Marketing teams still spend too much time guessing which content actually moves the needle, while dashboards pile up vanity metrics. AI in marketing analytics turns that guessing into a structured signal by correlating audience behavior, channel performance, and creative elements to reveal what drives conversions and retention. This shifts investment from volume-based publishing to outcome-driven content programs.
Using AI to analyze content marketing metrics uncovers patterns that humans miss: which headlines lead to quality leads, which formats sustain engagement, and how seasonality alters channel effectiveness. That makes measuring AI success less about model accuracy and more about business impact — higher-quality leads, faster content cycles, and predictable ROI. Picture a content team that reallocates resources in days rather than quarters after an AI identifies underperforming topics.
- What reliable signals to track when assessing AI-driven content recommendations
- How to map `KPIs` from impressions to revenue without losing fidelity
- Ways AI shortens experimentation time and improves content ROI
- Practical checks to validate AI outputs before production
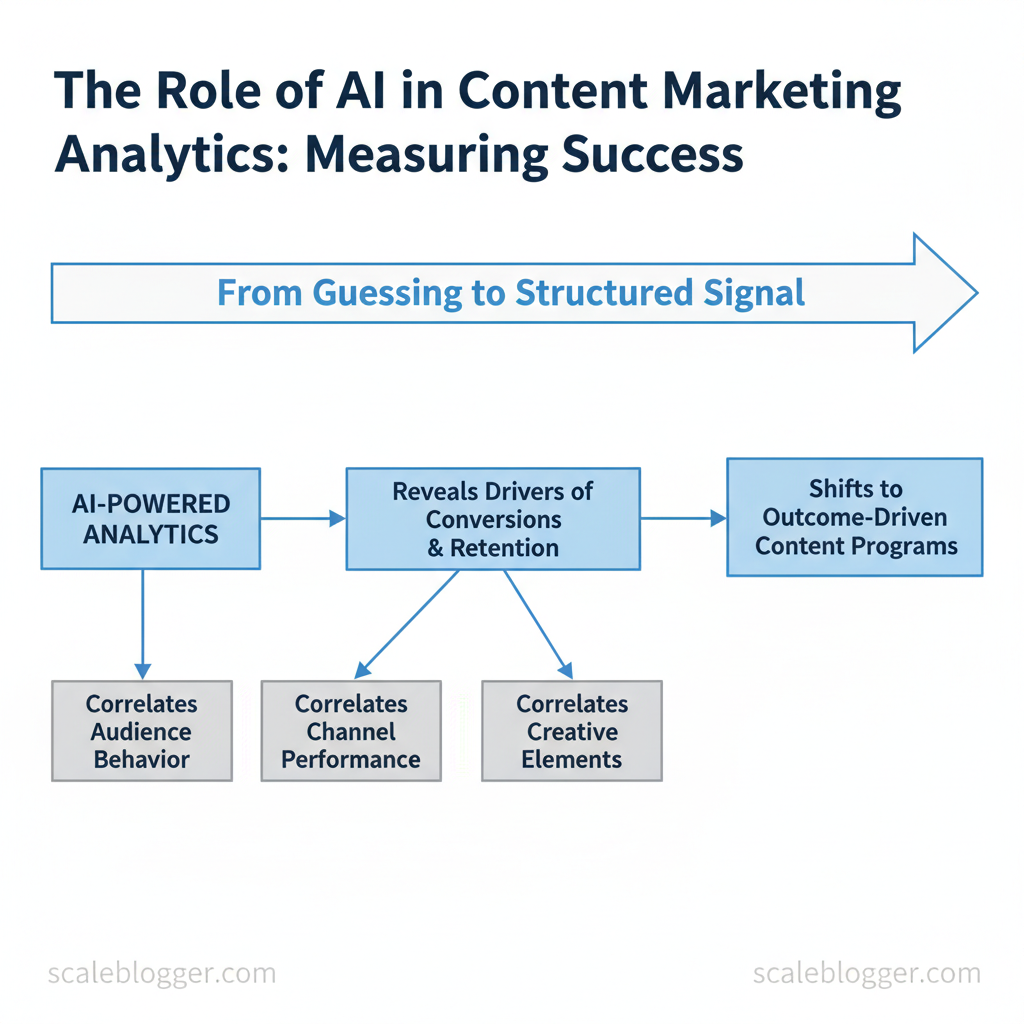
Foundations — What AI Brings to Content Marketing Analytics
AI transforms content marketing analytics by turning disparate signals into actionable decisions: it reads text at scale, forecasts which topics will move metrics, and automates the plumbing that keeps dashboards current. Teams that use AI stop guessing which posts will convert and start allocating effort based on probability and impact. This section explains the core capabilities that matter and how to translate metric-level signals into business outcomes.
