Can your content program prove impact without drowning in vanity numbers? Many teams track clicks and pageviews but fail to connect those signals to revenue, retention, or audience growth—leaving leadership unsure which efforts deserve scaling. Measuring the right content performance metrics and applying consistent benchmarking lets teams prioritize work, justify budgets, and iterate faster.
Across the next seven metrics, readers will learn how to:
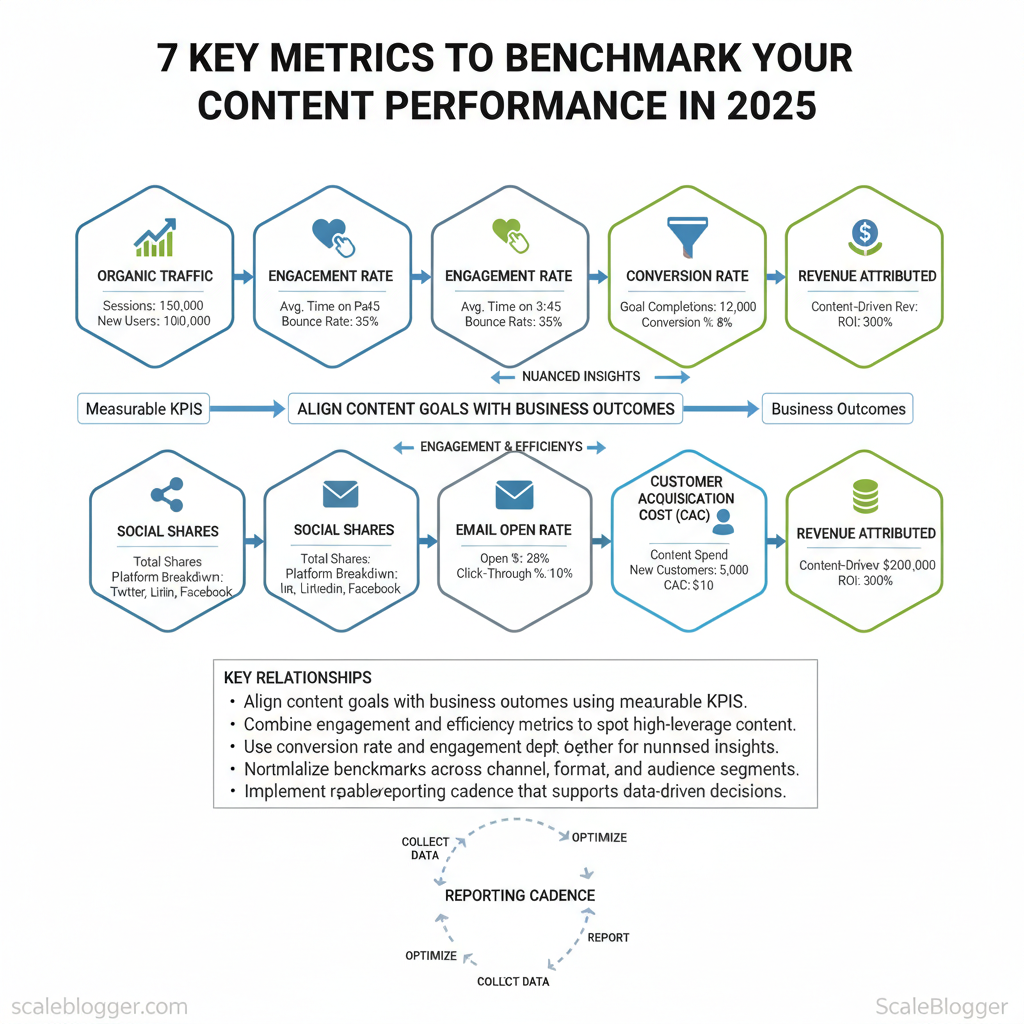
- Align content goals with business outcomes using measurable KPIs.
- Combine engagement and efficiency metrics to spot high-leverage content.
- Use `conversion rate` and `engagement depth` together for nuanced insights.
- Normalize benchmarks across channel, format, and audience segments.
- Implement a repeatable reporting cadence that supports data-driven decisions.
