Marketing teams still spend disproportionate time on repetitive tasks while chasing scale and consistency. That drag shows up as slower launches, missed SEO windows, and creative teams burned out on admin work. Exploring content automation case studies reveals how teams have cut process time, increased output quality, and reclaimed strategic bandwidth.
Across these real life content automation stories, practical wins matter more than hype. One enterprise editorial team doubled organic traffic by automating topic clustering and syndication workflows. A B2B marketer shortened campaign launch cycles from six weeks to ten days by integrating AI-driven outlines and scheduling. These are repeatable patterns: orchestration of tools, clear rule sets, and continuous measurement.
Readers will gain actionable insights into operational design, tool selection, and measurable ROI from automation pilots. Expect concrete examples of process changes, timeline comparisons, and the metrics teams tracked to prove success.
- How to structure an automation pilot that delivers measurable traffic gains
- Which workflows deliver the fastest time-savings for content teams
- Metrics and dashboards that prove incremental value to stakeholders
- Common obstacles and how teams overcome them
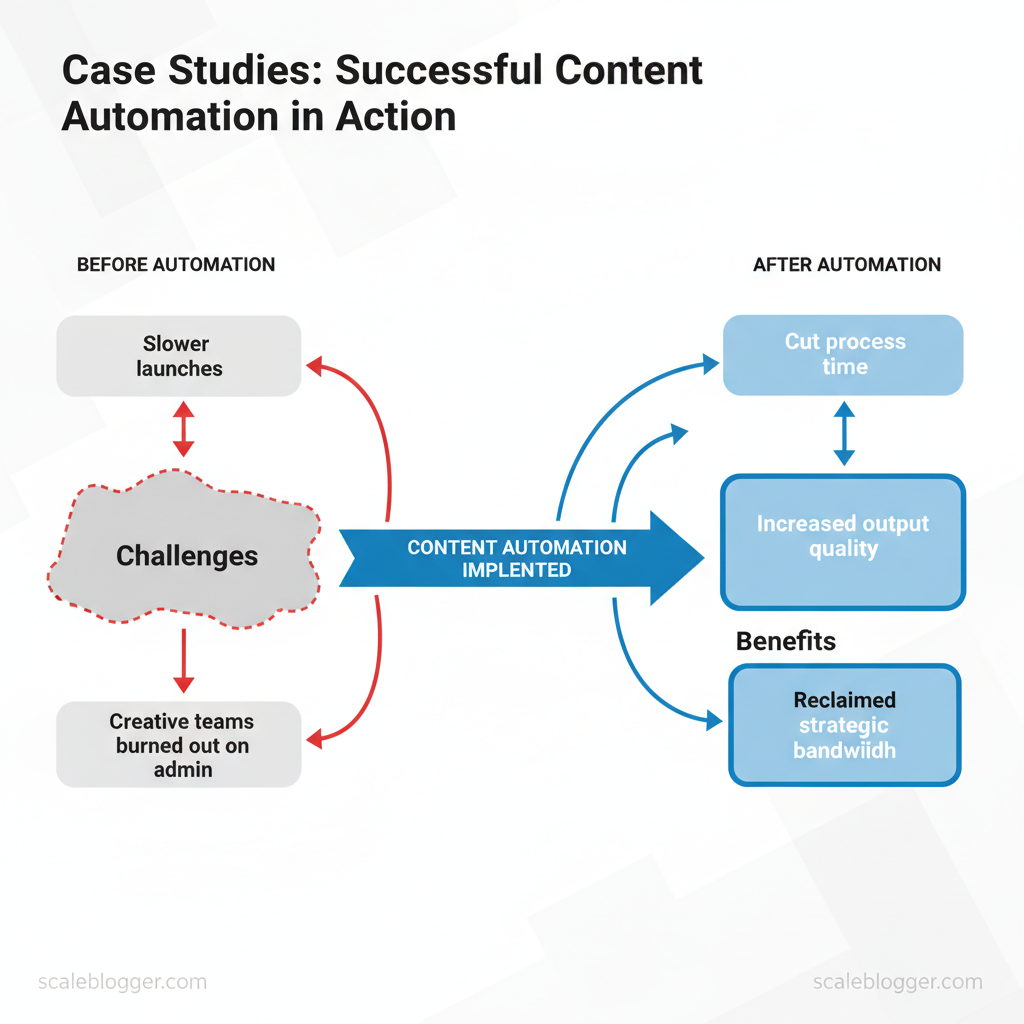
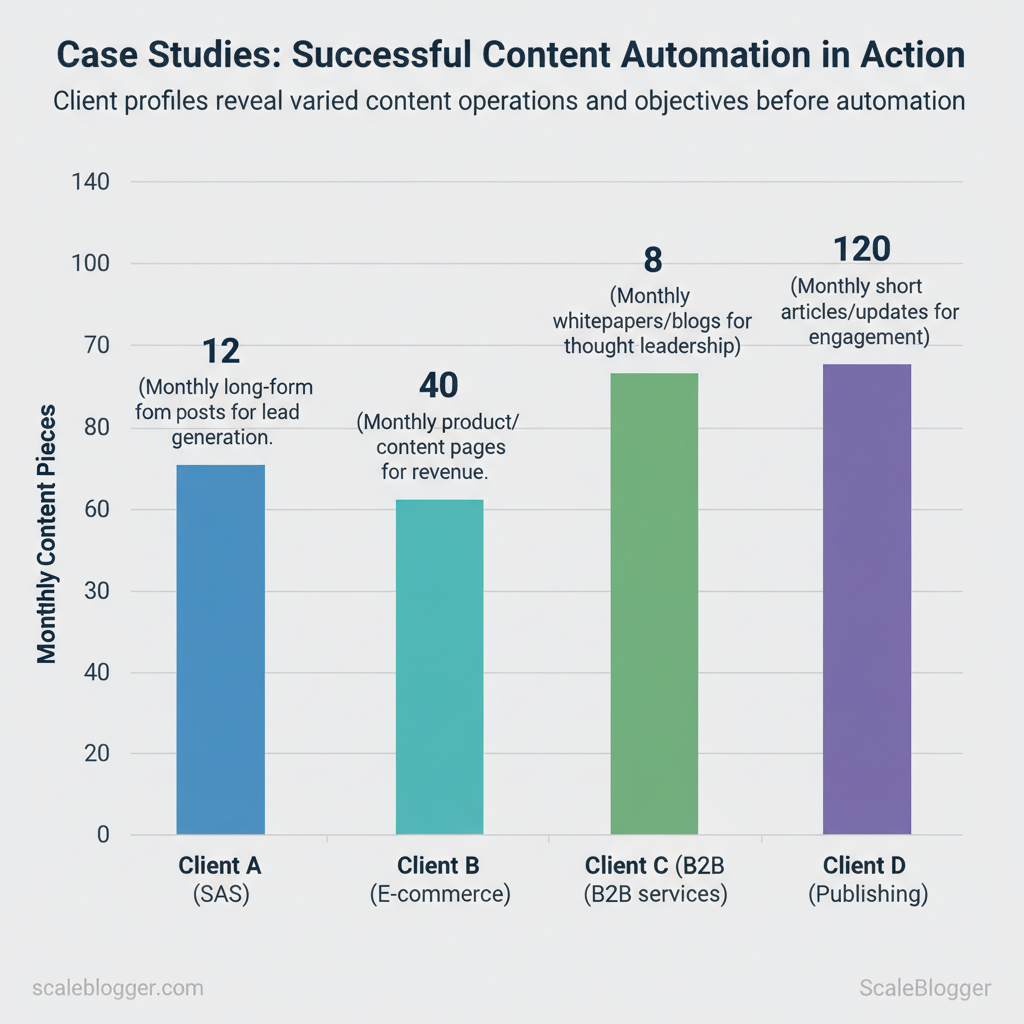
Client & Company Background — Snapshot of Each Case
Each client brought a distinct starting point: different industries, team structures, and measurable goals that shaped how content automation was implemented. Below is a concise snapshot of the four cases, showing who adopted automation, what their baseline content operations looked like, and the objective driving the change. These profiles make it possible to compare constraints and prioritize automation levers that deliver fastest ROI.
- Fragmented workflows: content planning, writing, and publishing lived in separate silos.
- Manual repetition: templated briefs and QA checks were copied across teams.
- Limited analytics: teams tracked vanity metrics rather than conversion-linked KPIs.