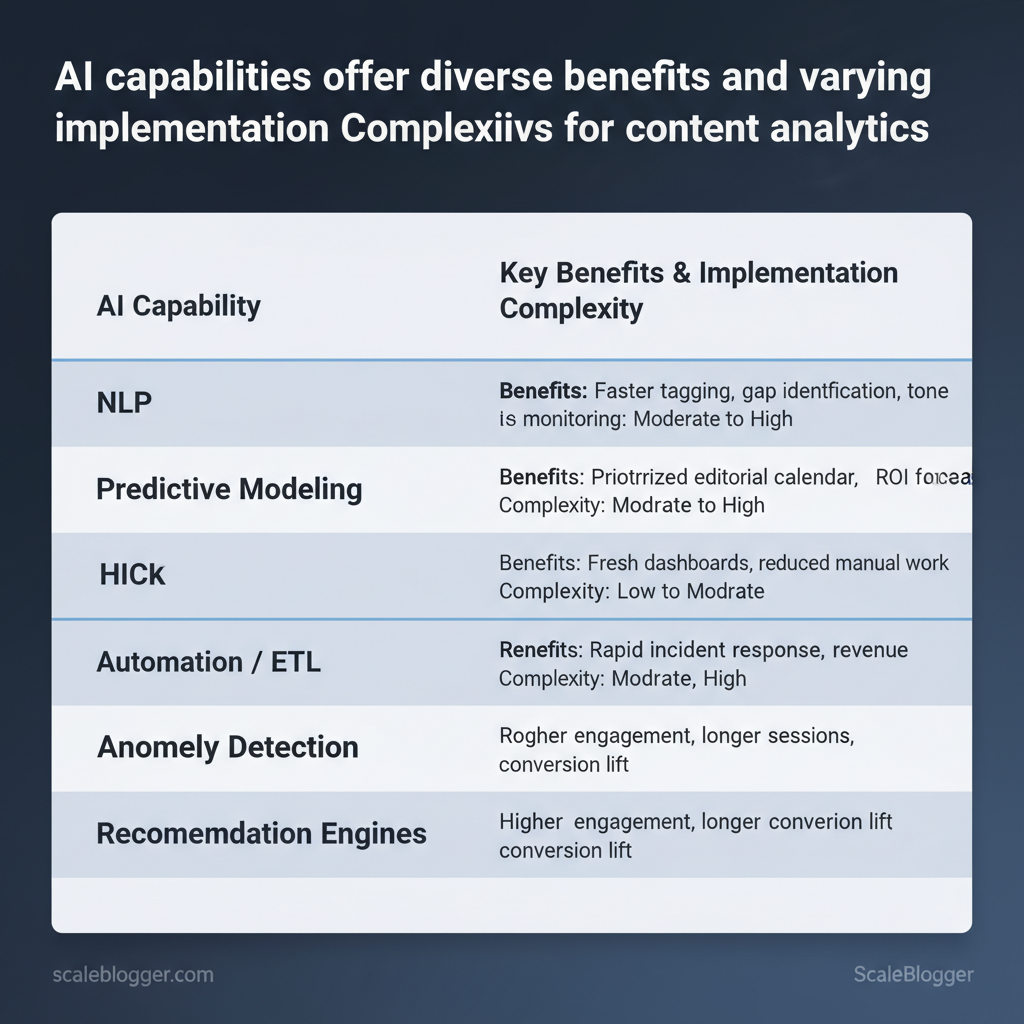
Key AI Capabilities (NLP, Predictive Modeling, Automation)
“`sql — Example pseudo-query: predict conversion probability per article SELECT article_id, predicted_conversion_prob FROM content_models.predict_conversion WHERE publish_date BETWEEN DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE, INTERVAL 90 DAY) AND CURRENT_DATE; “`
| AI Capability | Analytics Use-Case | Business Benefit | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLP | Sentiment, topic clustering, entity extraction | Faster tagging, gap identification, tone monitoring | Medium |
| Predictive Modeling | Forecast pageviews, conversions, churn risk | Prioritized editorial calendar, ROI forecasts | High |
| Automation / ETL | Data ingestion, transformation, pipeline scheduling | Fresh dashboards, reduced manual work | Medium |
