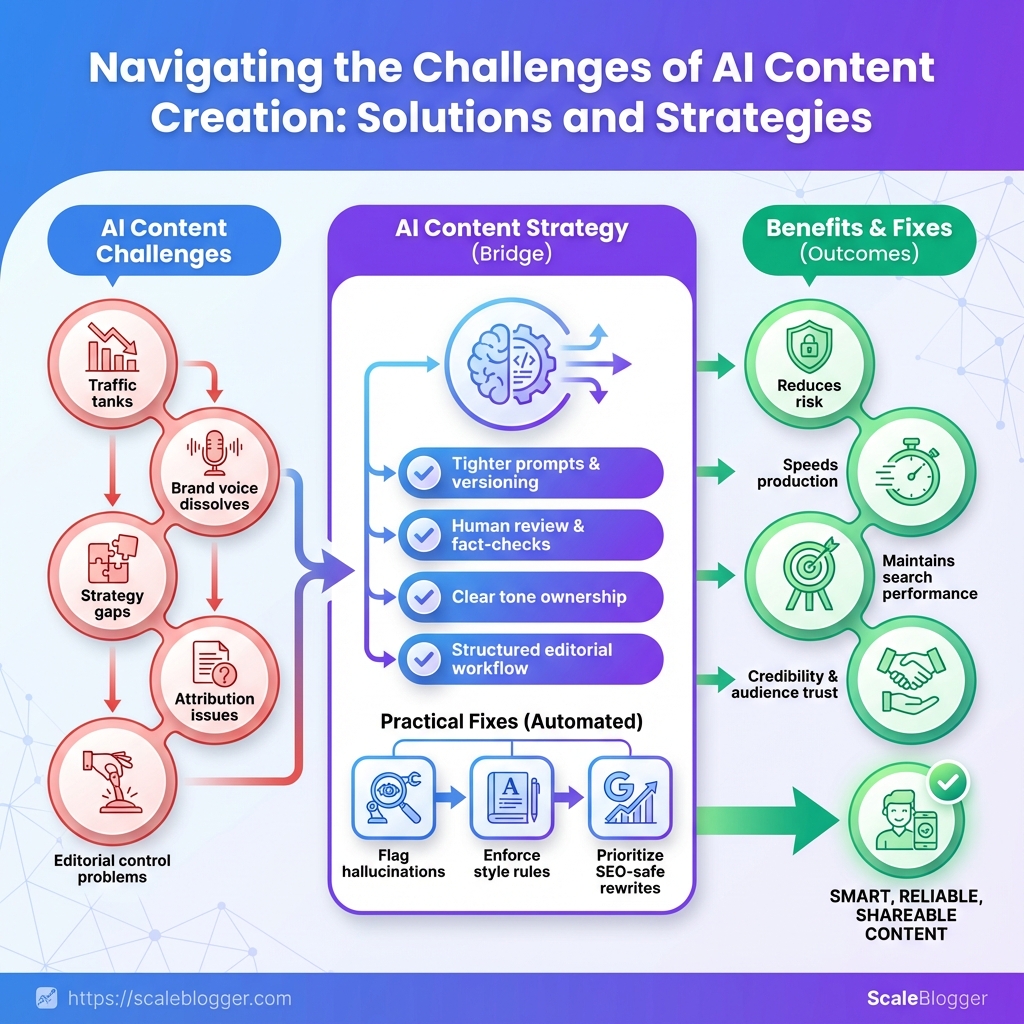
The flood of AI-generated drafts looks like an efficiency win until traffic tanks and brand voice dissolves into generic copy. Teams recognize the real problem: it’s not that models write poorly, it’s that they amplify gaps in strategy, attribution, and editorial control—those are the challenges of AI content that derail results fast.
What separates useful automation from wasted effort is a practical, defensible AI content strategy that guards search performance, credibility, and audience trust. That means tighter prompts, versioning, human review gates, and clear ownership for factual checks and tone.
Practical fixes can be automated without surrendering quality—content workflows that flag hallucinations, enforce style rules, and prioritize SEO-safe rewrites reduce risk while speeding production. Explore Scaleblogger to automate AI-safe content workflows and see how orchestration removes routine friction so your team focuses on the parts that still need human judgment.
