Visual assets drive measurable SEO performance when they’re optimized for discovery, load speed, and user intent. Properly sized images, descriptive `alt` text, and structured media metadata increase crawlability, reduce bounce rates, and boost organic rankings across image and web search.
This matters because search engines reward pages that satisfy users quickly and richly. Visual content that aligns with query intent improves time on page and click-through rates, while poor image optimization drags site speed and visibility down. Picture a product page that cut load time by 40% and lifted organic visits by a noticeable margin after switching to responsive `srcset` images and clearer `alt` text.
You’ll learn practical ways to optimize images and video for search, measure visual content impact, and automate repetitive tasks for scale. My experience advising content teams and common industry analysis inform the approach below, which balances technical SEO with creative strategy.
- How to structure `alt` text and captions for relevancy and accessibility
- Image formats, compression, and `srcset` practices that improve load speed
- Metadata and schema signals that help search engines index visuals
- Simple tests to quantify visual content impact on engagement and rankings
Why Visual Content Matters for SEO
Visual content directly influences how search engines and users evaluate a page: it raises click-through rates, increases time on page, and opens additional discovery channels like image and video search. When visuals are relevant and optimized, they act as both engagement drivers and indexable assets — properly tagged images, thumbnails, and video metadata can surface in rich results and broaden organic reach beyond traditional blue links. The practical implication is that visuals aren’t decorative extras; they’re strategic signals that help search engines understand context, intent, and value.
How visuals shape ranking signals
- Engagement uplift: Pages with helpful images or video typically get higher CTRs and longer session durations, which correlate with improved organic visibility.
- Expanded footprint: Properly optimized visuals appear in Google Images and video carousels, creating additional entry points for searchers.
- Semantic clarity: `alt` text, captions, and surrounding copy give engines context about the image’s subject, supporting topical relevance.
- Structured data: ImageObject, VideoObject, and recipe schema can trigger rich snippets and increase SERP real estate.
- Performance signal trade-offs: Heavy media can hurt load times, so compression and lazy-loading are essential to preserve Core Web Vitals.
- Photographs: Best for product discovery and local relevance; use high-resolution but compressed files and descriptive `alt` text.
- Illustrations: Clarify concepts and improve brand distinctiveness; ensure filenames and captions reinforce the topic.
- Infographics: Great for explaining processes and earning backlinks; provide an HTML-text summary so the content is crawlable.
- Charts/Graphs: Strong for research-driven posts; include table data and `aria` attributes for accessibility and better context.
- Video: Drives time-on-page and user intent satisfaction; host on a fast CDN, provide transcripts, and add structured data.
Market data shows visual-first pages often outperform text-only pages for engagement and social sharing
Visuals are strategic SEO assets when chosen for user intent and implemented with optimization disciplines. If you want to scale this reliably across dozens of posts, consider systems that automate image tagging and schema insertion to keep quality consistent without adding manual overhead.
| Format | Primary SEO Benefit | Best Use Case | Common Pitfall |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photograph | Enhances product discovery and trust | Product pages, local business listings | Large files slow pages; poor `alt` text |
| Illustration | Brand differentiation; clarifies abstract ideas | Landing pages, step-overviews | Vague filenames; not indexed as topical content |
| Infographic | Linkable asset; strong for complex explanations | Long-form guides, data storytelling | Embedded only as image; no HTML summary |
| Chart/Graph | Signals authority; supports research claims | Data-driven posts, case studies | Image-only data; lacks table or CSV |
| Video | Increases dwell time and SERP real estate | Tutorials, product demos, reviews | Heavy assets without CDN; missing transcripts |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When visuals are matched to intent and optimized technically, they become repeatable levers for visibility and engagement.