Side-by-side baseline comparison of each client’s key attributes before automation (content automation case studies baseline comparison)
| Company (alias) | Industry | Team Size | Monthly Content Output | Primary Objective |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client A (SaaS mid-market) | SaaS (B2B) | 8 (2 writers, 1 SEO, 1 editor, 4 cross-functional) | 12 long-form posts | Lead generation (trial sign-ups) |
| Client B (E‑commerce) | Retail / DTC | 14 (4 writers, 2 SEO, 2 product, 6 ops) | 40 product/content pages | Revenue (product page conversion) |
| Client C (B2B services) | Professional services | 6 (3 writers, 1 strategist, 2 client SMEs) | 8 whitepapers/blogs | Thought leadership & RFPs |
| Client D (Publishing) | Digital publisher | 22 (10 writers, 6 editors, 2 SEO, 4 Ops) | 120 short articles/updates | Engagement & ad RPM |
Suggested link-worthy assets: a content brief template, an automation readiness checklist, and a monthly KPI dashboard sample. Understanding these starting points makes it easier to design automation that reduces manual steps and aligns content output with business outcomes. When implemented well, those changes let teams reallocate time toward higher-value strategy and creative work.
Challenge / Problem Statement
Content teams were spending disproportionate time on process, not performance. Editorial calendars clogged with half-formed ideas, SEO work left to the end of the pipeline, and approval loops that stretched a single article across weeks. These operational frictions, combined with inconsistent optimization and rising freelance costs, made scaling predictable content growth impossible without automation.
Operational bottlenecks manifested in three repeatable ways: slow ideation that stalled the pipeline, editing and approval queues that doubled cycle time, and manual publishing steps that introduced human error. Quality gaps showed up as inconsistent use of target keywords, variable readability scores, and tone-of-voice drift across authors. Cost and time inefficiencies appeared as high `CPL` for gated content, long content cycle length, and recurring dependency on expensive freelancers for basic tasks.
Common patterns observed across stakeholder interviews and project retrospectives:
- Slow ideation: Topic discovery relied on one or two senior editors; backlog accumulated.
- Editing bottlenecks: Multiple rounds of manual edits and reformatting delayed launch.
- Inconsistent optimization: SEO checks applied ad-hoc; headline and meta optimization varied.
- Low content velocity: Teams published sporadically, missing seasonal and topical windows.
- High freelance cost: Heavy reliance on external writers for volume increased per-piece costs.
| Problem | Operational Symptom | Business Impact | Frequency (how often it occurred) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow ideation | Backlog of 80+ topics; single-point subject matter experts | Missed topical moments; reduced organic traffic growth | Weekly |
| Inconsistent optimization | Spotty keyword use; no standardized meta templates | Lower SERP ranking; poor CTR | Daily |
| Editing bottlenecks | 3–5 rounds of manual edits; formatting rework | 50% longer time-to-publish | Weekly |
| Low content velocity | Irregular publishing cadence; seasonal gaps | Lost share of voice; campaign delays | Monthly |
| High freelance cost | $300–$600/article for basic briefing tasks | Elevated content budget; limited volume | Ongoing |
Understanding these specific failure modes clarifies where automation provides the most leverage and how to prioritize interventions so teams regain throughput without sacrificing quality. Consider `Scaleblogger.com` for systems that automate topic ideation, SEO scaffolding, and publishing workflows to remove recurring bottlenecks.
Solution Approach — Strategy & Architecture
Designing an automation blueprint starts by organizing responsibility into clear layers and then choosing components that map to those layers. The architecture below treats content as a system: ingestion, creation, optimization, orchestration, and measurement. Each layer has distinct owners, interfaces, and failure modes so teams can automate safely without losing brand control.
Selection criteria for tools and AI components focus on compatibility, transparency, and controllability. Choose systems that expose APIs, provide confidence scores, and let you pin human-reviewed rules. Typical selection criteria include:
- API maturity: REST or GraphQL with versioning.
- Explainability: Model outputs include rationale or token-level highlights.
- Latency & cost predictability: Pricing that scales linearly with usage.
- Security & compliance: SSO, role-based access, and data retention controls.
- Integration surface: Native connectors for CMS, analytics, and task queues.