Quick Facts: Time, Difficulty, and Prerequisites
A small content batch (3–5 posts) typically takes 6–12 hours from brief to publish; a full content strategy overhaul runs 2–4 weeks depending on stakeholder sign-offs and audit depth. Difficulty scales with scope: tactical execution is straightforward if templates and roles exist, while strategic work (audits, governance, measurement) is moderate to hard because it requires cross-team alignment and data access.
Project Snapshot 1. Time estimate: 6–12 hours — small batch (3–5 posts, reuseable briefs) 1–2 weeks — recurring monthly production (planning, writing, editing) 2–4 weeks — strategy overhaul (audit, roadmap, governance)
2. Difficulty level: Tactical: Low–Medium — content creation workflows and AI prompts suffice. Strategic: Medium–High — analytics, taxonomy work, and executive alignment required.
3. Who you need / skill level: Writer/editor: Experienced with SEO and brief-following. Editor/reviewer: Senior editor for fact-checks and voice. Analyst: Basic GA4 skills to read traffic and intent signals. Technical owner: CMS & publishing permissions. * AI operator: Familiarity with chosen model prompts and guardrails.
Tools & materials commonly required
- Content brief template: standardized fields for intent, keywords, links.
- Analytics access: GA4 or equivalent for intent and performance baselines.
- AI writing tool: OpenAI, PaLM, Anthropic, or comparable model.
- Editorial reviewer: human-in-the-loop to catch nuance and compliance.
- Plagiarism/SEO checker: Surfer, Copyscape, or Grammarly/Turnitin for quality control.
Quick comparison of prerequisites and why each matters
| Prerequisite | Why it’s needed | Difficulty to obtain | Alternatives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content brief template | Ensures consistent intent & output | Easy | Reuse Google Doc templates |
| Access to analytics (GA4) | Measures intent, performance baseline | Medium | Search Console, SE Ranking |
| AI writing tool (OpenAI/PaLM/other) | Speeds first-draft generation | Medium | Jasper, Claude, local LLM |
| Editorial reviewer | Maintains brand voice & factual accuracy | Medium | Contract editors, peer review |
| Plagiarism/SEO checker | Prevents duplicate content & fine-tunes SEO | Easy | Grammarly, Surfer SEO |
Key insight: Having templates, analytics, AI access, and a reviewer covers most failure modes of AI content workflows. Missing any of these raises risk—analytics gaps lead to poor topic fit; no reviewer creates brand drift.
Bringing these elements together dramatically cuts iteration time and raises quality. For teams wanting automation plus governance, options like Scaleblogger.com can plug gaps in pipeline and measurement, letting creators focus on strategy and craft.
Step-by-Step: Audit Your Existing AI Content
Start by exporting a full content inventory and tagging anything that came from AI-generated prompts. That single act converts a guessing game into a prioritized project: you’ll know what to fix first, where misinformation might live, and which pages actually drive traffic or conversions.
Content inventory export: A CSV or spreadsheet listing URL, title, date, author, word count, and source tag.
Access: Google Search Console and GA4 permissions for performance data.
Tools & materials
- Spreadsheet tool: Google Sheets or Excel for tagging and tracking.
- Performance platforms: Google Search Console, GA4.
- Plagiarism check: Copyscape or similar.
- Fact-checking: Manual source verification and established fact-checking tools.
- Optional automation: Scaleblogger.com for pipeline automation and content scoring.
- Export your content inventory from the CMS or site crawl.
- Add a column for
Content Originand markAI-generated,Human, orHybrid. - Pull performance for each URL from Google Search Console and GA4; add traffic, impressions, CTR, and conversions to the sheet.
- Run a plagiarism scan on pages tagged
AI-generatedand flag exact matches or close rewrites. - Sample high-traffic and flagged pages for factual accuracy; check claims, dates, statistics, and named sources.
- Evaluate on-page SEO: title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and keyword intent alignment.
- Assess tone and voice consistency against brand guidelines; note pages that require rewrites for brand fit.
- Prioritize remediation by combining risk and impact: high-risk factual issues + high-traffic pages get highest priority.
What to prioritize: High risk, high traffic: Fix immediately. Low risk, high traffic: Optimize for SEO and conversions. High risk, low traffic: Decide between rewrite or archive. Low risk, low traffic: Schedule periodic review.