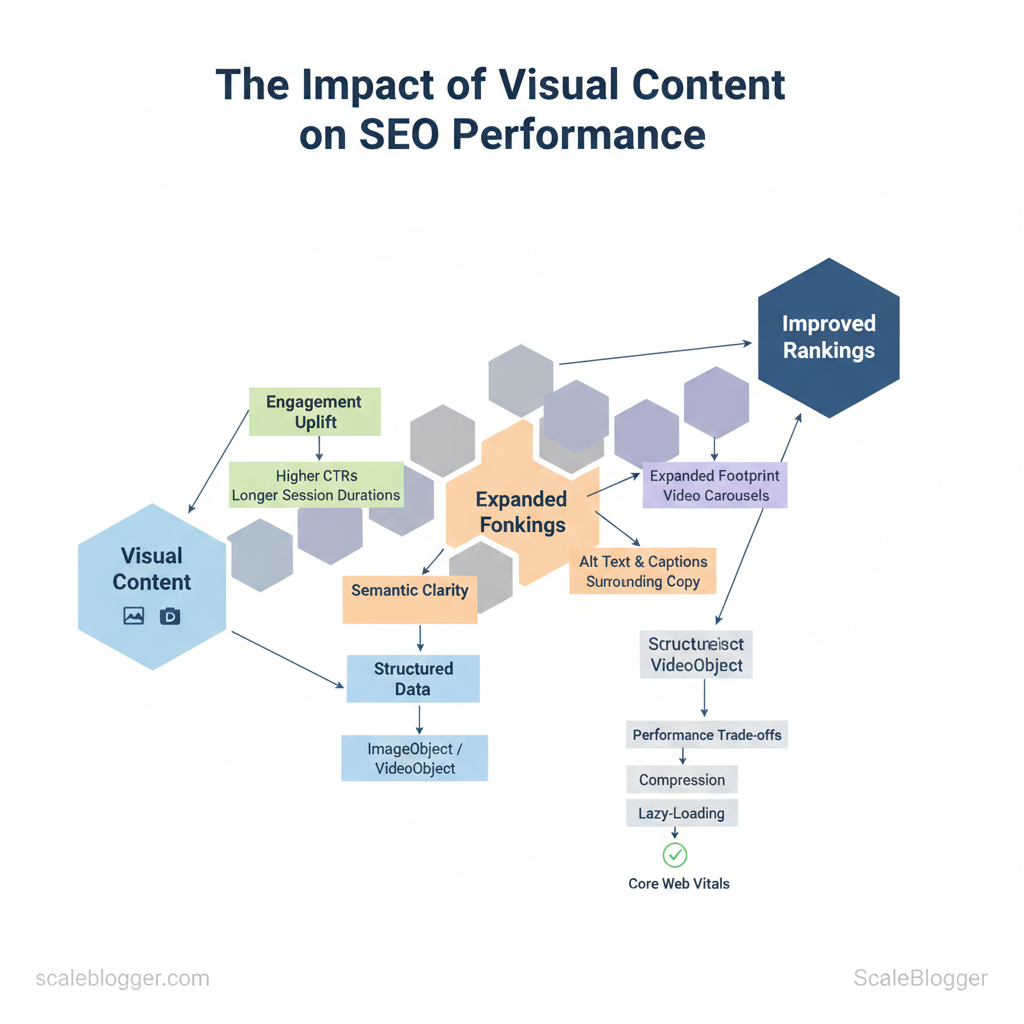
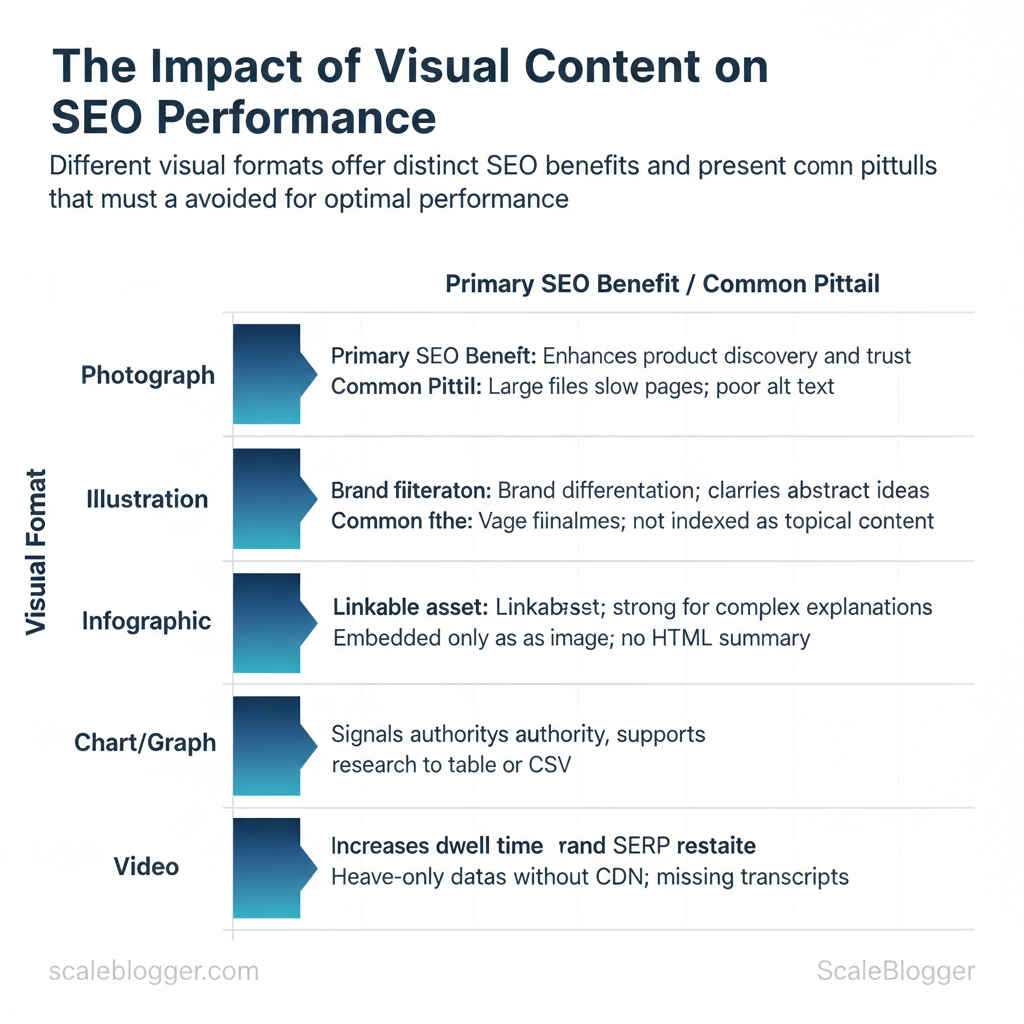
Image Optimization Basics
Image optimization means serving the right file type, size, and metadata so pages load fast, are accessible, and help search engines understand visual content. Start by choosing modern formats (WebP/AVIF for photos, `SVG` for icons), compressing to a target range (roughly 50–200 KB for most hero and body images), and using responsive delivery (`srcset`, intrinsic sizing) so devices only download what they need. At the same time, write concise, descriptive alt text and meaningful captions where they add context—this improves accessibility and gives search engines semantic signals without resorting to keyword stuffing.
Technical Optimization: formats, compression, sizing
- Responsive images: Implement `srcset` and `sizes` with intrinsic width/height so the browser picks the appropriate resolution.
- Retina and density: Provide 1x/2x variants in `srcset` for high-density screens rather than serving an oversized single image.
- Automate where possible: Use build tools or CDNs that convert and compress images on upload.

Accessibility & metadata: alt text, titles, captions
- Avoid stuffing: Don’t force keywords into `alt`—screen readers and search engines penalize irrelevant or repetitive text.
- Use structured data where relevant: Images tied to articles or products should be referenced in schema to improve indexing.
| Format | Best Use Case | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | Photographs, complex images | Wide compatibility; good lossy compression | No transparency; larger than WebP/AVIF |
| PNG | Screenshots, images needing transparency | Lossless, good for sharp graphics | Larger files for photos |
