Marketing teams often lose search visibility because older pages quietly decay while new content gets all the attention. Freshness matters: search engines reward timely, relevant content, and neglecting updates lets rankings slip.
Here’s the short answer: regularly refreshing content improves relevance signals and user engagement, which supports higher SEO rankings. Targeted `content updates` that fix accuracy, add depth, and match current intent deliver the fastest impact. Industry research shows search engines favor pages that reflect recent information and better match query intent.
Updating content reduces bounce rates and increases dwell time, improving organic performance across priority keywords. Consider a SaaS blog that revised ten evergreen posts, added recent stats and internal links, and saw steady traffic growth within weeks. Practical changes include refreshing titles, adding new examples, and republishing with current dates.
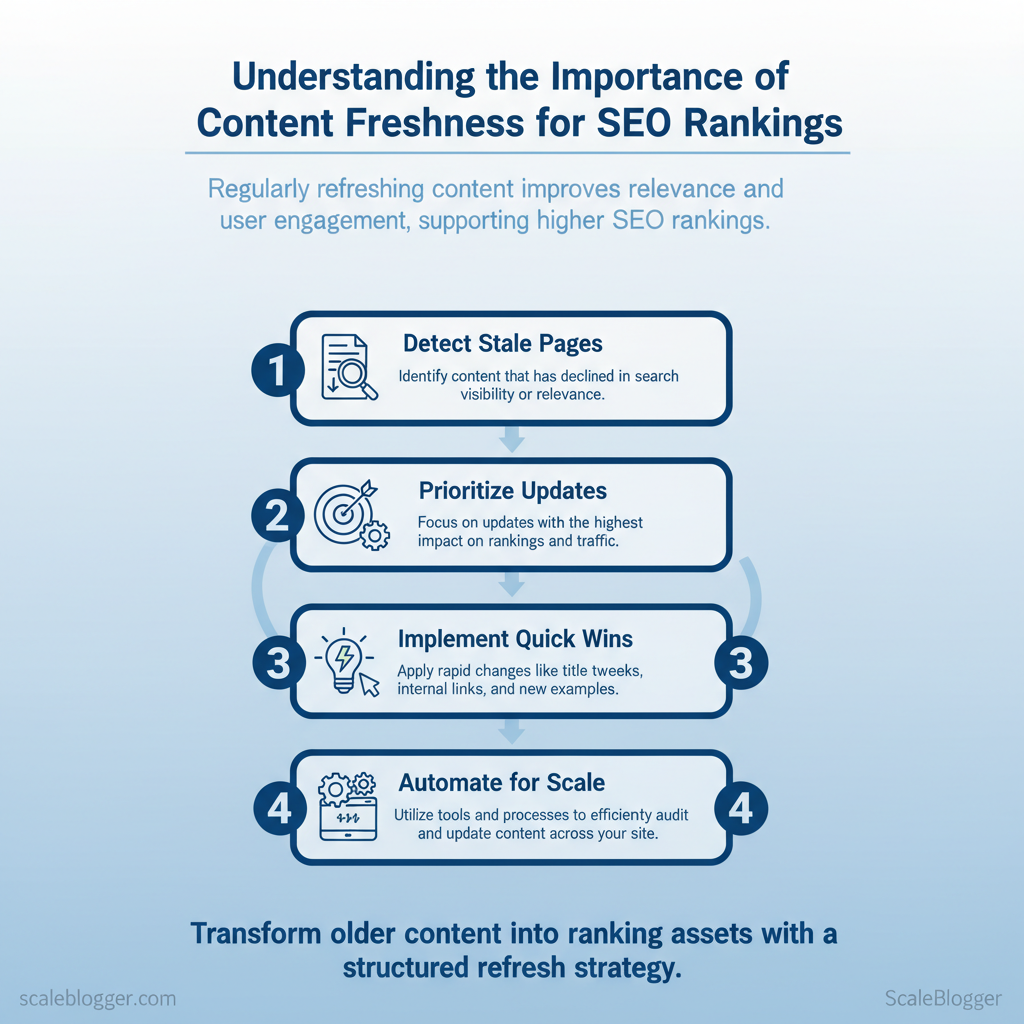
This introduction draws on common SEO principles and publisher experience rather than a single study. It previews how to diagnose stale content, prioritize updates, measure impact, and automate the audit process for scale. Expect one visual illustrating the update workflow after the next section.
