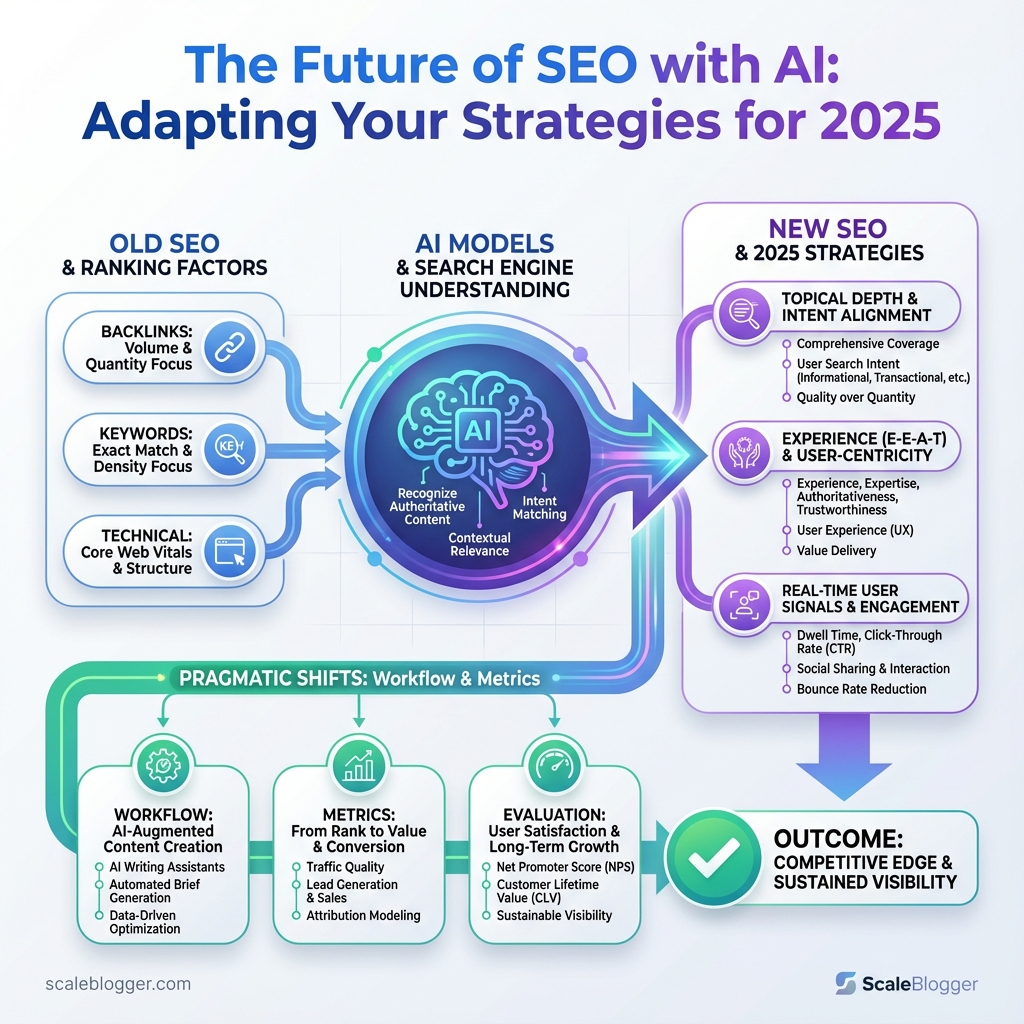
Search rankings stopped feeling like a puzzle and started behaving like a living system last year — pages that once climbed on backlinks now plateau without fresh signals. The shift came because AI SEO strategies began to change what search engines reward, blending topical depth, intent alignment, and real-time user signals into a single ranking pressure. That same pressure is forcing teams to rework their editorial calendars and measurement frameworks.
Content quality still matters, but the rules for proving quality have moved. Signals once inferred from links and keywords are now validated through engagement patterns, entity coherence, and content ecosystems that AI models recognize as authoritative. That makes lightweight optimization tactics obsolete and raises the value of tightly structured topical authority.
If your roadmap treats AI like a bolt-on tool rather than a redesign constraint, expect wasted budget and missed opportunity. Pragmatic shifts to workflow, editorial briefs, and performance metrics will decide who benefits from the future of SEO and who chases diminishing returns from yesterday’s tactics.
