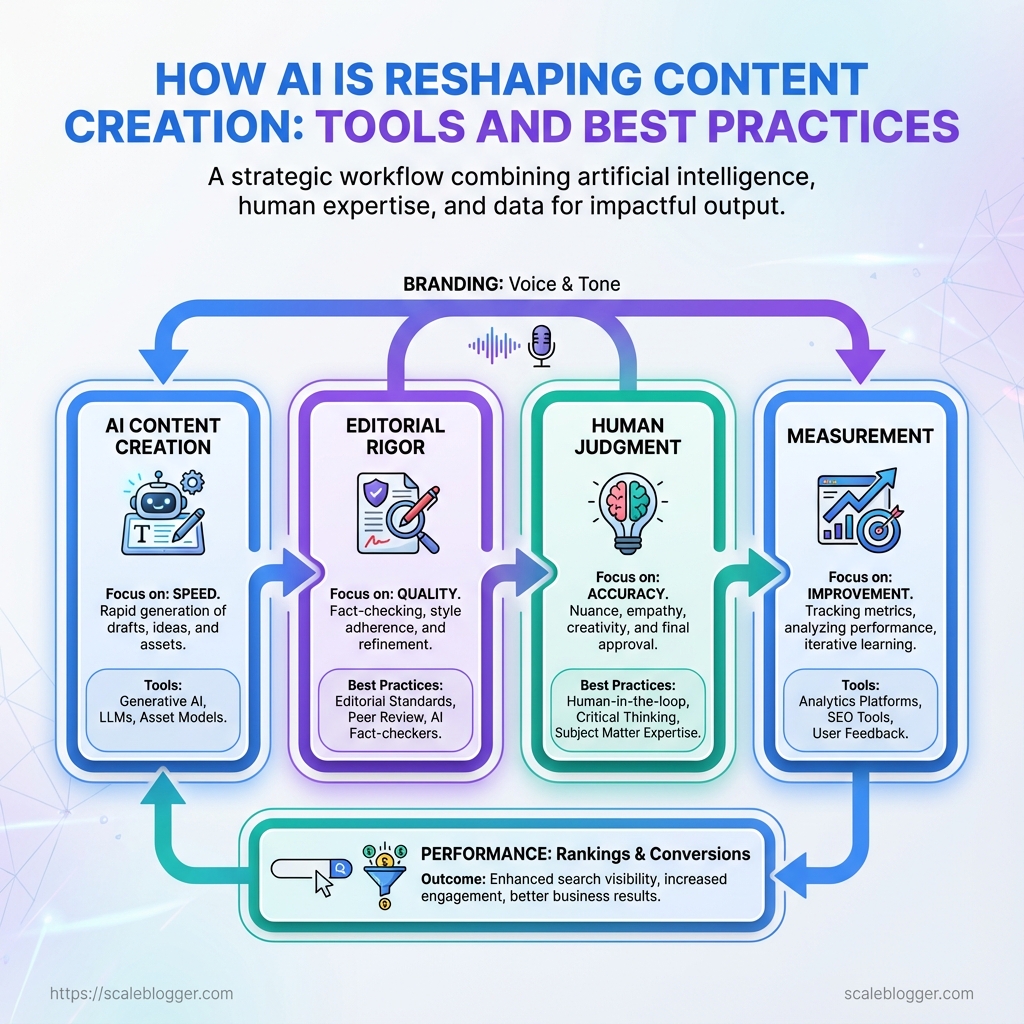
Drafts that used to take days are now edited, researched, and outlined in an hour, and that sudden speed hides a deeper shift: AI content creation is changing what counts as craft in content marketing. Teams juggling topical relevance, search intent, and consistent voice find themselves asking not whether to use automation, but how to make it produce durable, brand-safe work that actually ranks and converts.
Behind the neat interfaces sit failures readers notice—thin repeatable formats, factual drift, and tone that sounds like a neutral robot instead of a human voice. The practical question is how to combine AI writing tools with editorial rigor, human judgment, and measurement so content keeps getting better, not just faster.
