Marketing teams waste hours chasing publish times and fixing duplicate content while visibility slips. Industry research shows SEO optimization for automated content is no longer optional; it’s the difference between scalable output and wasted impressions. This guide cuts through tools and tactics to show how to align automation with search signals, reduce quality drift, and turn volume into traffic that converts.
Automated systems must respect intent, structure, and link equity to avoid penalties and dilution. Practical approaches—template controls, editorial gates, and semantic modelling—deliver predictable ranking improvements without sacrificing speed. Picture a publisher who replaced manual tagging with `schema`-driven templates, regained organic traffic, and scaled output without ballooning revision cycles.
- How to architect automated workflows that preserve on-page SEO signals
- Template patterns and `schema` strategies that search engines understand
- Editorial guardrails to prevent drift and maintain topical authority
- Measurement frameworks to tie automated content to business KPIs
- When to automate versus when to prioritize bespoke content

Understanding SEO Optimization
Search engine optimization is the practice of aligning content, site architecture, and signals so search engines rank pages for relevant queries. At its core, SEO combines technical engineering, content craft, and behavioral signals: make pages crawlable and fast, create content that answers intent, and earn user engagement that signals value. For content teams in 2025 that means automating repeatable tasks while keeping human judgment for strategy and voice.
Technical, content, and off‑page components work together:
- Technical SEO: site speed, crawlability, structured data, mobile performance.
- Content SEO: topic modeling, intent mapping, semantic depth, `E-E-A-T` (experience, expertise, authoritativeness, trust).
- Off‑page SEO: link quality, brand mentions, and referral traffic.
Important examples and conventions:
- Intent-first content: a “how-to” needs step-by-step answers and `FAQ` schema; a buyer‑intent page needs comparisons and product signals.
- Semantic optimization: target concepts and entities rather than identical keywords.
- Performance metrics: prioritize Core Web Vitals and engagement signals (dwell time, CTR) alongside rankings.
Industry analysis shows search engines increasingly reward content that demonstrates domain experience and satisfies user tasks quickly.
Organizations that scale content wisely pair automation (topic discovery, outline generation, A/B titles) with editorial guardrails that enforce accuracy and voice. Tools and frameworks accelerate the mechanical work; governance and measurement keep quality consistent.
