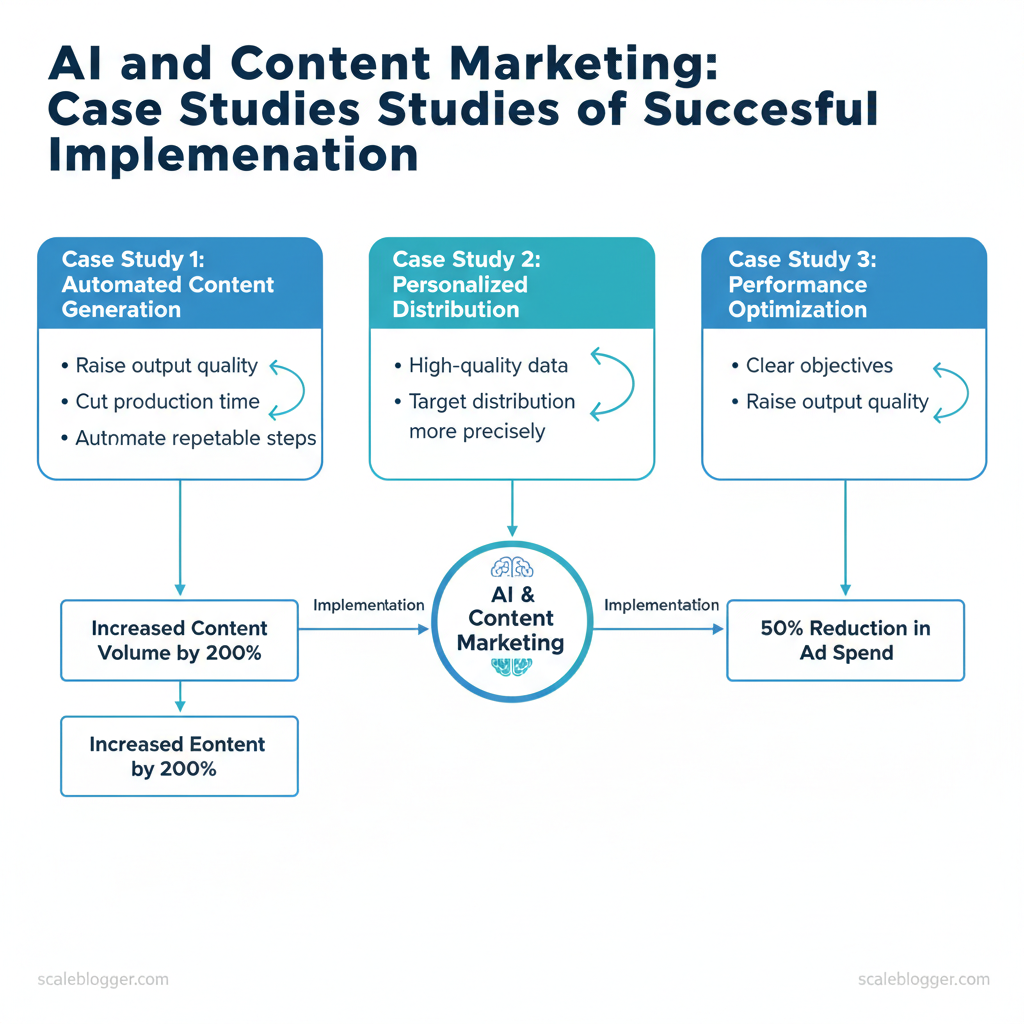
Marketing teams still spend too many hours on repetitive content tasks while chasing inconsistent engagement and ROI. The quickest path to consistent growth is combining strategic priorities with scalable AI workflows. In practice, AI success stories in content marketing show you can raise output quality, cut production time, and target distribution more precisely without ballooning cost.