The Importance of Content Performance Metrics
Content without measurable outcomes is an opinion dressed as strategy. Measuring performance turns creative effort into predictable business results by showing which topics, formats, and channels actually move the needle. Content metrics are the quantitative signals that answer whether a piece of content attracts attention, engages an audience, and converts that attention into value.
Start with definitions and types so teams speak the same language: Traffic metrics: Visits, unique users, pageviews* — show reach and discovery. Engagement metrics: Time on page, scroll depth, pages per session* — reveal whether content holds attention. Acquisition metrics: Channel source, referral, organic vs. paid* — identify where audiences originate. Conversion metrics: Leads, sign-ups, purchases, micro-conversions* — measure business outcomes tied to content. SEO metrics: Impressions, `CTR`, keyword rankings, backlinks* — connect content to search visibility. Quality & relevance metrics: Content scoring, relevance audits, bounce reasons* — quantify topical fit and user satisfaction. Velocity metrics: Publish frequency, time-to-publish, content backlog* — track throughput and capacity.
Why these matter:
Practical example: a blog post with steady organic impressions but falling `CTR` suggests title or meta mismatch; a 30–40% higher time on page after adding a data visualization indicates format matters for that audience. Content teams should embed `content scoring` into reviews to compare articles on the same scale—topic fit, depth, and outcome.
Automating measurement frees creative teams to iterate faster; tools that provide an automated content scoring framework and predictive signals reduce guesswork and shorten experimentation cycles. For organizations ready to scale, integrating AI content automation with measurement pipelines is a force multiplier—see options for `AI content automation` and how to `Predict your content performance` for frameworks that tie metrics to decisions.
Understanding and operationalizing these metrics shifts content from an art into a repeatable growth lever that teams can optimize continuously. This approach reduces wasted effort while amplifying the content that actually contributes to business goals.
1. Engagement Metrics
Engagement metrics are the primary signal that content actually resonates — they show whether a post stops scrolling, prompts a reaction, or starts a conversation. Track the obvious interactions (likes, shares, comments) alongside behavioral measures (time on page, bounce rate) to get a complete picture of audience intent and content quality. Start by standardizing how you measure each metric (per 1,000 impressions or per 1,000 followers) so comparisons across platforms are meaningful.
- Likes — quick social proof; useful for A/B testing headlines and visuals.
- Shares — amplification and network endorsement; high shares often correlate with referral traffic.
- Comments — depth of engagement and qualitative feedback; valuable for product insights.
- Time on Page — attention metric for long-form content; guides content length and structure decisions.
- Bounce Rate — first-pass relevance; signals mismatch between promise (title/preview) and content delivered.
| Platform | Average Likes (per 1k) | Average Shares (per 1k) | Average Comments (per 1k) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30–80 likes | 1–6 shares | 2–8 comments | |
| 10–40 likes | 2–8 shares | 1–5 comments | |
| 8–20 likes | 1–4 shares | 1–6 comments | |
| X (Twitter) | 5–20 likes | 0.5–3 shares | 0.5–3 comments |
| TikTok | 50–150 likes | 2–10 shares | 3–12 comments |
Operationalizing these metrics requires two practices. First, normalize metrics to the same denominator (per 1k impressions/followers) to compare across platforms. Second, pair quantitative signals with qualitative review: review the top comments to surface topical language and objections. For editorial planning, prioritize metrics by business outcome: use shares and time on page for reach and retention goals, and comments for product discovery or community building.
Pairing consistent measurement with automated dashboards — or leveraging an AI content pipeline to forecast engagement — shortens the feedback loop and lets teams iterate faster. Predict your content performance with tools that combine historical engagement and topic signals to prioritize content with the highest ROI. Understanding these engagement patterns helps teams refine content choices while keeping workflow efficient and focused on impact.
2. Traffic Metrics
Traffic composition determines what content to prioritize, how to measure success, and where to allocate promotion budget. Start by distinguishing the four primary sources — Organic, Direct, Referral, and Social — then map each source to appropriate KPIs and actions. Practically, this means using `GA4` or other analytics to segment sessions by source, tagging campaign links with `UTM` parameters, and aligning content types to the channel that drives growth.
- Segment by source and landing page to spot content that earns organic vs social attention.
- Compare conversion rates by source to decide which traffic to scale.
- Use behavioral metrics (time on page, pages/session) to infer content relevance per channel.
