Marketing teams lose momentum when evergreen pages quietly slide into decline, while competitors capitalize on timely tweaks. Search visibility erodes not because content was bad, but because content freshness slipped and search engines favored newer relevance signals. Updating the right pages at the right cadence directly moves the needle on SEO rankings, traffic, and conversion velocity.
A pragmatic approach treats `content freshness` as an operational metric: prioritize high-impact pages, schedule regular content updates, and measure ranking shifts against business goals. Industry practitioners observe that small, targeted edits—data refreshes, new internal links, concise CTAs—often outperform wholesale rewrites. Picture a product guide that reclaimed page one after a focused update to specs and examples; the traffic uptick translated to measurable leads within weeks.
This matters for teams balancing limited bandwidth and high expectations. Strategic, repeatable refresh workflows preserve domain authority and protect organic acquisition. The next sections show how to identify priority pages, set update cadences, and track lift without creating constant firefighting cycles.
- How to identify pages where freshness most influences rankings
- Practical signals that trigger immediate content updates
- A simple cadence to keep priority pages current without overwork
- Metrics to prove update ROI in search performance

What Is Content Freshness and How Search Engines Interpret It
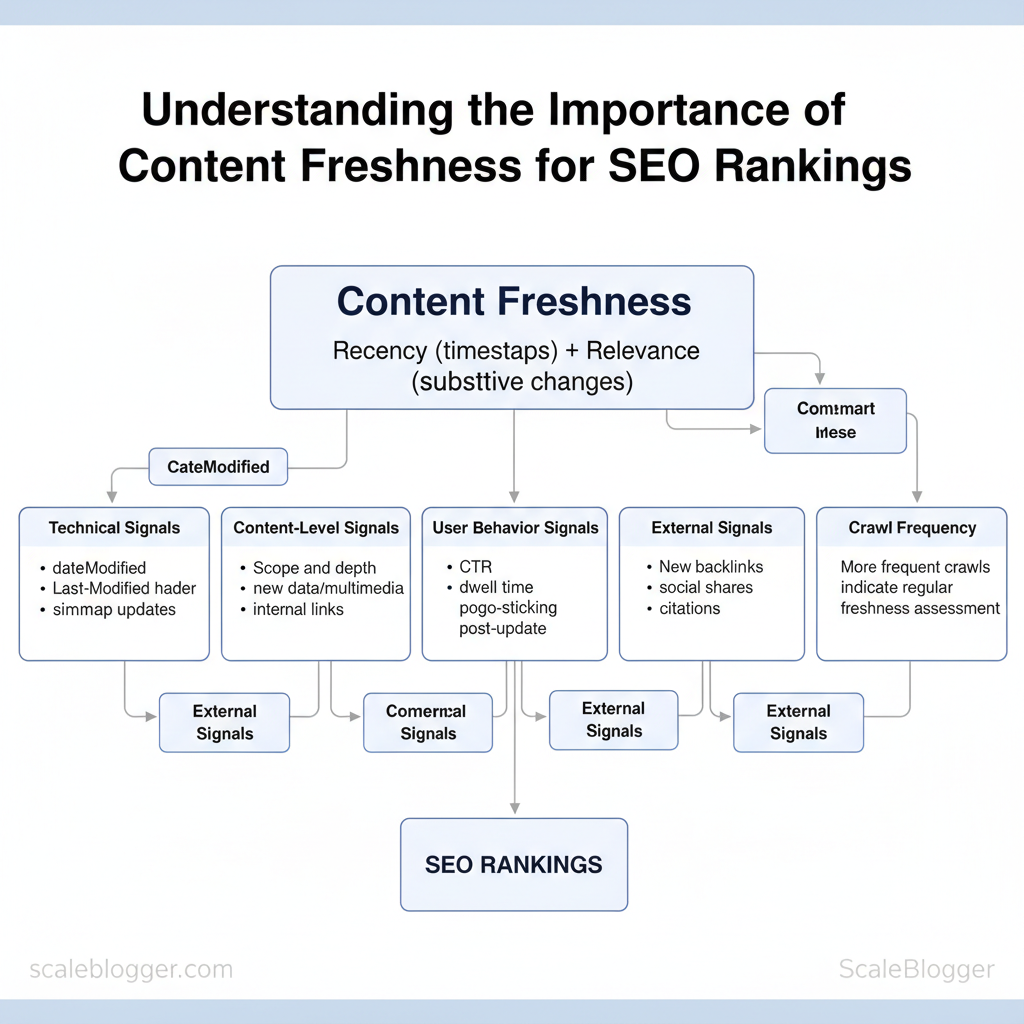
Content freshness describes how up-to-date and relevant a page’s information is to current queries. Search engines treat freshness as a composite signal: they note literal recency (timestamps) but also evaluate whether a page has meaningful, substantive updates that improve user value. Freshness matters more for time-sensitive topics (news, events, product releases) and less for evergreen reference material, yet even evergreen pages benefit from periodic substantive refreshes that reflect new data, examples, or best practices.