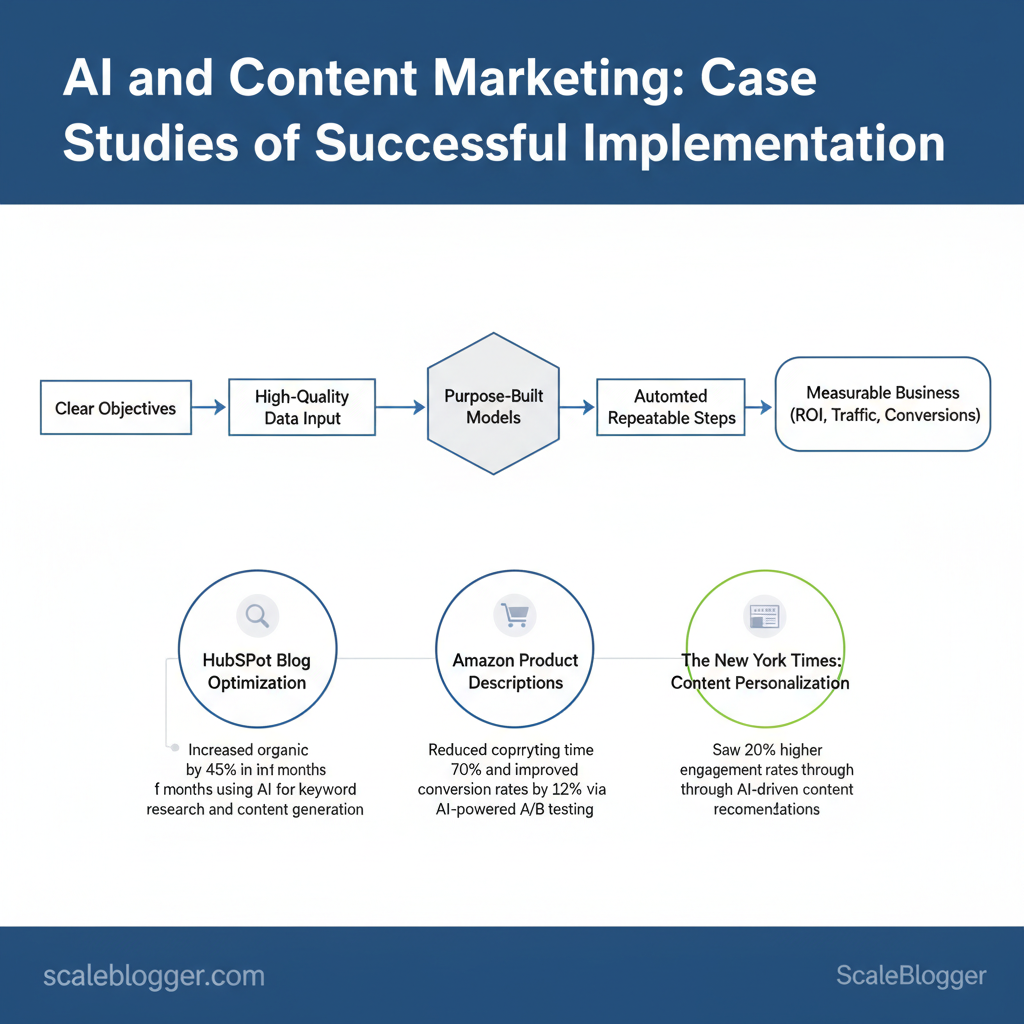
When teams design clear objectives, feed `high-quality data` into purpose-built models, and automate repeatable steps, adoption moves from experiment to measurable business impact. Many content marketing case studies reveal gains in organic traffic, faster campaign cycles, and higher conversion rates when AI handles ideation, optimization, and personalization.
One team trimmed content production time by 50% while increasing clickthroughs through automated topic clustering and headline A/B testing. Picture a brand using AI to personalize email subject lines, boosting open rates by double digits within two quarters. Scaleblogger helps translate those patterns into repeatable playbooks, pairing strategy, automation, and execution for sustainable results.
