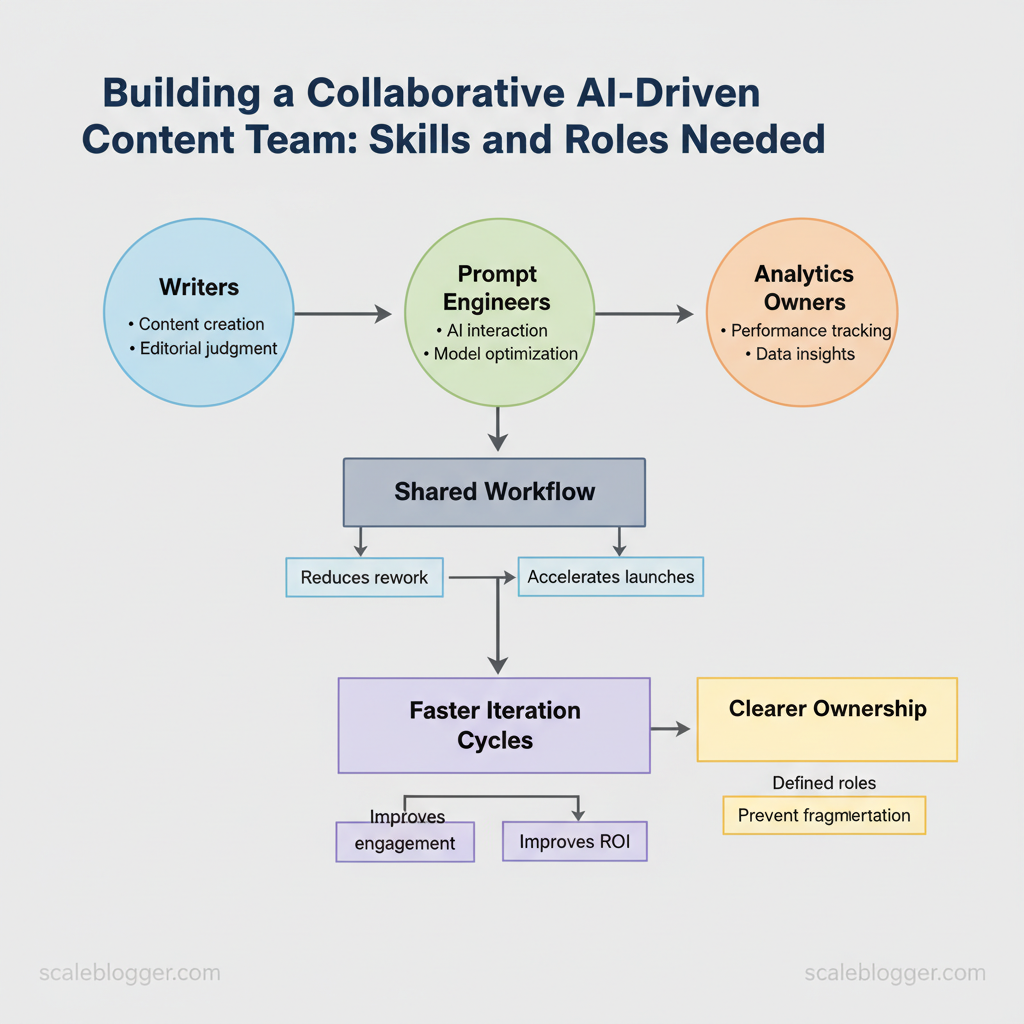
Industry teams shifting to AI-driven content report faster iteration cycles and clearer ownership, which directly improves engagement and ROI. Building that team requires hiring for distinct competencies—prompt craftsmanship, data literacy, editorial judgment, and cross-functional coordination—rather than doubling down on generalists.
Marketing leaders adopting this model see clearer content velocity, fewer bottlenecks, and more predictable results. One SaaS marketing team reorganized around AI-assisted roles and shortened their time-to-publish by half while maintaining quality control.
- What core roles compose a collaborative AI-driven content team
- How to map skills for AI marketing to existing org structures
- Practical role descriptions for writers, prompt engineers, and ops leads
- How to measure handoffs and protect editorial standards during automation
- Ways to pilot team changes with minimal disruption
The next section outlines the exact roles, competencies, and sequencing needed to staff and scale a high-performing AI content team.
