 45–90 minutes |
This table groups resources so a content operator can pick assets by need and estimate time to adapt them.
Practical prompt examples (copy/paste and tweak)
- Idea expansion: “Generate 12 blog post ideas about
topicaimed ataudience, each with a 10-word headline and 2-sentence audience hook.” - SEO outline: “Create an SEO-optimized outline for
keyword phrasewith H2s, suggested word counts, and three LSI keywords per section.” - Draft refinement: “Improve this paragraph for clarity and scanability, keep technical accuracy, shorten sentences to ~18 words.”
Sample automation recipe (step-by-step)
- Create a new row in
Content Audit Spreadsheetwhen an idea is approved. - Run an automated prompt (via API) to generate an outline and attach it to the sheet.
- Assign the outline to a writer and set a Content Due date in the sheet.
- On submission, trigger the QA Checklist — if any item fails, route back to the writer; if all pass, queue for publishing.
- On publish, post the URL to Slack and update the governance log with the publish timestamp.
s
Prompt: A movable instruction given to an AI model to produce content or data.
Audit score: A composite metric combining structure, keyword coverage, and editorial health.
Governance policy: Rules that define how AI is used, reviewed, and approved in publishing.
This appendix is meant to be practical: grab a prompt, drop it into your editor or API call, and use the accompanying spreadsheet and QA checklist to stop mistakes before they reach the live site. If you want a packaged setup that wires these pieces together, Scale your content workflow shows how to automate the whole pipeline end-to-end.
Conclusion
You’ve now got a practical route from a stalled editorial calendar to a repeatable, measurable content workflow: audit where time leaks happen, wire an AI-enabled pipeline for briefs and drafts, and scale output while enforcing quality checks. Teams that turned routine tasks—research, brief creation, and scheduling—into automated steps saw steadier publishing rhythms and fewer last-minute scrambles. If engineering help is limited, start with no-code integrations and focused prompts; if quality feels at risk, add a short human review stage and a consistent style checklist.
Start small and build: identify one repeatable task to automate this week, measure content output before and after, and create a 30/60/90 plan to expand automation. Expect early wins in throughput, then tune for voice and conversion. For teams looking to streamline or outsource parts of this process, platforms that specialize in AI tools for editorial pipelines can shorten the learning curve. To explore a dedicated option for scaling your content workflow, consider: Scale your AI-enabled content workflow with Scaleblogger.