| Anomaly Detection | Real-time drop/spike alerts in traffic or conversions | Rapid incident response, revenue protection | Low–Medium |
| Recommendation Engines | Personalized content and next-best-action suggestions | Higher engagement, longer sessions, conversion lift | High |
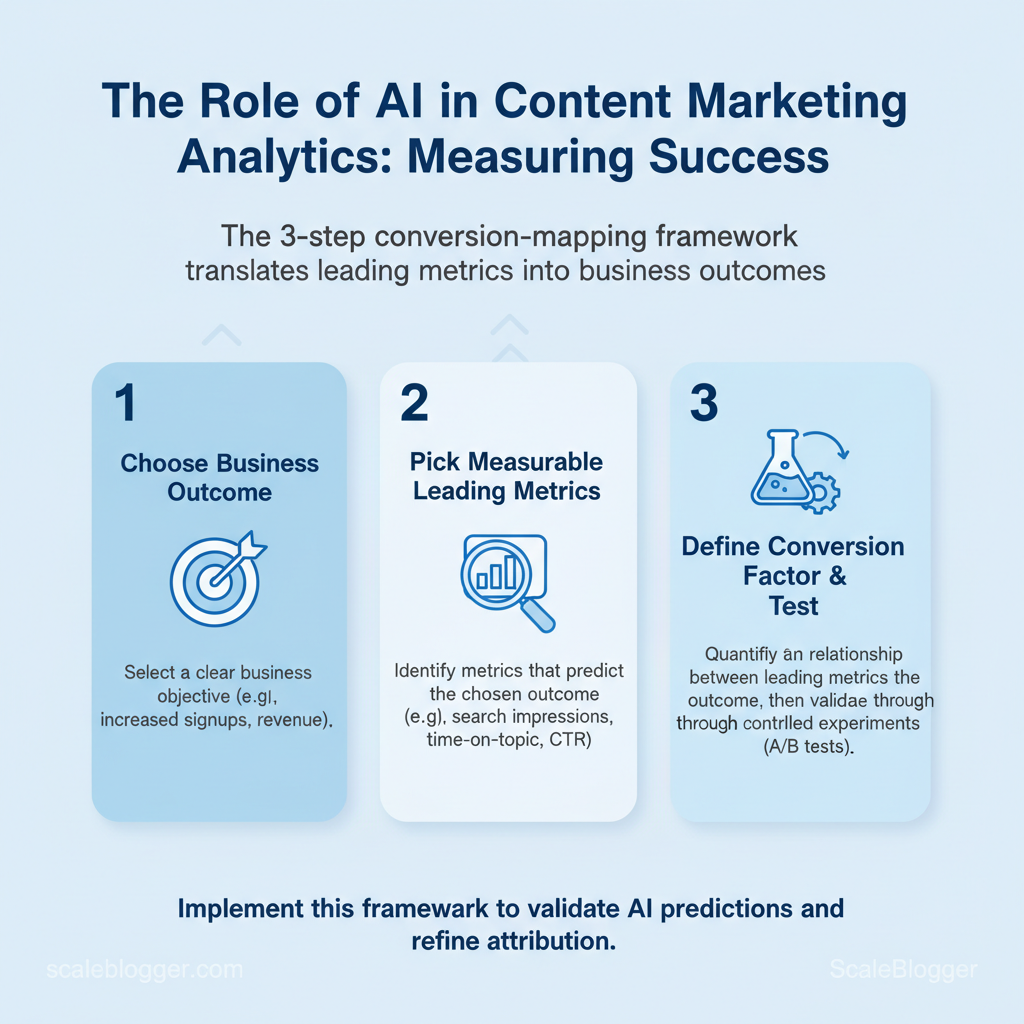
What ‘Success’ Means — Metrics vs. Outcomes
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
Setting Up an AI-Ready Analytics Stack
An AI-ready analytics stack starts with reliable inputs and a layered architecture that separates ingestion, storage, modeling, and consumption. Begin by identifying the content signals that matter most — traffic, engagement, search intent, and conversion touchpoints — then ensure those signals are clean, linked by consistent identifiers, and accessible to AI models for feature engineering. This approach reduces lead time for experiments and makes automated content decisions repeatable.