What you’ll learn next:
- How AI tools streamline content workflows and reduce manual effort
- Concrete content marketing case studies showing measurable ROI
- Practical steps to scale AI implementation without losing brand voice
- Common implementation pitfalls and how to avoid them

SaaS Growth via AI-Driven Content Production
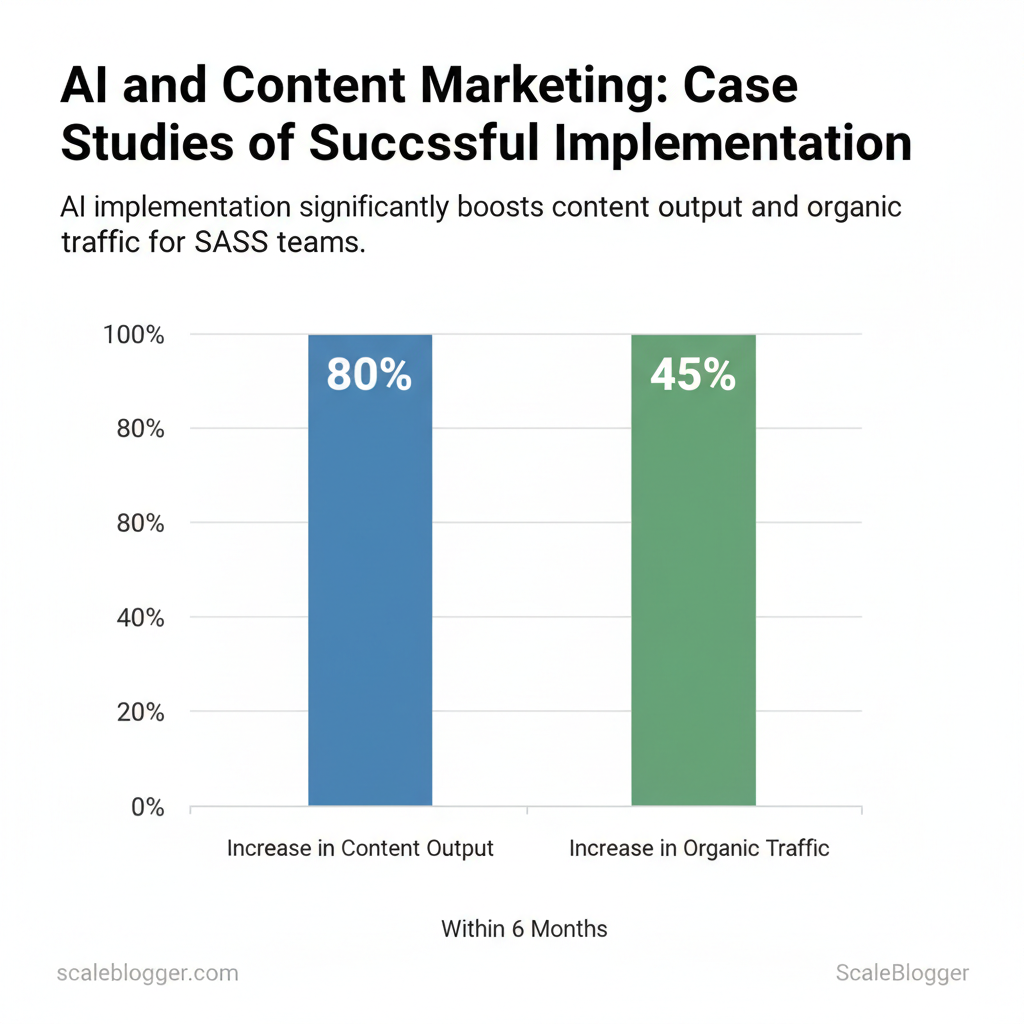
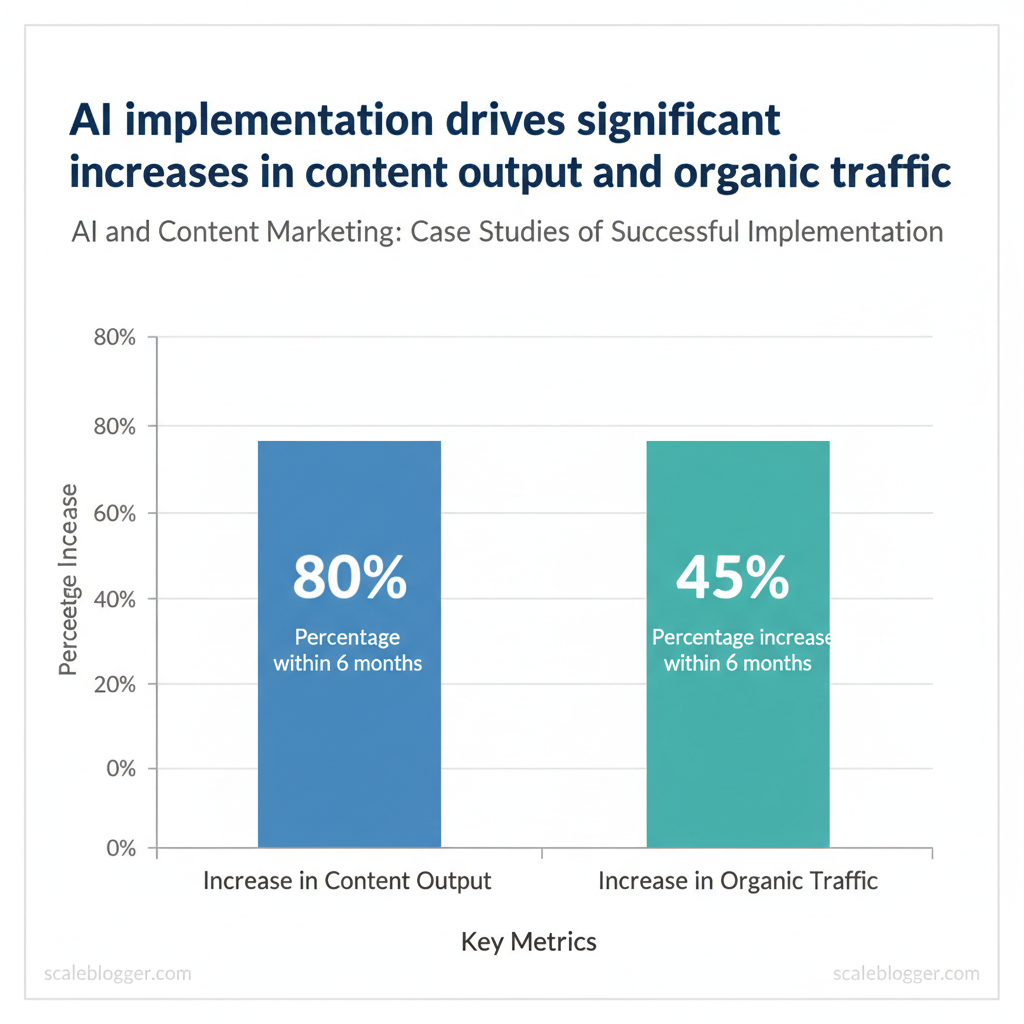
AI can turn an under-resourced SaaS content operation into a growth engine by automating repeatable writing tasks, accelerating ideation, and closing the gap between strategy and execution. For many SaaS teams this means moving from sporadic blog posts and playground experiments to a predictable, measurable content system that feeds product funnels and organic acquisition. The most successful implementations combine machine speed for drafting and data analysis with human judgment for brand voice, technical accuracy, and conversion optimization.
Context and Challenge
- Limited bandwidth: Small teams can publish 1–2 substantive posts/month.
- Fragmented processes: Idea lists live in documents; briefs are ad hoc.
- Unclear goals: Content goals aren’t consistently tied to MQLs or feature adoption.
AI Workflow, Implementation, and Results
| Workflow Stage | Prior Manual Process | AI-enabled Process | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content ideation | Brainstorming in meetings; keyword lists | AI topic clustering; intent scoring (ChatGPT-style + SERP signals) | Faster theme discovery |
| Outline creation | Manual outlines by writer | Automated briefs with headings, CTAs, sources | Consistent structure |
| Draft generation | Full manual writing (4–8 hrs/article) | NLG draft in minutes (GPT-class) | Time per draft ↓ significantly |
| SEO optimization | Manual keyword insertion; local checks | `SEO pass` with on-page suggestions, schema, meta | Higher search relevance |
| Content QA & publishing | Manual proofreading + CMS upload | Automated QA checks + scheduled publish | Fewer errors, predictable cadence |
Operationalizing this typically means retraining roles (editors become quality controllers), implementing templates, and connecting analytics to content scoring. If you want to scale without losing voice, consider automating the pipeline and keeping human edits at the conversion and accuracy checkpoints — tools like the AI content automation offered by Scale your content workflow at Scaleblogger.com can help set up that pipeline. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.