Audit checklist with tool recommendations and expected outputs
| Audit Task | Tool/Method | Expected Output | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Export content inventory | CMS export / Screaming Frog | Master CSV with URL, date, author, word count | 30 |
| Plagiarism check | Copyscape / Turnitin | Flagged matches, similarity percentage | 20 |
| Factual accuracy sample | Manual verification / fact-checking tools | List of incorrect/uncited claims to fix | 45 |
| SEO performance review | Google Search Console / GA4 | Traffic, impressions, CTR, conversions per URL | 40 |
| Tone/voice consistency check | Manual review / style guide checklist | Pages needing voice edits, exemplar rewrites | 30 |
Key insight: The table turns a broad audit into actionable chunks with realistic time estimates. Combine the outputs to generate a prioritized backlog: start with pages that are both high traffic and high risk, then move to optimization-focused tasks. Automate recurring exports and scoring where possible to make future audits faster and less error-prone.
Getting this audit done turns vague worries about “AI content risks” into a clear action plan — and it makes planning fixes, allocating writers, or using an automation partner like Scaleblogger.com a straightforward next step.
Step-by-Step: Fixing Common AI Content Issues
Start by triaging content for three failure modes: tone drift, factual errors, and poor SEO. Fix each with focused, repeatable steps so edits are fast and measurable rather than guesswork.
Editorial brief: Brand voice rules, audience persona, and approved vocabulary.
Audit log: CSV or doc listing URLs, generation prompts, and model version.
Tools & materials
- Human editor with subject expertise.
- Fact-checking tool or internal knowledge base.
- SEO tool for keywords and metadata (SERP tracker, keyword planner).
- Content pipeline to redeploy updated pages (CMS access).
- Run a quick content triage to classify each piece as Tone, Accuracy, or SEO problem.
- For tone issues: create a short style patch that enforces voice.
- Review three representative paragraphs and mark problematic phrases.
- Replace vague or generic phrasing with brand-specific alternatives.
- Add one or two exemplar sentences to the style guide that writers and models can copy.
- For accuracy issues: establish an audit trail and apply human verification.
- Flag claims that require sources (dates, numbers, named facts).
- Confirm each claim against the internal knowledge base or primary sources; add citations inline or in an editor’s note.
- If a claim can’t be verified, rewrite it as qualified or remove it.
- For SEO problems: optimize headings, metadata, and on-page signals.
- Map target intent to the page and select 1–2 primary keywords naturally.
- Rewrite H1/H2 to match user intent and include
schema.orgsnippets where appropriate. - Update meta title and description for click-through and include structured data for rich results.
Quick examples
- Tone: Replace “This tool helps” with “Our team uses this tool to reduce topic research time by half.”
- Accuracy: Change “research shows” to “According to industry reports, X,” and link to the source in the editor note.
- SEO: Convert a long paragraph into a bulleted list and add an H2 with a question users search for.
Remediation tactics by cost, time, and impact
| Tactic | Effort (hrs) | Estimated Impact | Tooling Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human edit for accuracy | 1–3 per article | High — prevents brand damage | $0–$100/article (editor time) |
| Automated fact-check layer | 0.5–2 setup + 0.2/article | Medium — scalable catch rate | $20–$200/mo (API access) |
| SEO re-optimization | 1–4 per article | High — improves rankings & traffic | $0–$100/article (tooling/subs) |
| Voice standardization | 0.5–1 for guide + 0.2/article | Medium — consistent brand perception | $0–$500 one-time |
| Schema/structured data update | 0.5–2 per template | Medium — improves SERP features | $0–$200 one-time |
Key insight: Human editing is the most reliable high-impact fix but doesn’t scale without automation. Automated layers and SEO rework lower cost per article and boost visibility; combine them with a short voice standard to keep content consistent. For workflow acceleration, consider integrating an AI-powered pipeline that enforces these checks before publish — for example, use an automated QA step and then a human final pass with your CMS.
A disciplined triage plus these repeatable fixes turns brittle AI drafts into reliable content assets, so the next round of automation produces fewer errors and higher traffic.
Step-by-Step: Preventing Future Issues — Process and Governance
Start by treating governance as operational work, not a one-off policy doc. Define allowed AI outputs, embed mandatory human checks into the CMS workflow, and assign clear accountability for review and approvals. That turns reactive firefighting into repeatable, auditable practice.
Governance sponsor: A named executive or content lead accountable for policy upkeep.