Data Collection & Cleanliness — Sources and Best Practices
Collect the smallest set of high-quality fields first, then expand. Prioritize data that directly affects content decisions: page-level performance, query intent, content metadata, and user journeys. Common quality issues include missing `page_id` keys, misaligned timestamps across systems, and duplicated social metrics due to API pagination. Resolve these by enforcing canonical IDs at ingestion, normalizing timestamps to `UTC`, and building deduplication steps into ETL.
- Critical sources to pull: CMS exports, web analytics, CRM lead data, social platform APIs, and Search Console query reports.
- Fixes that pay off quickly: canonicalize URLs, hash or map legacy IDs, standardize event schemas, and backfill missing publish dates.
- Prioritization strategy: collect page-level metadata and web analytics first, then add Search Console and social data, finishing with CRM linkage for attribution.
| Data Source | Typical Fields | Update Frequency | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMS (page content, metadata) | title, slug, publish_date, author, topic_tags | daily or on publish | anchors all content-level analysis and feature engineering |
| Web analytics (sessions, conversions) | sessions, pageviews, bounce_rate, conversions | near-real-time / hourly | primary behavioral signal for engagement and conversion lift |
| CRM (lead source, lifecycle stage) | lead_id, source_channel, lifecycle_stage, MQL_date | daily | connects content to revenue and pipeline outcomes |
| Social platforms (engagement data) | post_id, likes, shares, comments, reach | hourly to daily | measures distribution effectiveness and topic virality |
| Search Console (queries, impressions) | query, impressions, clicks, avg_position | daily | reveals search intent and keyword opportunity |
Tooling & Architecture — Choosing AI Tools and Dashboards
Choose tools based on scale, integration surface, and budget. For many teams a three-tier approach works: starter (low-cost, fast setup), mid-market (better integrations, automation), and enterprise (SLA, governance).
Use `SQL`-based feature tables and expose them to dashboards. Example ETL snippet to create a canonical page view table: “`sql CREATE TABLE canonical_page_views AS SELECT page_id, DATE_TRUNC(‘day’, event_timestamp) AS dt, SUM(pageviews) AS pageviews FROM raw_web_analytics GROUP BY page_id, dt; “`
Integrate automated pipelines with content workflow tools or services like Scaleblogger.com to accelerate content pipelines and tie analytics back to publishing cadence. When implemented correctly, this stack makes experimentation faster and decisions more defensible. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Designing Actionable Content Metrics with AI
Design metrics so teams can make fast, defensible decisions: define what to measure, who owns it, and what action follows each signal. Metrics that are clear, tied to specific actions, and consistent across formats let AI surface opportunities (for optimization, distribution, or pruning) instead of just producing dashboards. This section lays out practical design principles and ready-to-use AI-enhanced metric templates that map data to decisions.
Metric Design Principles — Clarity, Actionability, and Scalability
Clear, actionable metrics require precise definitions, ownership, thresholds, and consistent measurement across content types. Below is a practical comparison showing what to avoid and what to implement.
| Principle | Poor Design Example | Good Design Example | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clarity | “Engagement” undefined | “Engagement = avg. time on page + scroll depth” | Prevents misinterpretation and ensures consistent reporting |
| Actionability | “Improve traffic” (no trigger) | “Traffic drop >15% for 30d → trigger refresh” | Teams know exactly when to act |
| Consistency | Different formulas per channel | Unified `engagement_score` formula for web, email, social | Enables apples-to-apples comparison |
| Measurability | Reliant on manual tagging | `content_id` + automated UTM parsing ✓ | Automates tracking; reduces errors |
| Scalability | Per-article manual review | Aggregated cohort metrics by topic cluster ✓ | Scales decisions from single posts to topic portfolios |
AI-Enhanced Metrics — Examples and Templates
Start with a metric name, formula, required fields, AI enrichment method, and an explicit action. Use these templates directly in tracking and automation pipelines.