Section 1: Foundation — Why a Collaborative AI-Driven Content Team Matters
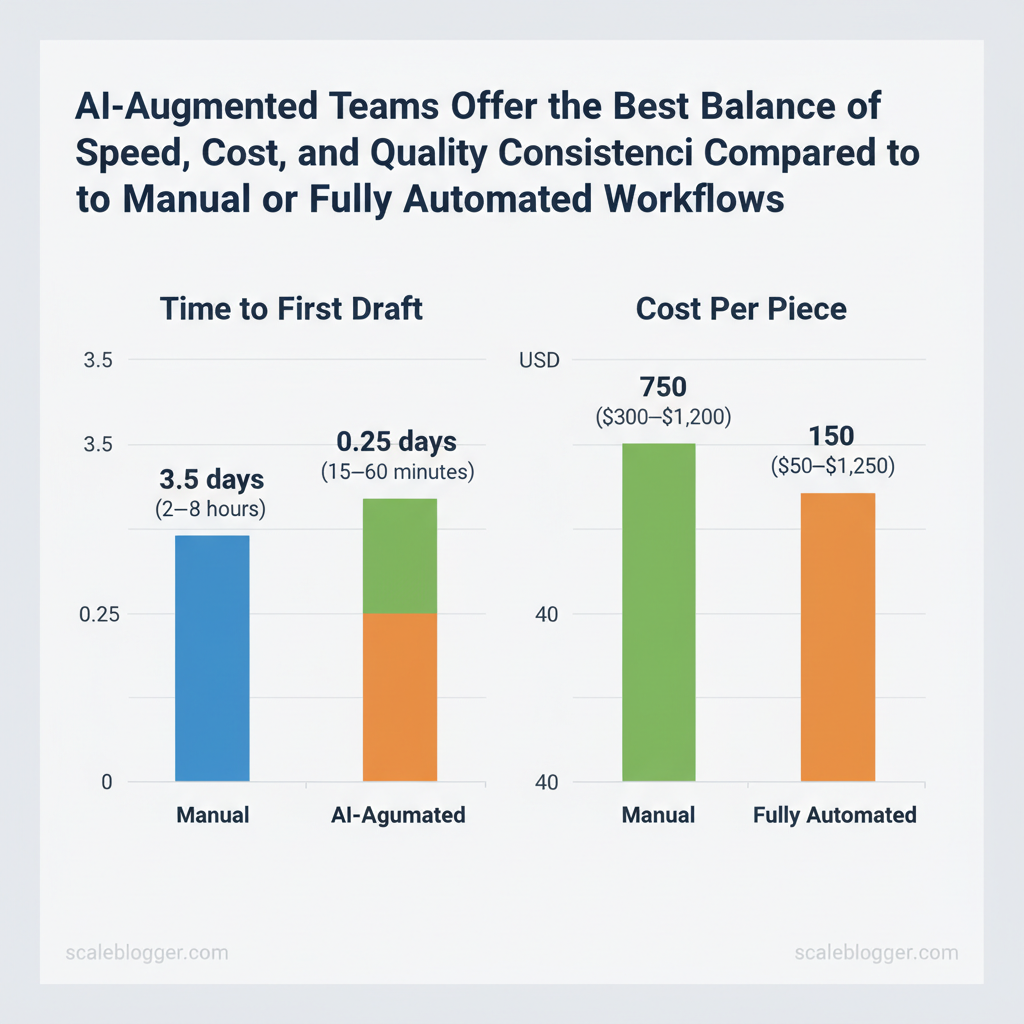
A collaborative AI-driven content team shortens the gap between strategy and execution by combining human judgement with machine speed. AI accelerates ideation and first-draft generation, enforces consistent brand voice across dozens or hundreds of pieces, and enables data-driven personalization that would be impossible at scale with humans alone. What that delivers in practice is faster experimentation cycles, predictable output quality when governed correctly, and measurable lift from content tailored to segment-level intent.
Prerequisites
- Organizational alignment: defined brand voice, editorial standards, and KPIs.
- Data access: analytics, keyword signals, and existing content inventory.
- Tool stack: editorial CMS, version control for content assets, and accessible AI models or APIs.
Why it matters (strategic benefits)
- Speed: AI accelerates ideation, outlines, and first drafts — reducing time-to-first-draft from days to hours.
- Scale: Systems reproduce brand voice across high-volume output without linear headcount increases.
- Consistency: `Templates` and model conditioning enforce style and structural standards.
Risks, ethics, and governance
- Hallucinations: models can invent facts — require fact-checking steps.
- Bias and representation: models reflect training data; enforce inclusive checks.