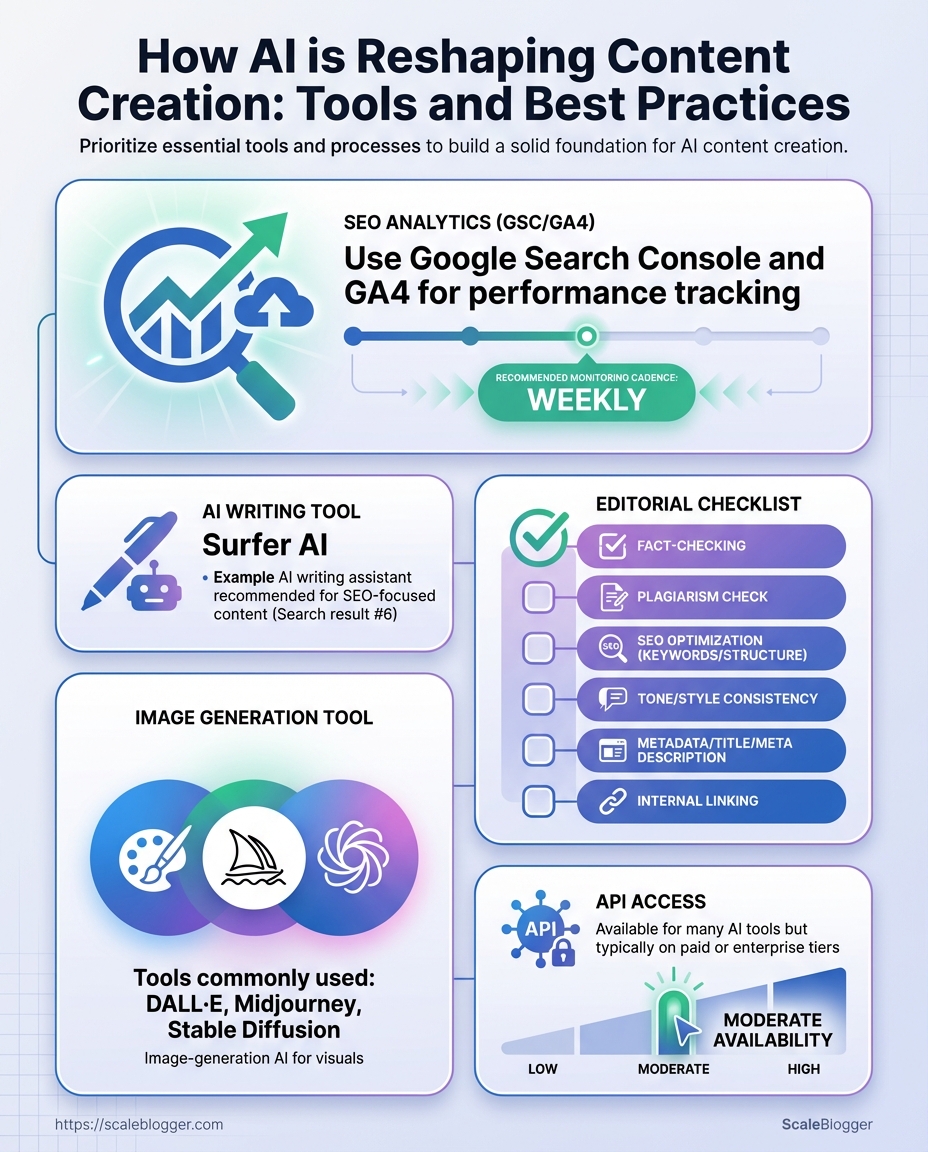
What You’ll Need (Prerequisites)
Start by getting the fundamentals in place: an AI writing platform, access to SEO and analytics, a human-led editorial process with a clear style guide, and basic prompt-engineering skills. These elements stop AI drafts from drifting off-target, make content discoverable, and ensure every post fits brand voice and performance goals.