Baseline SOPs: Existing editorial standards and CMS workflow documentation.
Access controls: Role-based permissions in the CMS and any model-access platform.
Tools & materials
- Policy template: A living doc that lists allowed outputs, restricted topics, and tone constraints.
- CMS workflow features: Approval gates, required fields, and pre-publish checklists.
- Model logging: Usage logs from the AI platform, saved prompt history, and version tags.
- Analytics: Content performance and moderation metrics integrated with dashboards.
Step-by-step process
- Draft the governance policy and publish it to the team knowledge base.
- Define explicit allowed outputs and forbidden content categories in the policy.
- Create a mandatory
Pre-publish checklistinside the CMS that includes model provenance, factual checks, SEO safety, and accessibility checks. - Configure CMS approvals so that every AI-generated or AI-assisted item requires an editorial sign-off before publishing.
- Instrument model usage logging to capture
model_name,prompt_hash, andoutput_idfor every generation. - Schedule quarterly content audits that sample AI-assisted posts for accuracy, bias, and performance.
- Train reviewers on
what to checkand set SLAs for review turnaround times. - Maintain a change log for the policy and publish a short digest to the team after each update.
Operational definitions
Allowed outputs: What AI can generate without additional review (e.g., meta descriptions, first drafts).
Mandatory human checks: Non-optional validation steps required before publish (factual verification, legal review where applicable).
Model usage logging: Recorded metadata about which model and prompt produced a piece of content.
Map governance elements to roles and tools
| Governance Element | Responsible Role | Recommended Tool | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policy maintenance | Head of Content | Confluence / Notion | Quarterly |
| Pre-publish checklist | Editorial Lead | Built-in CMS checklist (e.g., Contentful, WordPress plugin) | Every publish |
| Editorial approval | Senior Editor | CMS approval workflow / Asana | Every publish |
| Content audit schedule | QA Manager | Google Sheets + BI dashboard | Quarterly |
| Model usage logging | ML Ops / DevOps | Model provider logs + internal S3/DB | Continuous |
Key insight: Mapping each governance element to a role and tool removes ambiguity. Having the checklist as a CMS-enforced gate ensures compliance at scale, while continuous model logs create an audit trail for investigations or quality analysis.
Practical examples: require Fact-Checked and Legal-Reviewed checkboxes in the CMS for any AI-assisted claim; tag drafts with AI-draft so audit scripts can sample them automatically. Consider integrating a runbook for incidents that references the model logs.
Embedding these steps into daily workflows prevents drift and makes governance work scalable and defensible. When governance is operational, teams ship faster with fewer surprises.

Step-by-Step: Technical Safeguards and Tooling
Start by treating content pipelines like software releases: version-controlled prompts and templates, automated validations before publish, and explicit provenance/confidence metadata attached to every piece. That approach prevents regressions, makes audits straightforward, and keeps editorial teams confident when scaling AI-generated drafts. Implement guards in layers — machine checks first for speed, fall back to human gates for tricky cases, and always record who/what changed a prompt or model output.
Team roles defined: Clear owners for prompt engineering, validation, and publishing.
Source control access: A git-like system for storing prompts, templates, and generation scripts.
Telemetry & logging: Centralized logs for model calls, validation results, and publish events.
Tools & materials
- Prompt repo — store templates, test cases, and change history.
- Validation service — composable checks (regex, KB lookups, external APIs).
- Provenance tags —
source,model_version,confidence_score,editor_id. - CI for content — run validations on every pull request or generation job.
- Human review UI — lightweight panel for flagged drafts.
- Create a version-controlled repository for prompts and templates.
- Commit every prompt change with a descriptive message.
- Include unit-style examples that show expected outputs for each template.
- Add programmatic validations that run automatically after generation.
- Start with low-latency checks:
regexfor PII, blacklisted phrases, and date formats. - Chain medium-latency checks: internal knowledge-base lookup for factual consistency.
- Integrate higher-latency external APIs for fact-checking where needed.
- Tag each generated item with provenance and confidence metadata.
- Use structured fields like
model_version,prompt_id,confidence: 0.87. - Store tags in the CMS and in your audit logs for traceability.
- Gate publishing based on validation results and confidence thresholds.
- If
confidence < 0.6or any critical validation fails, route to a human reviewer. - Allow conditional auto-publish for evergreen, low-risk content with strict checks.
