Are you comfortable letting machines write the stories that shape your brand? Many teams accelerate production with automation only to find audiences questioning voice, intent, and trust. Industry conversations around ethical content automation now focus on preserving human judgment while capturing efficiency gains.
Automation can cut repetitive tasks and scale ideas without erasing the nuances that make content believable. Balancing content authenticity with faster workflows requires governance, clear attribution, and iterative human review. A marketing team using template-driven engines might boost output but lose distinct brand tone unless editors intervene at key touchpoints.
- How to design review gates that protect voice without slowing delivery
- Ways to measure authenticity alongside engagement metrics
- Practical guardrails for responsible `AI` prompts and data sources
- When to prioritize human authorship versus automated drafts
Automation should amplify human strengths, not replace them.
Scaleblogger’s approach to automation ethics pairs workflow automation with configurable review controls and attribution tracking, helping teams scale responsibly. The following sections unpack governance models, tooling choices, and tactical workflows that keep content trustworthy while accelerating production. Try Scaleblogger for ethical content automation pilots: https://scaleblogger.com
1 — Why Ethics Matter in Content Automation
Ethics matter because automation scales not only reach and efficiency, but also mistakes and bias. When content pipelines generate hundreds of articles, small errors become systemic problems: factual drift spreads, biased language normalizes, and legal exposure grows faster than teams can audit. The immediate payoff of speed and volume is real, but without guardrails those gains compound hidden costs — reputational damage, regulatory headaches, and erosion of reader trust.
Automation enables clear, practical benefits that change how teams operate:
- Speed and scale: produce drafts, meta descriptions, and content briefs in minutes to support rapid publishing cadences.
- Consistency and localization: enforce brand voice and localized terminology across markets at scale.
- Resource reallocation: free editors to focus on strategy, investigative reporting, and high-impact creative work.
- Data-driven optimization: run A/B tests and iterate faster using `API`-driven metrics and content scoring.
- Cost predictability: reduce per-piece production costs while improving benchmarking and forecasting.
- Misinformation and factual drift: model outputs may hallucinate or reframe facts; over time this creates systemic inaccuracies across an archive.
- Bias amplification: training data reflects social and historical biases; automation can unintentionally entrench harmful language or exclusions.
- Legal and compliance exposure: copyright issues from training data, undisclosed AI-generated content, and sector-specific regulations (health, finance) create liability.
| Risk | Typical Impact | Likelihood | Mitigation Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factual errors | Misinformation, lost credibility | High | Medium |
| Bias in outputs | Brand harm, audience exclusion | High | High |
| Copyright infringement | Legal claims, takedowns | Medium | High |
| Loss of brand voice | Reduced engagement, inconsistent UX | Medium | Low |
| Regulatory non-compliance | Fines, forced disclosures | Low–Medium | High |