Accounts, Tools, and Skills
AI writing tool: Use either a web UI (for ease) or API access (for automation). Popular choices include platforms with LLMs that support fine-tuning or adjustable temperature controls.
SEO analytics: Access to Google Search Console and Google Analytics (or GA4) is essential for monitoring impressions, clicks, and on-page performance.
Editorial checklist: A living editorial SOP that covers fact-checking, link policy, voice, headings, metadata, and sprint review cadence.
Image generation tool: On-demand image tools speed visual production; choose one that supports commercial licensing and consistent style.
API access & automation: API keys for the AI platform and CMS let you wire content into pipelines, schedule publishing, and run bulk optimizations.
Prompt-engineering skill: Know how to craft prompts that include goal, audience, constraints, and desired structure; this reduces rounds of human edits.
Practical setup steps
- Create accounts for your chosen AI platform and secure API keys.
- Claim property in Google Search Console and enable GA4 for the site.
- Draft a one-page editorial checklist and style guide; assign an editor.
- Choose an image tool with license clarity; prebuild 3-5 templates.
- Practice writing 5 prompts that produce an outline, full draft, and meta description.
Mandatory vs optional prerequisites and quick buy/setup guidance
| Prerequisite | Required/Optional | Why it matters | Quick setup tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI writing tool | Required | Enables rapid draft generation and content scaling | Start with a web UI, then add API for automation; pick a plan with prompt templates |
| SEO analytics (GSC/GA4) | Required | Measures visibility and identifies optimization opportunities | Verify domain in GSC and link GA4 to Search Console |
| Editorial checklist | Required | Keeps output accurate, on-brand, and publish-ready | Create a one-page SOP and store in shared drive; review weekly |
| Image generation tool | Optional | Speeds visual creation and maintains design consistency | Choose a tool with commercial use and save baseline prompts |
| API access | Optional (recommended) | Automates publishing, testing, and bulk edits | Generate keys, restrict IPs, and rotate keys periodically |
Key insight: Prioritize the three required items first — the AI tool, SEO analytics, and an editorial checklist — then layer in images and API automation. Getting those basics right reduces wasted output, accelerates iteration, and makes scaling predictable. For teams looking to automate content pipelines or benchmark performance, consider systems like Scaleblogger.com to connect AI drafting with SEO workflows and publishing automation.
Setting these prerequisites up properly saves dozens of hours per month and keeps growth focused on traffic and conversions rather than firefighting production issues.
Step-by-Step Workflow: From Brief to Publish
Start with a tight, data-driven brief and move each asset through repeatable handoffs so output stays high quality while scaling. This workflow balances machine speed with human judgment, so content ships faster without sacrificing accuracy or brand voice.
- Step 1: Create a data-driven brief
- Step 2: Craft prompts and test variations
- Step 3: Generate drafts and capture model outputs
- Step 4: Human edit, fact-check, and enforce style
- Step 5: Optimize for SEO and add metadata
- Step 6: Generate visuals and accessibility markup
- Step 7: Publish and set monitoring alerts
How each step actually works
- Step 1 — Brief creation: Pull search intent, top-ranking competitors, target keywords, audience persona, and desired CTA into a single document. Deliverable: 1–page brief with headings, target word count, and 3 prioritized angles.
- Step 2 — Prompt design: Write 4–6 prompt variants and A/B test them on short outputs to find the tone and structure that match the brief. Tip: Keep prompts modular so you can swap
voice,format, orlengthquickly.
- Step 3 — Draft generation: Use the winning prompt to produce multiple drafts, saving model outputs and temperature settings. Practice: Store raw outputs for auditability and reuse of strong paragraphs.
- Step 4 — Human edit & fact-check: Apply style guide, verify factual claims, and correct hallucinations. Must: Verify statistics and quotes against primary sources.
- Step 5 — SEO optimization: Optimize headings, internal links,
meta description, schema, and target keywords. Important: Ensure content satisfies search intent, not just keyword density.