Why AI Will Reshape SEO in 2025
AI is changing what search engines value, and that will alter SEO priorities more in 2025 than any single algorithm update in the past decade. Rather than treating keywords as discrete targets, search engines are now grouping user needs into intent clusters, ranking content by semantic relevance, behavioral signals, and multi-modal relevance. That shift means tactics that worked in a keyword-first world—keyword stuffing, superficial topic coverage, templated low-value posts—will steadily lose impact.
Intent modeling: Search engines will prioritize documents that map clearly to user intents (informational, transactional, navigational, exploratory), not just keyword matches.
Semantic and entity-based ranking: Models trained to understand entities, relationships, and context (think beyond BERT to newer multimodal transformers) will reward content that connects concepts coherently.
Behavioral signals: Click-through rates, dwell time, and repeat visits become stronger proxies for usefulness. Personalization driven by AI will amplify these signals at scale.
Multi-modal search growth: Images, audio, and video will influence rankings more. Content that mixes high-quality visuals and transcripts will perform better in blended SERPs.
What to expect practically:
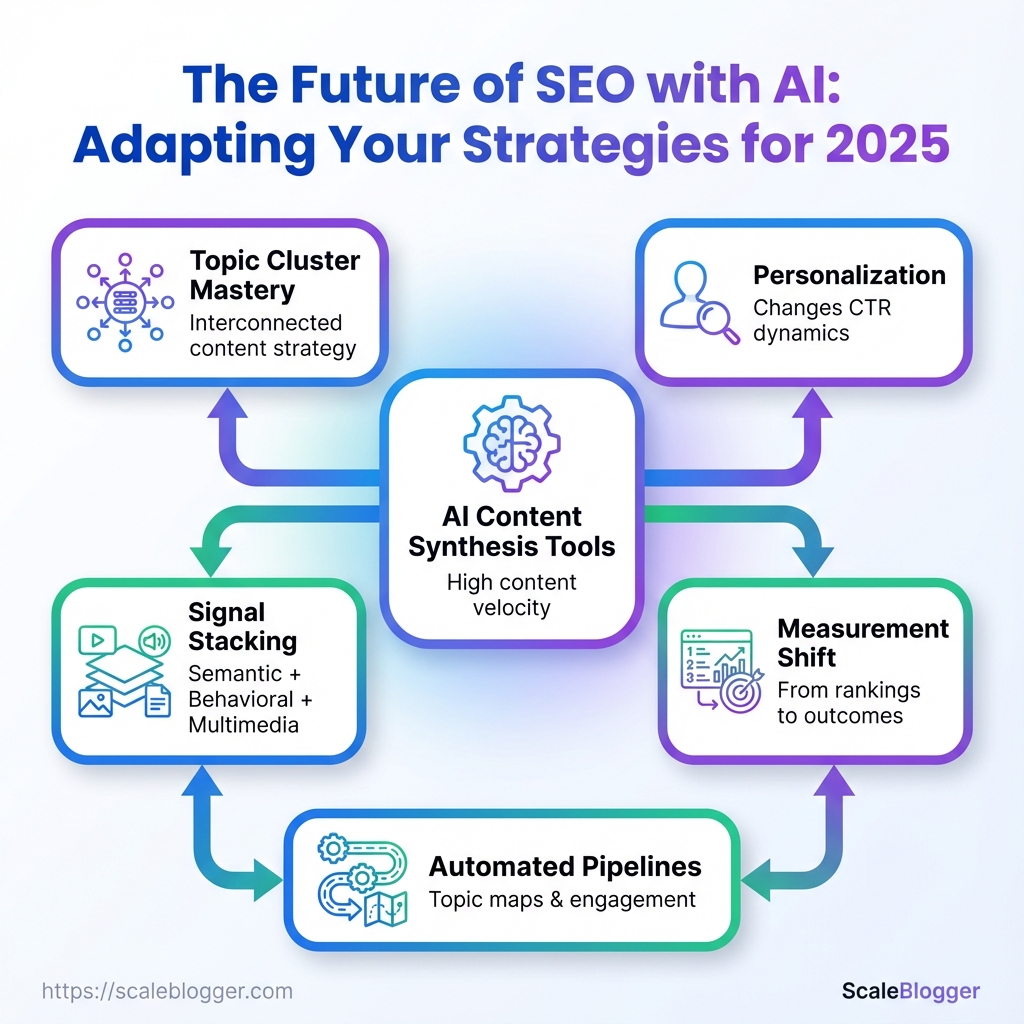
- Higher content velocity, higher stakes. AI content synthesis tools let teams produce far more pages. That increases coverage but raises quality and reputation risk.
