Search traffic increasingly arrives as spoken queries, and most content teams are still writing like the web expects short typed phrases. That mismatch wastes ranking opportunities and reduces visibility for high-intent searches. Industry research shows voice assistants prioritize conversational answers and quick, local results, so optimizing for voice search improves both discoverability and conversion.
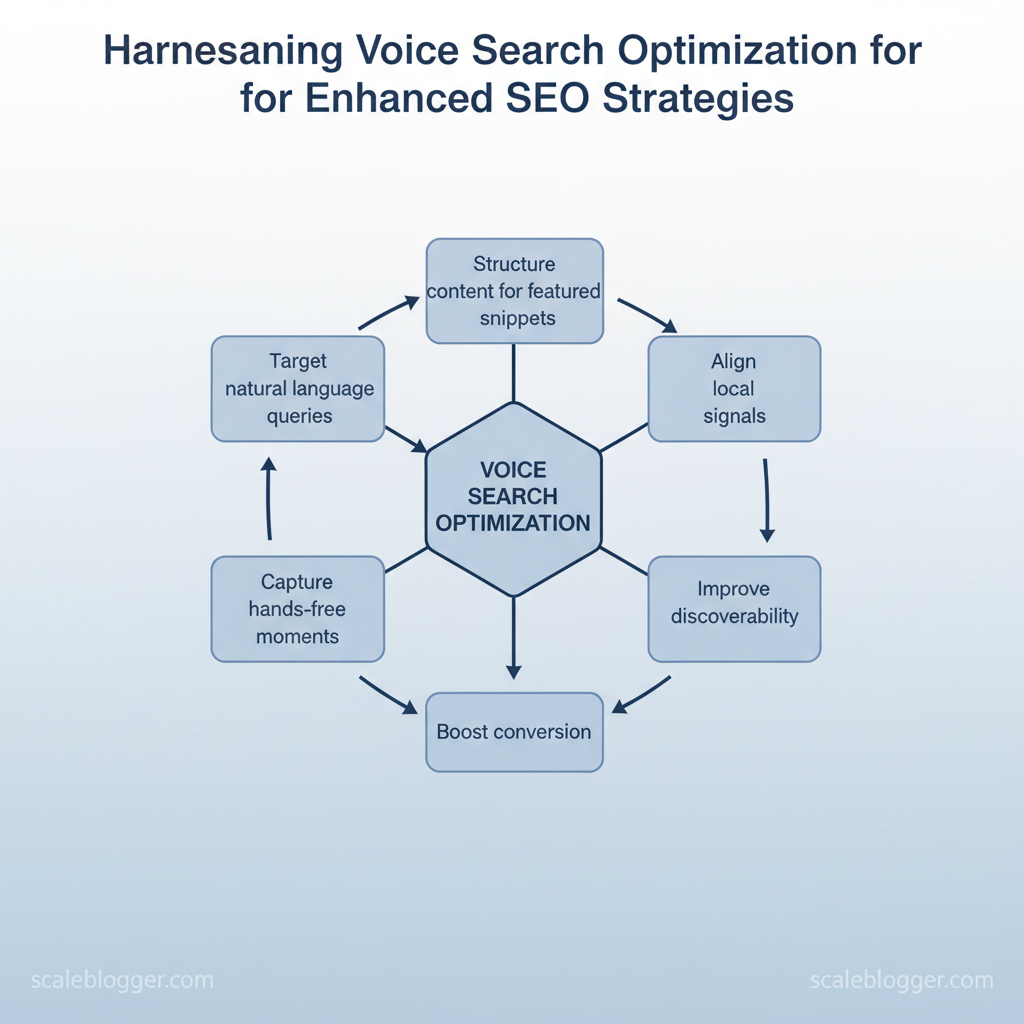
Targeting natural language queries, structuring content for `featured snippets`, and aligning local signals captures those hands-free moments. Teams that adopt this approach see faster gains in relevant traffic and better performance for question-driven queries.
- How to map conversational keywords to content and intent
- Techniques to structure pages for `featured snippets` and short answers
- Local SEO adjustments that boost voice visibility for nearby queries
- Content formats that satisfy voice assistants under 30 words
- Measurement approaches to prove voice-driven lift
Scale voice-optimized content with AI automation at https://scaleblogger.com
Understanding Voice Search and Its Impact on SEO
Voice search privileges conversational, context-rich queries over terse keywords, and that changes how searchers signal intent. Users ask full questions, devices deliver concise answers, and natural language understanding (`NLU`) plus device context — location, mic history, user preferences — decide which result wins. Speech recognition converts audio to text; `NLU` interprets intent and entities; ranking layers then prioritize answers that match conversational phrasing, local relevance, and answer-format suitability (snippet, local pack, or knowledge panel).