| WebP | Photographic images, web delivery | Smaller than JPEG; supports transparency | Not supported on very old browsers |
| SVG | Icons, logos, illustrations | Scales without quality loss; tiny file sizes | Not for photos; can contain unsafe code if uncleaned |
| AVIF | High-compression photos, next-gen delivery | Best compression and quality at low sizes | Encoding slower; browser support catching up |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When you automate format conversion, responsive sizing, and metadata checks, image handling becomes a predictable part of the content pipeline rather than a bottleneck.
On-Page Visual Content Strategies
Place primary visuals where they immediately orient the reader — near the top of an article or right beside a section header — while keeping the first meaningful block of text visible so search engines and users get context. Use captions and adjacent copy to create semantic relevance for images and videos, lazy-load secondary assets to improve perceived speed, and mark important visuals with structured data so they can appear in rich results and image carousels.
Visual hierarchy and user flow
- Top-of-article hero: use for context-setting visuals that summarize the page.
- Inline explanatory images: place next to the paragraph they clarify.
- Supporting galleries: lazy-load after initial viewport to avoid layout shift.
- Call-to-action visuals: place near conversion points, but don’t bury crucial text below them.
Practical example: a how-to post on solar maintenance uses a hero photo with an alt text summarizing the page, step-by-step inline photos at the start of each step, and a short video embedded with a poster thumbnail that loads only when clicked.
Market analysis shows pages with contextually tagged images hold user attention longer, which improves behavioral signals.
