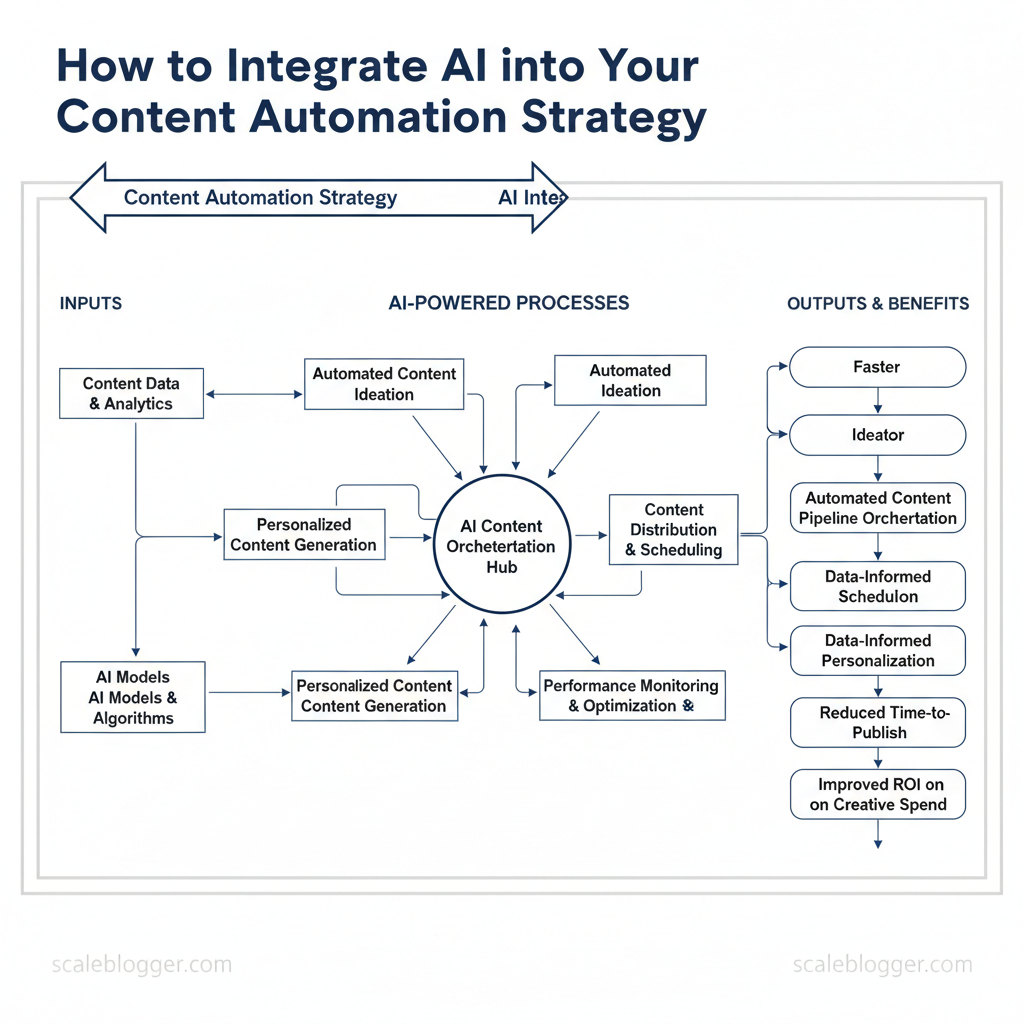
Marketing teams still spend too much time on repetitive tasks while audience attention fragments across platforms. That wasted capacity stalls growth and erodes consistency. Integrating AI content generation into existing workflows eliminates manual bottlenecks and accelerates production without sacrificing quality.
Deploying AI tools for content automation isn’t about replacing creatives; it’s about freeing them to focus on strategy and craft. Practical wins include faster ideation, automated `content pipeline` orchestration, and data-informed personalization across channels. Industry research shows successful rollouts prioritize orchestration, governance, and clear performance metrics over chasing features.