- How to detect stale pages that harm rankings
- Prioritization framework for content updates by impact
- Quick wins: title tweaks, internal links, and new sections
- Automation strategies to scale `content freshness` work
What Is Content Freshness and How Search Engines Interpret It
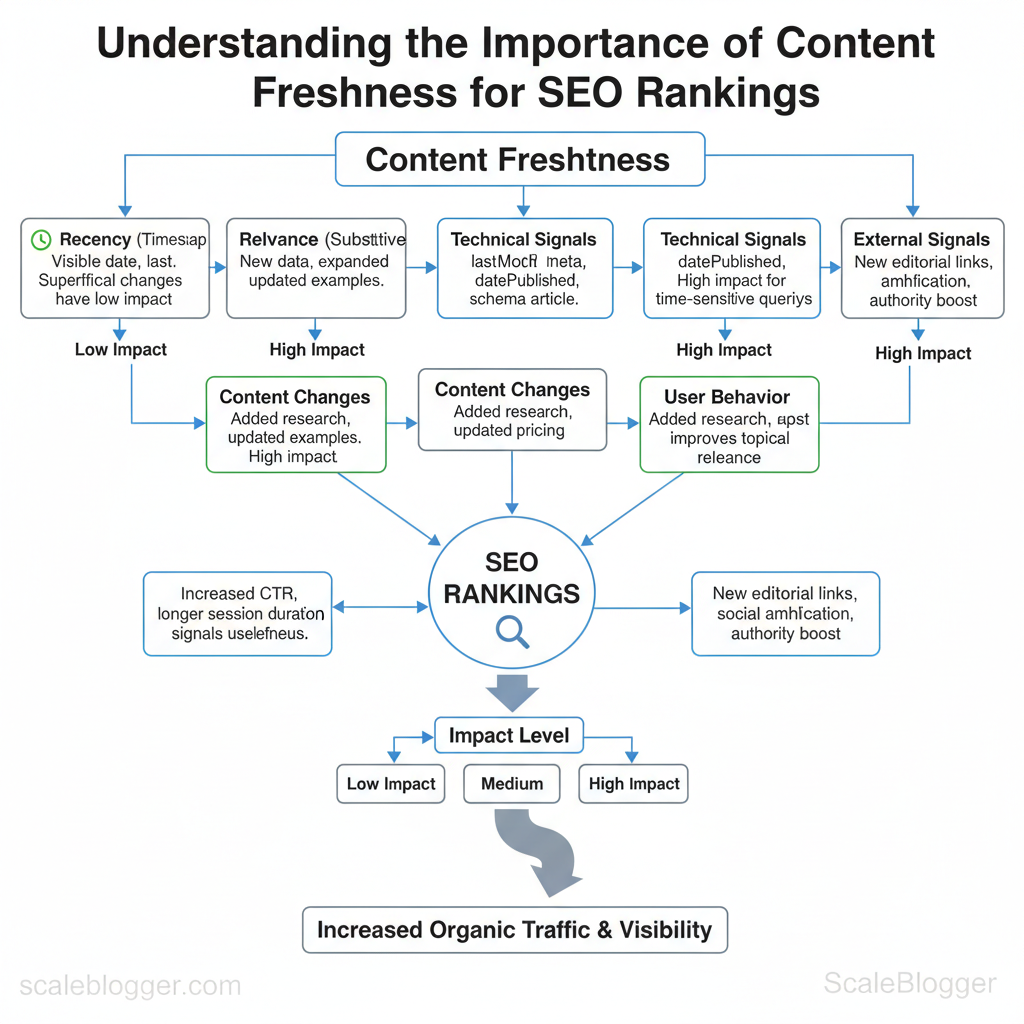
Content freshness is about more than the date in a post header: it’s a mix of recency, substantive updates, and signals that search engines use to decide whether a page still answers users’ queries. Search engines treat freshness contextually — some queries (news, live events, product releases) demand recent timestamps, while others (evergreen how-tos, reference guides) reward depth and updated accuracy. That means a timestamp change alone rarely moves the needle; meaningful edits that add new sections, current data, or restructured content are what search engines consider when recalculating relevance and ranking.
Defining content freshness — recency vs. relevance
- Why cosmetic updates fall short: Search engines evaluate the extent of changes; swapping a few sentences or changing the date without adding new information typically yields no ranking benefit.
- Examples of meaningful updates:
Updating with depth also improves user experience — longer dwell times and lower pogo-sticking if the page answers the updated intent.