- Instrument continuous monitoring and rollbacks.
- Track performance signals (CTR, bounce, flagged corrections).
- Revert to prior prompt templates when metrics drop or errors spike.
Practical checks to include: automated readability scores, citation presence, and a brief semantic-similarity check against the knowledge base to avoid hallucinations.
Validation methods by reliability, latency, and cost
| Validation Method | Reliability | Latency Impact | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| External fact-check API | High for factual claims (depends on provider) | Medium–High (network calls) | Typically per-call pricing; moderate to high |
| Internal knowledge-base lookup | High for domain-specific facts | Low–Medium (local DB) | Lower ongoing cost if infra exists |
| Regex/heuristics checks | Low–Medium for surface issues | Very low | Very low (one-time dev) |
| Human reviewer gate | Very high contextual reliability | High (slower) | High (time and salary) |
| Automated readability tests | Medium for style/readability | Very low | Low (open-source tools) |
Key insight: Combine low-latency heuristics and internal KB checks for everyday throughput, and reserve external APIs or human review for high-risk or high-impact content. That mix keeps latency manageable while preserving reliability.
Link tooling into existing CI/CD and CMS workflows; for example, run validations when a PR is opened and store provenance tags on the draft object. Scale considerations matter: as volume grows, shift more checks left (early) and push repeatable tasks into automation. If managing content at scale, consider using Scaleblogger.com to automate pipelines, scoring, and scheduling without rebuilding core infra.
Adopt these safeguards and the pipeline becomes auditable, predictable, and much less risky — which makes experimenting with AI-driven content practical rather than perilous.
Step-by-Step: Measuring Success and Iteration
Start by defining what “success” looks like for each content type, then measure, learn, and repeat. Successful iteration ties concrete KPIs to controlled experiments and a feedback loop that updates prompts, editorial rules, and distribution tactics. Use both content performance metrics and safety metrics so growth doesn’t outpace quality controls.
Baseline dataset: Historical traffic, conversions, engagement rates and any safety/brand-complaint logs.
Tools & materials: Analytics platform (GA4 or equivalent), A/B testing tool, content scoring framework, access to publishing CMS, and a simple dashboard.
- Define clear KPIs and safety thresholds.
- Run a small, controlled pilot.
- Measure with the right cadence.
- Analyze and create actionable fixes.
- Scale or iterate based on outcomes.
- Institutionalize feedback into content operations.
Set primary metrics (organic sessions, conversion rate, time on page) and secondary safety signals (toxicity score, fact-check failure rate). Set numeric targets and acceptable failure rates before testing.
Test one variable at a time: headline, meta description, prompt template, or distribution channel. Randomize audiences and keep sample sizes large enough to reach statistical power.
Collect immediate engagement data (first 7 days), short-term performance (30 days), and SEO indicators (90 days). Track safety signals continuously.
Compare results against baseline and thresholds. If a prompt produces more traffic but increases fact-check failures, prioritize prompt refinement over scaling.
If KPIs improve without safety regressions, expand the change to a larger cohort. If not, run an alternative experiment or roll back.
Update prompt libraries, editorial checklists, and automated filters. Capture lessons in a short playbook so the next team member doesn’t relearn the same lesson.
Common metrics to monitor Engagement: sessions, bounce rate, avg. session duration Outcome: goal completions, lead rate, revenue per visit * Safety: automated toxicity checks, manual fact-check pass rate, copyright flags
A measurement cadence and expected milestones
| Phase | Actions | KPIs | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline measurement | Export historical analytics, map content types, capture safety incidents | avg. sessions, conversion rate, fact-check fail % |
1–2 weeks |
| Pilot test | Run A/B tests on headlines/prompts with controlled audience | lift % in sessions, p-value, toxicity delta |
4–8 weeks |
| Scale rollout | Gradually expand winning variants across content clusters | organic sessions, leads, error rate ≤ threshold |
2–3 months |
| Full audit | Comprehensive review: SEO, content quality, policy compliance | content score avg, drop-offs, manual review % |
1 month |
| Quarterly review | Reassess KPIs, update targets, refresh prompts and playbooks | OKRs alignment, long-term trends, safety regressions | Every 3 months |
Key insight: The table shows a practical cadence where short pilots feed into cautious scaling, while regular audits catch drift and keep safety in check. Analytics platforms and A/B tools supply the measurement, but the process discipline — predefined thresholds, single-variable tests, and institutionalized feedback — makes iteration reliable.