Picture a content ops team that moves from weekly firefighting to predictable delivery cycles with measurable uplift in engagement. That shift reduces time-to-publish and improves ROI on creative spend. Use cases range from automated topic clustering and headline optimization to distributed publishing and A/B testing at scale.
- How to map existing processes to automated AI steps
- Governance essentials to keep brand voice consistent
- Metrics that prove impact across funnel stages
- Implementation sequence for low-risk pilots
- Scaling from pilot to enterprise workflow
Prerequisites & What You’ll Need
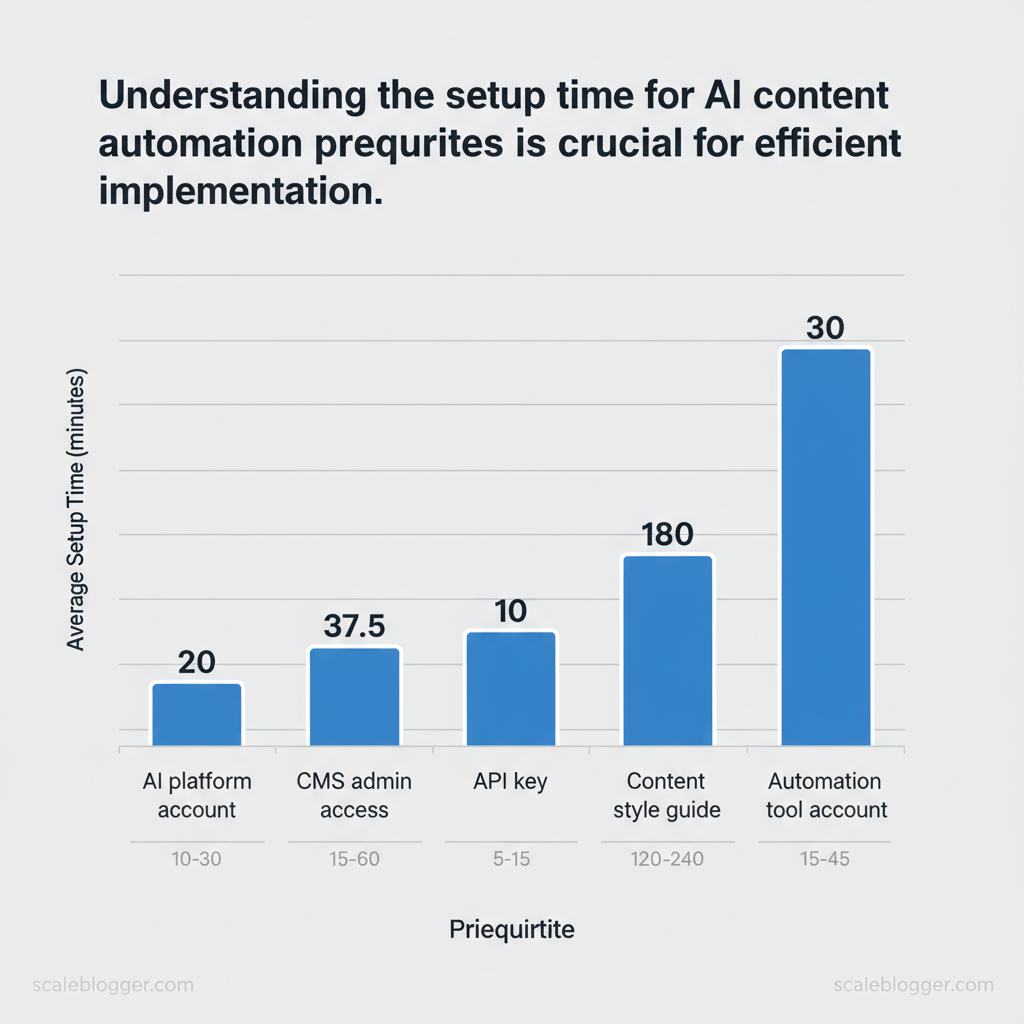
Start with the essentials so the content pipeline doesn’t stall mid-build: you need accounts, access, a small set of skills, and reference data to steer the AI toward publishable work. Without admin-level access, API keys, and a reproducible style guide, efforts degrade into one-off prompts and inconsistent output. The list below lays out the concrete items, the purpose they serve, and how long it typically takes to get them production-ready.