Signals search engines use to evaluate freshness
| Signal Type | Example | How to detect/update | Estimated SEO Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical (timestamps/structured data) | `lastModified` meta, `datePublished`, schema `article` | Check HTML meta, CMS settings; add/maintain schema.org fields | High for time-sensitive queries |
| Content changes (new sections/data) | Added research, updated pricing table | Use diff tools, CMS revision history; add clear “Updated” sections | High — improves topical relevance |
| User behavior (CTR/dwell time) | Increased clicks, longer session duration | Use GA4/analytics, Search Console CTR reports; A/B test titles/snippets | Medium–High — signals usefulness |
| External signals (new backlinks/shares) | New editorial links, social amplification | Monitor backlinks (Ahrefs, GSC) and referral traffic; outreach for updated page | Medium — authority boost |
| Crawl frequency | More frequent crawls after updates | Check crawl logs, GSC Coverage; submit updated sitemap or URL for indexing | Medium — enables faster re-evaluation |
Many teams automate detection of stale content and schedule meaningful updates; tools and services (including AI content automation like Scaleblogger.com) can help prioritize pages that need substantive revisions. Understanding these layers helps you target updates that search engines will actually notice and reward. When teams focus on adding value rather than cosmetic fixes, updates convert into measurable visibility and engagement gains.
Why Content Freshness Matters for SEO Rankings
Search engines reward content that is timely, accurate, and clearly maintained; fresher pages signal relevance for queries where currency matters, and updates can trigger recrawling and re-evaluation that lift visibility. For time-sensitive queries—news, product launches, price changes, or rapidly evolving how‑tos—search engines prioritize recent signals. But freshness also helps evergreen content by keeping facts, examples, and internal links current, which improves user satisfaction and gives you more opportunities to re-optimize meta tags and internal linking for higher click-through rates.
Direct ranking benefits and visibility improvements
Fresh content affects ranking in three concrete ways: it adjusts relevance signals for volatile queries, it increases crawl frequency for updated pages, and it provides new opportunities to optimize title/meta elements for improved SERP CTR. Prioritize updates where the return is highest: pages that already rank on page one for competitive terms, product/pricing pages, and cornerstone how-to guides. Small, meaningful changes—adding new stats, updating dates, refining headings—can push a page from stalling on page two into visible territory.
| Content Type | Benefit from Freshness | Recommended Update Cadence | Quick Update Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| News / announcements | High — immediate SERP visibility | Daily to weekly | Update headlines, add latest quotes |
| Evergreen how-to guides | Medium — long-term authority boost | Every 3–12 months | Refresh examples, add new screenshots |
| Product / pricing pages | Very high — conversion + rank for transactional queries | Immediately on change; weekly checks | Update prices, specs, structured data |
| Industry trend posts | High — relevance for analyst queries | Quarterly or when new data appears | Insert new charts, cite latest reports |
| Seasonal content | High seasonally — spikes in search demand | Annually, plus pre-season refresh | Update dates, add current promos |
Indirect benefits: user engagement and authority
Freshness boosts click-through rates by enabling updated meta titles and descriptions that reflect current events or offers. Users tend to spend more time on content that references recent developments or data, lowering bounce rates and improving behavioral signals. Over time these engagement improvements strengthen topical authority and increase shareability across social channels, which can generate natural backlinks.
Understanding these mechanisms helps you prioritize updates where they move the needle most, and tools like AI-assisted auditing can automate spotting high-impact refresh candidates. When implemented well, keeping content fresh reduces wasted effort and steadily improves organic performance.
How to Audit Your Content for Freshness Opportunities
Auditing for freshness means finding pages that deserve a light update, a full rewrite, or removal. Start by assembling the right data so decisions are evidence-driven, then score pages quickly against traffic trends, topical relevance, and estimated effort. This approach turns a noisy spreadsheet into an actionable worklist: low-effort wins, high-impact rewrites, and pruning candidates. Below you’ll find what to gather, how to export it at scale, and a repeatable prioritization framework with example thresholds you can apply immediately.
Preparing tools and metrics (what to track)
Use a mix of search, analytics, and crawl data to get a 360° view.
- Essential tools to assemble: Google Search Console, Google Analytics / GA4, a site crawler, and an SEO research platform.
- Exact metrics and ranges: Compare recent 90-day vs prior 90-day traffic and impressions, 12-month vs 3-month rankings, CTR, bounce rate, and number of referring internal links.
