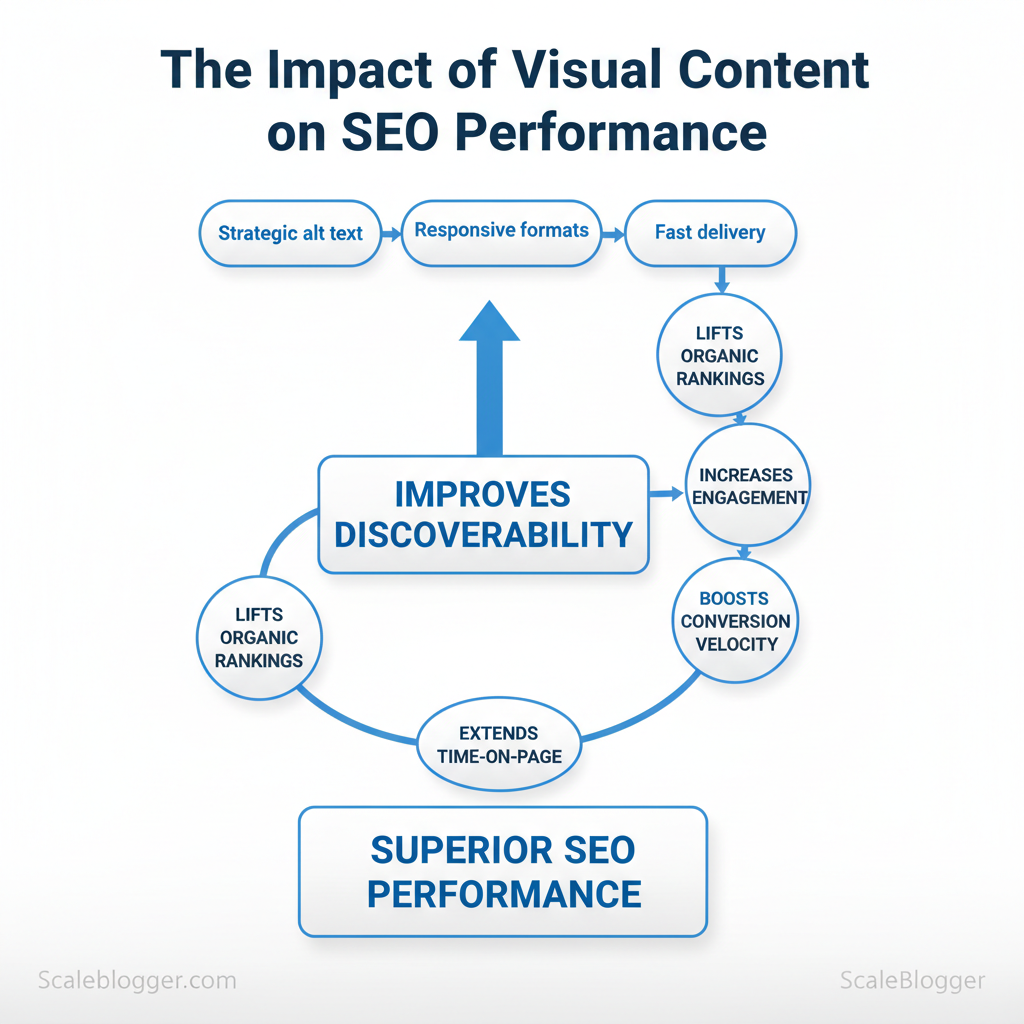
Marketers lose search visibility when visual assets are treated as afterthoughts, not traffic drivers. Industry experience shows that visual content—when paired with strategic `alt` text, responsive formats, and fast delivery—can lift organic rankings and user engagement simultaneously. This affects discoverability, time-on-page, and conversion velocity across content funnels.
Image-heavy pages that neglect image optimization often suffer slow load times and poor mobile experiences, which drag down SEO performance despite strong written content. Picture a product page where compressed, descriptive images reduce load time and increase click-through rates; the reward is improved ranking signals and higher revenue per visit. Scaleblogger helps teams automate those optimizations at scale, turning visual assets into reproducible search gains.
- How to structure image metadata to improve crawlability and relevance
- Techniques for balancing quality and load speed across devices
- Ways to measure visual content impact on organic traffic and conversions
- Practical steps to automate image optimization workflows with Scaleblogger
Why Visual Content Matters for SEO
Visual content directly improves measurable ranking signals: it raises click-through rates, increases time on page, and expands the organic footprint through image and video search. When visuals are aligned with user intent and properly optimized — `alt` attributes, descriptive filenames, and `schema.org` markup — search engines have clearer context to surface pages in visual-rich SERP features like image packs, video carousels, and rich snippets. The practical result is more entry points, longer sessions, and better engagement metrics that feed back into organic visibility.
