Marketing teams still lose weeks each quarter to misaligned briefs, duplicated drafts, and slow approvals—problems that scale as teams add AI tools. Build a collaborative, AI-driven content team by combining people who frame strategy, creators who calibrate AI, engineers who automate pipelines, and ops specialists who measure impact. This structure accelerates production, reduces rework, and turns AI from a novelty into predictable output.
Industry practice shows cross-functional roles outperform siloed teams when AI tasks are explicit and measurable. A tight roster including a content strategist, AI prompt-specialist, data analyst, workflow engineer, and project lead lets organizations run repeatable campaigns and scale personalized content. Picture a B2B marketing program that cuts time-to-publish by 40% by automating research and editorial checks while preserving voice through human oversight.
Credible teams document guardrails, version prompts, and track `content-ROI` to retain control as automation increases. Scaleblogger helps design these workflows and map skills for real teams, from role templates to automation playbooks. Discover AI content workflows and automation at Scaleblogger: https://scaleblogger.com
- What a hybrid team structure looks like and who owns what
- Practical skills for AI content roles and hiring signals
- How to connect prompts, pipelines, and analytics for consistent output
- Governance patterns to keep quality and brand voice intact
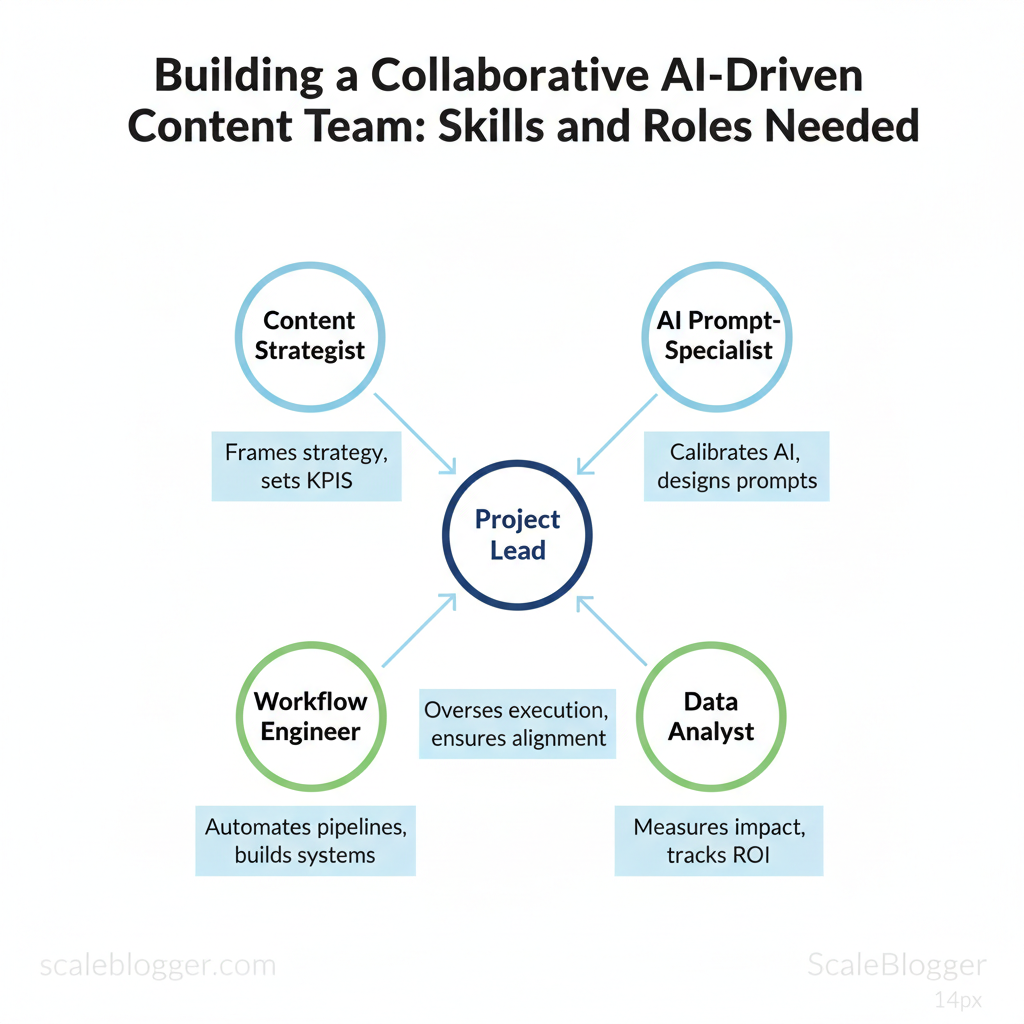
Section 1: Foundation — Why a Collaborative AI-Driven Content Team Matters
A collaborative AI-driven content team speeds up ideation and drafting, keeps brand voice consistent across scale, and unlocks data-driven personalization without doubling headcount. When writers, strategists, and automation systems work together, repetitive tasks move to AI while humans focus on judgment, nuance, and creative direction. That combination yields faster time-to-publish, predictable quality, and measurable lift from personalized content variants — all essential when competing for attention and search visibility.
Why this matters practically:
- Faster ideation: AI surfaces headline variants, topic gaps, and question clusters from keyword and SERP patterns.
- Consistent voice: Style guidelines encoded as templates keep output aligned across contributors.
- Personalization at scale: Parameterized templates + user signals let teams produce many personalized permutations quickly.
Roles that unite humans and AI
- Content strategist: sets KPIs, briefs `prompt` templates, and reviews model outputs.
- Writer-editor pair: crafts high-value sections and performs editorial QA.