Code template for implementing Topic Traction Score: “`python
compute normalized metrics, then weighted score
score = 0.5norm(sessions) + 0.3norm(backlinks) + 0.2*norm(ctr) “`Practical tips: ensure each metric has a single owner, encode thresholds as automation rules, and use topic clustering so measures scale across hundreds of pages. For teams moving from manual reporting to automation, integrate these metrics with an AI pipeline—`topic attribution`, `intent change detection`, and `path sequence models`—or use services that help you scale your content workflow like Scale your content workflow (https://scalebloggercom). Understanding and operationalizing these principles speeds decision-making and reduces firefighting across content teams.
From Insight to Action — Automating Decisions and Workflows
Automated decisioning turns signals from analytics and AI models into repeatable actions so teams can react faster and at scale. Start by defining the kinds of alerts that matter, who will own the response, and a small set of deterministic first steps that can be executed automatically or semi-automatically. The focus should be on reducing time-to-remediation for high-priority issues while delegating low-risk decisions to automation. This reduces manual firefighting and preserves human attention for strategy and creative work.
Automated Alerts and Playbooks — Triggering Actions from AI Signals
Define alert severity and ownership up front. High-severity alerts (e.g., sudden traffic loss) require on-call ownership and immediate remediation; medium alerts can trigger notifications with recommended tasks; low alerts feed weekly dashboards. For reliable automation, codify trigger logic in `if/then` rules and keep playbooks to three deterministic first actions.
Example `if/then` rule: “`yaml if: traffic_change_pct <= -30% and duration_hours >= 3 then: notify: oncall_seo create_ticket: priority=high “`
| Alert Type | Trigger Logic | Owner | First 3 Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traffic Drop | ≥30% drop vs 7-day avg for 3+ hours | SEO Ops | 1. Run quick crawl; 2. Check server errors; 3. Re-prioritize content fix |
| SEO Ranking Decline | Top-10 keyword moved >5 positions week-over-week | SEO Specialist | 1. Fetch SERP snapshot; 2. Surface competing content; 3. Update meta + CTAs |
| Content Going Viral | >5x baseline pageviews in 24h | Growth / PR | 1. Enable scaling CDN; 2. Push social CTAs; 3. Lock monetization tags |
| Negative Sentiment Spike | Sentiment score down >20% on brand mentions | Community Lead | 1. Pause any risky campaigns; 2. Draft response; 3. Escalate to comms |
| Conversion Rate Drop | CR falls ≥25% vs rolling 14-day average | Growth Marketing | 1. Run funnel health checks; 2. A/B rollback recent changes; 3. Trigger CRO experiment |
Experimentation & Measurement — Running AI-powered Tests
AI can generate hypotheses, content variants, and even draft experiment designs. Use AI to propose 3–5 headline variants or audience segments, then run controlled experiments.
- Primary KPI: conversion rate on page
- Secondary KPIs: bounce rate, time on page
- Sample size: calculate to reach 80% power (commonly tens of thousands of sessions for web CR changes)
- Duration: 2–4 weeks depending on traffic
Interpreting results means looking beyond p-values: check practical uplift, segment performance, and implement winners into the content pipeline. Use automation to roll out winners and feed results back into the model so future hypotheses improve.
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level while preserving strategic oversight.
Learn how to Scale your content workflow with AI-powered playbooks at https://scaleblogger.com
Measuring ROI and Demonstrating Value
Measuring ROI starts by converting activity-level metrics into dollar outcomes and isolating the incremental impact of automation. Use a simple, defensible framework: total costs (tooling, integration, people) versus incremental revenue (new conversions, upsells, retention uplift). Track attribution by experiment, cohort, or channel so AI-driven changes aren’t credited to broader marketing noise. This lets leadership see concrete financial outcomes and gives teams a repeatable method to scale what works.
ROI Calculation Frameworks — From Cost to Incremental Revenue
Begin with a template that captures inputs, assumptions, and outputs so calculations are auditable.
Reporting Templates and Stakeholder Narratives
Monthly and quarterly reports should tell different stories.