- Create channel-specific content playbooks — SEO-first for organic, amplified creative for social.
| Traffic Source | Advantages | Challenges | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic | High-intent visitors | Slow growth velocity | SEO optimization, topic clusters, internal linking |
| Direct | Strong brand recognition | Ambiguous attribution | Encourage bookmarks, use `short URLs` and campaigns |
| Referral | Third-party credibility | Traffic volume dependent | Guest posts, partnerships, targeted outreach |
| Social | Fast reach and testing | Short session durations | Platform-tailored creative, paid amplification |
Understanding traffic sources this way lets teams prioritize efforts that grow visibility without adding unnecessary complexity. When implemented consistently, this approach reduces wasted spend and surfaces the content that truly moves the needle.

3. Conversion Metrics
Conversion metrics measure how effectively content moves an audience toward a business outcome. Start by defining the action that represents value — a newsletter signup, demo request, purchase, or content upgrade download — then quantify it. Calculating conversion rates is straightforward but doing it consistently and in context is what separates noise from actionable insight.
Common conversion events to track:
- Newsletter signups — first-touch lead capture for nurture sequences.
- Free trial starts — high-intent indicator for SaaS.
- Content downloads — signals content-led demand generation.
- Demo requests — sales-ready qualification.
- Purchases — direct revenue conversion.
- Micro-conversions (time on page, scroll depth) — engagement signals that predict macro conversions.
- Form completions — often tied to lead scoring.
- CTA clicks — immediate indicator of content effectiveness.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Define Goal | Choose the primary conversion (e.g., newsletter signup, demo request). |
| Track Conversions | Instrument events in analytics (GA4, Mixpanel, HubSpot) using `event` and `goal` tracking. |
| Calculate Rate | Use formula `conversions ÷ unique visitors × 100` per page/channel/timeframe. |
| Analyze Results | Segment by source, landing page, device, and campaign; compare against benchmarks. |
Practical example: a blog post with 12,000 unique visitors and 240 newsletter signups has a conversion rate of `240 ÷ 12,000 × 100 = 2%`. Compare that 2% to other posts, to paid acquisition, and to historical trends to prioritize experiments — A/B testing CTAs, changing lead magnets, or revising intent alignment.
Automation and content pipelines help scale these measurements. Platforms that automate event collection and reporting reduce manual errors and accelerate iteration; for teams building that capability, AI content automation like the solutions at Scaleblogger.com can standardize tagging and performance benchmarks. Understanding and operationalizing conversion metrics enables rapid, evidence-driven decisions and clearer ROI on content investments.
4. SEO Metrics
Understanding which SEO metrics matter for content and how they interact lets teams prioritize work that moves the needle. Below are the essential metrics every content team should track, with a concise explanation and why each one drives better decisions.
1. Keyword Rankings
2. Organic Traffic
3. Backlinks
4. Domain Authority (DA/DR)
5. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
6. Engagement Metrics (Bounce Rate / Dwell Time)
| Metric | Average Value | Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Keyword Ranking | Typical top-10 share: 5–15% of tracked keywords | Tech / SaaS |
| Backlink Count | Typical referring domains: 300–2,000 | E-commerce |
| Domain Authority Score | Typical DA/DR: 25–55 (Moz/Ahrefs scale) | Finance / Publishing |
Tracking the right mix of ranking, authority, link, and engagement metrics turns hypotheses into measurable outcomes, so teams can iterate with confidence and scale content production without losing alignment to business goals.
5. Content Quality Metrics
Assessing content quality requires measurable signals that map directly to reader satisfaction and search visibility. Below are seven practical metrics to track, each with a concise explanation and why it matters for editorial decision-making.
1. Readability Score
2. User Feedback
3. Content Depth (Topical Coverage)
4. Visual Appeal and Layout
5. Evidence & Source Quality
6. Engagement Signals
7. Content Scoring and Automation
Track these metrics in tandem rather than in isolation; the combined signal directs smarter edits and resource allocation. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
6. Social Metrics
Social metrics quantify how content resonates and spreads; focusing on the right ones turns noisy dashboards into prescriptive signals for editorial decisions. Below are the essential social metrics to track, why each matters, and practical examples that move conversations into measurable actions.