- Automation engineer: builds pipelines for scheduling, metadata enrichment, and performance tracking.
- Data analyst: ties content variants to engagement signals and adjusts models.
Common risks and mitigation Hallucination risk:* mandate human fact-check for claims and data. Voice drift:* lock core brand voice elements in templates and linters. Bias amplification:* diversify prompt inputs and review outputs for representational fairness.
| Capability | Manual Team | AI-Augmented Team | Fully Automated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to first draft | 3–7 days | hours–24 hours | minutes–hours |
| Quality consistency | Variable by writer | High with human QA | Consistent, needs monitoring |
| Personalization at scale | Limited manual segments | Personalized variants at scale | High personalization via templates |
| Iteration speed | Slow (days–weeks) | Fast (hours–days) | Fastest (minutes–hours) |
| Cost per piece | $500–$2,000 | $50–$300 | <$50 |
For teams ready to operationalize this, tools that automate pipelines and measure performance—paired with a clear governance checklist—make the transition manageable. If you want a hands-on way to implement these patterns, consider how to `scale` your content workflow and measure results with an AI-powered content pipeline like those offered by services that automate scheduling, benchmarking, and optimization. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Section 2: Roles and Responsibilities — Defining the AI-Driven Content Team
An effective AI-driven content team blends traditional editorial skills with model-first technical roles so outputs map directly to business goals. Start by anchoring the team around four core roles — content strategist, AI/prompt engineer, editor, and data analyst — then extend into legal, UX, product, and project management to close governance and delivery gaps. This structure prevents model drift, protects brand voice, and turns raw AI drafts into measurable traffic and conversion gains.
Core role descriptions and how they interact
- Content Strategist: Aligns content topics to business objectives, defines audience segments, and sets KPIs like organic sessions, conversions per article, and topic-cluster growth.
- AI/Prompt Engineer: Designs and version-controls prompts, manages model selection and temperature settings, and maintains prompt libraries. Their output quality is measured by relevance score and reduction in human rewrite time.
- Editor / Fact-Checker: Applies brand tone, corrects factual errors, and enforces compliance; essential for reducing risk and maintaining trust.
- Data Analyst: Tracks content performance, builds dashboards, and uses model feedback loops to retrain prompts or fine-tune models based on engagement metrics.