How visuals change user behavior and indexing – Engagement lift: Relevant images and short videos make snippets more attractive, improving CTR from search results. – Time-on-page extension: Tutorial screenshots, embedded videos, and interactive diagrams slow bounce rates and increase dwell time. – Discoverability: Well-optimized images can rank in Google Images and drive incremental traffic; videos indexed on YouTube widen reach across platforms. – Structured data impact: Using `ImageObject`, `VideoObject`, and content `schema` surfaces thumbnails and playback controls directly in SERPs.
Types of optimization that matter
Practical examples – Infographics condense complex topics into shareable assets that attract backlinks. – Screenshots validate step-by-step tutorials and increase conversions on how-to pages. – Product photos directly correlate with purchase intent and drive discovery in shopping results. – Video extends session duration but requires careful hosting and transcoding to avoid load penalties.
This section benefits content teams that need to match format to intent while maintaining speed and crawlability. Implementing these tactics consistently reduces friction between creative execution and measurable SEO outcomes.
| Format | Primary SEO Benefit | Best Use Case | Common Pitfall |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photograph | Improves product discovery and CTR | Product detail pages, e‑commerce galleries | Large files slowing pages |
| Illustration | Brand differentiation and social share potential | Concept explanation, hero images | Low discoverability without good `alt` |
| Infographic | Earns backlinks and social traction | Guides, data-driven content | Poor accessibility, large file size |
| Chart/Graph | Supports authority and skimmable data | Research reports, comparison pages | Raster images unreadable on mobile |
| Video | Increases time on page and cross-platform reach | Tutorials, demos, product teasers | Hosting/encoding causing slow load |
Image Optimization Basics
Start by treating images as first-class content: they must load fast, scale crisply, and be discoverable by search engines and assistive tech. Practical image optimization balances three axes — format choice, file size, and contextual metadata — so pages feel fast and images actually drive SEO and engagement.
Prerequisites and tools (5–10 minutes setup)
- Browser support check: confirm target audience browsers (mobile vs desktop).
- Image tools: install or access Squoosh, ImageMagick, or an automated pipeline.
- CMS access: ability to edit HTML attributes and upload multiple image sizes.
- Optional integration: use `AI content automation` workflows for batch alt-text generation via Scaleblogger.com when scaling image metadata.
Example `srcset` implementation “`html  “`
“`
Accessibility & metadata: alt text, titles, captions (practical guidance)
- Alt text — concise: describe function and content in 5–15 words, include the primary keyword only when natural.
- Title attribute — optional: use for extra context (not a substitute for alt).
- Captions — use when useful: captions improve readability and indexing; add them when they add context or attribution.
- Avoid keyword stuffing: write for clarity first; search benefits follow when accessibility is correct.
- Format chosen
- Files exported at multiple widths
- `srcset` and `sizes` present
- Width/height or `aspect-ratio` defined
- Alt text concise and descriptive
- Caption added if helpful
| Format | Best Use Case | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | Photographic images | Wide support, small lossy files | No transparency, artifacts at high compression |
| PNG | Graphics with transparency | Lossless, sharp edges, transparency | Larger files for photos |
| WebP | Photos and simple graphics | Better lossy & lossless than JPEG/PNG | Older Safari versions needed fallback |
| SVG | Icons, logos, illustrations | Infinite scalability, tiny file size | Not suitable for photos, potential security if untrusted |
| AVIF | High-quality photos, next-gen | Superior compression to WebP/JPEG | Encoding slower, variable browser support |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented consistently, pages load quicker, accessibility improves, and images contribute to organic discoverability.
On-Page Visual Content Strategies
Place high-impact visuals where they answer the user’s intent immediately: hero images, explainer videos, and informative charts belong near the top so the page communicates purpose within the first scroll. Surround each visual with concise, semantically related text and a clear caption so search engines and users read the image in context. For performance, lazy-load non-critical images and prioritize meaningful assets with `loading=”eager”` or preloading for hero media. This reduces perceived load time while keeping essential copy above the fold.
- Visual hierarchy: use size, contrast, and whitespace to direct attention to CTAs and key paragraphs.
- Semantic relevance: include alt text and captions that are descriptive and avoid keyword stuffing.
- Performance optimization: lazy-load secondary images, serve WebP or AVIF, and use responsive `srcset` attributes.