2 — Principles for Ethical Content Automation
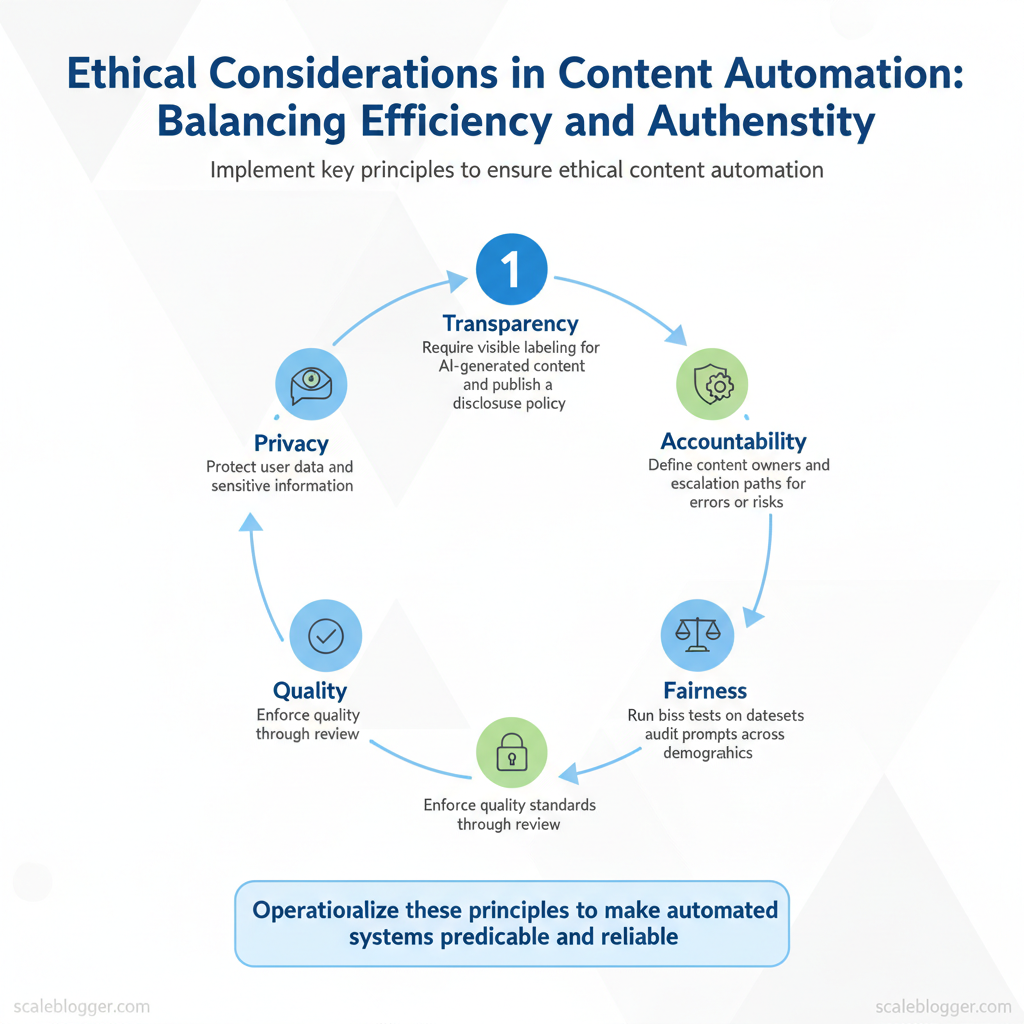
Ethical content automation rests on a few non-negotiable principles that translate directly into controls teams can implement. Start with transparent disclosure, assign clear accountability, test for fairness, enforce quality, and protect privacy—each principle becomes a checklist item in the content pipeline rather than an abstract ideal. When those principles are operationalized, automated systems behave predictably and human reviewers can focus on strategy and nuance.
Practical controls and ownership
- Transparency: Require visible labeling for AI-generated content, maintain `model_card` metadata for each output, and publish a brief disclosure policy on the site.
- Accountability: Define a content owner per topic who signs off on releases and an escalation path for errors or reputational risk.
- Fairness: Run bias tests on datasets, audit prompts across demographics, and include diverse voices in training samples.
- Quality: Use multi-stage human review with clear acceptance criteria, `readability_score` thresholds, and automated plagiarism checks.
- Privacy: Enforce data minimization, mask identifiable data in prompts, and maintain a data inventory for retraining audits.
| Principle | Practical Controls | Responsible Role | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transparency | AI labels on page, `model_card` metadata, disclosure page | Content Lead | % pages labeled, disclosure present ✓ |
| Accountability | Topic owners, incident escalation SOP, post-mortems | Editorial Ops Manager | Time-to-resolution (hrs), incident count |
| Fairness | Bias test suite, diverse training samples, inclusive prompt templates | Data Ethics Analyst | Bias score delta, subgroup error rates |
| Quality | Human review stages, plagiarism scan, SEO checklist | Senior Editor | Acceptance rate, organic CTR |
| Privacy | PII redaction, data retention policy, consent logs | Privacy Officer | Compliance audits passed, data retention days |
Governance checklist — quick-start implementation
Who to involve and how to gate decisions
- Editorial: content owners and senior editors for tone and accuracy.
- Data/ML: model selection, prompt engineering, bias testing.
- Legal/Privacy: consent, retention, regulatory risk.
- Product/Analytics: measurement frameworks and rollout schedules.
3 — Designing Workflows That Preserve Authenticity
Design workflows so automation does the repetitive heavy lifting while humans preserve voice, nuance, and trust. Start by deciding which stages require judgment (topic choice, claims, company positioning) and which can be automated (research aggregation, tag generation, formatting). That clear separation reduces cognitive load for creators and keeps content feeling like it came from real people, not a factory.
Hybrid workflow patterns: when to automate and when to require human input
- Automate for scale: Routine tasks like keyword expansion, meta descriptions, and initial outlines.
- Human for judgment: Claims verification, sensitive topics, legal/compliance checks, and brand voice decisions.
- Shared checkpoints: Use automated drafts with mandatory human sign-off for publishing on brand-sensitive pages.
- Parallel review: Assign SMEs to review factual accuracy while editors handle tone and structure.
- Escalation rules: If an automated confidence score falls below a threshold, route to a human reviewer.