- Topic cluster mastery wins. Instead of isolated pages, publish connected clusters that answer related intents across formats.
- Personalization changes CTR dynamics. One user’s ideal answer differs from another’s; snippets will become more personalized, so optimizing for a single universal SERP result is less reliable.
- Signal stacking matters. Semantic relevance + behavioral evidence + multimedia presence will beat thin but keyword-optimized pages.
- Measurement shifts from rankings to outcomes. Track conversions, returning visitors, and topical authority, not just positions.
that illustrate the change: a product page augmented with how-to video, structured entity markup, and an on-page mini FAQ will rank better than a longer keyword-stuffed description; a cluster of interlinked guides covering all user intents for a topic will capture featured snippets and voice-search results more often than standalone posts.
For teams reworking strategy, automated pipelines that produce topic clusters, test variations, and surface behavioral feedback become invaluable. Tools that help build topic maps and measure engagement—like the AI content automation and content scoring frameworks available at Scaleblogger.com—fit naturally into that workflow.
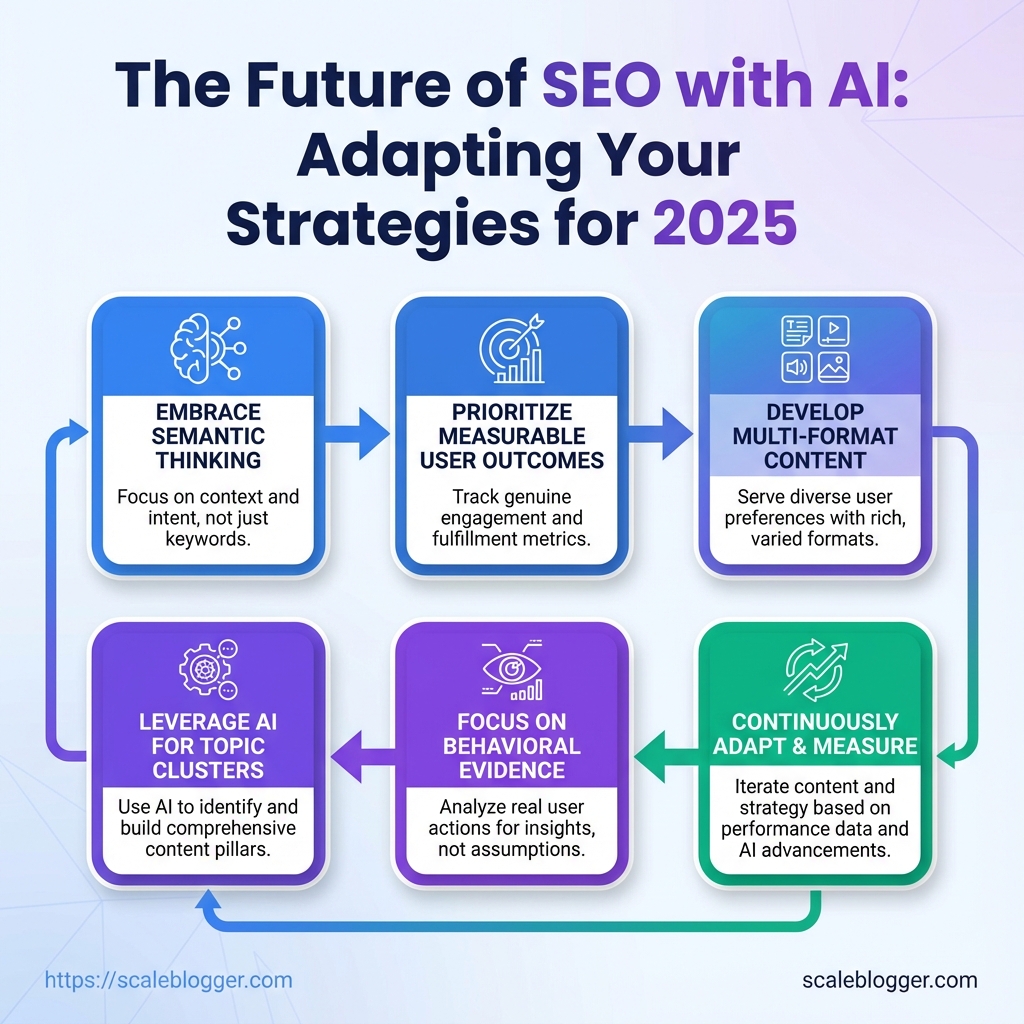
Expect SEO in 2025 to reward semantic thinking, measurable user outcomes, and multi-format content. Embracing those changes now keeps content competitive as search itself becomes more human-aware and context-driven.