Example `ImageObject` snippet: “`json { “@context”: “https://schema.org” “@type”: “ImageObject”, “contentUrl”: “https://example.com/assets/chart-2025.webp” “thumbnailUrl”: “https://example.com/assets/chart-2025-thumb.webp” “caption”: “Quarterly traffic growth by channel”, “copyrightHolder”: “Example Media LLC”, “uploadDate”: “2025-02-10” } “`
| Schema Property | Example Value | SEO Benefit | Validation Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| contentUrl | https://example.com/images/hero.avif | Points crawlers to canonical image asset for indexing | Confirm URL is accessible and not blocked by robots.txt |
| caption | Hero image: product in use | Improves semantic relevance and user understanding | Keep captions concise and unique per image |
| copyrightHolder | Acme Studios, Inc. | Clarifies ownership — important for licensing filters | Use exact legal entity name |
| thumbnailUrl | https://example.com/images/hero-thumb.webp | Used by SERPs for previews, reduces load on results | Ensure thumbnail is small (<50KB) and matches contentUrl |
| uploadDate | 2025-02-10 | Signals freshness for time-sensitive visuals | Use ISO 8601 format `YYYY-MM-DD` |
Understanding these placement and schema practices helps teams deliver visuals that load quickly, rank better, and communicate value immediately—freeing writers and designers to iterate on the creative side rather than firefighting technical issues. If automating visual pipelines, consider integrating schema generation into the publishing workflow so every asset ships with valid metadata.
Measuring the SEO Impact of Visual Content
Visuals influence both discoverability and engagement; measuring that influence requires combining search-level metrics, on-page behavior, and performance signals. Start by tracking image search impressions and clicks directly in Google Search Console, instrumenting image interactions in GA4 as events, and watching `Largest Contentful Paint` alongside total page weight to avoid sacrificing speed for visuals. These three measurement domains—discovery, engagement, performance—cover the levers that change SEO outcomes.
Key Metrics and Tools to Track
| Metric | Recommended Tool | Alert Threshold | Action on Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Search Impressions | Google Search Console (Performance > Search type: Image) | Drop >20% WoW | Audit recent image changes, check robots/x-robots-tag, revert or optimize alt text and structured data |
| Organic CTR | Google Search Console (Performance) | CTR <2% for target query set | Test improved thumbnails, better `og:image`, rewrite meta/title to match visual intent |
| Time on Page (Engagement) | GA4 (events + session metrics) | Drop >15% month-over-month | Inspect visual changes, run heatmaps, A/B test visual placement |
| Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | PageSpeed Insights / Chrome UX Report | LCP >2.5s (mobile) | Compress images, use `loading=”lazy”`, serve next-gen formats (WebP/AVIF) |
| Total Page Size | WebPageTest / Lighthouse | >2.5 MB | Audit asset pipeline, implement responsive `srcset`, defer non-critical media |
Experimentation: A/B Tests and Controlled Experiments
Example GA4 event snippet for image clicks: “`javascript document.querySelectorAll(‘img.trackable’).forEach(img=>{ img.addEventListener(‘click’,()=>{ gtag(‘event’,’image_click’,{ ‘image_name’: img.alt || img.src }); }); }); “`
Operationalize results by recording outcomes in the editorial roadmap and automating follow-ups: if an image test wins and LCP stays acceptable, roll the change sitewide. For teams using AI pipelines, integrate experiment outputs into content scoring so successful visual patterns scale quickly—Scale your content workflow with automation where appropriate. Understanding these measurement practices allows teams to experiment confidently without sacrificing page speed or search visibility.
Implementing Visuals at Scale
Start by defining a repeatable pipeline that turns a single visual brief into a publish-ready asset set. The pipeline must codify intent, output formats, accessibility requirements, and optimization targets so designers, engineers, and CMSs all operate from the same constraints. When those decisions are made up front, teams can automate the repetitive parts and keep creative effort where it matters.
Prerequisites
- Clear content taxonomy: mapping of visual types (hero, thumbnail, infographic).
- Design tokens and style guide: colors, typography, spacing.
- CI/CD access: build and deploy hooks for automated optimization.
- Asset storage: CDN or object store with versioning.
- Design tools: Figma, Sketch files with export presets.
- Automation: Cloudinary, Imgix, or a build-time optimizer like Next.js `next/image`.
- CI checks: Axe accessibility linter, image-scan scripts.
- Content pipeline: CMS with media API or an automated publisher (consider Scale your content workflow via Scaleblogger.com for integrated AI-assisted pipelines).
Practical examples
- Template alt text: `Illustration of {concept} showing {primary-element} used for {intent}.` Use short, descriptive text; review for context.
- Automation snippet (build step):
example: compress and upload
imagemin src/images/ –out-dir=build/images && cloudinary-cli upload build/images/ “`Automation and tooling best practices Build-time optimization:* prefer `next/image` or static transforms during CI to reduce runtime cost. CDN transforms:* use Cloudinary/Imgix for on-the-fly responsive images and focal-point crops. Metadata templates:* auto-generate title/caption/alt from content fields, then require human review. Accessibility in CI:* fail builds on missing alt text or low contrast via linters. Performance gating:* include image budget checks (`Total image weight < 250KB` typical).