- Step 6 — Visuals & accessibility: Create images, charts, and
alttext; add captions and semantic HTML for screen readers. Accessibility wins clicks and compliance.
- Step 7 — Publish & monitor: Deploy, schedule social posts, and set alerts for traffic, rankings, and errors. Follow-up: Triage user feedback and iterate.
Map each numbered step to time_estimate, responsible role, and success criteria
| Step | Objective | Time estimate | Responsible role | Success criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1: Brief creation | Build data-driven brief with intent & angles | 1–2 hours | Content Strategist | Brief approved; top 3 intents documented |
| Step 2: Prompt design | Create & test prompt variants | 30–60 minutes | Prompt Engineer / Writer | 2 prompts produce publishable outlines |
| Step 3: Draft generation | Generate 2–3 draft versions | 15–45 minutes | AI Writer / Specialist | One draft ≥70% target content satisfied |
| Step 4: Human edit & fact-check | Edit for voice, accuracy, citations | 1–3 hours | Editor / Subject Matter Expert | No factual errors; style compliance |
| Step 5: SEO optimization | On-page SEO, metadata, schema | 45–90 minutes | SEO Specialist | SERP-ready title/meta; internal links added |
| Step 6: Visuals & accessibility | Create visuals, add alt, captions |
1–2 hours | Designer / Accessibility Lead | Images optimized; WCAG basics met |
| Step 7: Publish & monitor | Deploy, schedule, set alerts | 15–30 minutes | Publisher / DevOps | Live page; alerts for performance set |
This table shows where time is spent and who owns each handoff, making bottlenecks visible and measurable. Integrating tools like Scaleblogger.com for automation at steps 2–5 can tighten cycles and improve predictability. When the process is repeatable, publishing frequency rises while quality stays consistent — and that’s what moves traffic and conversions over time.
Choosing the Right AI Tools
Choosing an AI tool starts with a clear use case: know whether the priority is brainstorming headlines, generating draft posts, optimizing for search intent, or automating publishing. Once the use case is locked, evaluate tools on accuracy, cost, API access, and integrations, then match those strengths to distinct stages of the content workflow (ideation, drafting, SEO optimization, publishing).
- Clarify the use case first. Are you replacing topic research, accelerating drafts, or automating publishing?
- Measure accuracy against real prompts. Run a short pilot with representative briefs.
- Check integration paths. Look for native CMS connectors or reliable
REST/GraphQLAPIs. - Estimate total cost. Include per-request API fees, seats, and content-review overhead.
- Verify governance features. Audit logs, content provenance, and model controls matter for scaled teams.
- Define the workflow stage you want to improve (ideation → drafting → SEO → publishing).
- Shortlist 3–5 vendors that match that stage and run identical prompts.
- Score outputs on relevance, factuality, and edit time saved.
- Choose the tool with the best ROI for ongoing costs and integration effort.
Side-by-side comparison of AI tool categories and evaluation criteria to guide selection
Market leaders sit across these categories, with mid-tier and emerging tools filling specific gaps. For teams that want an end-to-end, automated pipeline for idea-to-publish, explore platforms that combine SEO intelligence and publishing hooks rather than standalone generators. Scaleblogger’s AI content automation capabilities fit naturally when the goal is to scale content production while keeping SEO and publishing integrated: Scale your content workflow.
Pick the tool that reduces friction in your specific workflow rather than the one with the flashiest demo; the right fit saves editing hours and protects long-term ROI.
Prompt Engineering: Design, Test, and Iterate
Prompt design begins with a clear hypothesis about the output you want, then treats prompts like experiments: change one variable, measure the result, and iterate quickly. The practical payoff is faster convergence on prompts that produce consistent style, length, and factuality without endless manual editing. Below are concrete templates, a testing matrix for the core variables, and a short experiment workflow you can run in one afternoon.
Prompt templates
Template — Article brief (concise): Ask for a 600-word blog intro with three subheaders, use tone: conversational, include one data-backed stat, and provide a 2-sentence meta description.
