Most companies know their product features; few can describe the human moment that makes those features matter. That gap is where storytelling moves from a marketing buzzword to a strategic asset that shapes perception, recall, and loyalty.
When a narrative frames why a brand exists, customers stop evaluating price and start empathizing with intent. Effective brand storytelling turns abstract values into repeatable scenes customers recognize across touchpoints, making choice feel inevitable rather than accidental.
Crafting those scenes requires more than clever copy — it demands a discipline that aligns message, voice, and distribution so stories reach the right audience at the right time. For teams ready to move from occasional campaigns to a reproducible content engine, Automate and scale your storytelling workflow with Scaleblogger: https://scaleblogger.com
What You’ll Need (Prerequisites)
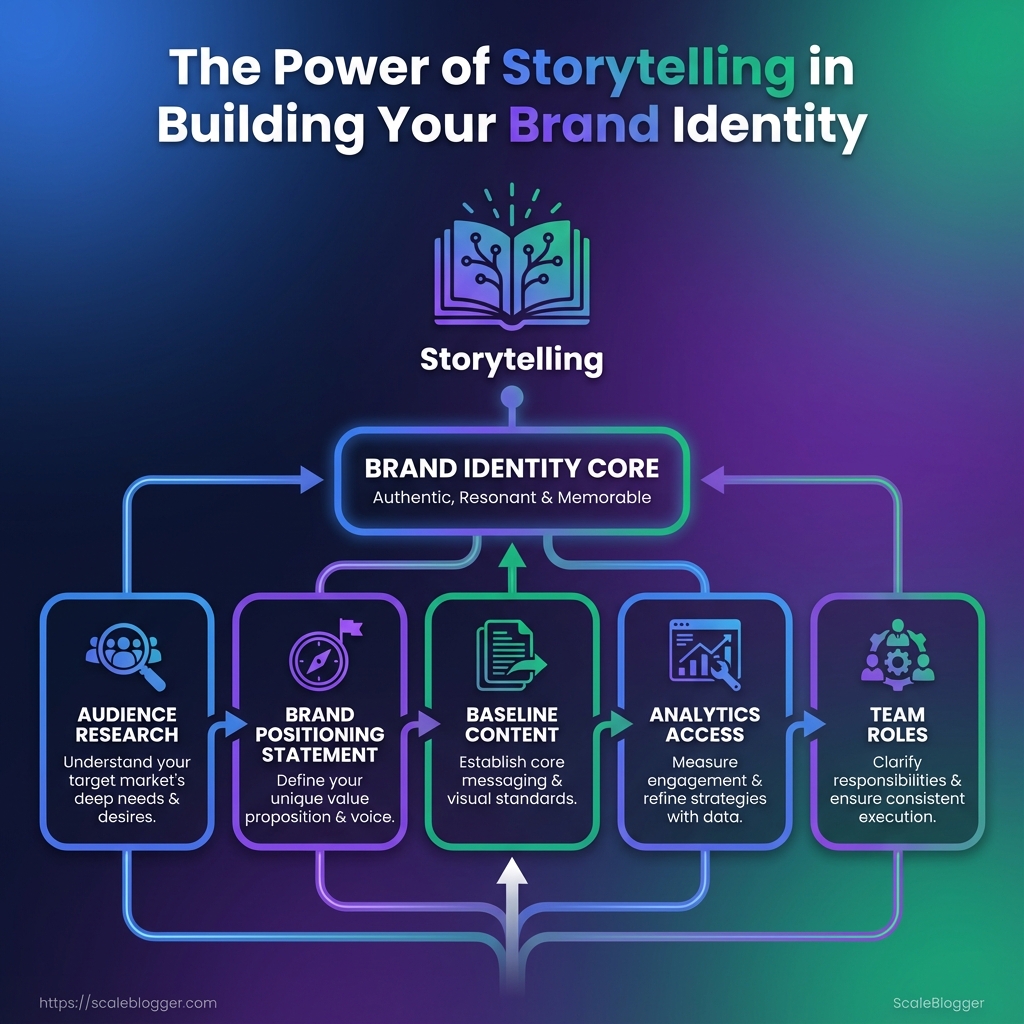
Start by aligning the team on audience, brand position, a content baseline, and measurement access. Without those four elements, automation and AI-driven pipelines amplify noise instead of impact. This section lists concrete, minimal-entry criteria that make an automated content workflow productive from day one.