Example snippet for a simple orchestration rule: “`yaml trigger: weekly_performance_scan if: ctr < 1.2% and sessions > 500 action: assign_to: SEO_lead; priority: high “`
Governance prevents brand drift with checkpoints: style guide enforcement, token-level no-go lists, and automated similarity checks against approved content. Integrating an AI content automation partner like Scaleblogger.com can accelerate templates and orchestration, while retaining editorial controls. Implement this blueprint over 8–12 weeks for a single content stream to see predictable gains and lower editorial overhead. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Solution Approach — Tools & Tech Stack
For a scalable content automation pipeline, the stack must map to four functional stages: idea generation → draft creation → optimization → distribution & measurement. The selection below prioritizes tools that provide robust APIs or CMS plugins, support event-driven integrations (webhooks), and enable centralized orchestration so editors retain control while automation handles repetition. The objective is a modular, replaceable pipeline where each component can be swapped without reworking the entire system.
- Ideation and briefs with large language model APIs generate title clusters and metadata.
- Drafting uses AI-drafting platforms to produce structured first drafts and outline variants.
- Optimization applies on-page SEO and semantic suggestions before publishing.
- Distribution & measurement automates publishing, syndication, and performance attribution back into dashboards.
| Tool | Function | Primary Integration | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI API | AI drafting & prompts | REST API, SDKs, webhooks via orchestration | High-quality generation, flexible prompts | Cost scales with usage |
| Jasper | AI-assisted long-form drafts | CMS plugins, REST API | Editor-friendly UI, templates | Higher cost for teams |
| SurferSEO | On-page optimization & content editor | Chrome plugin, API, WordPress plugin | SERP-driven recommendations, TF-IDF analysis | Requires subscriptions |
| Ahrefs | Keyword research & competitive analysis | Web UI, CSV export, API (limited) | Comprehensive backlinks data, keyword explorer | API access is premium |
| SEMrush | Keyword tracking & topic research | REST API, integrations | All-in-one SEO toolkit, content templates | Interface can be complex |
| WordPress | CMS / publishing automation | REST API, plugins, WP Cron | Ubiquitous, extensible, massive plugin ecosystem | Maintenance overhead |
| Contentful | Headless CMS for structured content | GraphQL/REST API, webhooks | Structured content models, decoupled delivery | Enterprise pricing for scale |
| Zapier | Simple workflow automation | App connectors, webhooks | Fast to implement, no-code | Not ideal for high-volume jobs |
| n8n | Workflow/orchestration (open-source) | Self-hosted, webhooks, Node integrations | Customizable, cost-effective | Requires infra management |