Template — Rewrite for SEO: Supply the original paragraph, then request rewrite to include target keyword organically, increase clarity, and keep length within 20% of original.
Template — Style mimic: Provide a short sample sentence, then instruct the model: match voice, tone: witty but professional, limit: 120-150 words.
Prompt variables vs. expected outcomes to speed experimentation and reduce guesswork
| Variable | Low setting | High setting | Expected change in output | When to use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 0.0 | 1.0 | Lower → deterministic, focused; Higher → creative, varied phrasing | Use low for factual content, high for ideation |
| Max tokens / length | 64 tokens (~short) | 1500 tokens (~long) | Lower → concise answers; Higher → detailed, multi-section outputs | Short for snippets; long for full drafts |
| Tone specification | “neutral” | “witty, conversational, authoritative” | Narrow tone yields predictable voice; broad gets varied styles | Specify exact tone for brand consistency |
| Inclusion of examples | none | include 2 examples + output format | With examples, model follows concrete structure; without, it infers style | Use examples when precision matters |
| Instruction strictness | loose guidance | explicit constraints + stepwise tasks | Loose → creative variance; Strict → consistent, repeatable outputs | Tight constraints for publish-ready text |
Key insight: This matrix turns guesswork into a checklist—adjust one cell at a time and record outcomes. Temperature and instruction strictness usually produce the largest perceptible differences, while length and examples control granularity and structure.
- Define your hypothesis and measurable success metric (e.g., “90% of outputs require no tone edits”).
- Create 3 prompt templates:
baseline,strict, andcreative. - Run 5 iterations per template, changing only one variable per run.
- Log outputs and rate them on clarity, tone match, and factual accuracy.
Experiment tracking (example columns)
Run: 1
Template: baseline
Variable changed: Temperature 0.2 → 0.6
Rating: Tone 4/5, Accuracy 5/5, Edit time 3 min
Tips: Track edit time as a proxy for operational cost. Use seed or fixed examples to reproduce stochastic models.
For teams optimizing content pipelines, integrate prompt versions into your content automation system so the best performer becomes the default. Tools like Scaleblogger.com can then take those winning prompts and automate publishing and performance benchmarking. Iteration turns promising prompts into reliable, low-friction content engines.
Human Review, Quality Control, and Ethics
Human oversight is non-negotiable: automated drafts are fast, but human review ensures accuracy, context, and ethical alignment. Reviewers catch nuance that models miss — outdated facts, subtle bias, or missing disclosures — and they turn a technically correct draft into a trustworthy asset readers can rely on.
Quality control checklist and practical steps
- Review the claimset line-by-line.
- Verify each factual claim against a primary source or an authoritative aggregator.
- For statistics, trace the number back to its original report or dataset rather than a secondary blog.
- Run automated scans.
plagiarism checkerto ensure originality.- Readability and tone tools to confirm the piece matches the target audience.
- Editorial pass for logic and bias.
- Flag loaded language or unbalanced framing.
- Rephrase or add context where omission could mislead.
- Legal and compliance review when applicable.
- Check for copyright risks and fair use.
- Ensure required disclosures and disclaimers are present.
QC checklist (use for every published post)
- Fact verification: Each non-obvious claim cites a primary source or official guidance.
- Originality: Passed a plagiarism scan with sources documented.
- Readability: Grade level and tone match the audience; long sentences trimmed.
- Bias audit: Potential framing issues identified and corrected.
- Disclosure: Paid partnerships, affiliate links, or AI-assisted generation are clearly labeled.
- Metadata check: Titles, tags, and structured data reflect article content and intent.
Ethical guidelines and real examples
Transparency: When AI tools were used in drafting, include a short disclosure line. Human accountability: Assign a named editor responsible for the final sign-off. Privacy: Remove or anonymize personal data unless explicit consent exists.