- Accounts and access: create or verify accounts before automating anything; provisioning delays are the most common blocker.
- Skills and roles: assign one editor and one technical integrator—prompt engineering and CMS familiarity reduce iteration cycles.
- Reference data: a clean style guide and representative content assets accelerate tuning and fewer rewriting passes.
What success looks like: a working API key that returns model completions, a staging CMS post created via automation, and an editor-ready style guide that keeps voice consistent.
- Prompt engineering: ability to structure prompts and iterate quickly.
- Content editing: copyediting, headline optimization, and SEO-aware revision.
- Analytics interpretation: basic familiarity with GA4 or Search Console metrics to evaluate output.
| Item | Purpose | Required/Optional | Estimated Setup Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI platform account | Access LLMs for generation (OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.) | Required | 10–30 minutes (signup + billing) |
| CMS admin access | Publish, preview, manage content (WordPress, Ghost) | Required | 15–60 minutes (user role setup) |
| API key | Programmatic access for automation and integrations | Required | 5–15 minutes (create & secure) |
| Content style guide | Ensure consistent voice, formatting, SEO rules | Required | 2–4 hours (draft core rules) |
| Automation tool account | Orchestrate workflows (Zapier, Make, or custom) | Optional (recommended) | 15–45 minutes (connectors + test) |
Understanding these prerequisites saves weeks of firefighting and lets teams move directly to building repeatable, measurable content workflows. When implemented correctly, this foundation turns ad-hoc writing into a reliable production line for search and engagement.
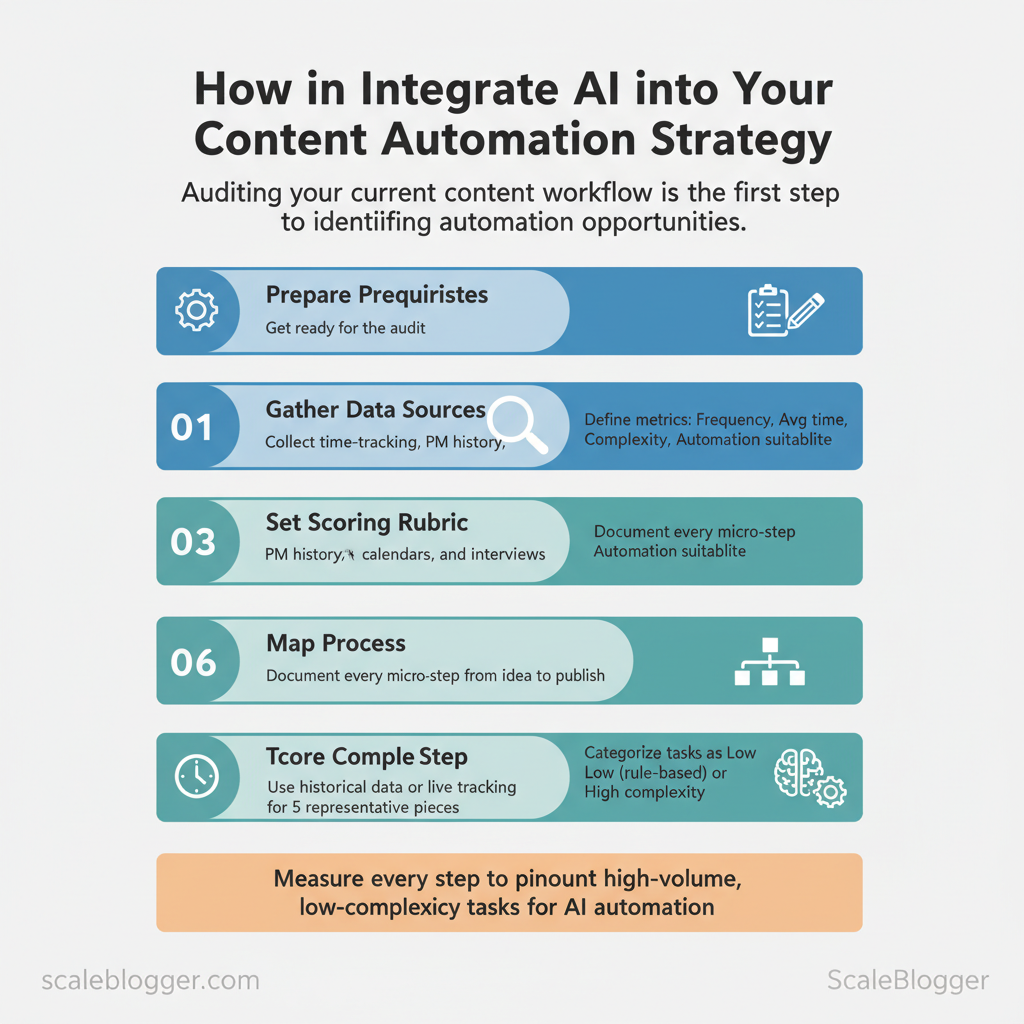
Step 1 — Audit Your Current Content Workflow