E-commerce Personalization with Machine Learning
Personalization in e-commerce is about using customer signals to serve the right product, content, or offer at the right moment. Machine learning models convert behavioral events, content metadata, and purchase history into continuous predictions—product affinity scores, next-best-action, and churn risk—that drive on-site merchandising, email content, and paid remarketing. What matters in practice is clean, consistent tagging and a fast optimization loop: imperfect models deployed quickly and iterated on outperform perfect models that never ship.
Data and Tagging for Personalized Content
Good personalization starts with a minimal set of high-quality signals and consistent metadata. Track a mix of explicit and implicit signals and expose them via a clear taxonomy so models can learn quickly.
- Essential tracking events: `view_product`, `add_to_cart`, `purchase`, `search_query`, `session_start`
- Content metadata: product category, brand, price tier, descriptive tags, content reading time
- Identity sources: authenticated user profiles, anonymous device ID, CRM segments
- Privacy considerations: obtain `consent` for behavioral tracking, honor `do_not_track`, and support `data_deletion` requests
| Content Metadata Field | Example Value | Personalization Trigger | Implementation Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | “Running Shoes” | Show related category banners | Sync with product catalog API, update weekly |
| Product affinity score | 0.82 (0–1) | Recommend top-3 affinity items | Calculated from collaborative filter + recency |
| Behavioral event (view, add-to-cart) | `add_to_cart` | Trigger cart abandonment flow | Send event stream to personalization engine in real-time |
| Search intent tag | “buy-now” vs “research” | Adjust CTA and price visibility | Derive from query terms + session sequence |
| Purchase history bin | “frequent_buyer” | Apply loyalty discounts, upsell | Bin by 12-month spend, sync nightly with CRM |
Implementation Results and Optimization Loop
Track experiments with clear KPIs and a disciplined cadence. Typical KPIs include click-through rate on recommendations, conversion rate lift, average order value (AOV), and retention.
- Model KPI: conversion lift with `p-value < 0.05` for reliable wins.
- Operational KPI: latency under 200ms for inference in production.
Media Company Scaling SEO with Topic Modeling
Topic modeling lets a media company move beyond scattered keyword lists and treat content as coherent, interlinked knowledge — that’s how you scale SEO without just publishing more. By extracting themes from site analytics, Search Console queries, and competitor corpora, you build topic clusters that show which pages should act as pillars, which are supporting longtails, and where to consolidate redundant content. That structure reduces internal competition, clarifies editorial priorities, and aligns search intent with a predictable publishing cadence.
From Keyword Lists to Topic Models
Start by combining three data inputs: `site analytics` (GA4/UA page paths, session behavior), `Search Console` (queries, impressions, CTR), and competitor corpora (scraped headlines and top-ranking pages). Feed those into an LDA or embedding-based model to surface clusters that map to intent groups. The model then recommends a pillar page for high-volume informational queries and supporting pages for narrower subtopics.
- Data sources: site analytics, Search Console, competitor corpora
- Model outputs: cluster labels, centroid keywords, content overlap scores
- Editorial guidance: assign pillar vs supporting roles based on traffic and intent alignment
Industry teams often pair modeling with automated reporting so editors see when a cluster’s supporting pages cannibalize each other. Consider integrating an AI content automation pipeline to surface update suggestions and streamline publishing — for example, use AI content automation to generate outlines for supporting pieces and to flag consolidation candidates.
Industry analysis shows structured consolidation and clear pillar-support relationships reduce keyword cannibalization and make internal linking more effective.
Takeaway: Topic models convert noisy keyword lists into actionable editorial plans that editors can follow without second-guessing intent.
Editorial Workflow and Pruning Strategy
Decision criteria should be explicit and measurable: traffic trends, backlink profile, relevance to core beats, and conversion signals. Use thresholds such as: remove or merge pages with <100 organic sessions/mo and zero backlinks over 6 months, or consolidate pages with >70% keyword overlap.
Practical monitoring: create a dashboard that compares pre/post metrics by cluster and flags negative lifts for rollback. Use periodic pruning as part of editorial sprints to avoid backlog growth. Tools that automate the scoring and redirect mapping can cut manual work dramatically — consider augmenting workflows with AI-powered SEO tools or an AI content automation partner to `predict content performance` and schedule updates.