Defining content freshness — recency vs. relevance
- Recency (timestamp): Visible indicators like `Last updated` dates or new publish dates tell crawlers and users when content changed.
- Relevance (substantive changes): Added research, new sections, updated statistics, or rewritten conclusions signal true value; cosmetic edits like swapping words or correcting typos rarely move the needle.
- Why cosmetic updates often fail: Search algorithms track change scope and user engagement; trivial edits generate low-impact signals and can even trigger re-crawls without ranking benefit.
Signals search engines use to evaluate freshness
- Technical signals: `Last-Modified` header, visible `datePublished` and `dateModified` structured data, sitemap update timestamps.
- Content-level signals: Scope and depth of changes, added data or multimedia, new internal links that change topical coverage.
- User behavior signals: Changes in CTR, dwell time, and pogo-sticking after an update indicate whether the refresh satisfied users.
- External signals: New backlinks, social shares, and citations after an update validate usefulness.
- Crawl frequency: Pages crawled more often are assessed for freshness more regularly.
| Signal Type | Example | How to detect/update | Estimated SEO Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical (timestamps/structured data) | `dateModified` schema, `Last-Modified` header | Add `dateModified` in JSON-LD, update HTTP headers | Medium–High |
| Content changes (new sections/data) | New research section, updated stats | Compare content diffs; publish substantial additions | High |
| User behavior (CTR/dwell time) | Increased dwell time after update | Monitor GA4/Google Search Console metrics | Medium–High |
| External signals (new backlinks) | Fresh editorial links to updated page | Use backlink tools; outreach for updated content | High |
| Crawl frequency | Shorter crawl interval after updates | Check server logs; update sitemap ping | Medium |
Scaleblogger’s AI-powered content pipeline can automate detection of stale pages and prioritize substantive updates when scaling a blog. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making update decisions at the content-cluster level.
Why Content Freshness Matters for SEO Rankings
Freshness affects where pages appear and how quickly search engines re-evaluate them. For queries tied to time, recent updates often outrank older pages; for evergreen topics, periodic refreshes keep content relevant and prevent gradual ranking decay. Search engines use signals like publish/update timestamps, internal linking to updated pages, and content changes to decide which pages to recrawl and reindex, so systematic freshness is a tactical lever that teams can control to influence visibility and traffic velocity.
Direct ranking benefits and visibility improvements
Fresh updates help with time-sensitive queries, trigger recrawling, and improve ranking signals for prioritized pages. Update behavior should be strategic rather than reflexive: focus on pages that map to high-intent keywords, pages with traffic decline, and those ranking on page two where a small boost moves them to page one.
- Freshness for time-sensitive queries: News, announcements, and regulatory changes demand immediate updates to retain or capture rankings.
- Recrawl and re-evaluation: Small, meaningful content changes and updated structured data increase the likelihood of a quick recrawl.
- Prioritization rule-of-thumb: Refresh pages that drive organic conversions, rank between positions 5–20, or show sustained CTR declines.
| Content Type | Benefit from Freshness | Recommended Update Cadence | Quick Update Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| News / announcements | High — ranking depends on timeliness | Real-time / daily during event | Add new facts, timestamps, canonicalize live posts |
| Evergreen how-to guides | Medium — prevents decay, improves UX | Every 6–12 months | Update steps, add new screenshots, refresh examples |
| Product / pricing pages | High — converts and needs accuracy | Weekly to monthly (as changes occur) | Sync pricing, update specs, refresh schema markup |
| Industry trend posts | Medium-high — authority signal for topical queries | Quarterly | Add new data points, expert quotes, link to new studies |
| Seasonal content | High seasonally — relevance spikes at predictable times | Annually + pre-season refresh | Update dates, imagery, seasonal CTAs, link to current offers |
Indirect benefits: user engagement and authority
Fresh content improves click-through rates when titles and snippets reflect current facts, and it increases dwell time when updates add value instead of padding. That combination strengthens behavioral signals—lower bounce, higher pages-per-session—that search engines consider when assessing authority. Measure ROI by tracking ranking movement, organic sessions, and conversion rate before and after updates. Use A/B tests on meta titles/descriptions to prove CTR lifts and maintain a content scoring dashboard to prioritize future updates.
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making content maintenance predictable and measurable.