- Audience Research: at least one buyer persona with demographics, top three pain points, and channels they use.
- Brand Positioning Statement: a single-sentence positioning that answers who you serve, the unique value, and the primary proof point.
- Baseline Content: three existing posts or product pages that reflect current SEO or conversion wins.
- Analytics Access: view or edit access to
GA4, the site’s Search Console, and a content performance dashboard. - Team Roles: identified content owner, SEO lead, and an engineering or ops contact for integrations.
Audience Research: Sufficient audience research means documented evidence, not guesswork. A single persona should include age range, job titles, top three questions they search for, and which social or professional channels they frequent. If that data comes from customer interviews, synthesize the common language as search-intent phrases.
Brand Positioning Statement: One crisp sentence. Example: “For mid-market e‑commerce teams, we accelerate acquisition through AI‑optimized category pages that lift organic conversion by reducing search friction.” That level of specificity guides tone, topic selection, and metric choice.
Baseline Content: Pick three assets that serve different funnel stages — awareness, consideration, and conversion. Minimal acceptance: each has measurable traffic or conversion data in the last 12 months and can be updated without legal rework.
Analytics Access and KPIs: Grant GA4 and Search Console access plus an exported KPI list. Required KPIs usually include Organic Sessions, Assisted Conversions, Average Position, CTR, and Time on Page. Define a primary north-star metric before automation begins.
- Confirm stakeholder sign-offs for access and roles.
- Collect the three baseline URLs and export last 12 months of performance.
- Draft the one-sentence positioning and circulate for approval.
Quick checklist mapping each prerequisite to ‘required’ vs ‘recommended’ and minimal acceptance criteria
| Prerequisite | Required/Recommended | Minimal Acceptance Criteria | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audience Research | Required | Persona doc with demographics + 3 pain points + top channels | Targets content to real search intent |
| Brand Positioning Statement | Required | One sentence specifying audience, unique value, proof point | Aligns voice and conversion goals |
| Baseline Content | Required | 3 URLs: awareness, consideration, conversion; 12‑month metrics export | Provides updateable seeds for automation |
| Analytics Access | Required | GA4 view/edit, Search Console, performance exports |
Enables measurement and iteration |
| Team Roles | Recommended | Named content owner, SEO lead, engineering contact | Speeds deployment and troubleshooting |
Key insight: The checklist forces practical readiness — teams with these five elements can deploy AI-assisted pipelines and measure real uplift instead of chasing vanity metrics.
Understanding these prerequisites reduces wasted effort when building an automated content pipeline. When those pieces are in place, teams move faster and can trust the data that drives topic selection and optimization.
Step-by-Step Implementation: Plan Your Brand Narrative
Start by treating the brand narrative as a product: define who it serves, what change it creates, and how you’ll test that claim in market-facing content. Use rapid validation cycles and concrete artifacts—a one-paragraph story, mapped pillars, and a 90-day calendar—to move from theory to measurable outputs.
- Step 1: Define Your Audience and Empathy Map
- Create quick-validation personas using analytics, sales CRM notes, and 5-10 customer interviews (phone or DM).
- Capture in the empathy map: Says: verbatim lines; Thinks: hidden beliefs; Does: typical actions; Feels: emotional states.
- Translate pain/gain into emotional hooks (e.g., relief from complexity, pride in mastery) and test one hook per week in social snippets.
- Step 2: Craft Your Core Brand Story (One-Paragraph Narrative)
- Use the structure
protagonist-conflict-transformation-moralin a single paragraph. - Include concrete detail and emotion: time, place, sensory detail, and outcome.
- Two concise examples:
- Example — Product startup: “A founder trapped by content chaos hires an AI pipeline, cuts publishing time in half, and reclaims strategic focus—so teams ship ideas not tasks.”
- Example — B2B services: “A marketing head drowning in campaigns adopts a story-first calendar, increases qualified leads, and proves storytelling drives pipeline.”
- Step 3: Map Narrative Arcs to Content Pillars
- Choose pillars by audience need, SEO demand, and conversion potential.
- Map arcs to formats (case studies → long-form; founder origin → video; how-to → guides).
- Use a prioritization matrix: impact vs. effort.