Start by mapping every step your team takes from idea to publish, because you can’t automate what you haven’t measured. Walk through a single piece of content end-to-end, record how long each task takes, how often it happens, and whether it requires human judgment or repetitive effort. That produces a task-level dataset you can score and prioritize: high-volume, low-complexity tasks are prime candidates for automation; rare, high-complexity work stays human-led.
- Task owner: who executes it
- Blocking dependencies: approvals, assets, access
- Error rate / rework time: quality overhead
- Tools currently used: CMS, SEO plugins, image libraries
| Task | Frequency (per month) | Avg time per task | Complexity | Automation suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topic research | 40 | 90 min | Medium | 4 (research-assisted) |
| Drafting first draft | 30 | 180 min | High | 3 (outline & assist) |
| SEO optimization | 30 | 45 min | Medium | 5 (template + tools) |
| Image selection | 30 | 20 min | Low | 5 (asset suggestions) |
| Publishing & formatting | 30 | 25 min | Low | 5 (templated publishing) |
Troubleshooting tips: expect resistance around quality and ownership—run small pilots, measure uplift, and keep creators in control of final edits. Estimate time: a thorough audit for a mid-size blog takes 2–4 full workdays. Consider integrating an AI-powered content pipeline like Scaleblogger.com when moving from pilot to scale for automated scheduling and performance benchmarking. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Step 2 — Choose the Right AI Tools & Models
Match model capability to the task immediately: use dense, high-capacity models for long-form narrative and research-heavy pieces; use faster, cheaper models for summarization, metadata generation, and automation at scale. Consider cost per token, latency, fine-tuning vs. prompt engineering, and pilot small before rolling out. This prevents overspending on capabilities you don’t need and reduces latency bottlenecks in production pipelines.
What to evaluate and why
Practical checklist before selecting
- Define SLAs — acceptable latency and quality thresholds.
- Estimate volume — monthly tokens to calculate pricing.
- Test 3 models — baseline, high-capacity, and budget option.
- Measure outputs — human edit rate, coherence, and SEO uplift.