- Speech-to-text + NLU: Speech recognition transcribes; `NLU` extracts intent and entities.
- Context signals: Device type, location, time of day, and prior queries influence rankings.
- Conversational queries: Long-tail, question-style phrases (Who, How, When) increase.
- Answer-first UX: Search engines prefer short, authoritative answers suitable for read-aloud.
- Local dominance: Many voice queries are location-based or transactional (`near me`, hours).
- Technical sensitivity: Page speed, structured data, and concise content formats matter more.
Voice assistants now answer a remarkable percentage of queries accurately, reinforcing voice search’s reliability and adoption in SEO strategies. See the Forbes analysis on voice assistant accuracy and implications for SEO: Voice-Activated Revolution: Harnessing Voice Search For Better SEO.
| Aspect | Typical Query Style | User Intent Signals | SEO Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query length and phrasing | Full questions, natural language | Conversational intent, follow-ups | Target long-tail, Q&A phrasing; use FAQs |
| Device / Location context | Mobile/smart speaker, often local | GPS, device type, time of day | Prioritize local SEO, mobile-first pages |
| Expected content format | Short, direct answers | Need for concise facts or instructions | Optimize for featured snippets and short summaries |
| Result format | Spoken snippet, local pack, rich answer | Single-result satisfaction | Structure content for `answer boxes` and schema |
| Interaction design (follow-ups) | Multi-turn conversation | Clarifying intent, session history | Build conversational content and internal links |
When teams adapt keyword strategy to conversational queries and tighten technical foundations — structured data, speed, mobile UX — content becomes discoverable by voice without sacrificing broader SEO goals. This is why modern content strategies prioritize automation—it frees creators to focus on what matters.
Keyword Research for Voice: From Short Queries to Conversational Phrases
Prerequisites
Tools / materials needed
- Analytics & Search Console (Google Search Console) — query volume and impressions.
- Customer support transcripts — real conversational language.
- Keyword tools — SEMrush, Ahrefs, Moz, AnswerThePublic, Keywords Everywhere, Ubersuggest, AlsoAsked.
- SERP inspection — manual checks for featured snippets and People Also Ask (PAA).
Start with conversational seeds
Prioritize by intent and opportunity
Tactical examples and tips
- Use `who is` or `how to` seeds for informational voice queries; use `where can I` or `near me` for transactional/local voice queries.
- Local and transactional voice queries often convert better because users are action-oriented.
- Reformat answers on-page into short, direct snippets (1–3 sentences), then add an expanded answer below.
Industry analysis shows voice assistants answer a high percentage of queries accurately, making snippet optimization more valuable than ever. (Reference: Voice-Activated Revolution: Harnessing Voice Search For Better SEO)
Provide a concise tool + method matrix for sourcing voice query ideas
| Tool/Source | How to use it for voice keywords | Best practice tip | Use case example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Autocomplete | Type seed prompts, capture suggestions | Use incognito + location filters | Find natural phrasing for FAQ pages |
| People Also Ask (PAA) | Expand boxes to capture related questions | Crawl repeatedly for new variations | Build layered Q&A content |
| AnswerThePublic | Visual question maps by seed | Export CSV for bulk processing | Generate 100+ long-tail questions |
| Customer support transcripts | Text-mine for exact user language | Normalize colloquialisms and contractions | Create conversational blog FAQs |
| SEMrush (filters) | Use question filters and SERP features | Sort by SERP feature presence | Identify snippet candidates ($129.95/mo) |
| Ahrefs (filters) | Use `Questions` report and clicks metric | Prioritize low-competition, high-clicks ($99/mo) | Spot high-intent voice queries |
| Keywords Everywhere | Pull related long-tail phrases in UI | Cheap credits; quick expansion ($10 credit) | Fast seed expansion during research |
| Ubersuggest | Content ideas and question reports | Good for budget-conscious teams (starts ~$12/mo) | Competitor phrase discovery |
| AlsoAsked | Visual question trees from PAA | Use to map intent paths | Discover follow-up conversational queries |
| Moz Pro | Keyword explorer question suggestions | Cross-check difficulty and organic CTR ($99/mo) | Validate targetability |
| AnswerThePublic (free tier) | Quick brainstorming without cost | Use alongside paid tools for breadth | Early-stage ideation |
Troubleshooting
- If voice traffic stalls, check snippet structure and answer length; reduce to `1–2` concise sentences.
- Low conversion on voice keywords often means missing local signals — add `schema` and GMB updates.