- Attribution and IP: clarify data sources and ownership in contracts.
| Capability | Manual Team | AI-Augmented Team | Fully Automated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to first draft | 2–5 days (writer dependent) | 2–8 hours (AI-assisted) | 15–60 minutes (templated) |
| Quality consistency | Variable (editor-dependent) | High with style prompts + review | Moderate; requires tuning |
| Personalization at scale | ✗ (costly) | ✓ (segment templates + data) | ✓ (dynamic content injection) |
| Iteration speed | Slow (weekly cycles) | Fast (daily/weekly) | Very fast (continuous) |
| Cost per piece | $300–$1,200 (agency/writer) | $50–$250 (human + compute) | $5–$75 (compute + minimal ops) |
Section 2: Roles and Responsibilities — Defining the AI-Driven Content Team
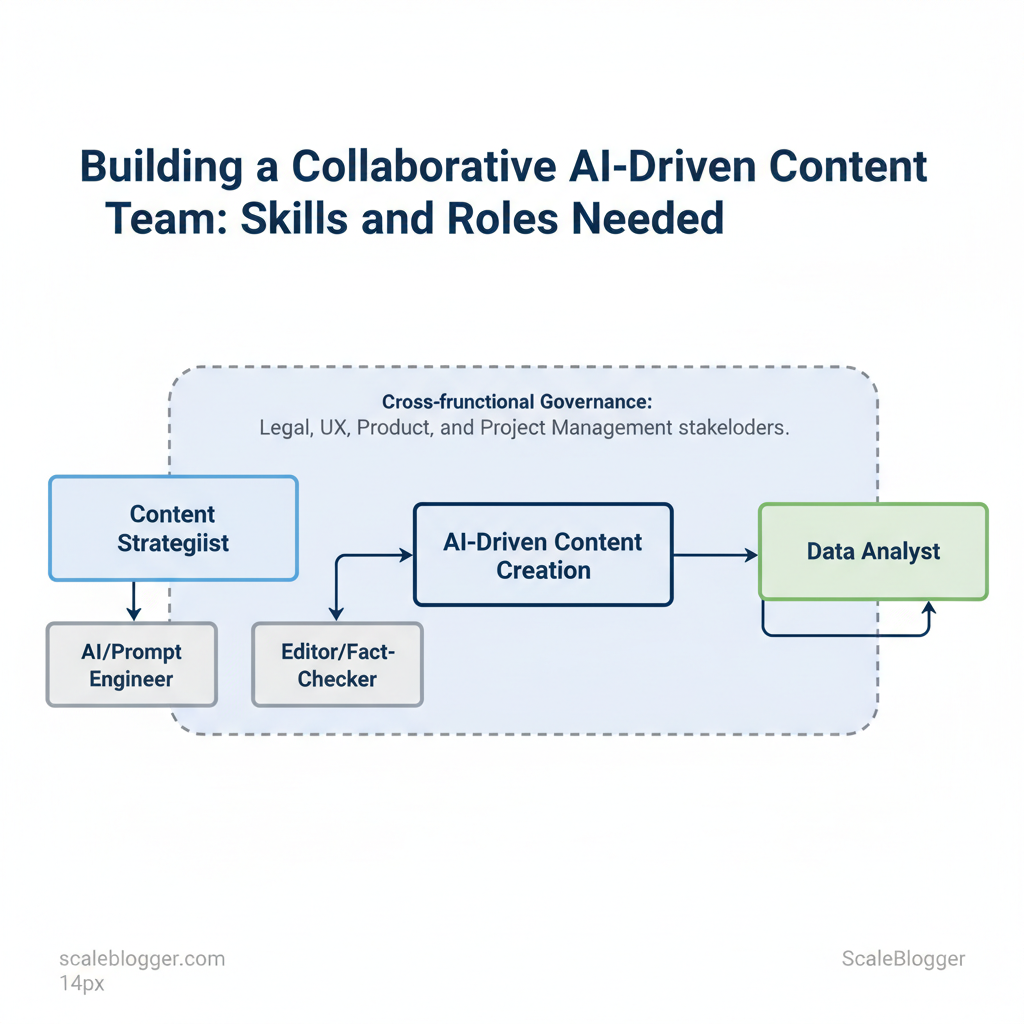
An AI-driven content team needs clear role boundaries so generative models amplify human expertise instead of creating chaos. Start by placing four core roles—content strategist, AI/prompt engineer, editor/fact-checker, and data analyst—as the operational nucleus, then fold in legal, UX, product, and project management stakeholders for cross-functional governance. This organizational clarity prevents duplicated effort, speeds iteration, and keeps content aligned with business goals.
Why each role matters and how they work together
- Content Strategist aligns outputs to business goals, oversees topical authority, and sets editorial calendars; without a strategist, AI produces high volume but poor alignment.