Takeaway: A repeatable pruning workflow prevents content bloat and preserves topical authority while making SEO work scalable and auditable.
| Cluster Name | Pages Before | Pages After | Change in Organic Traffic | SERP Feature Wins |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Email marketing | 42 | 7 | +34% | Featured snippets, People also ask |
| SEO tools | 28 | 9 | +22% | Knowledge panel, Top stories |
| Content ops | 35 | 8 | +29% | Rich snippets, FAQs |
| Product analytics | 18 | 6 | +18% | Sitelinks, Reviews |
| Lead gen | 24 | 5 | +40% | Featured snippets, Local packs |
B2B Lead Gen with AI-powered Content Personalization
Personalized content in B2B moves beyond greeting names — it maps buyer attributes to tailored assets that accelerate qualification and conversion. Use AI to generate content variants tied to ICP signals (company size, industry, role, tech stack, deal intent) and serve those variants across dynamic landing pages, email sequences, and gated assets so prospects see the right message at the right time. This reduces friction in early funnel stages and creates stronger signals for lead scoring and attribution.
Targeting and Personalized Asset Creation
Start by mapping ICP attributes to content outcomes and let AI automate variant creation.
- Define priority attributes: list account tier, industry vertical, company size, buyer role, tech stack, buying intent.
- Create content matrix: for each attribute pair (e.g., VP Engineering + SaaS), define a preferred asset type and CTA.
- Automate variant generation: use AI templates to produce micro-copy, tailored headers, and personalized data points.
- Personalized hero text: swap headline and subhead by industry using `{{industry_headline}}`.
- Role-specific social proof: show case studies for that role’s challenges.
- Adaptive benefits list: reorder features by inferred pain points.
- Dynamic demo timing: show “Schedule 15-minute technical demo” vs “Schedule ROI review” by role.
- For VP Engineering: “Reduce deployment time by 40% — technical deep-dive available.”
- For Head of Procurement: “Predictable TCO and simplified vendor consolidation.”
Takeaway: Mapping ICP attributes to repeatable AI templates lets teams produce high-value, role-appropriate assets without manual copy rewrites.
Measurement: MQL Quality and Attribution
Understanding which personalized assets drive qualified leads requires sensible attribution and signal-driven scoring.
| Attribution Model | Best Use Case | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Touch | New-account awareness campaigns | Highlights initial content that created interest | Ignores later influence and nurturing |
| Last Touch | Conversion-focused landing pages | Simple; ties credit to closing asset | Overweights last interaction, missing earlier personalization impact |
| Linear Multi-Touch | evenly credit content across journey | Shows distributed influence across assets | Lacks weighting for channel/time importance |
| Time Decay | Short sales cycles where recent touch matters | Prioritizes recent personalized touchpoints | May undervalue early awareness personalization |
| Algorithmic / Data-driven | Complex B2B funnels needing nuanced credit | Uses behavior and conversion lift to assign credit | Requires clean data and modeling expertise |
When personalization is implemented with disciplined measurement, teams can close the loop between tailored content and higher-quality pipeline — and free marketers to iterate on messaging rather than rebuild assets from scratch.
Automated Topic Research and the Content ROI Pipeline
Automated topic research turns scattered signals into a predictable content ROI pipeline by scoring ideas against measurable business inputs, then converting high-scoring topics into scheduled work. Start by quantifying search demand, competition, and business relevance; then convert those scores into clear priority bands that feed your editorial calendar. This makes decisions repeatable, defensible, and fast—so teams stop debating what to write and focus on executing content that moves the needle.
Building an Opportunity-Scoring Model
Build a scoring rubric around three core inputs: search volume, difficulty (competition), and business relevance. Typical approach: normalize each input to a 0–100 scale, apply weights aligned to strategy (example: 40% volume, 20% difficulty inverted, 40% business relevance), then compute a weighted sum. Calibration tips: start with equal cohorts, run the model on last 12 months of published posts, compare predicted priority to actual traffic/conversions, and adjust weights where predictions consistently miss.
- Search volume: use keyword tools to estimate monthly demand and normalize to 0–100.
- Difficulty score: invert competition metrics so lower competition gives higher scores.