Prerequisites — What You’ll Need
Get the basics in place before you start an AI-driven SEO audit: allocate about 6–10 hours for data collection and setup if this is a first pass, and expect an Intermediate difficulty level—comfort with SEO metrics and basic LLM usage will make the work smooth. At minimum, assemble the right mix of tools, account permissions, and people so the audit doesn’t stall halfway through.
Tools and access checklist (quick view):
- Time estimate: 6–10 hours to audit and prepare.
- Difficulty level: Intermediate — requires SEO familiarity and basic AI tooling.
- Roles needed: SEO analyst, content owner, site admin (CMS), developer for tracking fixes, and optionally a data analyst for deeper GA4 work.
- Permission notes: site admin access to CMS, read/write to analytics and Search Console, API keys for LLMs if automating prompts.
- Request these permissions in order:
- Site admin or editor access in your CMS so content changes can be staged.
editormanageaccess for Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and Google Search Console for property-level data.- API credentials for any LLM or automation platform you’ll use (OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.).
- Read access to backlink and crawl tools (Ahrefs, SEMrush) or export reports from whoever owns them.
Essential skills and quick definitions
SEO analysis: Ability to interpret organic traffic trends, CTR, and keyword intent.
CMS familiarity: Comfortable creating/updating posts, meta tags, and redirects.
GA4 basics: Can navigate reports and export event data.
LLM prompt basics: Knows how to craft prompts and assess model output quality.
Tools, access, and skills checklist
| Category | Recommended Tool(s) (Free) | Recommended Tool(s) (Paid) | Minimum Permissions/Skill |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analytics | GA4 (free) |
Adobe Analytics ($$$) | Read/manage GA4, interpret sessions & events |
| Search Console / SERP Tracking | Google Search Console (free) | Ahrefs ($99+/mo) | Property verification, SERP analysis skills |
| Content Creation / CMS | WordPress (free), Ghost (free tier) | Contentful ($$$), HubSpot CMS | Editor or admin access; content editing skills |
| AI / LLM Access | OpenAI free tier (ChatGPT/API), Anthropic free trials | OpenAI paid API ($0.002+/k tokens), Anthropic Claude (paid) | API keys, prompt engineering basics |
| Keyword & Intent Research | Google Keyword Planner (free) | SEMrush ($119+/mo), Ahrefs Keyword Explorer | Keyword research skills, intent mapping |
Key insight: This set-up balances free access with professional paid tools so teams can start audits quickly and scale. Permissions are the usual bottleneck — secure CMS and GA4 rights first, then add API access for automation.
If automation and scaling are goals, consider connecting this stack to an orchestration layer like AI-powered content automation to speed repetitive tasks and standardize outputs. Getting the right access and a single source of truth for metrics saves more time than chasing partial reports later.
Step-by-Step: Audit Your Current SEO Through an AI Lens
Start by treating the audit like a hypothesis-driven experiment: identify measurable problems, run focused checks, and use AI to scale interpretation. The first two steps below get you a clean baseline and quick content-intent triage using both traditional SEO tools and generative models. Each step includes exact prompts, expected outputs, and clear success criteria so the work produces decisions, not just data.
- Step 1: Crawl the site and create a baseline indexation & technical report
- Step 2: Audit content for search intent and semantic coverage using AI
Run a full-site crawl to capture status codes, canonical tags, indexation issues, page depth, and meta anomalies. Tools: Screaming Frog (bulk export), Sitebulb, or curl/wget for spot checks. Export CSVs for URLs, status, title, meta description, H1, word count, and canonical. Use Google Search Console to pull impressions and CTR for the same URL list.
Copy-ready prompt for AI-assisted analysis: Analyze this CSV: group pages by indexability issues, flag pages with missing or duplicate titles, and prioritize pages with >1000 impressions but CTR <1%
Expected output: prioritized list of technical fixes and pages that lose search visibility due to indexing or metadata problems.