- AI/Prompt Engineer crafts prompts, manages model settings, and curates system-level templates; treat this role as the bridge between product-level constraints and creative prompts.
- Editor/Fact-Checker enforces brand voice, accuracy, and compliance; editors convert model drafts into publishable assets.
- Data Analyst measures performance, builds dashboards, and trains / fine-tunes models using feedback loops to reduce drift.
How to create a practical RACI for AI content projects
| Role | Primary Responsibilities | Essential Skills | Key KPIs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content Strategist | Set editorial strategy, topic clusters, revenue alignment | Market research, content modeling, SEO strategy | Organic traffic, conversion rate, topical authority |
| AI/Prompt Engineer | Build prompts, manage model configs, create templates | Prompt design, API usage, LLM safety practices | Time-to-first-draft, prompt reuse rate, error rate |
| Editor / Fact-Checker | Review accuracy, enforce voice, legal compliance | Editing, fact-checking, domain expertise | Edit time per article, publish-quality score, corrections rate |
| Content Designer / SEO Specialist | Structure content, on-page SEO, UX copy | Information architecture, keyword strategy, HTML basics | SERP rank, CTR, dwell time |
| Data Analyst | Track performance, A/B tests, model retraining input | SQL, analytics, ML basics | ROI per piece, model lift, retention of topic clusters |
Section 3: Skills Matrix — What to Hire and Train For
Start by mapping the skills your team needs into two streams: technical AI capabilities that make automation reliable, and creative-collaborative capabilities that keep content on-brand and strategic. Hire for repeatable technical tasks at junior and mid levels; reserve senior hires for model governance, evaluation, and strategy. Train broadly on tool fluency and editorial judgment so creators and engineers speak the same language.
Technical roles focus on prompt engineering, model evaluation, and platform fluency. Creative roles emphasize narrative craft, ruthless editing, and cross-functional communication. Practical hiring balances: junior hires execute prompts and tagging, mids refine workflows and run A/B evaluations, seniors set standards, own metrics, and mentor. Examples of concrete work assignments: 1) junior: produce 30 SEO-first drafts using `system` prompts; 2) mid: run evaluation cohorts and label 1,000 outputs; 3) senior: design the model-evaluation rubric and integrate content scoring into analytics.
Practical exercises to build these skills:
- Prompt lab rotations: weekly 90-minute pair sessions to rewrite prompts for three content types.
- Evaluation sprints: label 500 samples for accuracy, factuality, and tone; calculate inter-rater agreement.
- Story workshops: cross-discipline editors and SEOs rewrite AI drafts to match brand voice.
Practical tips embedded in hiring decisions:
- Prioritize candidates who can explain a prompt decision in plain terms.
- Look for editors comfortable with version control and `content scoring` metrics.
- Hire at least one senior with experience running model evaluations and A/B experiments.
| Skill | Junior Proficiency | Mid Proficiency | Senior Proficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prompt Engineering | Basic prompt patterns, templates | Iterative prompt tuning, instruction chaining | Design prompt frameworks, prompt versioning |
| Content Strategy | Follow briefs, produce briefs | Develop topic clusters, gap analysis | Set editorial strategy, KPI alignment |
| SEO & Content Optimization | On-page SEO basics, keywords | Structured data, intent mapping | Technical SEO strategy, SERP feature targeting |
| Data Analysis & Metrics | Basic dashboards, GA4 reading | A/B tests, cohort analysis | Model evaluation metrics, ROI modeling |
| Editorial Judgment | Copy editing, tone matching | Style guides, content scoring | Brand voice governance, legal/factual oversight |
When hiring and training against this matrix, align job descriptions, interview tasks, and first-90-day learning plans so everyone knows which outcomes matter. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Section 4: Workflows and Processes — Designing AI-Ready Content Operations
Design the workflow so content flows through automated checkpoints where humans add judgment, not repetitive work. Start with clear ownership, measurable SLAs, and modular automation that plugs into the CMS and analytics stack. This reduces handoffs, speeds publishing, and preserves quality control.
Prerequisites
- Team roles defined: content owner, editor, SEO lead, analytics owner.
- Tooling baseline: CMS with API, versioned content repo, task manager (Asana/Jira), AI content engine.
- Governance rules: allowed automation scope, fact-checking policy, and safety prompts.
Tooling and automation: selection criteria
- Capability over hype: prefer tools with controllable prompts and provenance tracking.
- Integration-friendly: robust API, webhook support, and native CMS connectors.
- Observability: logging, version history, and content scoring metrics.
- Cost predictability: transparent pricing and usage limits.