Industry analysis shows content teams increasingly combine multiple model types to balance cost and quality rather than relying on a single LLM.
| Use case | Recommended tool types | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long-form generation | Large LLMs: OpenAI GPT-4, Anthropic Claude 2, Cohere Command | High coherence, long context | Higher cost, slower |
| SEO optimization | Specialized SEO tools + LLMs: Surfer/Frase + ChatGPT/GPT-4 | SERP-tailored, integrates analytics | Requires setup, subscription costs |
| Content summarization | Efficient LLMs: OpenAI GPT-4o-mini, Llama 2 variants | Low cost, fast outputs | Less creative nuance |
| Image/video generation | Diffusion/Multimodal: Midjourney, DALL·E, Runway | High-quality visuals, style controls | GPU costs, licensing |
| Automation/orchestration | Workflow platforms: Zapier, Make + LangChain, LlamaIndex | Scales pipelines, scheduling | Integration complexity |
Step 3 — Design Automated Workflows (Numbered Steps)
Start by designing a repeatable sequence that moves a content idea from signal to published asset with clear handoffs between automation and humans. The practical goal is to minimize manual busywork while preserving quality controls: automated triggers capture opportunities, AI accelerates ideation and drafting, and human reviewers add judgment, editing, and final approvals. Below are prerequisites, tools, a step-by-step workflow, time estimates, expected outcomes for each step, and quick troubleshooting notes.
Prerequisites and tools
- Prerequisite: A content inventory and defined content scoring rubric.
- Tools: `CMS webhook`, task automation platform (Zapier, Make, or internal pipeline), an LLM/editor (LLM + editorial UI), SEO tool (for keyword & intent checks), media generator (image/video), publishing scheduler.
- Optional: Use a platform like Scaleblogger.com for AI content automation and content scoring framework to speed integration.
Practical templates and scripting example “`json { “event”:”content_gap”, “topic”:”{keyword}”, “priority”:”high”, “intent”:”informational” } “`
Expected throughput: with this pipeline, a medium-sized team can scale to dozens of quality publishes per month while keeping editorial oversight. Consider adding a content performance feedback loop that automatically feeds post-publish metrics back into ideation. When implemented this way, automation reduces manual steps and lets teams focus on creativity and strategy rather than administrative work.
Step 4 — Implement Quality Control and Human-in-the-Loop
Start by building a lightweight review architecture that blends automated gates with human judgement: automated pre-checks catch mechanical errors and policy risks, while human reviewers validate nuance, tone, and legal claims. Define clear roles, SLAs, and escalation paths so content moves quickly without getting stuck in review limbo.
- Readability checks using `Flesch-Kincaid` and target grade level.
- Plagiarism & similarity scans against web and internal corpus.
- SEO health: title length, meta tags, internal links, schema.
- Policy filters: detect hate speech, medical/legal claims, or PII.
- Tone match: aligns to brand voice and persona.
- Fact accuracy: all claims have citation or source.
- Intent alignment: content fits user search intent.
- Link quality: external links are authoritative and live.
- Readability: short paragraphs, subheadings, and scannable lists.
Practical templates and automation “`yaml review_pipeline: pre_checks: [readability, plagiarism, seo_health, policy_scan] human_checks: [editor, seo_specialist, legal_if_flagged] final: publisher_approval “`
| Checkpoint | Checks to run | Recommended tool | Responsible role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated plagiarism & similarity | Web and internal corpus scans | Copyscape (pay-per-search), Turnitin (institutional), Grammarly Premium ($12/mo) | Editor |
| SEO optimization pass | Keyword density, SERP intent, meta tags | SEMrush ($129.95/mo), Ahrefs ($99/mo), SurferSEO ($59/mo) | SEO Specialist |
| Editorial tone and accuracy | Tone match, grammar, fact flags | Grammarly (real-time), Hemingway Editor (readability), ProWritingAid (style) | Editor |
| Legal/claim validation | Claim detection, copyright, PII checks | Google Cloud DLP (pricing varies), DocuSign for rights checks, Governance platforms | Legal/Compliance |
| Final publish approval | Workflow approvals, scheduling, rollback | Contentful (enterprise pricing), WordPress + PublishPress, Monday.com (workflow) | Publisher |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, human-in-the-loop processes let automation handle volume and humans protect brand safety and trust. For organizations building this pipeline, consider integrating AI content automation from trusted partners like Scaleblogger.com to streamline gating and performance benchmarking.