Success criteria: sitemap coverage matches crawl within 5%, zero critical index-blocking errors, and a prioritized backlog of 20–50 URLs with clear actions (fix canonical, add meta, remove noindex).
Sample high-value pages (top 200 by traffic + 100 pages with impressions but low clicks). For each page, extract H1, H2s, first 300 words, meta, and target keyword (if known). Use an LLM to classify intent and detect content gaps. Prompt example: Classify intent (informational/commercial/transactional) for each page, list 5 semantically-related subtopics missing, and suggest a 150-word intro rewrite optimized for that intent.
Tools: export to CSV and run batch prompts via the OpenAI API or a platform that supports prompt batching. Optionally use Scaleblogger.com for automating content scoring and topic-cluster suggestions.
Expected output: intent labels, missing topic bullets, suggested rewrites, and a content-priority score.
Success criteria: every priority page has an intent match or clear migration plan, a 20–30% uplift target in CTR/engagement for rewrites, and a 90-day content roadmap for fixes and new cluster pages.
These two steps quickly turn crawl noise into a tactical backlog and an AI-driven content plan that focuses effort where it moves metrics. When the baseline and intent labels are done, the rest of the audit becomes execution: fix the tech, rewrite high-impact pages, and measure.
Step-by-Step: Build AI-First Content Workflows
An AI-first content workflow treats models as skilled collaborators, not magic boxes. Start by defining a repeatable pipeline that moves a brief into a publishable piece through a mix of automated generation, human judgment, and SEO tuning. This keeps velocity high while protecting accuracy and brand voice.
- Briefing: create a
content briefwith target intent, keywords, audience, and 3 sample headlines. - Draft Generation: run an AI draft using a controlled prompt, temperature, and constraints; produce outline + 1,200–1,800 words.
- Human Editing: fact-check, tighten voice, add proprietary examples, and correct hallucinations.
- SEO Optimization: refine metadata, internal links, LSI keywords, and on-page structure; run SERP intent checks.
- Publish & Monitor: schedule, publish, and set performance triggers for updates (CTR, time-on-page).
Owner: SEO analyst / content strategist
Estimated time: 30–60 mins
Owner: Prompt engineer / writer
Estimated time: 15–60 mins
Prompt example: Write a data-driven, conversational 1,500-word article for [audience]. Include 5 headings, a short intro, conclusion, and two original examples. Reference common industry tools without inventing stats.
Sampling guidance: use temperature: 0.2–0.5 for factual drafts; raise to 0.7 for creative briefs.
Owner: Editor / subject-matter expert
Estimated time: 30–90 mins
Owner: SEO analyst
Estimated time: 30–60 mins
Owner: Publishing ops / analytics
Estimated time: 15–30 mins initially; monitoring ongoing
QA checklist before publish: Citations: every factual claim has a verifiable source or is labeled as an opinion. Factual accuracy: dates, names, and figures verified by editor. Originality: run through plagiarism checker and confirm unique angles. Voice match: final read aligns with brand guidelines. * Links: internal and external links are relevant and live.
A sample timeline for producing a single AI-assisted long-form article from brief to publish, including owner and time estimates
| Phase | Action | Owner | Estimated Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Briefing | Create brief, target keywords, headlines | SEO analyst | 30–60 mins |
| Draft Generation | Generate outline + AI draft, temperature set 0.3 | Prompt engineer / writer | 15–60 mins |
| Human Editing | Fact-check, add examples, fix voice | Editor / SME | 30–90 mins |
| SEO Optimization | Metadata, links, schema, keyword tuning | SEO analyst | 30–60 mins |
| Publish & Monitor | Schedule publish, set analytics alerts | Publishing ops | 15–30 mins |
Key insight: This cadence compresses a multi-day process into a single-day sprint for small teams while keeping quality controls intact. Owners are clear, times are realistic, and the split between AI output and human oversight prevents common content failures.
For teams wanting to scale, consider automating parts of the brief-to-draft handoff or integrating a tool like Scaleblogger.com to manage publishing and benchmarking. The practical payoff: faster cycles, consistent SEO coverage, and fewer surprises when content goes live.
Step-by-Step: Technical SEO & Signals for an AI-Driven SERP
Start by treating signals as telemetry: instrument what matters, validate structured output, and limit mass indexing from AI drafts. That combination prevents noisy signals, helps search systems trust pages, and makes pages more likely to be used as answers in AI-driven results.