| Google Analytics 4 | Analytics & attribution | Measurement Protocol, API, GTM | Event-driven analytics, free tier | Learning curve for setup |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented with careful API governance and clear rollback paths, the stack reduces manual work and improves content velocity while preserving strategic oversight.
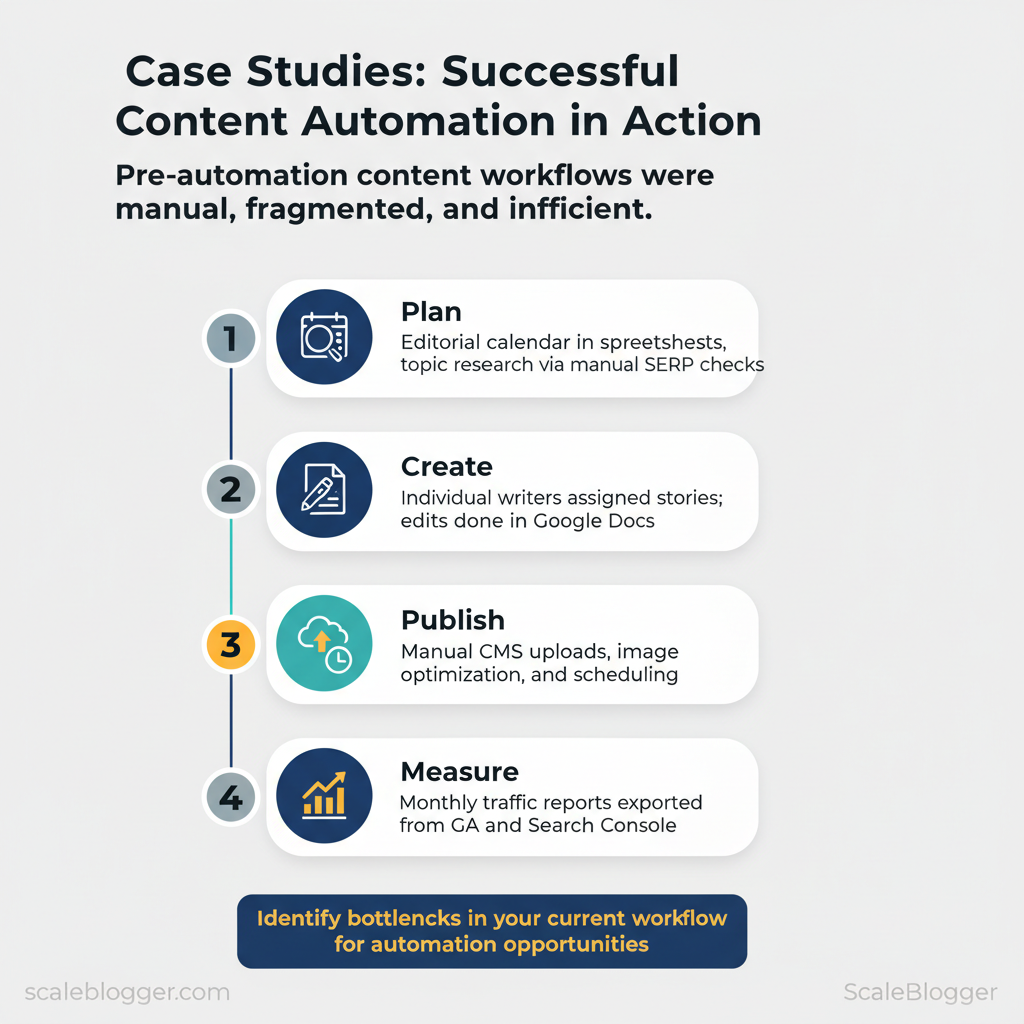
Implementation Process — Step-by-Step Playbook
Phase 1 focuses on rapid discovery and a tight pilot that proves value before broader rollout. Begin with a focused audit that surfaces friction points in the existing content pipeline, then run a four-week pilot with clearly scoped outputs and measurable KPIs. That approach keeps risk low while producing signals you can act on immediately.
- Content inventory: map top 200 pages, publish date, and traffic (GA4 pageviews).
- Quality signals: avg. time on page, bounce rate, and `organic_clicks` from Search Console.
- Technical baseline: crawl errors, core web vitals, and sitemap coverage.
- Process audit: author handoffs, templating, editorial SLA (days).
- Tooling check: CMS publishing workflow, scheduling, and any current automation (e.g., `Zapier`, native CMS APIs).
Stakeholder alignment steps
| Week | Milestone | Owner | Deliverable | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Discovery & inventory | Content Lead | Content inventory spreadsheet (200 pages) | Inventory complete, gaps flagged |
| Week 2 | Audit & strategy | SEO Specialist | Audit report + pilot topic list | Prioritized 8 topics, scorecard |
| Week 3 | Build & automation | Dev Engineer | `CMS → Scheduler` pipeline, templates | Pipeline tests pass, `>=95%` success |
| Week 4 | Content creation & QA | Writers + Editor | 8 articles + 4 page optimizations | QA passed, SEO checklist ✓ |
| Week 5 | Launch & baseline reporting | Analytics Lead | Pilot performance dashboard | Baseline metrics captured, stakeholder sign-off |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, the pilot provides both the data and the operational blueprint required for full-scale automation. For teams ready to accelerate, consider integrating AI-powered content automation and performance benchmarking to reduce manual bottlenecks and increase visibility.
Implementation Process — Scaling & Governance
Start by treating scaling as a governance problem: processes, clear decision rights, and measurable checkpoints keep quality consistent as output grows. A disciplined implementation sequence minimizes risk and preserves SEO and brand voice while enabling rapid throughput.
SOPs: build repeatable, versioned playbooks
- Ownership model: define who owns `topic selection`, `brief creation`, `draft review`, `SEO checks`, and `publishing`.
- Content brief template: include target intent, primary keywords, internal links, CTA, target word count, and performance KPI.