How to Audit Your Content for Freshness Opportunities
Start by looking for pages that once performed well and now show declining engagement; those are the fastest wins. Assemble a small toolkit, export historical performance, and score URLs against three dimensions — traffic trend, topical relevance, and effort to update — then run quick experiments on high-score pages. This approach surfaces where small edits or new sections return disproportionate traffic.
Preparing tools and metrics (what to track)
Gather these tools and pull comparable date ranges (90/180/365 days) so you can see seasonal shifts versus long-term decline. Export raw CSVs for large sites and use sample-based verification when exports hit size limits. Focus on metrics that show user intent and engagement: impressions, clicks, average position, sessions, % new users, bounce/engagement rate, conversions, time on page, and backlink counts.
Expected outcome: a sortable dataset that reveals decline patterns and content age at a glance. Troubleshoot export limits by batching URLs or using API pulls; Screaming Frog and GA4 APIs are particularly useful for large sites.
| Tool | Primary Use | Metrics to Pull | Free / Paid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Search performance | Impressions, clicks, avg position, queries | Free |
| Google Analytics / GA4 | User behavior & conversions | Sessions, engagement rate, conversions, time on page | Free |
| Screaming Frog | Site crawling & metadata | Status codes, meta titles, canonical, word count | Free (500 URLs) / Paid (£209/year) |
| Ahrefs | Backlink & organic research | Organic traffic estimates, backlinks, keywords | Paid (starts $99/month) |
| Semrush | Keyword & competitive analysis | Keyword trends, positions, visibility % | Paid (starts $129.95/month) |
| Moz Pro | Keyword + link metrics | Keyword difficulty, page authority, backlinks | Paid (starts $99/month) |
| Sitebulb | Technical crawl with reports | Crawl depth, log analysis, content issues | Paid (desktop licenses) |
| SurferSEO | Content gap & on-page suggestions | Content score, TF-IDF signals, keyword density | Paid (starts ~$59/month) |
| ContentKing | Real-time monitoring | Content changes, indexability alerts | Paid (starts €79/month) |
| DeepCrawl | Enterprise crawling | Indexability, render issues, sitemap coverage | Paid (enterprise pricing) |
Prioritization framework: traffic decline, relevance, and effort
Score each URL 1–10 on three axes and multiply for a composite prioritization score.
Scoring example: a page with 50% traffic drop (8/10), strong relevance (9/10), low effort (9/10) → composite ≈ 8.8, immediate edit.
Practical triage steps:
Expected outcome: a prioritized backlog that converts a few hours of work into measurable traffic recovery. Scaleblogger.com’s AI content automation can accelerate bulk updates and A/B test headline or section changes for prioritized pages when scaling the workflow. This method reduces guesswork and gets teams editing the right pages fast.
Step-by-Step Process to Update Content for Maximum SEO Gain
Start by treating content updates as a product cycle: pick the highest-impact pages, apply targeted edits, validate technically, publish, and measure. Updates that follow a repeatable workflow recover traffic faster and reduce rework because each change is tracked, tested, and tied to a hypothesis about user intent or rankings.
The update workflow (planning, editing, publishing, monitoring)
Log every change in a changelog: date, author, edit summary, prior metrics, expected outcome, and follow-up review date. Use `CMS changelog` entries and a master spreadsheet for auditability. Technical checklist before republish should include `robots.txt`/indexing, canonical verification, structured data validation, and URL redirects.
| Stage | Estimated Time | Responsible Role | Deliverable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selection & prioritization | 1–2 days | Content Strategist / Analyst | Prioritized page list with KPIs |
| Research & outline | 2–4 days | SEO Researcher / Writer | Keyword map + outline + intent notes |
| Content edits & asset creation | 3–7 days | Writer / Designer | Updated draft, images, charts |
| Technical QA & SEO checks | 1–2 days | SEO Specialist / Developer | On-page fixes, schema, redirects |
| Publish & monitor | 7–30 days | Publisher / Analyst | Published page + performance dashboard |
Quick wins and high-impact edits (what matters most)
- Meta retargeting: Update title and meta description to match top-of-SERP intent.
- Header restructuring: Add H2s that target related long-tail queries.
- Fresh data: Replace stale stats and include dated references for recency.
- Internal linking: Insert 2–3 contextual internal links to authority pages.
- Featured-snippet framing: Add concise `definition` paragraphs and list formats.
- Before: Title “Project Management Tips” — After: Title “Project Management Tips for Remote Teams — Tools & Templates” (CTR improvement expected).
- Before: 800-word overview — After: 1,600-word deep dive with FAQ and step checklist (dwell time uplift expected).
Understanding these steps makes iterative updates predictable and measurable; teams that adopt them recover lost visibility faster while keeping editorial quality consistent. When executed reliably, this process shifts maintenance from firefighting to continuous growth.