- If tools disagree on volume, trust on-site analytics and adjust weights accordingly.

Content Formats and Writing Techniques for Voice Queries
Voice queries demand answers that a human can speak and a machine can parse quickly. Begin every voice-optimized answer with a short, direct lead — one or two sentences that resolve the user’s intent — then expand with structured, scannable supporting content that maps to featured snippet patterns.
- Active voice: Keeps responses immediate and natural.
- Conversational tone: Use everyday phrasing that mirrors how people speak.
- Short sentences: Aim for 12–18 words on average; one key idea per sentence.
- Pacing cues: Use pauses implied by commas and short sentences rather than long clauses.
Market analysis shows voice assistants now answer a high percentage of queries accurately, making concise spoken answers more valuable to ranking and user experience. See the Forbes piece on the voice-activated revolution for context: Voice-Activated Revolution: Harnessing Voice Search For Better SEO.
Practical templates and examples
- Use `What is X?` headings for definition intents and a 15–25 word lead.
- For how-to, present steps as numbered instructions and include an estimated time or tools list.
- For local queries, include precise address formatting, phone number, and operating hours for spoken answers.
How to reset a router
Short answer: Press and hold the reset button for 10 seconds to restore factory settings.
- Power off, wait 10s.
- Press reset for 10s.
| Query Type | Ideal Lead Format | Approx. Answer Length | Supporting Elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition / What is | One-line definition, plain-language | 15–25 words | FAQ heading, short paragraph, `definition` schema |
| How-to / Step-by-step | Direct short answer + steps | 20–50 words total | Numbered steps, `HowTo` schema, time/tools |
| Local / Near me | Direct location answer + directions | 10–20 words + contact | Address, hours, phone, `LocalBusiness` schema |
| Comparison / vs | One-sentence recommendation + pros/cons | 20–40 words | Bulleted pros/cons, comparison table, spec list |
| Transactional / Where to buy | Direct purchase pointer + availability | 10–20 words | Purchase link, price, stock, `Product` schema |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented consistently, voice-optimized content reduces friction for users and improves the chances of securing both featured snippets and spoken answers.
Technical SEO and Site Architecture for Voice
Begin by aligning site architecture with conversational discovery patterns: voice assistants prioritize clear, concise answers and fast, stable experiences. Start with these prerequisites and tools, then follow the step-by-step implementation.
Prerequisites
- Access to CMS (ability to edit templates and inject JSON-LD)
- Analytics and lab tools: GA4, Lighthouse, WebPageTest
- Server/hosting access: ability to configure CDN and caching
- Content inventory: prioritized pages for conversational queries
- CDN provider (Cloudflare, Fastly) and server monitoring
“Voice search assistants boasting an impressive accuracy rate, answering 93.7% of search queries…” — Forbes council article on voice-activated revolution
| Schema Type | Best Use Case | Voice Benefit | Implementation Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAQ | Q&A pages, support docs | Quick spoken answers, featured snippets | Use `FAQPage` JSON-LD; keep Q/A concise; Google supports rich result rendering |
| HowTo | Process/steps content | Readable step sequences for assistants | Use `HowTo` with `step` objects; include time/difficulty where relevant |
| LocalBusiness | Storefronts, service areas | Local voice queries, directions, business facts | Add `address`, `geo`, `openingHours`, `telephone`; keep NAP consistent |
| Speakable | Short news summaries, updates | Explicit eligibility for speech responses | Implement `SpeakableSpecification` limited to small passages; follow Google guidance |
| Product | Ecommerce product pages | Quick facts: price, availability, SKU | Use `Product` with `offers`, `aggregateRating`; ensure up-to-date `availability` |

Local and Conversational UX: Capturing ‘Near Me’ and Multi-Turn Queries
Prerequisites: verified Google Business Profile (GBP), clean NAP (name, address, phone), site accessible on mobile, basic schema/flexible CMS for Q&A blocks. Tools/materials: Google Business Profile dashboard, structured data validator, analytics (GA4), content pipeline that can publish localized landing pages quickly (an AI-powered content pipeline accelerates this). Estimated time: initial setup 2–6 hours; ongoing maintenance 30–90 minutes/week.
Start by treating local voice and conversational queries as a distinct UX layer — short, immediate answers for voice assistants and a smooth follow-up path for multi-turn dialogue. Voice search favors concise, well-structured facts (hours, services, wait times), while multi-turn flows need chaining: anticipate the next question and surface the answer before the user asks it.