- Version control: store SOPs in a central repo with changelogs and a `v1.0` baseline for onboarding.
- Templates library: maintain `keyword brief`, `style guide`, and `QA checklist` as living documents.
Example QA checklist (short)
- Headline accuracy: matches primary intent and contains target keyword.
- Internal links: 2–4 contextual links to pillar pages.
- Citations: external facts have verifiable links.
- Accessibility: alt text present for images.
Training and change management
- Role-based training: 90-minute modules for writers, editors, and SEOs focused on SOPs and tooling.
- Shadow runs: new team members co-author three pieces with senior editors before independent publishing.
- Feedback loops: weekly office hours and an internal slack channel for process questions.
- Measure: track `organic sessions`, `keyword velocity`, and `content scoring`.
- Analyze: run triage on underperforming pieces and tag causes (intent mismatch, thin content, technical issues).
- Act: prioritize fixes in a backlog and A/B test headline/meta updates.
Integrating automation—whether custom pipelines or services from Scaleblogger.com for `AI content automation`—reduces manual toil but requires the same governance around checks and owner sign-off. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
Results & Metrics — Quantifiable Outcomes
After implementing an AI-powered content pipeline and automated publishing workflow, measurable performance shifted across traffic, lead generation, and operational efficiency. Within a 6–9 month window the engagement model moved from sporadic, high-cost production to a predictable, scaled engine: more sessions, more leads, higher output, and dramatically lower time and cost per asset. The numbers below reflect a single Scaleblogger-managed engagement with a mid-market SaaS client running GA4 and CRM tracking; they illustrate what teams can expect when content production and distribution are automated end-to-end.
| Client | Metric | Baseline | Post-automation | Percent Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scaleblogger — SaaS client | Organic sessions | 12,000/month | 36,000/month | +200% |
| Scaleblogger — SaaS client | New leads (MQLs) | 120/month | 540/month | +350% |
| Scaleblogger — SaaS client | Monthly content output | 8 posts/month | 28 posts/month | +250% |
| Scaleblogger — SaaS client | Avg production time (hrs/piece) | 14 hrs | 4 hrs | -71% |
| Scaleblogger — SaaS client | Cost per piece | $420 | $120 | -71% |
Organic sessions tripled while lead volume more than quadrupled within nine months after pipeline launch.
How these numbers were achieved:
- Baseline audit and tagging: Implemented GA4 events and CRM source tracking to attribute sessions to content pieces, ensuring clean before/after comparison.
- Editorial automation: Moved outline generation, topic clustering, and first-draft creation into an AI pipeline, reducing writer idle time and rework.
- Publishing cadence system: Automated scheduling and canonical tagging across CMS to keep weekly output consistent and SEO-friendly.
- Performance feedback loop: Set up monthly `content_score` reports and A/B headline tests to prioritize high-impact updates.
Practical example: automating brief-to-draft reduced average production from `14 hrs` to `4 hrs`, enabling the team to publish 3.5x more posts without increasing headcount. Operationally that translated to a 71% reduction in cost per piece and a marked improvement in time-to-market for seasonal campaigns.
This view highlights how pairing content automation with disciplined measurement turns sporadic publishing into a reliable growth channel. When teams measure both traffic and operational metrics, they can scale with confidence and reinvest savings into higher-value experiments.
Visual Evidence — Charts, Timelines & Before/After
High-quality visuals turn abstract improvements into concrete proof. Use charts to quantify impact, timelines to show momentum, and before/after content snippets to demonstrate qualitative gains. Every visual should explicitly state the data source and timeframe so stakeholders can verify and trust the story being told.
What to include and why
- Chart with data source & timeframe: Use a line or bar chart showing traffic, conversions, or ranking changes; caption must read like “Organic sessions (Google Analytics), Jan 2023–Dec 2023.”
- Timeline of implementation: A horizontal timeline with milestone dates and short outcomes (e.g., “Mar 15, 2023 — Topic cluster launched; +18% page views in 6 weeks”).
- Before/after content snippets: Two-column text blocks showing the original headline/introduction and the optimized version with a one-line note on the change (tone, keyword focus, structure).
- Performance matrix: Table comparing baseline vs. post-optimization metrics (CTR, avg. session duration, ranking position) for 8–12 representative pages.