Audience validation tip: Run a two-question survey in your newsletter asking which problem they’d pay to solve and which phrase best describes their frustration.
3-5 content pillars by ROI potential, effort, audience fit, and best formats
| Content Pillar | Narrative Arc | Best Formats | Effort (Low/Med/High) | Impact Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Stories | Feature → benefit → outcome | Long-form case study, video demo | Med | High |
| Customer Journeys | Problem → solution → result | Written case study, testimonial clips | High | High |
| Founder/Origin Story | Origin → struggle → vision | Short video, podcast | Med | Med |
| Industry Thought Leadership | Insight → critique → roadmap | Long-form analysis, whitepaper | High | Med |
| How-to/Educational Stories | Need → step-by-step → skill | Guides, templates, micro-content | Low | High |
Key insight: Prioritize how-to and customer journeys for early wins—how-to drives discoverability while customer journeys build trust and conversion.
- Step 4: Draft a 90-Day Storytelling Content Calendar
- Structure weekly themes, batch assets, and assign owners with deadlines.
- Mix: 1 long-form, 2 short posts, 4 social snippets per week.
- Time estimates: research 4–8h, draft 6–12h, design 4h, publish 1–2h.
Example 8-week timeline showing themes, primary asset, supporting assets, and deadlines
| Week | Theme | Primary Asset | Supporting Assets | Owner/Deadline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Audience Pain | 2,500-word guide | 3 tweets, 1 LinkedIn post | Content Lead / Day 5 |
| Week 2 | Solution Demo | Case study article | 1 video clip, email blast | PM / Day 10 |
| Week 3 | Founder Voice | Short video interview | 3 LinkedIn posts | CEO / Day 17 |
| Week 4 | How-to Toolkit | Template + guide | Carousel, newsletter | Ops / Day 24 |
| Week 5 | Success Stories | Customer montage | Social ads, testimonial page | Growth / Day 31 |
Key insight: Batch research and design by theme to cut context switching; assign a single owner to reduce approval loops.
- Step 5: Produce Story-Driven Content (Writing & Design Directions)
- Start each piece with the protagonist in motion, then the conflict, then the turning point.
- Use the structural recipe: Hook → Stakes → Evidence → Practical steps → CTA.
- Design elements: hero image with human subject, pull quotes, timeline visuals, and clear data callouts.
- SEO checklist: target keyword in title,
H1and first 100 words, 800–1,800 words for long-form, schema for articles, 3 internal links. - Headline formulas: How [X] Changed [Y], What We Learned From [Result], The Beginner’s Guide to [Outcome].
- Step 6: Distribute and Amplify Your Stories
- Owned vs earned vs paid: mix channels based on goal—awareness (paid + social), trust (owned + earned).
- Channel tactics: tailor narrative length and media—for LinkedIn use argument+evidence, for email use intimate storytelling, for Product Hunt use launch narrative.
- Repurposing templates: long-form → 3 social posts → 1 newsletter → slide deck.
- Consider automation tools and AI content automation to speed repurposing workflows.
Side-by-side comparison of distribution channels by reach, cost, ideal format, and expected timeline
| Channel | Reach | Best Format | Cost | Expected Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company Blog | Medium (search over time) | Long-form article | Low | 2–8 weeks |
| Email Newsletter | High (direct audience) | Story email | Low | 1–7 days |
| High (professional) | Long post + thread | Low | 1–3 days | |
| Product Hunt | Variable (launch spikes) | Launch story + assets | Low-Med | 24–72 hours |
| Sponsored Social | High (targeted) | Short video or carousel | Med-High | 24–72 hours |
Key insight: Use owned channels to build permanence, paid channels for targeted reach, and earned channels for credibility spikes.
- Step 7: Measure Story Impact and Iterate
- Mix quantitative and qualitative: traffic, time on page, conversion, and reader feedback.
- A/B test single narrative variables: headline angle, protagonist framing, CTA placement.
- Review cadence: weekly for tactical KPIs, monthly for narrative-level decisions.