- Export tips for large sites: Pull GSC in 1-month chunks via CSV export, use GA4’s exploration export for segments, and run crawler exports by subfolder to avoid timeouts.
| Tool | Primary Use | Metrics to Pull | Free / Paid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Search performance | impressions, clicks, CTR, avg pos | Free |
| Google Analytics / GA4 | Engagement & conversions | sessions, engaged time, conversions | Free |
| Screaming Frog | Technical crawl & meta audit | status codes, meta, word count | Free tier / Paid from £209/yr |
| Ahrefs | Keyword & backlink research | organic keywords, backlinks, traffic est | Paid from $99/mo |
| Semrush | Keyword + competitive insights | keyword positions, gaps, traffic est | Paid from $119.95/mo |
| Moz Pro | Keyword tracking & page optimization | rank tracking, on-page suggestions | Paid from $99/mo |
| Surfer SEO | Content optimization | NLP terms, content score, SERP analysis | Paid from $59/mo |
| ContentKing | Real-time indexing & change tracking | index status, change alerts | Paid from $49/mo |
| Sitebulb | Visual crawl diagnostics | crawl maps, page-level issues | Paid from ~$13/mo |
| Botify | Enterprise crawl & log analysis | log parsing, bot behavior, scale | Enterprise pricing |
Prioritization framework: traffic decline, relevance, and effort
Score each page quickly on three axes: Traffic Trend (T), Relevance (R), and Effort (E). Use simple numeric scores to rank.
- Traffic Trend (T) — 0–3 points: +3 (↑ traffic), +1 (flat), 0 (↓ <30%), -1 (↓ 30–70%), -2 (↓ >70%)
- Relevance (R) — 0–3 points: +3 (core topic), +2 (related), +1 (marginal), 0 (off-topic/outdated)
- Effort (E) — 0–3 points, but invert for ROI: +3 (quick edit <1 hour), +2 (rewrite partial, 2–4 hours), +1 (full rewrite, 1–2 days), 0 (redesign or heavy research)
Practical example: a product guide losing 45% traffic (T = -1), still highly relevant (R = 3), and needs a 2-hour content refresh (E = 3) → priority high; update title, add 2025 stats, refresh CTAs.
Understanding how to score and export these metrics moves teams from guesswork to predictable refresh cycles. When implemented, this approach surfaces fast wins and clarifies where deeper investment will actually improve search performance.
Step-by-Step Process to Update Content for Maximum SEO Gain
Start by treating an update like a mini product launch: pick the right pages, set measurable goals, and run a short, repeatable workflow that combines editorial judgment with SEO signals. Successful updates prioritize intent alignment, on-page relevance, and technical health — not cosmetic edits. This section walks through a hands-on workflow, quick high-impact edits, and practical examples you can replicate in a week-long sprint.
The update workflow (planning, editing, publishing, monitoring)
Tip: Keep a `changelog.md` for each page so you can audit what changed and when.
“`markdown
changelog for /example-page
– 2025-11-05: Updated H1, added FAQ, optimized meta description (A/B test) – 2025-11-06: Compressed images, fixed mobile layout shift – 2025-11-14: Monitored 14-day traffic uplift: +12% clicks “`Takeaway: Log changes, assign clear owners, and give the update a monitoring window — that simple discipline separates guesses from measurable improvements. If you want to automate parts of the pipeline (briefs, prioritization, performance alerts), tools for AI content automation like Scaleblogger.com can help scale the process without losing editorial control.
Quick wins and high-impact edits (what matters most)
Start with the edits that move SEO metrics fastest: improve intent match, increase CTR, and eliminate friction.
- Bold headline updates: rewrite H1 to match highest intent query.
- Bold meta description tests: create two variants for A/B CTR testing.
- Bold internal linking fixes: add 2–3 contextual links from high-authority pages.
- Bold content expansion: add 300–600 words where topical gaps exist.
- Bold schema adoption: add `FAQ` or `HowTo` where applicable.
When teams prioritize these edits and enforce a simple workflow, updates become predictable and measurable. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Measuring Impact and Iterating Post-Update
When you push an update, measure fast but decide slowly: watch early signals to catch regressions, then let trends mature before making major course corrections. Start with a clear baseline, monitor primary KPIs across short and longer windows, and use explicit action triggers so the next steps — rewrite, expand, merge, or retire — are repeatable and low-friction. Practical thresholds turn opinion into process and protect SEO equity when content changes.