Example `prompt` template for consistent voice: “`text Write a 600-word blog intro in a confident, conversational tone. Use the brand voice pack “Practical Expert.” Avoid jargon; explain terms in one sentence. Include a single CTA at the end. “`
Style guides, voice packs and governance
- Clear rules: Tone (confident, approachable), Jargon (allowed list), Citation (always link primary source).
- Versioning: Tag voice assets (`v1.2`) and require migration tests when updating.
- Roles: Editor owns voice; SME owns factual accuracy; Compliance flags regulated claims.
| Workflow Pattern | Best Use Case | Human Touchpoints | Authenticity Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outline generation + human write | Thought leadership pieces | Author drafts from outline | Low |
| Draft generation + editor polish | Regular blog posts | Editor revises, author approves | Medium |
| Automated SEO + human content update | Evergreen topics | SEO specialist suggests, author edits | Medium |
| Auto-localization + local reviewer | Regional landing pages | Local reviewer adapts tone | High (cultural nuance) |
| Automated summaries + source link checks | Research roundups | Fact-checker verifies links | Medium-Low |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this structure reduces rework and keeps creators focused on storytelling rather than repetitive tasks.
4 — Transparency, Disclosure, and Audience Trust
Transparency must be explicit: tell readers what you used, why it matters, and where judgment replaced automation. Audiences expect clear signals about editorial independence, AI usage, and commercial relationships. When those signals are consistent across formats — blog posts, newsletters, video descriptions — trust becomes measurable and actionable rather than an abstract hope.
Disclosure best practices (how much to reveal and where)
- Be explicit about AI use: State when content was generated or assisted by `AI` and describe the model’s role in one sentence.
- Declare commercial relationships: Disclose sponsorships, affiliate links, and paid placements near the top of the content and again next to the call-to-action.
- Document editorial checks: Note if a human editor reviewed facts and what verification steps were taken.
Placement and visibility rules
Measuring trust: signals and feedback mechanisms
- Quantitative signals: track engagement trends, correction rates, and NPS changes.
- Qualitative feedback: use comment audits, customer support logs, and periodic reader surveys.
- Action loop: surface low-trust signals to editors, run micro-audits, and publish corrections visibly.
| Metric | How to Capture | Monitoring Frequency | Early Warning Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engagement drop per article | GA4: pageviews, avg. time on page, CTR | Weekly | >10% drop vs. 4-week average |
| Correction/edit rate | Editorial audit logs, CMS change history | Monthly | >5% of published pieces |
| Direct user complaints | Support tickets + social mentions aggregator | Weekly | >3 complaints per article/week |
| Automated fact-check fails | Internal fact-check tool / third-party APIs | Daily | Any critical-fact failure flagged |
| NPS / brand sentiment changes | Customer surveys, social sentiment tools | Quarterly | ≥5-point NPS decline |
Clarity in disclosure reduces friction with readers and speeds corrective action when trust falters. When implemented consistently, these practices let teams scale content while keeping audience confidence intact. For organizations building automated pipelines, integrating disclosure flags and these monitoring hooks into the workflow ensures transparency without slowing production—an efficient way to scale responsibly.
For teams ready to operationalize this, consider how your content pipeline surfaces disclosure metadata and trust metrics to editors; it’s the difference between post-hoc apologies and proactive integrity.
5 — Tools, Tests and Metrics for Ethical Automation
Automation must be measured like any production system: tests gate output, monitors detect drift, and audit trails assign accountability. For content pipelines that use AI, build a layered testing strategy that includes factuality, bias, copyright, toxicity, and SEO/spam checks; each should be automatable, have clear pass thresholds, and trigger escalation when thresholds are violated.
Start with concrete, automation-friendly checks:
- Factuality checks: run claims through a fact-checking API or a knowledge-base match; require ≥90% claim-match confidence for publish.
- Bias tests: run demographic parity or equalized odds metrics per content dimension; flag >10% disparity for human review.
- Copyright scans: run plagiarism/similarity and require <15% exact-match across web/corpora before publish.
- Toxicity: apply a safety classifier with a conservative threshold (e.g., toxicity probability >0.2 → hold for editor review).