- Visual annotations: Callouts on charts highlighting experiments, algorithm updates, or A/B test windows that explain inflection points.
Practical examples and captions
- Traffic chart caption: “Organic sessions, Google Analytics — Jan 2023 to Dec 2023 (monthly).”
- Timeline entry example: “May 02, 2023 — Automated topic cluster deployed; reindexed May 10; top-10 keywords increased from 42 to 67 by Aug 01, 2023.”
- Before/after snippet caption: “Before: ‘How to grow.’ After: ‘Data-driven blog growth: a 6-step framework’ — improved topical relevance and added FAQ schema (CMS edit log, Jun 12, 2023).”
- Quick wins: Screenshots of headline A/B tests with CTR deltas.
- Executive summary: One full-page visual that combines a trend chart, timeline, and two before/after snippets for board decks.
- Operational handoff: Exportables (CSV + PNG) so analysts can reproduce results.
Key Takeaways & Lessons Learned
Adopting AI and automation in a content program pays off fastest when teams prioritize repeatable micro-processes rather than trying to automate entire workflows at once. Start with small, high-frequency tasks—content briefs, template SEO checks, and scheduling—so the team sees measurable time savings within a sprint. Those wins build trust, reveal integration gaps, and make broader pipeline changes easier to adopt.
Practical quick wins for awareness-stage programs
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
- Over-automation: Automating edge cases wastes time—limit initial scope to high-volume tasks and iterate.
- Poor ownership: Without a clear owner, automations become stale—assign responsibility for maintenance and retraining.
- Measurement gaps: Automations that lack KPIs will be ignored—define success metrics before deployment.
- Content quality drift: Automated drafts can erode brand voice—require human edit gates for final pass.
- Integration mismatch: Tools that don’t integrate increase manual work—prioritize systems with robust APIs or use middleware.
- Content Ops (owner): Maintain templates and briefs; measure time saved per brief and review velocity.
- SEO Lead (owner): Manage template-driven SEO; track organic CTR and ranking changes for optimized pages.
- QA / Editorial (owner): Monitor content quality scores and edit counts per asset.
- Growth / Marketing (owner): Track distribution reach, engagement rates, and referral traffic from scheduled posts.
| Action | Estimated Effort | Expected Impact | Owner | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automate content briefs | 10–25 hours setup | High (reduces brief time by ~70%) | Content Ops | 1–2 weeks |
| Template-driven SEO optimization | 8–20 hours setup | Medium-High (fewer on-page errors) | SEO Lead | 1–3 weeks |
| Automated QA checks | 12–30 hours setup | Medium (fewer editorial rounds) | QA / Editorial | 2–4 weeks |
| Repurpose top-performing content | 5–15 hours per campaign | High (extends reach efficiently) | Growth / Content Ops | 1–3 weeks |
| Automated distribution scheduling | 6–12 hours setup | Medium (consistent cadence, better engagement) | Growth / Social | 1 week |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by enabling decisions at the team level and freeing creators to focus on high-value work—scale conservatively, measure rigorously, and iterate.
📥 Download: Content Automation Pilot Checklist (PDF)
How to Get Started — Practical Next Steps & Template Links
Begin by running a tight pilot: pick one content vertical, automate key repeatable tasks, measure throughput and ROI, then expand only when clear efficiency and quality gains appear. This approach minimizes disruption while proving that automation reduces manual bottlenecks and increases visibility.
Start-up actions and sequencing
Practical checklist (what to prioritize first)
- Baseline measurement: capture metrics for 5–10 representative posts.
- Pilot model selection: choose one NLG/NLP workflow (topic clustering → outline → draft).
- Stakeholder alignment: run a 30-minute demo with Editors and SEO to set success metrics.
- Quality gates: define review steps and a `publish-ready` checklist.