Access to site telemetry: Server logs, Google Search Console, and a frontend analytics tool that can record custom events.
CMS or deployment control: Ability to add structured data, meta tags, and robots directives.
Tooling for validation: Access to Google Rich Results Test and a schema linter.
Tools & materials
Google Rich Results Test: Validate schema markup quickly. Analytics stack (GA4 / Snowplow / PostHog): Capture custom events. Indexing controls: robots.txt, noindex meta, and sitemaps.
- Audit and validate structured data with the Google Rich Results Test.
- Instrument specific telemetry events that matter for answer quality.
Validate every schema variant you add (Article, FAQ, HowTo, Product). * Action: Run the Rich Results Test, fix missing @type fields, ensure datePublished and author are present where required.
- Scroll depth: Record percent scrolled to capture content consumption.
- Time on meaningful content: Start timer when primary content is visible, stop on navigation away.
- Answer click: Capture clicks on in-page answers, copy-to-clipboard, or structured answer interactions.
- Interaction with media: Video play, audio play, and image expand events.
- Implement safe content-generation limits and index controls.
- Action: Tag AI-drafted pages with a
noindexuntil they pass a human QA checklist. - Action: Rate-limit automated publishing to avoid mass low-quality pages that dilute signals.
- Use progressive indexing strategies.
- Action: Publish to a staging sitemap, measure engagement, then move high-engagement URLs to the primary sitemap.
- Action: Use
lastmodupdates and priority scoring to guide crawler attention.
- Improve multi-modal accessibility with descriptive alt text examples.
- Monitor signal drift and prune stale content.
Alt example 1: Aerial view of Manhattan skyline at sunset, tall glass towers reflecting orange light Alt example 2: Diagram: three-step AI content pipeline showing input, model, and publish stages Write alt text that conveys content utility, not keyword stuffing.
- Action: Quarterly check for pages with falling “time on meaningful content” and consider consolidation or canonicalization.
- Measure downstream impact and iterate.
- Action: Correlate telemetry with ranking or SERP feature appearance and prioritize fixes for pages that show strong engagement but poor visibility.
Instrumenting the right signals and being conservative with AI drafts reduces noise and increases trust from AI-driven SERPs. Over time, this approach turns raw telemetry into a prioritized roadmap for content that actually gets used in answers.
Measuring Success: Metrics & Reporting for AI-Enhanced SEO
Measuring AI-driven SEO means tracking a mix of traditional SEO signals plus behavior metrics that reveal whether AI-generated content truly earns attention. Focus on metrics that show utility (longer engaged sessions, multi-modal interactions) and search visibility (organic sessions, SERP features). Pair those with experiment tracking so it’s clear which content variants — AI-first, human-first, or hybrid — move the needle.
- Define the reporting workflow and owners.
- Instrument data sources (GA4, Search Console, internal telemetry).
- Run A/B or multi-variant experiments for content types, with clear naming conventions.
- Collect weekly and 30-day aggregates; trigger alerts when thresholds hit.
- Review outcomes, iterate content model, and feed learnings into the content pipeline.
Primary KPIs
Organic Sessions: Total visits from search. Long-Click Rate: Percentage of clicks that remain on site rather than returning to SERP quickly. SERP Feature Impressions: How often pages appear in featured snippets, knowledge panels, or image packs. Time on Page (meaningful): Median engaged time that correlates with content consumption. Multi-modal Asset Engagement: Interactions with video, audio, or downloadable assets on page.
Provide a KPI reference table mapping metric, why it matters for AI SEO, recommended measurement tool, and alert threshold
| KPI | Why it matters | Measurement tool | Suggested alert threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Sessions | Visibility and topical relevance | GA4 / Search Console | 15% drop over 30 days |
| Long-Click Rate | Signals satisfying search intent (long-click rate) |
Internal telemetry + GA4 | 20% drop over 14 days |
| SERP Feature Impressions | Gains from structured content and schema | Search Console | 10% drop over 30 days |
| Time on Page (meaningful) | Indicates content depth and engagement | GA4 engaged time | 25% drop over 30 days |
| Multi-modal Asset Engagement | Shows value of audio/video/interactive assets | Internal telemetry | 30% drop over 30 days |
Key insight: Tracking both search-sourced and engagement-centered KPIs reveals whether AI content is being found and whether it satisfies users. Use GA4 and Search Console for visibility metrics and internal telemetry for fine-grained engagement signals.