- SEO/spam detection: run spam/keyword-stuffing heuristics and require readability and organic keyword density within bounds.
pseudocode for a publish gate
if factuality_score < 0.9: escalate('fact-check queue') elif toxicity_score > 0.2: escalate(‘safety review’) elif copyright_similarity > 0.15: escalate(‘copyright review’) else: publish() “`Monitoring and continuous improvement: build a dashboard that tracks KPIs and an immutable audit trail.
| Test | Purpose | Representative Tools | Integration Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factuality checks | Verify claims vs. KB/web | ClaimBuster, Google Fact Check Tools, OpenAI Evals | Medium |
| Bias / fairness | Measure demographic parity | IBM AI Fairness 360, Fairlearn, Aequitas | Medium |
| Copyright similarity scans | Detect text duplication | Copyscape ($5+), Turnitin (institutional), Grammarly plagiarism (paid) | Low |
| Toxicity / safety checks | Filter abusive content | Perspective API (free tier), Hugging Face Detoxify, OpenAI content filters | Low |
| SEO / spam detection | Detect keyword stuffing, spam | SEMrush (paid), Surfer SEO, Moz Pro | Medium |
| Hallucination rate measurement | Track unsupported assertions | OpenAI Evals, Human-in-the-loop review tools | High |
| Privacy / data-leak detection | Prevent PII exposure | Microsoft DLP, Google Cloud Data Loss Prevention | High |
| Regression & performance tests | Ensure model behavior stable | CI with unit tests, MLflow, Weights & Biases | Medium |
| Readability & style | Maintain brand voice | Hemingway API, Readable.com, Grammarly | Low |
| Accessibility checks | Ensure inclusive content | Axe, WAVE, Tenon | Low |
Practical governance requires escalation rules that are deterministic, dashboards with clear owners for each KPI, and immutable logs for every publish decision. When teams implement these controls, content velocity increases because fewer manual checks are surprises and more decisions are made at the team level. For organizations seeking to scale, consider embedding these checks into the content pipeline or using an AI content automation partner to handle orchestration and reporting.
📥 Download: Ethical Content Automation Checklist (PDF)
6 — Future-Proofing: Policy, People and Technology
Future-proofing content systems means building governance, skills, and modular tech so decisions are fast, auditable, and adaptable. Start with a short-cycle policy and skills roadmap that scales into organization-wide controls: a 30-day pilot to validate risks, a 90-day expanded pilot to tune controls, a 180-day operational rollout, and a 365-day maturity review that ties ethics to KPIs. Simultaneously staff the right roles, run recurring training, and use disciplined vendor selection to avoid vendor lock-in and compliance gaps.
Staffing, training and vendor selection
- Chief AI Content Owner: accountable for policy and outcomes, cross-functional decision maker.
- Data Steward: ensures datasets are documented, labeled, and privacy-reviewed.
- Content Operations Lead: runs the pipeline, release cadence, and incident triage.
- Learning & Development Partner: builds training modules and assessment.
- Core capability: documented APIs, exportable content, and rate limits.
- Governance features: audit logs, explainability metadata, and model versioning.
- Security & privacy: SOC2/GDPR posture and data retention controls.
- Integration ease: connectors to CMS, analytics, and CI/CD pipelines.
Outline milestones, owners, and success criteria for ethical automation maturity over 1 year
| Timeframe | Milestone | Owner | Success Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 days | Policy baseline + pilot scope defined | Chief AI Content Owner | Pilot plan, risk registry, pilot data sanitized |
| 90 days | Pilot expanded to 2 product lines | Content Operations Lead | 2 pilots live, audit logs enabled, bias checks passing |
| 180 days | Platform controls implemented | Data Steward | Model versioning, access controls, rollback tested |
| 365 days | Organizational rollout + KPI alignment | Exec Sponsor | Automated audits, content KPIs tied to ethics metrics |
| Ongoing reviews | Quarterly governance reviews | Governance Board | Updated playbooks, incident response tested, compliance verified |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
Conclusion
Balancing speed and trust in content production is a practical — not philosophical — challenge. Embrace automation where it saves time, but pair it with human-led guardrails that preserve voice and intent. Teams that treated AI as a first draft saw content velocity improve without sacrificing audience trust; likewise, editorial frameworks that require clear attribution and a review checklist reduced brand drift. Focus on measurable outcomes: shorten review cycles, maintain consistent tone, and track engagement changes after automation is introduced.
A few concrete actions to put into practice now: – Define editorial guardrails: publishable tone, allowed content types, and a mandatory review step. – Measure audience impact: compare engagement, dwell time, and sentiment before and after rollout. – Pilot with a small workflow: iterate rapidly and scale only after meeting trust and quality targets.
For teams looking to streamline pilot programs and keep ethical control over automation, platforms like Try Scaleblogger for ethical content automation pilots can accelerate setup while preserving editorial oversight. Start a focused pilot, track the metrics above, and expand the program only when the data shows stable or improved audience trust.