Practical steps for Local Voice Queries and ‘Near Me’ searches
Industry reporting notes voice assistants answer a high percentage of queries with high accuracy; accuracy figures approach 93.7% in recent analyses, reinforcing the value of precise local data (Forbes council on voice-activated search).
| Task | Priority | Estimated Effort | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verify Google Business Profile | High | 1–2 hours | High — visibility in local pack |
| Add FAQ with schema | High | 2–4 hours | High — voice snippet eligibility |
| Create local landing pages | High | 4–8 hours per page | High — targeted long-tail traffic |
| Collect and respond to reviews | Medium | 30–60 min/week | Medium — trust + conversion |
| Ensure mobile load times | High | 2–6 hours audit + fixes | High — reduces bounce / voice retrieval |
Design patterns for multi-turn conversations
- Structured Q&A blocks: place short answers and linked follow-ups; tag questions with intent labels.
- Anticipatory content: include likely follow-ups within the first paragraph to satisfy chained queries.
- Surface related content: tag and surface nearby pages or topics to reduce friction.
- Analytics-driven refinement: track conversational paths and add missing answers iteratively.
📥 Download: Voice Search Optimization Checklist (PDF)
Measuring Success and Scaling Voice Search Optimization
Measuring voice search performance starts with signals that differ from traditional web analytics: featured snippet impressions, long conversational query volume, local pack visibility, and voice assistant result attribution. Focus measurement on these outcomes and build a repeatable playbook so teams can scale optimization without recreating discovery work every time.
“Voice search assistants answer 93.7% of search queries with high accuracy on many platforms” — Forbes discussion on voice search adoption and impact. https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2024/12/17/voice-activated-revolution-harnessing-voice-search-for-better-seo/
Scaling Process: SOPs, Templates, and Automation
- Create a standard operating procedure (SOP) that converts high-value queries into content tasks: discovery → snippet draft → schema injection → monitoring.
- Build snippet templates: Question (H2) → 40–60 word direct answer → supporting bullets → microcopy for featured snippet formatting.
- Automate schema deployment with CMS plugins or CI scripts that inject `FAQ` and `Speakable` schema based on template fields.
- Schedule recurring audits (quarterly) and prioritize remediations using an ROI matrix: traffic potential × conversion intent.
- Use automation to tag pages that generate conversational queries and queue them into content sprints.
| Tool | Voice-specific signals | Best for | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Featured snippet impressions, query snippets, SERP positions | Snippet performance | Free, direct snippet data |
| Google Analytics (GA4) | Local conversions, voice-driven events (calls/form fills) | Conversion tracking | Use `event` tagging for voice actions |
| SEMrush | Question keyword volume, SERP feature tracking | Keyword discovery + competitive analysis | Tracks featured snippets and intent |
| Ahrefs | Long-tail query discovery, SERP feature history | Backlink + organic research | Strong keyword explorer for question phrases |
| Moz Pro | Rank tracking with SERP feature insights | Mid-market SEO teams | Useful keyword intent tagging |
| BrightLocal | Local pack visibility, review monitoring | Local businesses | Tracks local rankings, citations |
| Yext | Local listing accuracy, knowledge graph signals | Enterprise local presence | Automates local data across platforms |
| Rank Ranger | Question-filter rank tracking, SERP feature reports | Custom rank reports | API-friendly for dashboards |
| Amazon Alexa Dev Console | Skill invocation metrics, answer performance | Alexa-specific testing | Device-level metrics, developer-focused |
| Google Assistant Console | Action analytics, conversational queries | Assistant-specific testing | Conversation accuracy and engagement |
Understanding these measurement patterns and building SOPs with reusable templates lets teams scale voice optimization efficiently and keeps technical debt low while increasing the chances of appearing where voice queries land. When implemented, this approach streamlines decision-making and turns conversational demand into reliable traffic and conversions.
Conclusion
Voice-driven search is reshaping how audiences ask questions, so content must shift from short keyword fragments to conversational, intent-rich answers. Rewriting headlines and meta to mirror spoken queries, structuring content around brief vocal answers plus deeper context, and automating variant generation are practical moves that produce measurable gains—teams that adopt this pattern see higher long-tail rankings and more engaged sessions. As Forbes highlights, voice search behavior is growing fast, so prioritize conversational intent, build concise vocal snippets, and automate variant creation to capture those queries at scale.
Start by auditing top pages for question-driven gaps, then create 1–2 voice-ready snippets per pillar page and deploy an automated pipeline to generate conversational variants. For professional implementation and rapid scaling, consider technical content automation platforms—Scale voice-optimized content with AI automation is a practical next step to operationalize these tactics and turn spoken-query opportunities into predictable traffic.