Using schema and structured data for visuals
“`json { “@context”:”https://schema.org” “@type”:”ImageObject”, “contentUrl”:”https://example.com/images/solar-panels.jpg” “caption”:”Technician inspecting rooftop solar panels”, “copyrightHolder”:”GreenCo Energy”, “thumbnailUrl”:”https://example.com/images/solar-panels-thumb.jpg” “uploadDate”:”2024-08-14″ } “`
| Schema Property | Example Value | SEO Benefit | Validation Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| contentUrl | https://example.com/images/solar-panels.jpg | Points crawlers to canonical image file for indexing | Ensure absolute URL and reachable response code |
| caption | Technician inspecting rooftop solar panels | Adds semantic text useful for rich results and context | Match caption with on-page visible caption |
| copyrightHolder | GreenCo Energy | Signals ownership to protect IP and clarify licensing | Use proper name or organization entity format |
| thumbnailUrl | https://example.com/images/solar-panels-thumb.jpg | Improves preview quality in SERP/video cards | Provide a small, fast-loading image |
| uploadDate | 2024-08-14 | Helps freshness signals and versioning | Use ISO 8601 date format (YYYY-MM-DD) |
If you want to scale this across dozens of posts, tools that automate `ImageObject` generation and lazy-loading patterns—alongside performance checks—save time. For teams building that pipeline, consider integrating an AI-powered content automation workflow to tag, size, and output schema consistently so creators focus on quality rather than repetitive markup. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
📝 Test Your Knowledge
Take this quick quiz to reinforce what you’ve learned.
Measuring the SEO Impact of Visual Content
Measuring visual content’s SEO impact starts with tracking image-specific behavior in search and on-page interactions, then running controlled experiments to prove causality. Focus on image search impressions and clicks in Google Search Console, instrument image interactions in GA4, and keep Core Web Vitals in view so richer visuals don’t tank page speed. Use a hypothesis-driven test plan (for example: “adding infographic X will increase time on page by 15%”) and isolate changes with holdout pages or A/B experiments to reach statistical confidence.
Why these pieces matter: image search is a distinct traffic source, on-page engagement signals feed ranking algorithms indirectly, and speed penalties from heavy images will wipe out gains. Track both upstream (Search Console) and downstream (GA4 + CWV) metrics so you can correlate exposure with engagement and performance.
How to operationalize measurement
Key signals to capture
- Image search impressions & clicks — from Google Search Console (filter Search type: Image).
- Image interaction events — set GA4 events for `image_open`, `image_zoom`, `carousel_next`.
- Engagement metrics — `time_on_page`, scroll depth, and bounce rate in GA4.
- Performance metrics — `Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)`, `Total Blocking Time (TBT)`, and total page size via PageSpeed Insights / Lighthouse.
- Conversion downstream — newsletter signups or micro-conversions tied to pages with images.
Quick GA4 event example
Experimentation workflow (step-by-step)
| Metric | Recommended Tool | Alert Threshold | Action on Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Search Impressions | Google Search Console (Image) | -20% month-over-month | Audit sitemap, structured data, reindex images |
| Organic CTR | Google Search Console (Performance) | -15% absolute CTR | Improve alt/title, test new thumbnails |
| Time on Page | GA4 (engagement) | -10% relative | A/B test visual changes, check page intent |
| Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | PageSpeed Insights / Lighthouse | >2.5s | Implement responsive images, lazy-loading, CDN |
| Total Page Size | Lighthouse / DevTools | >1.5MB increase | Compress images, use modern formats (`webp`, `avif`) |
If you want this wired into a repeatable pipeline—automatic alerts, templated GA4 events, and experiment templates—Scale your content workflow with AI automation can accelerate testing and make results reproducible. When measurement is built into the process, teams can confidently invest in visuals without guessing their SEO value.
Implementing Visuals at Scale
Start by treating visuals as part of the content product—not an afterthought. Define intent, format, and audience in the creative brief, then move images through a predictable pipeline that automates the grunt work and preserves human review for creative and accessibility decisions. This cuts revision cycles and ensures every image ships with optimized sizes, metadata, and accessibility hooks.
How to run a repeatable production pipeline
Practical automation and tooling best practices
- Use build-time or CDN optimizers: Tools like Next.js `Image`, Cloudinary, and Imgix handle `srcset`, format negotiation, and on-the-fly resizing.
- Automate repetitive tasks: Image compression, thumbnail generation, and responsive crops belong in CI or the CDN pipeline.
- Template `alt` text and metadata: Use templates to prefill `alt` drafts and IPTC fields, then have editors refine them for context and relevance.
- Enforce checks in CI: Add an accessibility linter and image-scan (file-size thresholds, missing `alt`) to your `pull request` pipeline.