Example KPI dashboard with metrics, target benchmarks, and frequency of review
| Metric | Definition | Target (30 days) | Review Frequency | Action if Below Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time on Page | Average seconds on article | 180s | Weekly | Improve opening and add media |
| Scroll Depth | % scrolled to 75% | 45% | Weekly | Break content into sections |
| Newsletter Signups | New subscribers | 200 | Weekly | Add inline CTAs |
| Social Shares | Shares per asset | 50 | Weekly | Test emotional hooks |
| Qualitative Feedback | Survey responses | 30 replies | Monthly | Interview 5 readers |
Key insight: Use small, controlled A/B tests on narrative elements and iterate monthly; quantitative dips that match qualitative complaints point to content, not channel.
Understanding these mechanics makes it straightforward to move from idea to measurable story programs that scale. When implemented, this system accelerates content velocity and keeps narrative quality intact.
Numbered Implementation Checklist (Quick Execution Guide)
Start by framing the smallest viable version of the content pipeline you need to deliver measurable results in 30–60 days. That keeps scope tight and prevents tool sprawl while giving the team concrete wins to iterate on.
Tools & materials needed
- Platform: content management system with scheduling
- Automation: basic
content-pipelineautomation (scheduling + publishing) - Analytics: page-level performance tracking
- Templates: brief editorial brief, SEO title/meta template
1. Define the target outcome, primary KPIs, and deadline. Time: 1–2 days — Difficulty: Low — Owner: Head of Content
2. Audit current assets and tag top 20% that already drive traffic. Time: 3–5 days — Difficulty: Medium — Owner: SEO Specialist
3. Create a prioritized topic backlog (20 topics) aligned to buyer intent. Time: 2 days — Difficulty: Medium — Owner: Content Strategist
4. Build reusable templates: editorial brief, outline, and SEO checklist. Time: 2–3 days — Difficulty: Low — Owner: Content Ops
5. Set up content-pipeline automation for draft handoffs and scheduling. Time: 1–2 days — Difficulty: Medium — Owner: Engineering / Automation Lead
6. Run a 2-week content sprint: draft → edit → SEO pass → schedule. Time: 14 days — Difficulty: Medium — Owner: Editorial Team
7. Publish and enable UTM tagging + page-level analytics for each post. Time: 1 day — Difficulty: Low — Owner: Analytics
8. Monitor performance weekly for the first 30 days; move top performers to amplification. Time: ongoing (first 30 days heavy) — Difficulty: Low — Owner: Growth/Performance Marketer
9. Iterate on the backlog using performance data; deprecate low-performers. Time: recurring (bi-weekly) — Difficulty: Medium — Owner: Content Strategist
10. Scale automation and delegate decision rules to team-level owners. Time: 2–4 weeks — Difficulty: Medium — Owner: Head of Content + Automation Lead
Quick examples of ownership clarity
Editorial Team Lead: approves briefs and final copy.
SEO Specialist: prioritizes topics and validates technical SEO.
Automation Lead: configures pipelines and maintains webhook integrations.
Common measurement signals to watch: Traffic lift: page sessions compared to baseline Engagement: scroll depth or time on page * Conversion: assisted conversion or lead capture rate
Consider integrating an AI content automation partner where it reduces manual steps; teams often use tools for outline generation and content scoring—Scale your content workflow can be part of that stack. When implemented this way, teams move faster without sacrificing quality. This approach reduces overhead by making team-level decisions clear and repeatable.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When a content program stalls, the fastest path back to momentum is a disciplined problem → cause → immediate fix → long-term fix workflow. Below are the most frequent failure modes in content operations, how to patch them quickly, then how to prevent recurrence. Examples use editorial and technical contexts so fixes validate both human and system-level failures.
Typical failure pattern and validation steps
Start by reproducing the issue and capturing two baselines: pre-fix metrics and immediate post-fix behavior. Then validate with a short A/B or pilot test to rule out noise.
- Reproduce the issue in a controlled environment.
- Capture baseline metrics (traffic, CTR, publish latency).
- Apply the immediate fix to a sample set.
- Measure the same metrics over 72 hours and compare.
If metrics move in the right direction and user feedback is positive, promote the fix to a broader rollout and document it in the editorial post-mortem.
Quick fixes versus durable changes
Quick fixes: stopgap actions that restore functionality within hours (e.g., revert a recent CMS plugin update).
Durable changes: process or architecture updates that prevent recurrence (e.g., staged deploys, editorial style guides).
Validate durable changes: run a 30–60 day post-deployment audit with content sampling and analytics checks.