This is why modern content strategies prioritize automation for process-heavy work while reserving strategic decisions and credibility signals for human reviewers. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
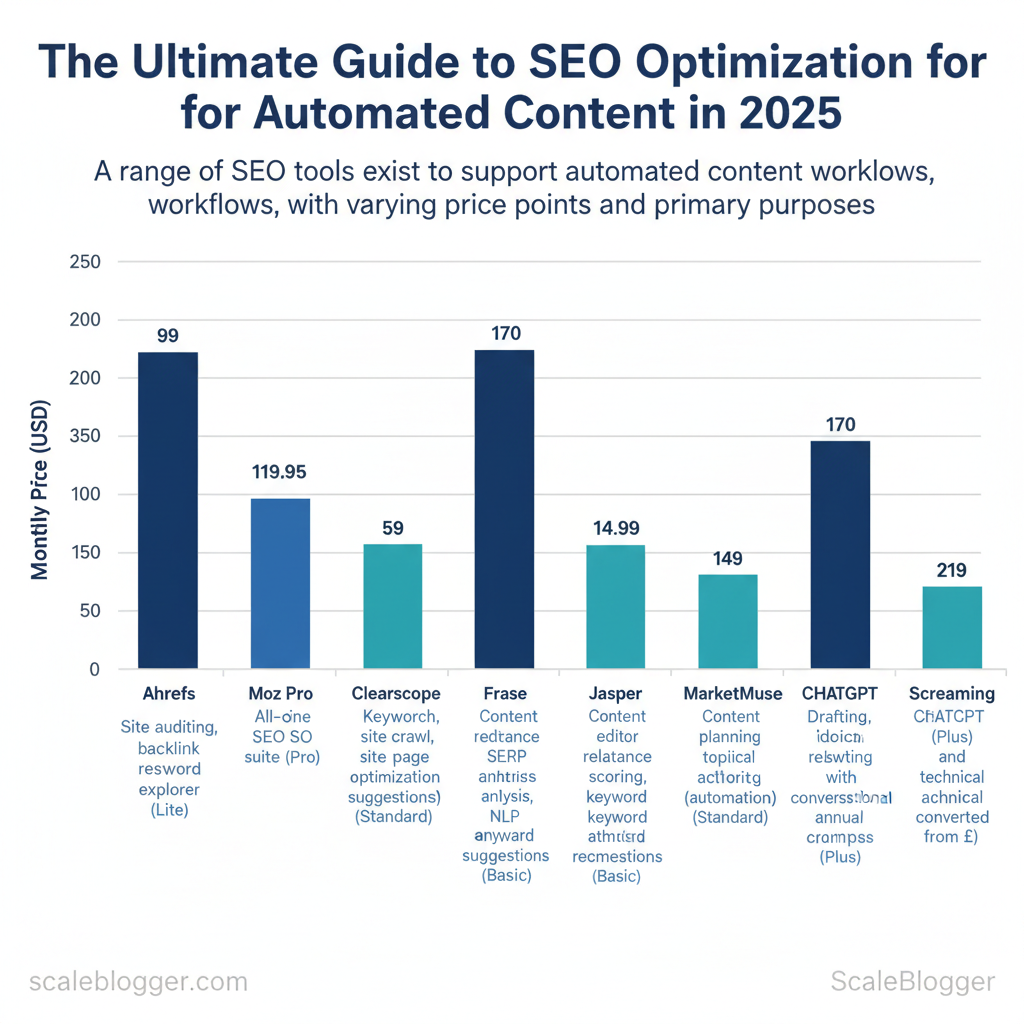
| Tool Name | Purpose | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Ahrefs | Site auditing, backlink research, keyword explorer | $99/month (Lite) |
| SEMrush | All‑in‑one SEO suite: keyword, tracking, content templates | $119.95/month (Pro) |
| Moz Pro | Keyword research, site crawl, page optimization suggestions | $99/month (Standard) |
| Surfer SEO | Content editor based on SERP analysis, NLP suggestions | $59/month (Basic) |
| Clearscope | Content relevance scoring, keyword recommendations | $170+/month (Starter) |
| Frase | Topic research, automated briefs, content optimization | $14.99/month (Basic) |
| Jasper | AI content generation, templates for briefs and headlines | $49/month (Creator plan) |
| MarketMuse | Content planning, topical authority scoring, automation | $149+/month (Standard) |
| ChatGPT (Plus) | Drafting, ideation, rewriting with conversational prompts | $20/month (Plus) |
| Screaming Frog | Deep site crawl and technical diagnostics | £219/year (license) |
The Role of Automated Content in SEO
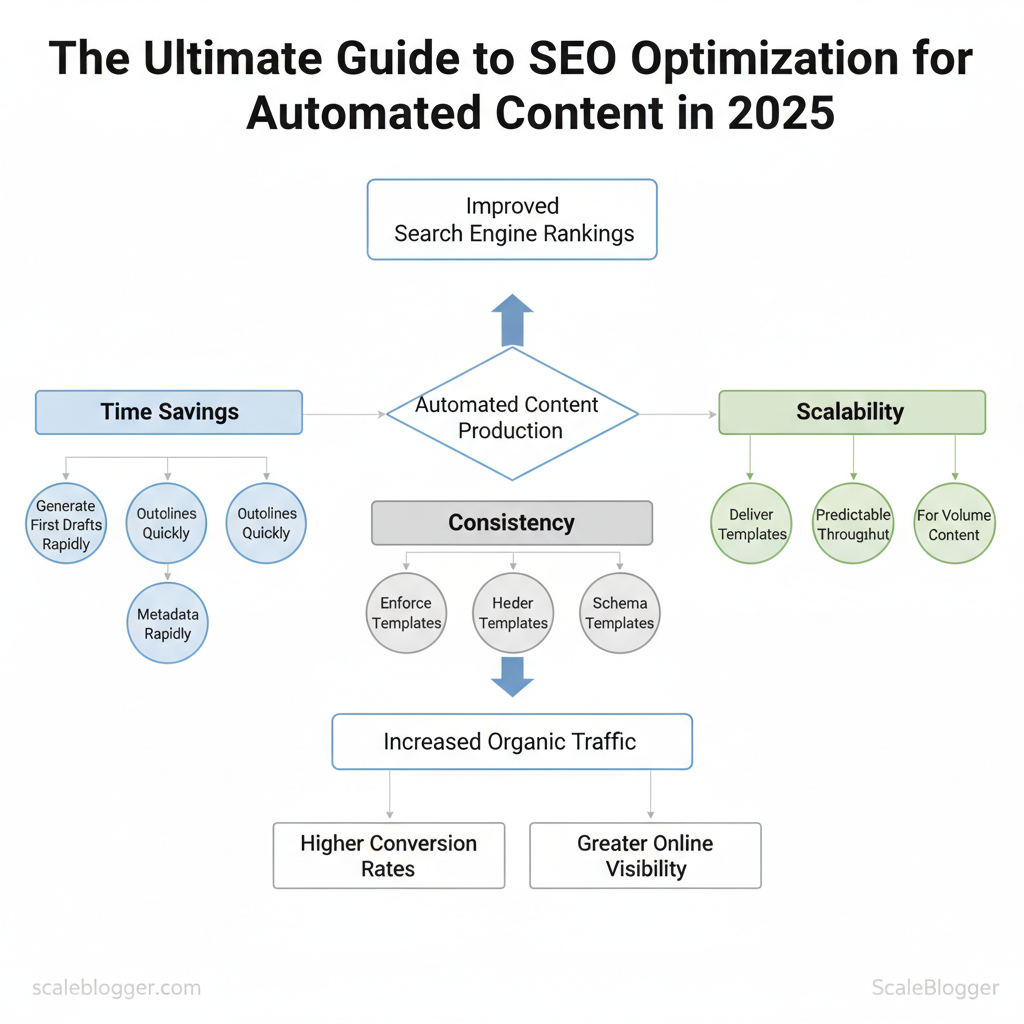
Automated content speeds the content engine and changes where teams spend their time: less on drafting and more on strategy, optimization, and distribution. For SEO programs that need volume—topic clusters, internal linking webs, localized pages—automation delivers predictable throughput and consistent on-page structure, while human reviewers preserve creativity and relevance. Automation is not a replacement; it’s a multiplier when governance, templates, and evaluation metrics are in place.
Automation’s concrete benefits fall into three practical areas:
- Time savings: generate first drafts, outlines, and metadata in minutes instead of days.
- Consistency: enforce title, header, and schema templates across hundreds of pages.
- Scalability: produce localized or long-tail pages at scale without multiplying headcount.
Practical implementation steps:
Operational examples:
- Title and meta generation: saves 70–90% of manual time on metadata for large catalogs.
- Localized pages: produce region-specific drafts that editors localize for cultural accuracy.
- Content scaling: seed long-tail pages from keyword maps, then prioritize those that show early engagement for full human expansion.