Consider integrating automated pipelines to surface winners faster; services like Scaleblogger.com can help automate scoring and scheduling so experiments move from idea to rollout without manual bottlenecks. Keep iteration tight: shorter cycles mean faster learning and fewer costly mistakes.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
AI content systems fail in predictable ways; spotting the pattern quickly is half the fix. Start by reproducing the symptom, then run a short diagnostic that isolates whether the problem is model-generated (content-level), pipeline-related (publishing/SEO), or process-driven (editing/data). Quick mitigations stop immediate damage; permanent fixes remove root causes and add validation so issues don’t recur.
Common quick checks Check recent changes: Rollbacks or prompt edits often introduce errors. Inspect editorial logs: Look for manual overrides or bulk edits. * Run a small sample: Re-generate 3–5 pieces with the same prompt to confirm reproducibility.
- Reproduce the failure locally with the same prompt and model settings.
- Compare the output to a version that previously performed well to spot drift.
- Check publishing metrics (e.g., click-through, impressions) to confirm real-world impact.
Issues with symptoms, immediate fixes, and permanent fixes for quick scanning
| Issue | Symptoms | Immediate Fix | Permanent Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hallucinations | Confident but false facts; fabricated citations | Stop publish; add “verification required” flag | Strengthen prompt with verify_source:true; integrate fact-check step |
| Tone drift | Voice inconsistent across posts | Reapply style guide; replace tone tokens in prompt | Create a tone_profile template and enforce in pipeline |
| SEO ranking drop | Lower impressions/CTR after publish | Revert to previous version; resubmit sitemap | Implement content scoring and monthly SERP audits |
| Plagiarism | High similarity scores from detection tools | Pull content; notify editors; rewrite | Add automated plagiarism checks in CI and author attribution rules |
| Indexing issues | Pages not appearing in search; crawl errors | Inspect robots.txt and meta tags; fetch as Google | Automate sitemap updates and monitor Search Console alerts |
Key insight: the table highlights that many visible symptoms have a fast containment step (pull, revert, flag) and a longer-term technical/process fix (automation, templates, validation).
Detailed diagnostic steps often include running curl to fetch published HTML, checking rel=canonical tags, and inspecting server response codes. After applying fixes, validate by republishing a single article and monitoring immediate signals (indexing, similarity score, tone check). For recurring problems, stitch these checks into an automated post-publish workflow or use an AI content pipeline that enforces them.
Bringing these checks into your content pipeline prevents repeated mistakes and protects SEO traction; for teams looking to automate this reliably, solutions like Scaleblogger.com can plug these validation steps into publishing workflows. Fix once, verify always — that’s how confidence in AI-generated content scales.
📥 Download: AI Content Creation Strategy Checklist (PDF)

Tips for Success and Pro Tips
Start with a simple operating principle: prioritize predictable processes over one-off inspiration. Consistent workflows make it far easier to scale, measure, and iterate your content program. The suggestions below turn that principle into concrete actions you can apply this week.
- Start small: Pick one content funnel and optimize it before expanding.
- Automate repetitive work: Use automation for drafts, scheduling, and basic optimization.
- Measure what matters: Track organic traffic, time-to-rank, and conversion events.
- Create reusable assets: Templates, standardized briefs, and
CMScomponents speed production. - Human edit every AI output: AI scales volume; humans keep the signal.
Three extended pro tips (with mini implementation steps)
- Build a content-score rubric and enforce it
- Define 5 scoring categories (intent match, topical depth, E-E-A-T signals, on-page SEO, conversion clarity).
- Assign numerical thresholds for publish vs. revise.
- Run a monthly audit to adjust weights based on performance.
- Turn topic clusters into production pipelines
- Identify a pillar topic and list 8–12 related long-tail ideas.
- Create a template for cluster posts (brief, internal links, CTAs).
- Batch-create outlines and use automation to generate first drafts, then humanize and publish.
- Implement a fast feedback loop with measurable experiments
- Pick one hypothesis (e.g., longer intros improve time-on-page).
- Run the experiment on 6 similar posts using A/B or time-blocked comparisons.
- Measure outcomes for 4 weeks and iterate on winners.
Practical operational tips
- Batch planning: Reserve one day for strategy, two for writing, one for editing.