Extended stakeholders and collaboration rituals
- Legal/Compliance: Reviews riskier content and maintains a checklist for claims and IP.
- UX/Product: Ensures content fits user journeys and feeds product roadmaps.
- Project Manager: Coordinates sprints, backlog, and SLAs for content delivery.
Creating a RACI for AI content projects helps avoid handoff confusion:
- Responsible: Prompt Engineer, Editor
- Accountable: Content Strategist
- Consulted: Legal, UX, Product
- Informed: Marketing Ops, Stakeholders
| Role | Primary Responsibilities | Essential Skills | Key KPIs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content Strategist | Topic strategy, editorial calendar, KPI alignment | SEO strategy, audience research, stakeholder management | Organic sessions, CTR, conversions |
| AI / Prompt Engineer | Prompt design, model selection, prompt versioning | NLP concepts, prompt engineering, Git/version control | Draft accuracy, rewrite reduction (%) |
| Editor / Fact-Checker | Tone, accuracy, legal checks | Editing, fact-checking, CMS workflow | Error rate, publish time, brand consistency |
| Content Designer / SEO Specialist | On-page SEO, content structure, internal linking | Technical SEO, UX writing, schema | SERP rankings, time on page |
| Data Analyst | Performance dashboards, feedback loops | SQL, analytics (GA4), A/B testing | Engagement, conversion uplift, model drift metrics |
Understanding these responsibilities lets teams move faster while keeping quality and compliance intact. When implemented properly, these roles reduce bottlenecks and make content decisions measurable at the team level.

Section 3: Skills Matrix — What to Hire and Train For
You should hire for a blend of technical AI fluency and classic creative judgment: hire juniors who can execute repeatable tasks and learn tooling, mids who bridge prompts to strategy, and seniors who set evaluation standards and maintain brand voice. That means investing in core technical skills—prompt engineering, model evaluation, and platform fluency—while simultaneously training people in editing, narrative craft, and cross-functional collaboration so AI-generated drafts feel authentic and useful. Practical training pairs short, measurable tasks (prompt A/B tests, labeling exercises) with creative workshops (story arcs, brand voice drills) so teams deliver predictable quality at scale.
Technical and AI-specific skills
- Prompt engineering: teach prompt decomposition, context windows, and result conditioning with `system`/`user` role prompts.
- Model evaluation: simple metrics (relevance, factuality, hallucination rate) plus human-review workflows.
- Tool fluency: hands-on with content platforms, CMS integrations, and basic API use (export/import, scheduling).
- Editing and voice: exercises where writers rewrite AI drafts to match style guides.
- Storytelling: teach structure templates—hook, problem, resonance, CTA—and force-fit AI output into them.
- Cross-functional communication: establish clear briefs and feedback loops with PR, product, and SEO teams.
Code example: simple prompt template “`text System: You are a concise B2B SaaS copywriter. User: Write a 60–80 word paragraph for {product} emphasizing {benefit} and include a soft CTA. “`
| Skill | Junior Proficiency | Mid Proficiency | Senior Proficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prompt Engineering | construct basic prompts, use templates | iterate prompts, prompt chaining | design prompt frameworks, optimize cost/latency |
| Content Strategy | follow briefs, topic research | map topic clusters, brief authors | set editorial calendar, ROI modeling |
| SEO & Content Optimization | keyword research basics, on-page SEO | technical SEO flags, schema use | strategy across funnels, performance forecasting |
| Data Analysis & Metrics | read dashboard KPIs, basic A/B tests | cohort analysis, attribution basics | experiment design, LTV/content impact modelling |
| Editorial Judgment | copy editing, grammar | voice consistency, structural edits | brand stewardship, sensitive content review |
If you want, I can adapt this matrix into role-specific job descriptions or a 90-day training plan aligned with your content pipeline and automation goals—useful if you plan to Scale your content workflow with AI. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
📝 Test Your Knowledge
Take this quick quiz to reinforce what you’ve learned.