Practical notes: Use consistent naming: Tag AI-generated variants with ai_v1, ai_v2 and human variants with human_v1. Automate alerts: Wire alert rules into Slack or email when thresholds hit. * Experiment tagging: Record hypothesis, variant, and expected lift in each experiment record.
Pairing these measurements with automation reduces guesswork and keeps the content pipeline moving. For teams that want to scale reporting and automate iteration, tools that connect GA4, Search Console, and internal telemetry — or solutions like Scale your content workflow — make the process far less manual and more repeatable. Tracking the right mix of metrics ensures AI efforts translate into real search visibility and measurable engagement gains.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When a content workflow breaks, start by isolating the fault quickly so damage is limited and recovery is predictable. Begin with simple diagnostics — is the issue content quality, indexing, publishing automation, or a technical SEO problem? Run targeted checks, contain the problem by unpublishing or adding noindex where necessary, and escalate only when diagnostics point beyond content ops.
Quick diagnostics to run now
- Check crawl status: Look for drops in indexed pages or crawl errors in your search console dashboard.
- Verify publishing logs: Confirm the scheduler completed runs and that the CMS returned success codes.
- Audit recent commits/changes: Correlate the time of failure with deployments or plugin updates.
Step-by-step containment and rollback
- Unpublish the affected pages or set
noindexin the page header immediately. - Revert to the last known-good content version in the CMS or git repo.
- Disable the automated pipeline component that triggered the issue (for example, the formatter or deploy hook) while running further tests.
- Re-run a single article through a staging pipeline and validate HTML, canonical tags, and sitemap entries.
CLI and dashboard checks to run
- Run a sitemap curl test:
curl -I https://example.com/sitemap.xmlto confirm 200 status and accessibility. - Fetch page headers:
curl -I https://example.com/post-urlto checkX-Robots-Tagand canonical headers. - Inspect logs:
tail -n 200 /var/log/publish.logor check the CMS publish history for error messages.
When to escalate
- Engineering: Escalate if server errors (
5xx), broken pipelines, or database integrity issues appear. - Legal/PR: Escalate immediately for copyright takedown, defamation, or sensitive data exposure.
- SEO specialist: Escalate if core indexing or widespread ranking drops persist after fixes.
Rollback example: If a content transformation script corrupted 300 posts, unpublish them, revert the script in the repo, redeploy, then republish in controlled batches while monitoring indexing.
Tools worth adding to your checklist include link-checkers, scheduled index-status reports, and content scoring alerts. If automation caused the failure, consider adding a gated staging run that fails the pipeline on critical SEO flag violations.
Tackling these issues fast protects traffic and reputation; the goal is to contain first, diagnose next, then restore confidently so content continues driving growth.
📥 Download: AI-Driven SEO Strategy Checklist for 2025 (PDF)
Tips for Success & Pro Tips
Start by treating AI as a production tool, not a replacement for editorial judgment. Use automation to handle repeatable tasks—topic generation, first-draft outlines, metadata—but keep humans in control of brand voice, factual accuracy, and final approvals. That separation preserves quality while unlocking scale.
- Governance first: Define who signs off on what and make approval gates explicit.
- Transparency always: Track when content was AI-assisted and what model/version produced it.
- Human-in-the-loop: Assign reviewers for facts, tone, and legal/brand risks.
- Prompt/version control: Keep prompt histories and standardize templates.
- E-E-A-T protection: Guard expertise, experience, authority, and trustworthiness in each piece.
- Measure as you scale: Use content scoring and KPIs, not just publishing velocity.
E-E-A-T: Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trust—ensure each article shows clear authorship, sources, and demonstrable subject-matter experience.
Human-in-the-loop: A reviewer or editor who checks AI output for accuracy, tone, and compliance before publication.
Prompt/version control: step-by-step process
- Create a canonical prompt template that includes intent, audience, constraints, and examples.
- Save the initial prompt as
v1.0and record any edits as new versions with short change notes. - Tag generated drafts with the prompt
version_id, model name, and timestamp. - Require editorial sign-off on any content produced with an updated prompt before it goes live.
Practical safeguards that work in the wild: Use short audits: Randomly sample 5% of AI-assisted posts weekly for fact and tone checks. Keep an errors playbook: Log common failure modes and the corrective prompts that fixed them. * Limit model scope: Use different models for ideation vs. final text to reduce hallucination risk.