- Editorial briefs: Always include target intent, top 3 competitors, and desired user action.
- Internal linking: Link from new posts to at least two pillar pages within 48 hours.
- Repurpose smartly: Turn top posts into newsletters, short videos, and social snippets.
- Use tooling: Integrate an AI content pipeline and performance dashboard to free up creative time — consider Scaleblogger.com for automation and benchmarking.
Measure every change against the process and KPIs described earlier so wins are repeatable. These tactics shift content from sporadic effort to a predictable growth machine that scales without losing quality.
Appendix: Templates, Checklists, and Resources
Start here: drop these copy-ready templates into your content pipeline, pair each with the right tool, and you’ll shave hours off planning and production.
Editorial brief template: One-paragraph summary, target keywords, search intent, audience persona, CTA, and primary references.
Content calendar template: Date, topic cluster, headline, author, status, publish channel, promotion plan.
Quick fact-check checklist: Claim → source → source credibility (author, date, outlet) → citation link → note if evergreen or time-sensitive.
Templates to copy and paste Brief: Title / 1-sentence angle / primary keyword / 3 supporting points / CTA Calendar row: Publish date / Headline / Status / Owner / Promo window * Distribution blurb: 1-line social hook / 2-line summary / suggested image alt text
- Install tracking and editorial tools before publishing.
- Map each template to a responsible role (writer, editor, SEO).
- Run the quick fact-check before scheduling content.
Provide an at-a-glance tools and resources list with use-cases
| Tool | Primary Use | Why Recommended | Pricing model |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI (ChatGPT / API) | AI content generation, prompts | Strong generative quality, flexible API for pipelines | Free tier / pay-as-you-go API |
| Jasper | Long-form AI writing & templates | SEO-focused workflows, collaboration features | Starts around $39/month |
| Writesonic | Rapid drafts, landing pages | Affordable, built-in SEO modes | Free tier / paid plans from ~$15/month |
| Copy.ai | Short-form copy, ideas | Fast ideation, friendly UI | Free tier / paid from ~$35/month |
| Grammarly | Editing, tone, plagiarism detection | Integrated writing checks, style consistency | Free / Premium from ~$12/month |
| Copyleaks | Plagiarism & originality scanning | Developer-friendly API, bulk scanning | Tiered credits / enterprise |
| Google Fact Check Tools | Fact verification & claim tracing | Integrates with public fact-check corpora | Free to use |
| Google Analytics 4 (GA4) | Traffic & engagement analytics | Event-based insights, cross-channel tracking | Free / paid enterprise options |
| WordPress + Editorial plugins | CMS + workflow (scheduling, approvals) | Ubiquitous CMS, extensible editorial plugins | WordPress free / hosting varies |
| Scaleblogger.com | AI content automation & performance benchmarking | Automates content pipelines, content scoring framework | Contact for pricing (enterprise-focused) |
Key insight: The right stack pairs generation (OpenAI/Jasper) with editing (Grammarly), originality checks (Copyleaks), and analytics (GA4). WordPress or a headless CMS holds the workflow together, while tools like Scaleblogger.com add pipeline automation and performance benchmarking.
These templates and tools are meant to be actionable — drop the brief into a new doc, connect the AI step to your CMS, and track results in GA4. Use the checklist to keep quality consistent as you scale.
Conclusion
By now it's clear why the initial rush of AI drafts often turns into a slow leak of traffic and diluted voice: problems show up in content audits, in governance gaps, and in tooling that treats generation as a finished product instead of a draft. Revisit your audit results, fix confidence-misleading passages and factual drift, and lock a feedback loop between writers and reviewers — these moves stop most traffic erosion and restore brand clarity. For teams that ran the checklist earlier, the case where a content operations team recovered a 25% traffic drop after reworking governance and templates is a practical example of how targeted fixes pay off.
If wondering how to prioritize next — start with a quick content triage (high-traffic pages first), add automated checks for hallucinations and freshness, and codify editorial rules into your CMS. Set a weekly review cadence, add technical safeguards, and measure lift with controlled A/B tests. For teams looking to automate this workflow, Explore Scaleblogger to automate AI-safe content workflows can speed implementation while preserving editorial control. For more on the audit steps, see undefined. Take those next steps now: pick one page, apply the checklist, and measure the difference this month.