1. Shares
2. Comments
3. Followers Growth
4. Engagement Rate
5. Impressions & Reach
6. Click-through Rate (CTR)
7. Sentiment & Brand Mentions
8. Save/Bookmark Rate
| Platform | Average Engagement Rate | Average Follower Growth (monthly) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.10% | 0.8% | |
| Twitter (X) | 0.045% | 0.6% |
| 1.10% | 2.5% | |
| 0.54% | 1.2% |
📥 Download: Content Performance Metrics Checklist 2025 (PDF)
7. Customer Feedback Metrics
Collecting customer feedback is not optional — it’s the signal stream that guides product, content, and UX decisions. Start by mapping what you need to learn (satisfaction, friction points, feature requests, advocacy) and match each question to a measurement channel. That keeps feedback focused and reduces noise.
Use a mix of quantitative and qualitative inputs:
- Surveys — structured questions to track trends over time, especially `NPS`, CSAT, and effort scores.
- Comments & support transcripts — rich qualitative context for recurring problems.
- Social listening — discovers sentiment and topical patterns at scale across public channels.
- Behavioral signals — micro-conversions, churn triggers, and engagement dips that correlate with sentiment.
Measure these core metrics and why they matter: Net Promoter Score (NPS) — `(% promoters – % detractors) 100`; good for tracking advocacy trends and predicting referral growth.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) — short, transactional surveys after interactions; useful for pinpointing support or UX issues.
- Customer Effort Score (CES) — measures friction during a task; lower effort correlates with higher retention.
- Qualitative themes — tag free-text responses by topic to quantify recurring issues or feature asks.
- Sentiment trend (social listening) — monitors brand health and amplifies emergent problems before escalation.
- A SaaS product uses a post-onboarding CSAT to reduce churn by 12% after redesigning setup flows.
- A consumer brand tracks social sentiment and spots a packaging issue within 48 hours, avoiding wider returns.
- Automate routing so `promoters` get referral asks and `detractors` get immediate follow-up.
- Use sampling to avoid survey fatigue; trigger surveys on meaningful events.
- Combine qualitative tags with behavioral cohorts to prioritize fixes by impact.
| Tool | Purpose | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Google Forms | Simple surveys, free response export | Free |
| Typeform | Conversational surveys, conditional logic | Free tier; paid from $25/month |
| SurveyMonkey (Momentive) | Scalable survey platform, advanced analytics | Free tier; plans from $25/month |
| Qualtrics | Enterprise experience management, deep analytics | Enterprise pricing (custom) |
| Hotjar | Session recordings + on-site surveys | Free limited; paid from $39/month |
| Zendesk | Support + CSAT surveys, ticket-driven feedback | Support plans from $19/agent/month |
| Intercom | In-app messaging + surveys, routing workflows | Starter from ~$74/month |
| Sprout Social | Social listening, sentiment monitoring | Plans from $99/month |
| Mention | Brand monitoring, alerts, social analytics | Plans from $29/month |
| Delighted (by Qualtrics) | Quick NPS/CSAT/CES surveys, simple integrations | Plans from $49/month |
Integrating feedback into content and product cycles accelerates learning and reduces rework. Use automation to route insights and let teams act on signals rather than search for them. This is why workflows that connect survey output to prioritization boards and content pipelines produce measurable improvements in engagement and retention. For teams scaling content, an AI-powered content pipeline can turn those insights into topic priorities and testable content experiments — consider Scale your content workflow with Scaleblogger for automating that translation from feedback to production.
Conclusion
Across this piece, the practical path forward is clear: map metrics to revenue, stop measuring vanity numbers in isolation, and automate measurement where repetitive tasks eat time. Teams that tie content to specific funnel stages and run small experiments—like A/Bing conversion-focused templates or automating lead attribution—consistently improve qualified leads and retention. If the immediate question is “How do I start?” begin by choosing one content type, defining the downstream KPI, and instrumenting a simple test; evidence suggests iterative learning outperforms big-bang overhauls.
For step-by-step playbooks and templates that make those experiments repeatable, explore the Scaleblogger resources and consider piloting an automated attribution workflow. When ready to scale, start small, measure rigorously, and iterate rapidly. Visit Scaleblogger.com for more insights on optimizing your content strategy.