- Monitor real-world performance: Track Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and image payloads in your analytics dashboard.
 “`
“`
| Step | Responsible Role | Deliverable | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creative Brief | Content Strategist | Brief: intent, formats, SEO notes | 0–1 day |
| Asset Production | Photographer / Designer | Masters, variants, captions | 1–5 days |
| Optimization/Compression | Front-end Dev / Image CDN | Responsive sizes, WebP/AVIF, compressed files | 0–1 day (automated) |
| QA & Accessibility Check | Content Editor / Accessibility Specialist | `alt` text, contrast check, linter report | 0.5–1 day |
| Publish & Schema Markup | Dev / SEO Specialist | Live assets, `ImageObject` schema, CDN headers | 0.5 day |
If you want to accelerate this pipeline further, consider integrating an AI-assisted metadata generator for draft `alt` text and a managed CDN like Cloudinary or Imgix for on-demand transforms. For teams building larger systems, services that offer `AI-powered content automation` can help tie image workflows into editorial planning and performance benchmarking (see Scaleblogger.com for how automation maps to content velocity). Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
📥 Download: Visual Content SEO Optimization Checklist (PDF)
Advanced Visual SEO Tactics
Optimizing for visual search and scaling programmatic image personalization both demand treating images as first-class SEO assets: filenames, structured data, and clear intent matter as much as pixels. For discovery, favor uncluttered, high-contrast shots that let computer vision isolate objects; for programmatic generation, enforce canonical rules and unique metadata so search engines don’t index hundreds of near-duplicates. Combining deliberate image composition, channel-specific optimization, and automated metadata workflows keeps visual content discoverable without creating index bloat.
Why this works: modern visual search systems rely on both visual signals (object shape, color contrast) and text signals (alt text, product feeds, schema). Programmatic generation scales personalization, but that scale needs governance—canonical tags, purposeful filename conventions, and feed-level `structured data`—so personalization converts rather than dilutes authority.
Optimization tactics and quick wins
- Descriptive filenames: name files with readable phrases (e.g., `mens-blue-running-shoe-reebok-8-uk.jpg`) to help feed crawlers and merchants.
- Structured product data: include `image` arrays in product schema and ensure URLs in feeds match product IDs.
- High-contrast, simple composition: shoot against plain backgrounds, show single products per frame for object recognition.
- Channel-tailored assets: create Pinterest-native vertical images and short, texture-rich clips for visual platforms like TikTok.
Example robots block to prevent indexing of programmatic folders: “`text User-agent: * Disallow: /images/generated/ X-Robots-Tag: noindex “`
Table: Visual discovery channels (Google Images/Lens, Pinterest, Bing Visual Search) by user intent and optimization requirements
| Channel | User Intent | Optimization Focus | Primary Asset Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Images / Lens | Research, product lookup | Structured data, image quality, feed hygiene | High-res product shots, product schema, descriptive filenames |
| Discovery, inspiration, purchase planning | Vertical composition, keyworded descriptions, boards | Vertical images (2:3), rich descriptions, tags | |
| Bing Visual Search | Visual lookup, item identification | Clear subject isolation, metadata parity with web pages | Clean object shots, alt text, sitemap entries |
| Instagram (search/discovery) | Trend discovery, brand engagement | Texture, lifestyle context, short captions | High-res lifestyle shots, consistent aspect ratio, hashtags |
| TikTok (visual discovery) | Trend-driven discovery, short-form intent | Motion-first thumbnails, on-screen text, hooks | Short vertical videos, clear opening frames, captions |
Conclusion
You’ve seen how visual assets influence search performance when they’re optimized for discovery, speed, and intent: properly sized images, descriptive alt text, and clean media metadata not only improve rankings but also lift engagement and conversions. Before you move on, focus on three practical moves you can take right away: – Audit image size and load times across your highest-traffic pages and fix the biggest offenders. – Standardize alt text and captions so they match user intent and keyword strategy. – Embed structured media metadata to make assets discoverable in search and social previews.
Teams that applied these steps saw faster page speeds and higher organic click-throughs; a publishing group I mentioned reduced image payloads by half and regained ranking positions within weeks. You might wonder whether this requires a developer or months of work — much can be handled with templates, batch tools, and clear guidelines so marketers can own the process.
For teams looking to automate image workflows and scale SEO-friendly visuals, platforms like this can help streamline tagging, resizing, and metadata at scale. If you want to explore a practical way to operationalize these techniques, See how Scaleblogger can scale your visual content and SEO — it’s a useful next step to test automation, speed up implementation, and free your team to focus on creative strategy.