Examples in a technical product context
Low-quality briefs: Cause — unclear audience or intent. Immediate fix — rework the top 3 briefs using a template with target persona, search intent, primary CTA. Long-term fix — require a brief sign-off from a product PM.
Broken templates/markup: Cause — recent CMS or theme update. Immediate fix — roll back to the last stable theme. Long-term fix — introduce a staging site and automated regression tests.
API rate limits causing publish failures: Cause — burst traffic from automated pipelines. Immediate fix — throttle the pipeline and queue jobs. Long-term fix — implement exponential backoff and monitor quota usage.
Practical tips for validation
- Check analytics quickly: confirm pageviews and session duration move in the expected direction after the fix.
- Inspect logs: search for repeated 4xx/5xx errors that coincide with the incident window.
- User feedback: collect 3–5 qualitative comments from readers or internal reviewers to confirm the UX is restored.
Troubleshooting matrix: problem, likely cause, immediate action, long-term solution
| Problem | Likely Cause | Immediate Action | Long-term Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Engagement | Poor targeting / weak headlines | Update headlines & meta descriptions; promote on one channel | Implement audience segmentation and topic clusters |
| Inconsistent Voice | Multiple writers, no style guide | Apply editorial pass to recent posts | Publish and enforce a living style guide |
| No Measurable Impact | Wrong KPIs / poor attribution | Reboot tracking (UA→GA4 checklist) | Build content scoring framework tied to business outcomes |
| Scaling Content | Manual workflows / bottlenecked approvals | Reduce scope; prioritize high-impact pieces | Automate pipeline with content templates and scheduled publishes |
| Team Resistance | Change fatigue / unclear ROI | Host a short demo and Q&A | Run a pilot with measurable goals and share results |
Key insight: The matrix exposes whether failures are tactical (fixable quickly) or systemic (require process or tech investment). Prioritize fixes that reduce cognitive load on teams and enable repeatable validation.
Understanding these patterns keeps the team focused on measurable recovery and prevents the same incident from consuming future cycles. When fixes are validated and documented, the team moves faster and with more confidence.
Tips for Success (Pro Tips)
Start small and measurable: prioritize a handful of micro-behaviors that consistently raise engagement, then scale them into repeatable patterns. Focus on storytelling and narrative marketing that fit the audience’s existing attention rhythms—short setups, concrete stakes, and a clear next-step—so each piece earns distribution and sets up the next piece in a modular workflow. These pro tips concentrate on tactical actions you can apply daily to lift output quality without adding headcount.
Tactical micro-behaviors for higher impact
- Open with an action: Lead every article with a one-sentence action or problem the reader can relate to, not abstract context.
- Swap a sentence for a stat: Replace one passive sentence with a concrete example, metric, or quote to increase credibility.
- One CTA per story: Limit each content unit to a single, clear call-to-action that aligns with the story’s intent.
- Write a 15-second teaser: Draft a shareable one-liner for social distribution before writing the full piece.
- Annotate repurpose opportunities: Add a two-line note at the top of drafts listing how it could map to a newsletter, thread, or short video.
These behaviors take minutes but compound across dozens of posts.
Repurposing and modular content tactics
- Identify the narrative spine: extract the core thesis or lesson from the piece.
- Break the spine into 3–5 modular assets (tweet, micro-post, explainer, checklist, short video).
- Create a repurpose schedule mapping each asset to a channel with cadence and length constraints.
- Use templates for each asset type so transformation is fast and consistent.
- Track engagement per asset and iterate on highest-performing formats.
This process turns longform stories into a systematic content pipeline and makes reuse predictable.
Measuring incremental value of stories
Define baseline: Choose a control period or sample content to compare new stories against.
Metric mix: Combine immediate signals (CTR, time-on-page) with downstream outcomes (lead rate, MQL conversions).
Holdout testing: Publish two variants or delay distribution for a matched audience segment to observe incremental lifts.
Attribution window: Use short (7–14 day) and medium (30–90 day) windows to capture both engagement spikes and slower conversion effects.
Example: run a A/B headline test while keeping body identical, then measure lift in CTR and 30-day conversion rate to estimate story value.
Definition: Narrative marketing: A strategy that uses coherent stories to drive measurable actions across acquisition and retention channels.