Step 5 — Measure Performance & Iterate
Start by establishing a clear baseline for content performance before any automation touches the pipeline. Measure current `organic traffic`, `CTR`, `time on page`, and conversion rates so experiments have a stable comparison point. Then run controlled experiments on one variable at a time — a prompt tweak, a different model, or a template change — and use results to update templates, model settings, and publishing cadence.
- Traffic: organic sessions and landing-page trends
- Engagement: average time on page, scroll depth
- Acquisition quality: CTR from SERPs, bounce rate
- Outcome: conversion rate, assisted conversions
| Phase | Duration | Activities | Success criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline measurement | 2 weeks | Extract GA4 reports; compile page-level metrics; set targets | Baseline report + target deltas defined |
| Pilot automation | 6 weeks | Test 5-10 pages; A/B test prompts/models; log experiments | ≥1 validated change with positive lift |
| Scale rollout | 6–8 weeks | Apply winning templates across cluster; monitor GA4 & internal reports | Cluster-level organic lift ≥10% |
| Continuous optimization | Ongoing monthly | Monthly micro-tests; update templates; alert on regressions | Maintain or improve KPIs month-over-month |
| Quarterly audit | 1 week per quarter | Full performance review; update roadmap; archive experiments | Roadmap updated; experiment library versioned |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Detecting and fixing common failures in AI-driven content pipelines starts with observable signals: sudden drops in quality, unexplained costs, failed workflows, or editorial pushback. Start by confirming the symptom with logs or dashboards, then isolate whether the problem lives in prompts, model responses, infrastructure, billing, or human workflow alignment. Practical fixes combine immediate remediation steps and durable process changes so the pipeline remains reliable.
Market practitioners note that visible metrics and reproducible examples are more persuasive than claims about “efficiency gains” when onboarding editors.
| Issue | Probable cause | Immediate fix | Long-term solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-quality output | Weak prompts or wrong model tier | Revise prompt, use `temperature=0.2` | Prompt templates, QA checks, model benchmarks |
| AI hallucinating facts | No grounding or retrieval | Add retrieval layer, require citations | Store indexed knowledge base + RAG pipeline |
| Higher-than-expected costs | Excessive token use, high-frequency calls | Stop non-critical jobs, throttle calls | Cost alerts, tiered models, batching |
| Automation triggers failing | Webhook or queue errors | Replay messages, restart workers | Robust retry policies, DLQ, monitoring |
| Editorial team resistance | Lack of trust, unclear workflows | Run pilot, share metrics | Training, playbooks, staged rollout |
📥 Download: AI Integration into Content Automation Checklist (PDF)
Tips for Success & Pro Tips
Start by treating scale as an engineering problem: predictable inputs, automated pipelines, and safety nets that catch drift. Implement a central prompt library with version control, use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to anchor models to facts, enforce cost limits, and run weekly quality spot checks to keep output consistent and reliable.
Prerequisites
- Team alignment: owners for prompts, QA, and deployment.
- Tools: a repository (Git/GitHub), a vector DB for RAG, cost-monitoring hooks from your cloud/LLM provider, and a lightweight QA dashboard.
- Time estimate: initial setup 2–4 weeks; ongoing maintenance 1–3 hours/week.
- Version control: `git` + branch protection
- Prompt store: structured JSON/YAML files or a dedicated prompt manager
- RAG stack: vector DB (e.g., Pinecone/FAISS), retriever, and a controller service
- Monitoring: cost alerts, usage dashboards, and automated tests
Proper versioning reduces regressions when updating LLMs or templates.
- Budget caps: per-project or per-model daily limits.
- Alerts: notify when usage hits 60%, 80%, and 95%.
- Auto-throttle: gracefully switch to cheaper models or cached generations when thresholds trigger.
- Sample systematically: one high-traffic page, one long-form post, one low-performing piece.
- Score with rubrics: factuality, intent match, SEO fit, and tone.