Metrics to monitor and timing for evaluation
| Metric | Baseline Window | Short-term Window (7–14d) | Long-term Window (30–90d) | Action Trigger |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic impressions | Last 28–90 days average (`GSC`) | % change vs baseline in 7–14d | Trendline over 30–90d | Drop >20% or no recovery in 30d → investigate indexing/coverage |
| Average position | 28–90 day avg (`GSC`) | Position shifts in 7–14d | Stable trend across 30–90d | Drop >5 positions → rollback title/markup changes |
| CTR | Last 28–90 days by query | Immediate CTR delta after title/meta change | Sustained CTR improvement or decline 30–90d | CTR ↓10%+ after update → test meta/title variants |
| Organic sessions | Monthly avg (`GA4`) | 7–14d session change, bounce behavior | 30–90d session trend and engagement | Traffic drop >25% or bounce ↑ → audit UX/redirects |
| Backlinks to page | Referring domains (Ahrefs/SEMrush) | New/lost links in 7–14d | Authority growth over 90d | Major link loss or none gained after promotion → outreach SOP |
Iteration loop — when to rework, expand, or retire content
- Rewrite brief (template): use this to scope focused rewrites
- Merge SOP: map redirects, canonicalize strongest URL, preserve internal links, update site maps, and monitor for traffic consolidation over 30–90 days.
- Archive process: keep a lightweight landing page explaining reason, add 301s to closest topic, retain analytics tag for historical data.
Industry analysis shows refreshed content frequently stabilizes rankings within 30–90 days, while immediate UX fixes appear in engagement metrics within a week.
Understanding these workflows makes iterating less risky and faster, so teams can focus energy on high-impact content instead of firefighting. This approach helps keep content healthy while preserving long-term search value.
📥 Download: Content Freshness SEO Checklist (PDF)
Scaling a Content Freshness Program Across Your Site
Start by treating freshness as an operational program, not a one-off task: assign clear roles, set predictable cadences by content type, and automate wherever the risk/reward favors it. When teams know who owns category audits, who signs off on factual updates, and what gets auto-refreshed, you scale without drowning in ad-hoc requests. The goal is repeatable handoffs and measurable throughput — pages updated per month, time per update, and quality checks — so you can reallocate effort toward high-impact creative work.
Organizational roles, cadences, and governance
- Content Owner: accountable for topical accuracy and performance.
- Editor/Quality Lead: approves tone, SEO, and factual changes.
- SEO Analyst: provides keyword shifts, traffic signals, and priority lists.
- Automation/Dev: implements scheduled exports, CMS scripts, and publish hooks.
- Use version-controlled drafts in your CMS or Git-backed content repo.
- Maintain an update log with reason codes (data update, UX, SEO).
- Escalation path for controversial edits (legal/research sign-off).
| Team Size | Monthly Pages Updated | Recommended Tools | Estimated Monthly Effort (hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solo creator | 5–15 | `Notion`, `GSC`, `ChatGPT` | 10–40 |
| Small team (2–5) | 30–120 | `Ahrefs`, `SurferSEO`, `Zapier` | 80–300 |
| Mid-size (6–20) | 200–800 | `SEMrush`, `Contentful`, `Screaming Frog` | 600–2,000 |
| Enterprise (20+) | 1,000+ | `BrightEdge`, `Adobe AEM`, `BigQuery` | 4,000+ |
Automation and tooling to streamline updates
Example: scheduled GSC export → Google Sheet → Zapier → CMS draft
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
Conclusion
You can stop letting older pages slip away—start by prioritizing regular content audits, measuring impact, and automating routine updates so relevance compounds instead of decays. Across the examples earlier, teams that reworked stale pages into focused guides regained organic traffic within weeks, and editorial teams that automated metadata and internal-link fixes freed hours each month. If you’re wondering which pages to tackle first, focus on mid-performing posts with steady impressions; if you’re asking how often to revisit content, aim for a lightweight audit every quarter and a deeper refresh annually.
– Audit consistently: schedule recurring checks for traffic, links, and freshness – Fix high-impact issues quickly: headline, intent, and internal links move the needle fast – Automate what repeats: template updates, metadata fixes, and content flags
For teams looking to cut the manual drudge and scale updates across hundreds of pages, platforms that automate audits and batch changes can make this process repeatable and measurable. As a practical next step, try one quarterly audit, prioritize ten pages for refresh, and set up automation for recurring fixes. To streamline this work, consider Automate content audits and scale updates with Scaleblogger as one option to accelerate audits and push bulk updates without drowning your team in manual tasks.