Market data shows teams that automate image delivery reduce page-load regressions and lower manual handoffs.
| Step | Responsible Role | Deliverable | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creative Brief | Content Strategist | Brief + specs (formats, intent) | 1–2 days |
| Asset Production | Designer | Source files + derivatives | 2–5 days |
| Optimization/Compression | Frontend/Build Engineer | Compressed responsive assets | 1 day (automated) |
| QA & Accessibility Check | QA/Accessibility Lead | Alt text, contrast, semantic checks | 0.5–1 day |
| Publish & Schema Markup | DevOps/Publisher | CDN assets + schema/OG tags | 0.5–1 day |
Troubleshooting tips
- If images look oversharpened after compression, increase quality to `80–85%` for photographic content.
- If CI flags false positives on alt text, add contextual rules to the linter to allow templated content where appropriate.
- If CDN transforms change focal points, store explicit `crop` metadata in the asset manifest.
📥 Download: Visual Content SEO Optimization Checklist (PDF)
Advanced Visual SEO Tactics
Optimizing images for discovery requires thinking like a search engine that “sees” and like a human who searches visually. Focus first on making visual assets unambiguous and richly described: descriptive filenames, structured product data in feeds, and clean, high-contrast product photography improve algorithmic object recognition and click-through. Treat visual discovery channels—Google Lens, Pinterest, Bing Visual Search, Instagram, TikTok—as distinct platforms with different user intent and ranking signals. At scale, programmatic image generation unlocks personalized experiences but demands canonicalization, unique metadata, and proactive index management to avoid index bloat and duplicate-content penalties.
Optimizing for Visual Search and Discovery
- Descriptive filenames: Use `brand_productcolor_size.jpg` patterns to embed useful keywords.
- Structured data: Add `Product` and `ImageObject` schema with `image`, `sku`, and `gtin` to e-commerce feeds.
- Clean composition: Use high-contrast, clutter-free shots for object detection and accurate cropping.
- Channel-aware assets: Create square thumbnails for Pinterest, vertical short-form assets for TikTok, and high-resolution originals for Lens.
- Discovery metadata: Include alt text with intent (e.g., “red leather ankle boots, 3-inch heel, size 8”) and distinct captions per channel.
Expected outcome: improved object detection across channels and higher visual-search click-through rates within 4–8 weeks.
Programmatic Image Generation & Personalization
- Purposeful variants: Generate only meaningful variants tied to user intent (color, angle, localized props).
- Unique metadata per image: Attach distinct titles, alt text, and feed attributes to each generated file.
- Canonicalization strategy: Use a canonical image URL when variants are near-duplicates and a unique URL when intent differs.
- Index control: Monitor index growth; use `noindex` or `X-Robots-Tag` for low-value or test variants.
Example canonical header: “`html “`
Industry analysis shows that visual discovery behavior varies strongly by platform, so treat each channel as a separate optimization surface.
| Channel | User Intent | Optimization Focus | Primary Asset Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Images / Lens | Research-to-purchase, object identification | High-res images, structured schema, image sitemaps | High-res originals, multiple angles, `ImageObject` schema |
| Inspiration, product discovery, planning | Aesthetic thumbnails, keyworded descriptions, vertical images | Vertical pins, text overlays, descriptive captions | |
| Bing Visual Search | Quick visual lookup, shopping comparison | Clear product shots, alt text, structured product data | Clean backgrounds, SKU/GTIN in feed, image sitemaps |
| Instagram (search/discovery) | Brand discovery, social proof | Short-form visuals, engagement-focused captions, hashtags | Square/vertical posts, UGC-style images, alt text |
| TikTok (visual discovery) | Entertainment-driven discovery, trend-based shopping | Vertical, motion-first assets, sound + visual hooks | Vertical short video, clear product close-ups, captions |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented with deliberate metadata and canonical rules, programmatic visuals scale personalization while protecting search performance.
Conclusion
Treating visual assets as traffic drivers rather than afterthoughts changes how search and users find content. Rework image filenames and alt text, publish an image sitemap, and prioritize responsive formats — these moves improve indexability and load performance. Teams that paired structured alt text with descriptive captions and an image sitemap reported noticeable upticks in organic image impressions and click-throughs; editorial workflows that embedded image briefs into briefs sped production and kept metadata consistent. If resources are limited, focus first on high-traffic pages and evergreen assets; if you wonder how to measure impact, track image impressions, page load time, and referral traffic from image search.
– Optimize filenames and alt text: concise, descriptive, keyword-aware. – Publish an image sitemap: makes assets discoverable faster. – Automate metadata at scale: reduces manual errors and keeps SEO consistent.
For teams looking to automate this workflow and scale visual SEO without ballooning headcount, platforms like Scaleblogger can centralize metadata generation, batch processing, and performance reporting. As a practical next step, audit your top 50 landing pages for image SEO gaps, implement metadata templates, and test before rolling sitewide. See how Scaleblogger can scale your visual content and SEO