Scaling without sacrificing brand: automate routine tasks—internal linking suggestions, meta descriptions, A/B headline tests—but route anything that impacts trust (medical, legal, financial claims) through senior editors. Tools can help; for enterprise workflows consider platforms that provide audit trails and content scoring. Scale your content workflow can be helpful for automating pipelines while keeping oversight.
A strong prompt/version control habit plus clear governance and human review prevents growth from turning into reputation risk. Keep those practices tight as volume increases and the payoff becomes reliable.
Next Steps: Run a Pilot and Scale
Run a focused 90-day pilot on a small, measurable slice of content to validate AI-driven SEO changes before committing budget and headcount. A tight pilot reduces risk, surfaces real-world signals (traffic, engagement, cost), and creates a repeatable playbook for scaling.
Pilot design (high level)
- Define scope. Pick 30–50 pages that represent different content intents (informational, transactional, evergreen).
- Set baseline metrics. Capture current
organic clicks,long-click rate,time-on-page, conversion rate, and editorial cost per page. - Deploy changes. Use one of three approaches (conservative, aggressive, hybrid) to create updates or new drafts and publish in a controlled cadence.
- Measure continuously. Daily index checks, weekly traffic/engagement reviews, and a formal 30/60/90-day evaluation against go/no-go criteria.
Concrete go/no-go criteria
- Traffic uplift: +8–12% organic clicks on pilot pages at 60–90 days.
- Engagement: ≥10% relative lift in
long-click rateor ≥15% lift intime-on-page. - Cost efficiency: ≥20% reduction in editorial cost per updated page (or neutral cost with better ROI signals).
- Safety net: No page should drop >25% organic clicks without a technical cause; any drop triggers rollback for that page.
Stakeholder communication cadence
- Weekly: Triage email with quick metrics and action items.
- Biweekly: 30-minute working session with SEO, content, and analytics.
- Monthly: 60-minute review with product/marketing leadership covering learnings and go/no-go decisions.
- Ad-hoc: Immediate alerts for significant traffic anomalies.
Tools & materials
- Baseline analytics: GA4 + Search Console export.
- Content ops: CMS with versioning and tagging for pilot pages.
- Automation:
AI content pipelinefor drafts and editorial suggestions. - Benchmarking: Simple dashboard showing pilot vs. control cohort.
Pilot approaches: conservative (human-in-loop) vs. aggressive (automated drafts) vs. hybrid—show risk, speed, cost, and quality tradeoffs
| Approach | Risk Level | Speed | Cost | Quality Controls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative (Human-in-loop) | Low | Moderate | $500–$1,000/week | Editorial review, fact-check, human editing |
| Aggressive (Automated) | High | Fast | $200–$600/week | Automated QA, spot human audits |
| Hybrid | Moderate | Faster than conservative | $350–$800/week | Automated draft + human final pass, A/B tests |
Key insight: Conservative pilots minimize reputation risk and are best when brand trust matters; aggressive pilots move fastest and cost least but need tight rollback rules; hybrid often hits the best balance for scaling.
Running a disciplined 90-day pilot like this makes the decision to scale evidence-driven rather than hopeful. When the metrics and stakeholder cadence are in place, scaling becomes a matter of repeatability and governance—not guesswork.
Conclusion
By reframing SEO as a living system—where signals, context and content feed each other—teams can stop chasing yesterday’s tactics and start building resilient, scalable advantage. Work through the audit steps, lock in the prerequisites, and convert a handful of high-value topics into AI-first workflows; doing that addresses technical gaps, speeds content production, and improves topical relevance. Teams that pilot AI-driven briefs and editorial automation often close content gaps faster and catch emerging intent shifts sooner, which matters because search is now about signal refresh and semantic fit, not just backlinks.
If there’s one practical move to make this week: pick a narrow pilot (three to five pages), run the audit steps from the article, and implement the content workflow changes. Measure uplift with relevance and engagement metrics, and iterate on prompts and templates until quality stabilizes. For teams looking to automate this workflow and scale the pilot into a program, platforms like Run your AI-SEO pilot with Scaleblogger can streamline execution and reporting. Questions about what to test first or how long a pilot should run? Aim for 6–8 weeks for meaningful signal changes, and prioritize pages tied to business goals. This approach makes the future of SEO manageable: small experiments, clear metrics, and repeatable processes that turn AI SEO strategies into consistent growth.