Example: If a post cites “industry adoption rates,” link to the original vendor report rather than repeating a quoted percentage found on a third-party marketing blog. If using AI for outlines or first drafts, note that in the byline and ensure a human verified all claims.
Automation can scale quality when paired with disciplined review. Tools like Scaleblogger.com help automate workflow and content scoring, but the final ethical judgments and factual sign-offs should always come from a person. Good human review turns speed into trust, and that trust is what keeps readers coming back.
SEO and Performance Optimization for AI Content
AI-generated drafts still need classic on-page and performance checks before hitting publish. Start by mapping a primary keyword and two secondary intent keywords, then validate headings, meta, schema, accessibility, and analytics events. These steps make AI content discoverable, fast, and measurable — not just readable.
Quick practical workflow
- Identify target keywords and intent.
- Optimize H1, H2s, and meta description manually for clarity and CTR.
- Add structured data where relevant and test it.
- Run accessibility and performance tests; fix any blockers.
- Hook up analytics events to measure engagement and conversions.
What to test and why
- Keyword mapping: Map one primary keyword and two secondary keywords to avoid keyword cannibalization.
- Headings and meta: H1 should match user intent; H2s should support topical subqueries. Meta description must sell the click in 140–160 characters.
- Structured data: Use
Article,FAQ, orHowToschema as applicable so search features can surface the content. - Accessibility: Ensure images have
alttext and pages pass basic contrast and keyboard navigation checks. - Analytics/event tracking: Measure scroll depth, CTA clicks, and form submissions to evaluate content ROI.
Step-by-step pre-publish checklist
- Map primary keyword and two secondary keywords to the article and update internal linking targets.
- Manually rewrite H1 and all H2s so they read naturally and include intent signals.
- Craft a meta description focused on action and benefit; keep it within 140–160 characters.
- Implement structured data using
JSON-LDand validate in a structured data tester. - Run Lighthouse for performance; fix any TTI, CLS, or Largest Contentful Paint issues.
- Run accessibility audit (Lighthouse or axe-core) and resolve high-priority issues.
- Set up GA4 and Tag Manager events for engagement signals (scroll, CTR, conversions).
- Final crawl with a site-audit tool to catch broken links and canonical issues.
Quick pre-publish checklist with pass/fail criteria and estimated time per task
Quick pre-publish checklist with pass/fail criteria and estimated time per task
| Task | Pass criteria | Estimated time | Tool to use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keyword mapping | Primary + 2 secondaries assigned to headings | 15–30 min | Keyword planner / Semrush |
| Meta description | 140–160 chars, unique, CTA present | 10–15 min | Yoast / SurferSEO |
| Schema markup | Valid JSON-LD, no errors in validator |
15–30 min | Structured Data Testing Tool / Rich Results Test |
| Accessibility checks | No critical contrast/aria failures | 20–40 min | Lighthouse / axe-core |
| Analytics event setup | Events firing in debug mode | 20–45 min | GA4 + Google Tag Manager |
Brief analysis: The checklist balances quick editorial checks (meta, headings) with technical validations (schema, performance, analytics). Running these tests removes basic discoverability and measurement gaps so AI content can actually drive traffic and conversions.
For recurring workflows, automate parts of this pipeline — for example, schedule a final Lighthouse run and schema validation via CI. Tools like Scaleblogger.com can plug into editorial pipelines to automate keyword mapping, schema insertion, and performance gating so teams spend less time on repetitive checks and more on strategy.
Get these checks habitual and the content will behave like intentionally built pages, not experiments.
Publishing, Monitoring, and Iteration
Start by treating publication as the start line, not the finish. Set up tracking and alerts before content goes live, then monitor impressions, CTR, time_on_page, and conversions closely for the first 90 days. Use those early signals to decide whether a piece needs distribution, on-page tweaks, or a rewrite. Establish simple iteration rules that turn metrics into action so editorial effort gets allocated to the pages that will move the needle fastest.
Tracking: UTM parameters on all promotion links and page_location + page_referrer captured in GA4.