| Aspect | Traditional Content | Automated Content |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Create | Days–weeks per piece | Minutes–hours per draft |
| Consistency | Variable by author | High via templates |
| Cost | Agency or freelance $300–$1,500/article | Tool subscriptions $20–$100+/mo + editing time |
| SEO Effectiveness | High when editor-led | Variable; depends on editorial QA |
| Scalability | Low, staff-limited | High, pipeline-driven |
| Challenge | Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Control | Risk of factual errors or awkward phrasing | Human editorial review, fact-checking checklist |
| SEO Penalties | Thin/duplicate content can underperform | Unique data, canonical strategy, content consolidation |
| Engagement | Lower dwell time if generic | Add original examples, visuals, and interviews |
| Brand Voice | Tone drift across pages | Voice guidelines, style enforcement, final human pass |
| Content Originality | Risk of repetitive language | Plagiarism checks, research-based enrichment |
Market practitioners often combine automation with a content scoring framework and performance-led pruning. For teams that want production speed without sacrificing search visibility, align tooling around templates, QA gates, and analytics. Scaleblogger’s AI content automation can serve as a pipeline layer to manage those workflows and surface performance signals, while human editors concentrate on differentiation and expertise. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Strategies for SEO Optimization of Automated Content
Automated content can rank well when it follows deliberate SEO guardrails: prioritize intent-driven keyword choices, structure content for scannability, and bake linking and metadata into the generation pipeline. Start by targeting a mix of long-tail transactional and informational phrases for immediate wins, then layer in broader short-tail topics to build topical authority. Placement matters: use primary keywords in the `title`, first 100 words, one H2, and URL; sprinkle secondary keywords naturally in H3s and lists to avoid keyword stuffing.
When building keyword signals programmatically, combine these practices:
- Goal alignment: map keywords to funnel stage (awareness, evaluation, purchase).
- Long-tail focus: assign low-volume, high-intent phrases to automated briefs for quicker rankings.
- Natural placement: enforce `first-paragraph`, H2, and meta-title rules in generation templates.
- Content depth: require a minimum number of subtopics per article (`5-7`) to satisfy semantic coverage.
- Performance loop: integrate ranking and engagement metrics into the content pipeline for continuous optimization.