Section 4: Workflows and Processes — Designing AI-Ready Content Operations
Start by treating content operations as a production line: you need clear stages, owners, measurable SLAs, and automation where it reduces friction. An AI-ready workflow codifies which tasks AI handles (drafting, metadata, variants) and which require human judgment (fact-checking, brand voice, legal). This lets teams scale output without multiplying review bottlenecks and makes handoffs predictable—so deadlines, quality gates, and analytics all become reliable inputs to continuous improvement.
Stage-by-stage workflow and checkpoints
- Clear owners: assign one accountable person per stage to avoid review ping-pong.
- Defined SLAs: use timeboxes (e.g., 24–72 hours) to keep flow predictable.
- Quality gates: acceptance criteria at each stage prevent noisy rework.
Tooling and automation: selecting platforms and building integrations
- Platform fit: choose AI tools that export structured content (Markdown, JSON) to preserve metadata.
- Integration patterns: use webhooks, middleware (Zapier/Make), or CMS APIs for hands-off handoffs.
- Automation opportunities: auto-generate meta descriptions, create GA4 event tags, or spin up A/B headline variants.
SLA and responsibility table showing stage, owner, typical time, and acceptance criteria
| Stage | Owner | Typical Time | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brief & Keyword Research | Content Strategist | 1–3 days | Keyword intent documented; target URL list; editorial brief |
| AI Draft Generation | AI Editor / Content Engineer | 1–2 hours | Structured draft (H2/H3), sources list, suggested CTAs |
| Human Edit & Fact-Check | Senior Editor | 1–2 days | No factual errors; brand voice match; plagiarism check |
| SEO Optimization | SEO Specialist | 4–8 hours | Title + meta complete; internal links added; content score ≥ threshold |
| Publication & Distribution | Publishing Manager | Same day or scheduled | Correct taxonomy, publish date set, analytics tags present |
Practical templates and integrations (CMS API snippets, release checklists, and a `content-metadata.json` pattern) turn this into an operational system. If you’d like, I can provide a ready-to-use checklist or a sample webhook mapping for common CMS platforms. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level and frees creators to focus on high-impact work like narrative and research.
If helpful, Scale your content workflow with an AI content automation partner like Scaleblogger.com to prototype integrations and SLAs quickly.
Section 5: Measurement and Iteration — KPIs and Feedback Loops
Measure what matters: focus on production throughput, content performance, and model quality together so you can diagnose whether problems are editorial, distributional, or model-driven. Start by instrumenting a small set of high-signal KPIs (time-to-publish, pieces/month, organic traffic per piece, conversion by content, and model hallucination/error rate). Those let you separate process bottlenecks from content effectiveness and model drift. What follows is a practical way to track those KPIs, capture user feedback at scale, and run a quarterly playbook that turns insights into prioritized fixes and retraining cycles.
What to track and why
- Production KPIs: measure velocity and predictability so resourcing decisions are evidence-based.
- Performance KPIs: measure reach and business impact to prioritize topics and formats.
- Model KPIs: measure factuality and relevance to know when to retrain or change prompts.
Example: how these KPIs map to action
Capture feedback and close the loop
- Instrumented feedback: embed micro-feedback widgets (thumbs, short reason) and capture session data via analytics.
- Qualitative signals: rotate short user interviews and content audits monthly.
- Model logs: log prompts, response confidence, and post-edit rates for every generated asset.
| KPI | How to Measure | Owner | Target Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to First Draft | Avg hours from brief to draft (CMS timestamps) | Content Ops | 8–24 hours |
| Pieces Published / Month | Count of published posts (CMS report) | Editorial Lead | 8–20 posts |
| Organic Traffic per Piece | 30-day sessions from GA4 / piece | SEO Owner | 500–5,000 sessions |
| Conversion Rate by Content | Goal completions / sessions (GA4) | Growth/Product | 0.5%–3.0% |
| Model Error/Hallucination Rate | % flagged inaccuracies in model logs / audits | ML Lead | <2–5% flagged answers |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented consistently, the loop from analytics to playbook to retraining means fewer surprises and steadily improving ROI from your content systems.