Events: content_view, cta_click, newsletter_signup, and lead_submit mapped to conversions.
Baseline: Historical averages for impressions, CTR, time_on_page, and conversion rate by content type.
How to prioritize and run iterations
- Set up dashboards and alerts.
- Create a GA4 exploration for impressions, CTR,
engagement_time, and conversions per URL. - Add automated Slack or email alerts for a sudden drop (>30%) or spike (>50%) in impressions or conversions.
- Define iteration thresholds:
- If CTR < historical CTR - 20% and impressions > 1,000 → test new title/meta.
- If engagement_time < median by content type → add visuals, TL;DR, or restructure.
- If conversions low but traffic high → add or A/B test CTAs and forms.
Practical checks and who does what
- Editorial owner: Reviews titles, H1s, intros based on CTR drops.
- SEO/analytics owner: Validates tracking, inspects SERP positions, checks for indexing issues.
- Growth/paid owner: Boosts or pauses paid promotion depending on performance.
30/60/90 day iteration plan mapping metrics to actions and ownership
| Day range | Primary metric focus | Action | Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-30 days | Impressions & CTR | Refresh title/meta, monitor SERP features, quick promo push | Content Editor |
| 31-60 days | Time_on_page & engagement | Add visuals, reorder sections, internal links, update examples | Content Editor |
| 61-90 days | Conversions & SEO velocity | A/B test CTAs, optimize forms, expand topic cluster pages | Growth Lead |
| Ongoing monitoring | Traffic quality & retention | Weekly dashboards, monthly content audits, backlinks outreach | SEO/Analytics |
| Escalation triggers | Sudden drops/spikes | Immediate tracking validation, rollback recent changes, deep diagnostic | Analytics Lead |
Key insight: Early impressions and CTR point to discoverability issues, while engagement and conversions reveal product/offer fit. Mapping owners to actions prevents churn and keeps iterations surgical.
Useful tools and automation
- Set UTMs: Standardize
utm_source,utm_medium,utm_campaign. - Automate alerts: Use GA4 + Slack or Looker Studio scheduled reports.
- Score content: Use a simple rubric (traffic, CTR, engagement, conversions) to rank pages for rewrite.
For teams wanting to scale iteration workflows, consider plugging analytics into an automated content pipeline—services like Scaleblogger.com streamline scheduling, tracking, and content scoring so iteration becomes repeatable and fast.
When tracking is disciplined and ownership is clear, small changes compound quickly into measurable traffic and conversion gains.
📥 Download: Content Creation with AI: Step-by-Step Checklist (PDF)

Troubleshooting Common Issues
When an AI content pipeline breaks, the fastest path back to usable output is diagnosing the exact failure mode and applying surgical fixes. Below are common problem–solution pairs that come up when using AI writing tools and content automation, with practical steps you can run right away.
Hallucinations: Confident-sounding but false claims in generated copy.
Fix: 1. Use explicit fact-checking prompts that ask the model to cite sources and flag uncertain claims. 2. Cross-check suspicious facts against authoritative pages and add citations or remove the claim. 3. When reusing model output, insert an editorial pass that marks any claim without a verifiable source for human review.
Inconsistent tone across assets: Articles from the same pipeline read like different authors.
Fix: 1. Create a concise voice guide (3–5 lines) and include it in the system prompt. 2. Re-prompt with examples: paste a short paragraph and ask the model to match its tone and cadence. 3. Use temperature lower for deterministic tone and higher for creative sections, then normalize in copyediting.
SEO underperformance (poor rankings, cannibalization): Content doesn’t rank or competes with your own pages.
Fix: Manual editing: update titles, meta descriptions, and internal links to clarify intent. Canonicalization: ensure the correct page uses the rel="canonical" tag to consolidate signals. * Keyword intent audit: map each URL to a single search intent and merge or re-target overlapping pages.
Duplicate or near-duplicate content: Repetitive AI outputs causing index bloat.