- Webhook-first: AI engine posts draft to a review queue via webhook.
- Two-way sync: CMS stores `ai_version` and editor changes sync back to model for retraining.
- Event-driven publishing: `publish_ready` events trigger automated distribution and analytics tagging.
- Auto-generate structured metadata and suggested internal links.
- Auto-schedule A/B headline tests and push variants to social channels.
- Auto-tag by intent and push to segmentation for personalized distribution.
- Draft generation: 2 hours from brief → draft; target 95% success.
- Human edit turnaround: 24–48 hours; measured by reviewer queue time.
- SEO sign-off: 24 hours; acceptance when organic checklist passed.
- Time-to-publish: 3–5 business days end-to-end; track median and 95th percentile.
| Stage | Owner | Typical Time | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brief & Keyword Research | Content Strategist | 4–8 hours | Brief with intent, keywords, target URL |
| AI Draft Generation | AI Operator | 0.5–2 hours | Draft with sources, `citation_list` |
| Human Edit & Fact-Check | Editor | 24–48 hours | Factual accuracy, tone, `verified:true` |
| SEO Optimization | SEO Specialist | 12–24 hours | Metadata, headings, schema applied |
| Publication & Distribution | Publisher | 0.5–2 hours | Live URL, analytics tags, social queue |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When automation handles repetitive steps, creators can focus on insight and strategy.
Section 5: Measurement and Iteration — KPIs and Feedback Loops
Measure to decide, not to collect. Focus on production, performance, and model-level KPIs that directly change behavior: reduce friction in the content pipeline, shift investment to high-return topics, and reduce model drift/hallucinations. Below are the essential metrics to instrument, why they matter, and how to operationalize continuous improvement loops from user signals back into model and editorial updates.
Tools and materials Analytics:* GA4, Search Console for organic signals. Content ops:* CMS reports and editorial calendar. Model telemetry:* inference logs, prompt/version tags. Optional:* AI content automation from Scaleblogger.com to link content scoring to pipeline automation.
| KPI | How to Measure | Owner | Target Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to First Draft | Median hours from brief creation to draft in CMS | Content Ops | 8–48 hours |
| Pieces Published / Month | Count of published URLs per month | Content Lead | 8–30 pieces |
| Organic Traffic per Piece | `Total Sessions / Pieces Published` (30–90 day window) via GA4 | SEO Owner | 500–5,000 sessions |
| Conversion Rate by Content | `Goal Completions / Sessions` per content type | Growth/Product | 0.5%–5% |
| Model Error / Hallucination Rate | % of sampled outputs failing human review (weekly sampling) | ML Engineer | <2% weekly sample |
Feedback loops and continuous improvement (practical steps)
Expected outcomes
- Faster iteration: fewer manual reviews per draft.
- Higher impact: disproportionate traffic gains from top 20% of topics.
- Safer models: reduced hallucinations and editorial overhead.
📥 Download: Collaborative AI-Driven Content Team Checklist (PDF)
Section 6: Roadmap — Hiring, Upskilling, and Scaling the Team
Start by treating the first 12 months as an experiment-driven operating budget: prove impact with a small cross-functional team, stabilize processes and tooling, then scale hiring and automation where ROI is clear. The approach below gives a phase-based timeline, concrete hiring and interview artifacts, and a 90-day L&D sprint to turn hires into productive contributors.
Hiring and training playbook
Practical tip: integrate an automation partner like Scaleblogger.com to accelerate pipeline setup and free writers to focus on creative tasks. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Conclusion
Balancing roles, skills and automation turns AI projects from brittle experiments into reliable publishing engines. Teams that restructured around clear content roles and lightweight automation saw fewer missed deadlines and higher output quality; one mid-market SaaS that ran a two-month pilot halved review cycles by delegating routine SEO edits to an automated workflow while keeping writers focused on narrative. Expect upfront effort to map competencies, redesign handoffs, and build small repeatable automations — these are the steps that reduce fragmentation and stop work from collapsing into busywork. If you’re asking whether to hire more people or refine processes first, prioritize role clarity and a pilot automation that proves the handoff; if you wonder how to measure success, track cycle time, publish frequency, and engagement lift.
– Clarify roles before automating — avoids duplicated effort and stalled approvals. – Start with a focused pilot — validate ROI on one content flow in 6–8 weeks. – Measure cycle time and engagement — use those metrics to scale automation.
To streamline this transition, consider platforms and partners that specialize in content workflows. For teams looking to automate publishing and governance, Discover AI content workflows and automation at Scaleblogger is a practical next step to evaluate demo options and pilot programs.