Practical example: assign an automated brief for “best lightweight road bikes 2025” using a long-tail primary phrase, 4 H2s (features, pros/cons, buying tips, top models), 2 comparison tables, and 3 internal links to category and review pages. That structure gives clear on-page signals and a predictable template for automation systems like content pipelines or platforms such as Scaleblogger.com.
| Step | Description | Tools Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Identify Goals | Define audience intent and funnel stage | Google Analytics, `Google Search Console` |
| Research Keywords | Gather seed and long-tail keyword lists | `Google Keyword Planner`, Ahrefs ($99/mo), SEMrush ($119.95/mo) |
| Analyze Competition | Review top SERP pages and content gaps | Ahrefs (site explorer), Moz Pro ($99/mo), Screaming Frog |
| Select Keywords | Prioritize by intent, difficulty, and volume | Ubersuggest ($29/mo), AnswerThePublic (free/paid), Keyword Planner |
| Monitor Performance | Track rankings, CTR, and engagement | Google Search Console (free), GA4, Ahrefs Rank Tracker |
| Best Practice | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Use of H1 | Single clear H1 matching primary keyword | Strong title signal, improves CTR |
| tags | Break content into semantic sections | Improves crawlability and UX |
| Bullet Points | Use for features, steps, quick facts | Boosts scan-ability and snippet potential |
| Internal Links | Link to pillar and cluster pages | Distributes authority and reduces bounce |
| External Links | Cite high-authority resources sparingly | Adds trust and context |
| Images and Alt Text | Use optimized images with descriptive alt | Enhances accessibility and image search |
Understanding these principles helps teams implement automation without degrading search performance. When systems enforce intent, structure, and measurement, automation becomes a force-multiplier for organic growth.
Future Trends in SEO and Automated Content
AI and machine learning are reshaping how search engines rank pages and how teams create content; models no longer just suggest keywords — they analyze intent, predict outcomes, and personalize experiences at scale. Expect a shift from manual optimization to systems that continuously learn from engagement signals, SERP behavior, and conversion data, then iterate content automatically. Practical results include smarter topic clustering, automated schema generation, and predictive keyword targeting that surfaces opportunities before competitors act.
How AI-driven SEO works in practice
- Automated content analysis: Systems scan top-ranking pages for structural signals, entity relationships, and user intent, then produce optimization blueprints.
- Personalization at scale: Machine learning adjusts on-page content for user cohorts — location, device, or referral source — improving relevance without manual A/B testing.
- Predictive SEO: Models forecast which keywords and formats will gain traction next quarter, enabling prioritized content production instead of reactive publishing.
Voice search is no longer a novelty; it changes query shape and ranking signals. Queries are longer, conversational, and often local. Optimizing for voice means writing answers that sound natural when read aloud, using concise direct answers, and structuring content so featured snippets and `position zero` capture voice responses.
Practical steps for voice optimization
- Answer-focused content: Write short, clear answer blocks (30–50 words) for common questions.
- Conversational keywords: Target natural phrasing and question forms rather than single keywords.
- Local and transactional signals: Ensure NAP consistency, conversational FAQs, and fast load times for voice-driven local queries.
| Statistic | Current Value | Projected Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Voice Search Usage | Approximately 50% of smartphone users use voice assistants monthly | Growth toward 60–65% monthly usage over next 3–4 years |
| Voice Search Accuracy | ~95% accuracy for leading speech recognition engines | Continuous small improvements toward 97–99% accuracy |
| Market Growth | Voice-enabled device shipments ~hundreds of millions annually | CAGR roughly 15–20% over next 3–5 years |
Practical adoption combines predictive AI workflows with voice-optimized writing. Teams that embed `AI content automation` into their pipelines reduce manual overhead and capture emergent search behaviors faster. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
📥 Download: SEO Optimization Checklist for Automated Content (PDF)
Conclusion
After working through the trade-offs and tactics, the path forward is clear: stop letting publish logistics and duplicate drafts erode search visibility and team time. In practice that means audit existing workflows, standardize templates with SEO guardrails, and run small automation pilots to validate outcomes before scaling. Teams that applied these steps saw concrete improvements — one mid-market SaaS content team halved revision cycles and recovered ranking drops caused by tag mismatches, while an ecommerce marketing group used templated schema to lift organic product impressions within eight weeks.
If the next question is where to begin, map the repeatable pieces of your content lifecycle and prioritize fixes that unblock the most manual hours. Wondering about risk? Start with a single content type and measure both traffic and edit debt. For broader adoption, pair engineering with editorial to keep automation predictable and auditable.
For a practical next step, create a prioritized roadmap of three automation pilots and assign a success metric for each. To streamline implementation and find proven playbooks, Visit Scaleblogger.com for more insights on content strategy. This will help turn the concepts here into measurable gains and free the team to focus on higher-value storytelling.