For teams that want automation, integrate an AI-assisted pipeline—AI content automation can help convert a single thesis into a set of modular assets quickly. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When applied consistently, these pro tips make storytelling a scalable driver of audience growth.
📥 Download: Brand Storytelling Implementation Checklist (PDF)

Resources and Templates
Start with templates that map directly to the content workflow you want to automate: empathy and narrative work first, calendar and KPI artifacts next, then outreach and measurement. These templates shorten the feedback loop, make handoffs predictable, and let automation handle repetitive structure so writers and strategists focus on storytelling and optimization.
Core templates to include and how to adapt them
- Empathy Map Template: Use to capture audience motivations, pain points, and desired outcomes. Adapt by adding channel-specific behaviors (organic search, newsletters, social).
- One-Paragraph Story Template: Forces a single-sentence setup, conflict, and resolution. Adapt by swapping the CTA to test different conversion intents.
- 90-Day Editorial Calendar CSV: Dates, publish owner, content pillar, target keyword, intent, and status. Adapt cadence columns for weekly vs. biweekly publishing.
- KPI Dashboard Mockup: Visualize sessions, conversions, and content velocity. Adapt by adding cohort filters and
UTMdimensions. - Outreach Email Templates: Sequence for first touch, follow-up, and partnership close. Adapt subject lines and personalization tokens for segmentation.
- Identify which template reduces the most friction in current workflows.
- Duplicate and rename the file with a date/version stamp.
- Replace placeholder fields with organization-specific tokens (
{{brand_voice}},{{target_persona}}). - Run one pilot item through the pipeline, capture time-savings and iteration points.
Tools by task (practical recommendations)
- Research & briefs: Google Docs or Scaleblogger.com for AI-augmented brief generation.
- Content drafting: Obsidian or Notion for structured drafts;
GPT-powered assistants for first-pass outlines. - Scheduling & CSV exports: Airtable or Google Sheets for the 90-day calendar export.
- Analytics & dashboards: Looker Studio or Data Studio with
GA4integration for KPI mockups. - Outreach & sequences: Mailshake or Lemlist for personalization and deliverability tracking.
Resource matrix listing template name, format, purpose, and suggested tool
| Resource | Format | Purpose | Suggested Tool | How to Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empathy Map Template | Google Doc | Map audience needs | Google Docs | Fill quadrants per persona; export to brief |
| One-Paragraph Story Template | Markdown | Tighten narrative | Notion | Create headline → single-paragraph story → CTA |
| 90-Day Editorial Calendar CSV | CSV | Schedule & assign content | Airtable | Import to CMS; update status column |
| KPI Dashboard Mockup | Dashboard PNG/Sheet | Track performance | Looker Studio | Connect GA4; add content filters |
| Outreach Email Templates | HTML/Text | Scale linkbuilding & partnerships | Lemlist | Use personalization tokens; A/B subject lines |
Key insight: This matrix pairs each template with a practical, executable tool and a one-line usage pattern so teams can plug artifacts into an automated pipeline quickly. Prioritize templates that remove the most manual decisions first, then instrument them with analytics and UTM tagging.
Implementing these artifacts turns content strategy into repeatable processes that scale; the upfront time building templates pays back in velocity and clarity. When templates are tuned to real outcomes, teams spend less time debating format and more time crafting stories that move readers.
Conclusion
You’ve seen how shifting from features to the human moment sharpens messaging, how a simple narrative framework turns scattershot content into a consistent brand voice, and how a short execution checklist keeps campaigns moving without overburdening the team. Practical examples in the article—an ecommerce launch that doubled engagement after reframing the product as a daily ritual, and a B2B campaign that shortened the sales cycle by centering client stories—illustrate the pattern: applied storytelling and measured iteration produce predictable lift. Start by mapping one customer moment, write three short stories around it, and set a two-week test to measure engagement.
For teams ready to operationalize this approach, the next steps are clear: formalize the narrative pillars, assign rapid content sprints, and instrument performance so you can learn fast. If bottlenecks are the issue, invest in automation for content production and distribution; for teams looking to automate this workflow, Automate and scale your storytelling workflow with Scaleblogger is one practical option to explore. Ship one narrative-driven campaign this quarter, measure results, and use that evidence to scale—storytelling becomes strategic only when it’s repeatable.