Measuring Impact and Iterating Post-Update
Measure immediately and plan to iterate: start by tracking primary SEO and engagement signals in short windows, then validate with longer-term trends before making major structural changes. Early lifts in impressions or CTR are useful indicators; durable gains in sessions, average position, and backlinks across 30–90 days confirm whether the update succeeded. Use short windows to catch regressions quickly and long windows to assess sustained ranking behavior.
Metrics to monitor and timing for evaluation
Monitor a focused set of primary and secondary KPIs on a schedule that separates early detection from reliable validation.
- Primary KPIs to watch
Industry analysis shows short-term volatility is normal after algorithm-sensitive updates; treat the first 7–14 days as signal-check, not final verdict.
Iteration loop — when to rework, expand, or retire content
Decision thresholds and repeatable next steps reduce guesswork.
- Decision thresholds
“`text Rewrite Brief Template: – Target URL: – Objective: (Improve CTR / Intent match / E-E-A-T) – Primary keywords: – Competitor gap list: – Top 3 action items: “`
Preserve SEO value when retiring by 301-redirecting to the best topical page, updating internal links, and retaining structured data where applicable. Use automation to track post-redirect drops and recover any lost internal equity.
📥 Download: Content Freshness SEO Checklist (PDF)
Scaling a Content Freshness Program Across Your Site
Scaling a content freshness program requires shifting from ad-hoc updates to predictable, measurable operations. Start by defining clear roles and handoffs, then bake automation into the cadence so routine signals (traffic dips, outdated facts, algorithm shifts) trigger low-friction updates. What separates teams that scale smoothly from those that stall is governance that delegates decisions to the lowest competent level, plus tooling that reduces manual overhead while preserving editorial judgment.
Organizational roles, cadences, and governance
Begin with a simple RACI that aligns authority to outcome: who identifies update candidates, who verifies facts, who rewrites, who publishes, and who measures impact. Recommended review cadences vary by content type:
Role responsibilities and handoffs:
Governance and versioning best practices:
- Bold policy: require changelogs for edits older than 30 days.
- Versioning: use CMS drafts with timestamped edit notes; store exported snapshots for rollback.
- Approval gates: allow minor updates to skip full review if they meet criteria (≤150 words, no structure change).
| Team Size | Monthly Pages Updated | Recommended Tools | Estimated Monthly Effort (hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solo creator | 10–30 | Google Sheets, `Yoast` or `RankMath`, Zapier | 20–40 |
| Small team (2–5) | 50–150 | Ahrefs, Google Search Console, Airtable, Zapier | 80–200 |
| Mid-size (6–20) | 300–800 | SEMrush, Contentful/WordPress, Looker Studio, Cloud functions | 400–1,200 |
| Enterprise (20+) | 1,000–5,000+ | Custom CMS + APIs, Data warehouse, Enterprise SEO platforms (Conductor), CI/CD | 1,500–6,000 |
Automation and tooling to streamline updates
Automation removes repetitive work but introduces trade-offs; apply it where signals are reliable and low-risk. Typical automation opportunities:
- Detection: scheduled exports from `Google Search Console` to detect CTR drops.
- Prioritization: traffic + conversion delta scoring in a spreadsheet to rank update candidates.
- Publishing: CMS APIs to push approved updates, with automated pre-publish SEO checks.
Scheduled GSC export -> Google Sheet -> Airtable -> Slack alert
When not to automate: any update that changes intent, requires brand voice decisions, or touches legal/compliance content must include human review. Automation should surface candidates and perform boilerplate fixes (meta tags, canonical updates, schema corrections), not author judgment. Consider platforms like Scaleblogger.com for AI-powered pipelines that handle detection and scheduling while preserving editorial control—use such tools to accelerate the pipeline, not replace the editor.
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
Conclusion
Refreshing evergreen pages on a predictable cadence, measuring a small set of core metrics, and delegating ownership to a single content owner prevents the slow erosion of search visibility—those are the practices that consistently reverse decline. Teams that ran quarterly content audits and prioritized low-effort, high-impact updates reclaimed traffic within weeks, while editorial squads that tracked ranking momentum and conversion lift avoided repeat regressions. Ask yourself: who will own the audit, how often will you update priority pages, and what small A/B test will prove the value? Assign one person, schedule recurring audit sprints, and start with a single hypothesis-driven edit to build momentum.
To streamline these steps, create a repeatable audit checklist, measure before-and-after outcomes, and automate update workflows where possible so human effort focuses on judgment, not manual tracking. For teams looking to automate that workflow and scale updates without losing control, Automate content audits and scale updates with Scaleblogger is one practical option that integrates auditing, prioritization, and rollout. Take those three actions this week: schedule the next audit, pick five priority pages, and instrument one metric to track lift—those small moves compound into lasting visibility gains.