📥 Download: Downloadable Template (PDF)
Section 6: Roadmap — Hiring, Upskilling, and Scaling the Team
Start by running a tightly scoped pilot to validate the content stack and ROI, then stabilize processes and hire for capacity before scaling with automation and specialization. Over 12 months you should move from experimentation to repeatable production, using clear go/no-go criteria at each phase so hiring and tooling spend align with measurable output (traffic, conversions, throughput). Prioritize a small core team first — editor, SEO specialist, and AI/automation engineer — then layer in creators and analysts as cadence stabilizes. Use automation to reduce headcount pressure and redirect budget into L&D sprints and tooling that multiplies output.
Hiring and training should be playbook-driven: publish concise job ads, evaluate candidates with practical tasks, and run a structured 90-day onboarding that mixes shadowing, `tool` training, and progressive ownership. For upskilling, run 2–4 week L&D sprints focused on specific capabilities (SEO writing with AI, prompt engineering, analytics dashboards) and measure skill adoption with live content experiments. Consider integrating an AI content automation partner to accelerate pipeline setup — for example, use an `AI content automation` service to standardize prompts and publishing workflows before hiring high-volume writers.
- Job ad (SEO writer): 3–5 years writing experience, proven organic growth case, comfortable using `content briefs` and AI-assisted drafting, portfolio link required.
- Job ad (AI engineer): Experience with API orchestration, workflow automation, and data pipelines; examples of `automation` projects preferred.
- Job ad (Content analyst): Strong SQL or GA4 skills, experience with content experiments and cohort analysis.
90-day onboarding sprint
| Phase | Months | Key Milestones | Hires/Resources | Go/No-Go Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pilot | 0–2 | Build content stack, 10 live posts, baseline analytics | 1 Editor, 1 SEO specialist, automation tooling | Achieve initial CTR uplift or time-to-publish < 30% baseline |
| Stabilize | 3–5 | 30–50 posts, repeatable briefs, publishing SLA | +1 Writer, +1 Analyst, CMS integrations | Consistent weekly cadence and 3x content reuse rate |
| Scale | 6–8 | Topic clusters, A/B testing, 100+ posts | +2 Writers, AI automation engineer, scheduling tool | Cost-per-post drops; organic traffic growth month-over-month |
| Optimization | 9–10 | Content refresh program, personalization tests | +1 Growth PM, tooling for analytics | Positive lift from refreshes; experiments exceed control |
| Expansion | 11–12 | New verticals, partnership content, internationalization | Localization writer(s), CRO specialist | New verticals reach minimum traffic threshold and ROI > target |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level and freeing creators to focus on high-impact content.
Conclusion
We’ve shown how misaligned briefs, duplicated drafts, and slow approvals sap weeks from marketing calendars, and how a few disciplined changes—clear role templates, version control plus AI-assisted first drafts, and streamlined approval gates—repair that friction quickly. Teams that piloted these steps reported faster approvals and fewer rewrites; one content team cut review cycles by half after centralizing briefs and adding AI early in the draft stage. To get started, focus on small experiments that prove the workflow, then scale the pieces that reduce rework.
– Standardize briefs and roles to eliminate back-and-forth. – Use AI for first-pass drafts and outlines, not final copy. – Automate review handoffs so approvals happen inside the workflow.
If you’re wondering how long this takes to show results, most teams see improvements within one or two content cycles; if you ask who should lead, the content ops or marketing manager usually drives rollout. For teams looking to automate these workflows and measure impact faster, try a focused pilot and iterate—and if you want a platform that combines AI drafting, collaboration, and approval automation, consider this next step: Discover AI content workflows and automation at Scaleblogger.