- Business relevance: score 0–100 based on conversion potential, alignment to product-led goals, or revenue attribution.
| Topic | Search Volume Estimate | Difficulty Score | Business Relevance | Final Priority Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topic 1 (high volume, medium difficulty) | 18,000/mo → 88 | 60 → 40 | 70 | 72 |
| Topic 2 (niche, high relevance) | 900/mo → 20 | 30 → 70 | 95 | 76 |
| Topic 3 (low volume, low difficulty) | 120/mo → 8 | 20 → 80 | 30 | 35 |
| Topic 4 (high conversion potential) | 2,200/mo → 50 | 45 → 55 | 90 | 74 |
| Topic 5 (competitive but strategic) | 12,000/mo → 75 | 80 → 20 | 85 | 60 |
From Score to Calendar: Operationalizing Priorities
Convert scores into scheduling rules so content planning is mechanical and consistent.
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
Ethical, Legal, and Governance Considerations in AI Content
AI-generated content accelerates production but introduces ethical, legal, and operational risks that must be governed proactively. Organizations should treat AI content like any other corporate output: define who is responsible, what standards apply, and how pieces are verified before publication. Practical governance balances editorial discretion, technical controls (e.g., model restrictions, data handling), and auditability so teams can scale without amplifying errors or legal exposure.
Common Risks and Operational Controls
AI content risks cluster around accuracy, IP, bias, personalization, and data protection. Below are common risks with real-world-style examples and controls teams can adopt.
| Risk | Example Impact | Recommended Control | Verification Checklist Item |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factual errors / hallucination | Misinformation in a product guide causing user confusion | Editorial signoff; fact-checking SOP; source-attribution requirements | Confirm citations; cross-check against primary sources; signer initials |
| Copyright infringement | Generated copy mirrors a competitor blog paragraph-for-paragraph | Reuse policy; model prompt constraints; copyright scanner | Run plagiarism check (95%+ original); record model prompt |
| Toxic or biased language | Ad copy contains unintentionally discriminatory phrasing | Bias testing; inclusive-language checklist; sensitivity review | Run automated bias detector; human reviewer clearance |
| Misleading personalization | Email uses inferred user attributes causing privacy backlash | Personalization policy; consent checks; segmentation rules | Verify user consent flags; sample emails reviewed |
| Data privacy breaches | Training on protected customer data leaks PII in outputs | Data governance; allowed-data lists; redaction pipeline | Confirm training data sources; PII scanning logs |
Governance Framework and Policy Template
Start with a concise policy that defines scope, roles, and audit cadence. Essential sections: purpose & scope, acceptable use, data handling, copyright rules, editorial workflows, incident response, and training requirements.
- Chief Content Officer (CCO): final approval authority for policy changes.
- AI Governance Lead: maintains model inventory and risk assessments.
- Editors: enforce editorial signoffs and factual verification.
- Legal/Compliance: reviews high-risk content and incidents.
“`text Policy excerpt: “All AI-assisted content requires documented prompt, data source list, and editor signoff before publishing. High-risk categories (legal, medical, financial) must pass Legal review.” “`
Governance is practical: embed checks into workflows, maintain clear ownership, and train teams so automation scales reliably. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
Conclusion
You’ve seen how pairing clear strategic priorities with targeted automation removes busywork and rebuilds bandwidth for growth — editorial planning aligned to audience intent, repeatable templates for speed, and automated performance audits to iterate faster. Teams that adopt these patterns often cut content production time dramatically while improving engagement: one marketing group shrank edition cycles by half after standardizing templates and A/B testing headlines; another improved organic traffic by focusing AI on topic clusters rather than one-off posts. For clarity, remember these points: – Align topics to business goals so every piece advances measurable outcomes. – Automate repetitive steps (outlines, metadata, distribution) to reclaim creative time. – Measure and iterate with short feedback loops, not bulky quarterly reviews.
If you want practical next steps, start by auditing one content workflow, pick two repetitive tasks to automate, and run a four-week experiment measuring time saved and engagement lift. To streamline that process for teams, platforms like editorial automation tools or consultative services can accelerate setup and governance. For a hands-on option, consider Explore Scaleblogger’s AI content strategy services to book a consult or view service offerings and turn these steps into an actionable roadmap.