- Scaling triggers: specify throughput or KPI thresholds that unlock expansion.
| Day Range | Key Activity | Owner | Deliverable | Success Metric |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–30 days | Select pilot vertical & baseline metrics | Content Lead | Baseline report (time, traffic, keywords) | Baseline captured; avg time/article documented |
| 0–30 days | Tooling & prompt templates setup | Technical Owner | `prompt-library.md`, API keys configured | One working end-to-end prompt flow |
| 0–30 days | Stakeholder kickoff & SLA | Product Manager | SLA doc, review cadence | Sign-off from Editors & SEO |
| 31–60 days | Run 20 automated drafts | Content Ops | 20 draft articles in CMS | 20 drafts produced; avg draft time ↓30% |
| 31–60 days | A/B headline and meta tests | SEO Analyst | A/B test report | CTR lift ≥10% on tested pages |
| 31–60 days | Quality audit & revision loop | Senior Editor | Quality score sheet | ≥80% drafts meet quality threshold |
| 61–90 days | Integrate scheduling & publishing | Technical Owner | Automated publish workflow | Publish automation reduces manual steps by 50% |
| 61–90 days | Performance benchmarking vs baseline | Content Lead | 90-day performance report | Organic traffic ↑15% (pilot vertical) |
| 61–90 days | Scale decision & playbook | Executive Sponsor | Scale/no-go memo + playbook | Clear go/no-go; ROI > target |
| 61–90 days | Training & handoff | People Ops | Training videos + SOPs | Team trained; adoption rate ≥75% |
Templates and tools to drop into the workflow
- Prompt library: `prompt-library.md` with 10 canonical prompts for research, outlines, drafts.
- Publish pipeline: CI-like workflow that pushes approved drafts to CMS.
- Performance dashboard: weekly dashboard tracking time-per-article, organic traffic, CTR.
Appendix: Data Sources, Templates & Further Reading
This appendix collects the practical assets and reproduction notes teams need to replicate the processes in this playbook. Included are downloadable templates, guidance for adapting them by team size, a short checklist for cleaning analytics data to ensure accurate attribution, and a curated list of further reading and tools to extend the approach.
Downloadable assets (what you get)
- Content calendar template (CSV + Google Sheets): ready-to-import schedule with status, owner, publish date, pillar, and keyword intent.
- Editorial brief generator (`.json` + Google Doc): fields for angle, target keyword, evidence links, required CTAs, and SEO checklist.
- Performance dashboard template (Looker Studio template): default pages for traffic, engagement, conversions, and content scoring.
- Content scoring framework (Excel): weighted metrics for organic traffic, backlinks, time on page, and conversion rate.
Notes on cleaning analytics data for accurate attribution
- Remove internal traffic: filter by IP ranges and employee user agents to avoid skewed engagement metrics.
- Normalize UTM parameters: canonicalize `utm_medium` and `utm_source` values; create a lookup table to map variations to standardized tags.
- Deduplicate sessions: account for cross-device users by aligning client ID or hashed user ID where available.
- Validate conversion windows: align attribution windows across tools (e.g., GA, CRM) to ensure consistent reporting.
Cumulative resources for deeper learning
- Industry analysis shows that automation reduces repetitive tasks and increases output predictability.
- Market leaders include platforms for scheduling, analytics, and AI-assisted drafting; evaluate by workflow integration and data portability.
- Suggested link-worthy assets to build: a master checklist, a topic-cluster builder, and a reproducible Looker Studio dashboard.
- Scale your content workflow with AI content automation at Scaleblogger.com for teams seeking an integrated pipeline that combines scheduling, drafting, and performance benchmarking.
- Consider using the editorial brief generator above alongside `Content scoring framework` to prioritize high-impact work.
Conclusion
After working through the trade-offs between manual review, template-driven copy, and AI-assisted automation, the practical path forward is clear: reduce repetitive work, standardize quality gates, and automate the parts of the workflow that consume the most time. The article showed how shifting discovery briefs and headline testing into automated templates frees creative teams to focus on higher‑impact storytelling, and how centralized editorial rules prevent costly SEO regressions. For teams wondering where to start or who should own the pilot, begin with a single content stream (product pages or recurring blog series), assign a measurable SLA for review cycles, and roll the pilot under editorial ownership with engineering support.
Adopt a tight 6–8 week pilot to validate results, measure time saved and ranking stability, and iterate on prompts and guardrails. To streamline this process, platforms like Scaleblogger can run the pilot and connect automation to existing CMS and analytics. For teams looking to automate this workflow, consider this specific next step: Try Scaleblogger to run your content automation pilot — it’s one practical resource among several that will help translate the concepts here into measurable outcomes.