Fix: Add unique research: insert original examples, data, or interviews into each piece. Cite and quote: attribute sources to create distinct value. * Use content scoring: prioritize pages with original insight and prune low-value duplicates.
API errors and rate limits: 429 responses, timeouts, or throttled throughput.
Fix: 1. Implement exponential backoff with jitter for retries.
- Queue and batch non-urgent requests to smooth peaks.
- Monitor usage and set alerting thresholds; consider scaling plan or sharding requests across endpoints.
Practical checklist before republishing: Validate facts on any contentious claim. Confirm tone by comparing to a 100–200 word exemplar. Run an SEO quick-audit for titles, headings, and canonical tags. Check uniqueness with a brief research insertion or citation.
For teams using an AI-driven content workflow, tools that combine automation with editorial checkpoints reduce these failures dramatically. For example, integrating an AI content automation partner like Scale your content workflow can add governance layers for fact-checking and canonicalization while keeping throughput high. Keep iteration tight: small, repeatable fixes beat heavy overhauls when deadlines loom.
Tips for Success and Pro Tips
Treat AI as a production assistant, not a replacement for editorial judgment. Start by versioning everything you feed into models so every prompt, dataset, and output has a history you can audit and iterate on. Keep a human in the loop for framing, fact-checking, and final approval; automation should handle grunt work, not narrative voice or legal risk. Use metrics to decide what to scale: engagement, time-on-page, backlink velocity, and conversion rates tell a lot more than vanity output counts. Where possible, turn recurring decisions into prompt templates and small scripts so work moves faster, but gate full autopublish behind a quality threshold.
What follows are 12 practical, battle-tested tips to make AI-generated content sustainable and defensible in the long run.
- Version prompts and store examples: Keep a changelog of every prompt and output, including model, temperature, and seed.
- Maintain a human-in-the-loop: Always assign an editor to approve tone, accuracy, and compliance before publishing.
- Automate repetitive tasks: Use automation for outlines, meta descriptions, and image generation, not final copy.
- Limit full autopublish: Require a content score or manual sign-off for anything that will publish without review.
- Build
prompt templates: Standardize structures for intros, CTAs, and FAQs to reduce variance and bias. - Use iterative testing: Publish A/B variants for 2–4 weeks and optimize based on real engagement metrics.
- Score content with clear metrics: Track organic clicks, time on page, bounce rate, and SERP movement.
- Preserve editorial voice: Create a style guide snippets library and enforce them through prompts and tooling.
- Audit for hallucinations: Run factual checks against trusted sources and flag risky claims for human verification.
- Recycle and repurpose responsibly: Turn high-performing pieces into topic clusters, not near-duplicate posts.
- Monitor model drift: Re-evaluate prompts after model updates; what worked on one version may change behavior.
- Pipeline orchestration: Orchestrate creation, review, and publish steps with a scheduler—tools like Scaleblogger.com can help automate pipelines while preserving checkpoints.
These practices reduce risk, improve quality, and let teams scale without losing control. Treat the system as an evolving machine: small, tracked improvements compound into durable content advantage.
Conclusion
You’ve seen how a tight workflow — clear briefs, iterative prompt testing, topic clustering, and a human-review gate — turns drafts that used to take days into publishable pieces within an hour. Teams that automated keyword research and topic clustering saw steadier topic coverage and faster drafts; others who layered human fact-checking avoided accuracy slips and tone drift. Keep three habits: iterate prompts quickly, keep a human reviewer for final quality control, and measure search performance weekly so the system learns what actually moves traffic.
If questions are sitting at the back of your mind — “How do I preserve brand voice?” or “When do I automate vs. hand-edit?” — treat automation as the draft engine, not the editor. Start with small batches, compare outcomes, then scale what works. For teams looking to streamline production or test AI writing tools across your content stack, platforms like Try Scaleblogger’s AI content services can speed setup and tie automation to measurable SEO wins. Take one concrete next step today: run a single-week experiment with automated briefs and a human edit pass, measure results, then repeat. That cycle is where consistent growth lives.