- Performance snapshots: traffic, leads, conversion lift
- Operational metrics: content produced, time saved
- Quick wins: experiments launched, immediate learnings
- Financial summary: cumulative incremental revenue, CAC impact
- Cohort analysis: retention and lifetime value shifts
- Roadmap alignment: investments and next-quarter experiments
- Trend chart: conversions and conversion rate over time
- Cohort chart: retention or revenue per cohort
- Channel contribution pie: revenue by acquisition channel
For operationalizing reporting and automation, consider integrating an AI content pipeline like Scaleblogger to standardize measurement and reduce manual reporting overhead. Understanding these principles makes it straightforward to show finance how content investments translate into revenue and to scale automation where it pays off.
📥 Download: AI in Content Marketing Analytics Checklist (PDF)
Ethics, Accuracy, and Continuous Improvement
Ethics and accuracy are operational constraints, not optional extras. Design content pipelines so privacy, fairness, and measurable accuracy are baked into every release — from prompt engineering to publishing — and treated as living systems that require continuous monitoring and targeted retraining. That keeps audience trust intact while letting automation scale reliably.
Bias, Privacy, and Compliance Considerations
Start with privacy-first data practices and explicit consent. Protecting user data and preventing biased outputs are twin governance priorities that need concrete controls.
- Privacy-first collection: Collect only required fields, log consent with timestamps, and use `pseudonymization` where possible.
- Consent management: Store consent versions and link them to training snapshots for auditability.
- Bias sources: Training data imbalance, labeler bias, and prompt framing all create systematic skew.
- Mitigation techniques: Use balanced sampling, adversarial testing, and counterfactual augmentation.
- Governance hooks: Implement approval gates for sensitive topics and demographic-sensitive content.
| Risk Type | Potential Impact | Mitigation | Monitoring Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Privacy violation | Regulatory fines, loss of trust | Minimal collection, consent logs, encryption | Consent coverage %, breach count |
| Model bias (topic/demographic) | Offended audiences, brand damage | Balanced datasets, adversarial tests, reviewers | Output disparity by slice |
| Data quality decay | Accuracy drop, increased edits | Data validation, deduplication, source tagging | Error rate, edit frequency |
| Misattribution of conversions | Wrong investment decisions | Robust UTMs, server-side tracking, attribution models | Attribution mismatch rate |
| Over-personalization | Creepy UX, filter bubbles | Rate-limit personalization, privacy thresholds | Personalization engagement delta |
Continuous Improvement — Monitoring Accuracy and Retraining
Measure model health continuously and make retraining an event triggered by signal thresholds. Focus on precision, recall, and drift detection rather than vanity metrics.
- Key metrics: precision, recall, F1, and data drift measured with population stability index (PSI).
- Retraining triggers: Persistent drop in precision >5%, PSI >0.2, or quarterly schedule for high-velocity domains.
- Human-in-the-loop: Route low-confidence outputs to editors; capture corrections as labeled retraining data.
Expected outcomes include fewer manual edits, clearer audit trails, and measurable lift in content KPIs. Scale your content workflow by automating checks while keeping humans in the loop to catch nuance. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Conclusion
After walking through how AI shifts marketing analytics from guesswork to measurable action, the practical path forward becomes clear: focus on signal over noise, automate repeatable analysis, and tie every metric to business outcomes. Teams that adopt event-level attribution and model-driven content scoring report faster decisions and higher-impact publishing—one midmarket SaaS team reduced content ideation time by half while increasing qualified leads; a retail marketer reclaimed budget by cutting low-performing campaigns identified through automated cohort analysis. Common questions—How quickly will this show ROI?—typically resolve within 8–12 weeks when data pipelines and KPIs are aligned. Concerns about data quality are legitimate; start with a small, well-instrumented test and iterate.
– Prioritize instrumentation: capture the right events before scaling analytics. – Automate routine reports: free analyst time for strategic insights. – Measure impact: map content to revenue or qualified actions, not just traffic.
Next steps: run a focused 8–12 week pilot that instruments 3–5 high-priority journeys, set clear success metrics, and build one automated dashboard that answers a single business question. To streamline this process, platforms like Explore Scaleblogger’s AI content analytics can accelerate setup and surface the most actionable signals from your content program.