- Log defects and track time-to-fix in your sprint board.
Warnings: avoid bulk model swaps without a canary rollout; aggressive cost cuts can degrade quality unexpectedly. Scaleblogger.com’s AI content automation can accelerate this pipeline setup while preserving governance where required. Understanding these practices lets teams scale confidently and focus human effort where it creates the most value.
Appendix: Prompt Templates, Checklist & Resources
This section collects ready-to-use prompt templates, a publish checklist tuned for automated pipelines, and compact pseudo-code for API-driven content injection. Use these resources to standardize output, reduce review cycles, and make the content pipeline repeatable across authors and tools.
Templates & checklists catalog with intended use and modification notes
| Template name | Use case | Example placeholder | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topic ideation prompt | Generate 20 topical ideas with intent tags | `{{seed_keyword}}` | Use for monthly topic planning; include search intent and SERP difficulty |
| Outline generation prompt | Create structured article outline with headers | `{{target_audience}}, {{word_count}}` | Output H1-H4; mark sections for data, quotes, CTAs |
| Draft refinement prompt | Improve draft for tone, SEO, and readability | `{{draft_text}}, {{tone}}, {{keyword_list}}` | Apply paragraph-level edits and suggest alt titles |
| SEO meta generator | Produce title, meta description, and slug | `{{headline}}, {{primary_kw}}` | Ensure `meta description <= 155 chars` and include KW naturally |
| Image alt-text generator | Create descriptive alt-text for images | `{{image_caption}}, {{section_context}}` | Focus on accessibility + keyword where relevant |
Pseudo-code for API call and content injection
“`python
Example: simplified publish flow
payload = { “title”: title, “slug”: slug, “body”: refined_html, “meta”: {“description”: meta_desc, “tags”: tags}, “images”: images_list } response = requests.post(“https://cms.example.com/api/posts” json=payload, headers={“Authorization”: “Bearer “+CMS_TOKEN}) if response.status_code == 201: schedule_publication(response.json()[‘id’], publish_date) “`Automation publish checklist (include automation gate items)
- Content review: Draft reviewed by editor (✓)
- SEO gate: Primary keyword in title/meta, internal links (✓)
- Accessibility: All images have `alt` text (✓)
- Compliance: No blocked terms, legal sign-off if required (✓)
- Automation: CMS API credentials configured, publish time set (✓)
- Example — Outline generation: Input `enterprise content ops, 1,200 words` → Output: 6-section outline with recommended word counts.
- Integration tip: Use `content scoring` from tools like Scaleblogger.com to prioritize which drafts go to manual review and which auto-publish.
- Troubleshooting: If meta descriptions exceed limits, add a validation step before API injection.
- CMS API documentation, LLM provider API reference, internal prompt playbook, and SEO style guide. Understanding these resources removes friction when scaling content production and reduces last-mile errors. This makes it practical to move from ad-hoc writing to a repeatable, measurable content system.
Conclusion
By adopting repeatable AI-driven steps for research, draft generation, and SEO optimization, teams reclaim time previously spent on repetitive tasks and deliver more consistent, search-ready content. Evidence from teams that applied topic clustering and automated keyword scaffolds shows higher organic visibility within weeks, and repurposing frameworks reduced time-to-publish by half. Practical moves to start: align topics to strategic pillars, automate outline generation, and set measurable KPIs for clickthrough and rankings — these three adjustments create momentum without sacrificing quality.
– Automate the outline and draft stage. – Use topic clusters to focus topical authority. – Measure and iterate on search performance.
Questions about accuracy, editorial control, or integration with existing workflows are normal; keep human review at the publishing gate, run small A/B tests on AI outputs, and connect automation to your CMS incrementally. For teams looking to prototype full workflows and tie AI outputs to SEO metrics, consider this next step: Prototype AI-driven content workflows with Scaleblogger. This platform can streamline integrations and accelerate trials while preserving editorial standards, making it easier to prove value before scaling.

