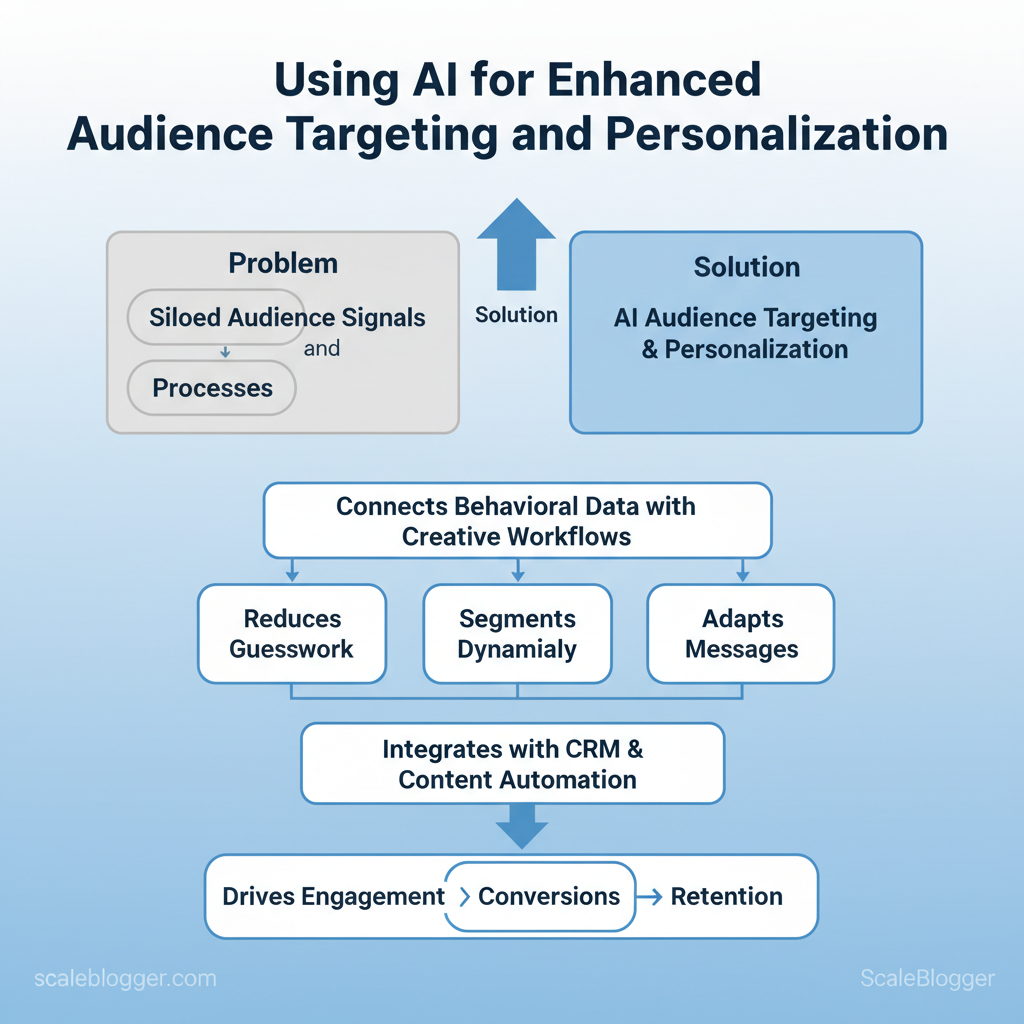
Marketing teams still spray broad campaigns and hope for resonance, burning budget on content that never finds the right reader. Industry analysis shows that targeted personalization separates high-performing campaigns from the rest, but execution stalls when audience signals remain siloed and manual processes dominate.
The solution lies in AI audience targeting and personalization in marketing that connect behavioral data with creative workflows. These systems reduce guesswork by scoring intent, segmenting dynamically, and adapting messages in real time. When paired with `CRM` and content automation, content marketing AI converts insights into tailored journeys at scale.
That shift matters because relevance drives engagement, and engagement drives measurable lift in conversions and retention. Picture a mid-market ecommerce brand that doubles email open rates after replacing static segments with predictive propensity scores and AI-led subject-line tests.
Scaleblogger.com helps operationalize these patterns, turning audience signals into repeatable content plays that integrate with existing martech stacks. The next sections show practical steps to map signals, choose models, and deploy personalized content without bloating workflows.
Prerequisites & What You’ll Need
Start with the data and systems that let personalization and AI-driven content actually act on users. For effective audience targeting and automated personalization you need clean event-level analytics, persistent user attributes, an AI model or service you can call programmatically, and a test-and-measure layer to validate impact. Below are concrete artifacts to assemble before building the pipeline and the practical skills you’ll use to operate it.
- Event-level analytics: instrument pageviews, clicks, conversions, and custom events so each user action is queryable.
- User identity store: a CRM or unified profile that maps device IDs, emails, and lifetime attributes.
- AI access: either an off‑the‑shelf API (LLM or recommendation engine) or an on-premise model with inference endpoints.
- Testing & experiment platform: A/B or feature-flagging system to measure lift and guardrails.
- Content delivery: CMS that supports programmatic personalization or edge rules.
Helpful skills and quick tools
- SQL proficiency: for aggregations and segments.
- Basic Python or no-code connectors: for ETL and model calls (`pandas`, `requests`).
- Familiarity with event schemas: `client_id`, `user_id`, `event_name`, `timestamp`.
- Experiment design basics: sample size and power calculations.
- Optional: familiarity with MLOps or feature stores for production-grade models.
| Tool/Resource | Role in workflow | Minimum requirement | Why it’s needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Analytics 4 (GA4) | Behavioral analytics, event store | GA4 property, event schema | Event-level tracking, sessionization |
| Segment (Twilio Segment) | Customer data routing | Workspace + sources | Identity stitching, stream to destinations |
| HubSpot CRM | User attributes & outreach | Free CRM tier available | Persistent profiles, email sync |
| Salesforce | Enterprise user database | Sales Cloud license (custom pricing) | Centralized user records, B2B mapping |
| Braze | Cross-channel personalization | Custom pricing | Real-time segmentation, message orchestration |
| Optimizely (Full Stack) | Feature flags & A/B testing | SDKs for web/mobile | Experimentation and rollout control |
| VWO | A/B testing and heatmaps | Starting tiers (paid) | Visual tests and behavioral analysis |
| WordPress + WP Engine | CMS with personalization plugins | Hosting plan + personalization plugin | Programmatic content rendering |
| Contentful | Headless CMS with API delivery | Team plan (paid) | Structured content, API-first delivery |
| Recombee | Recommendation engine | API access (tiered pricing) | Personalized content/recommendations |
Use the checklist above to confirm readiness before building or automating workflows—this reduces rework and speeds reliable experimentation. Understanding these pieces helps teams move faster without sacrificing measurement or compliance.
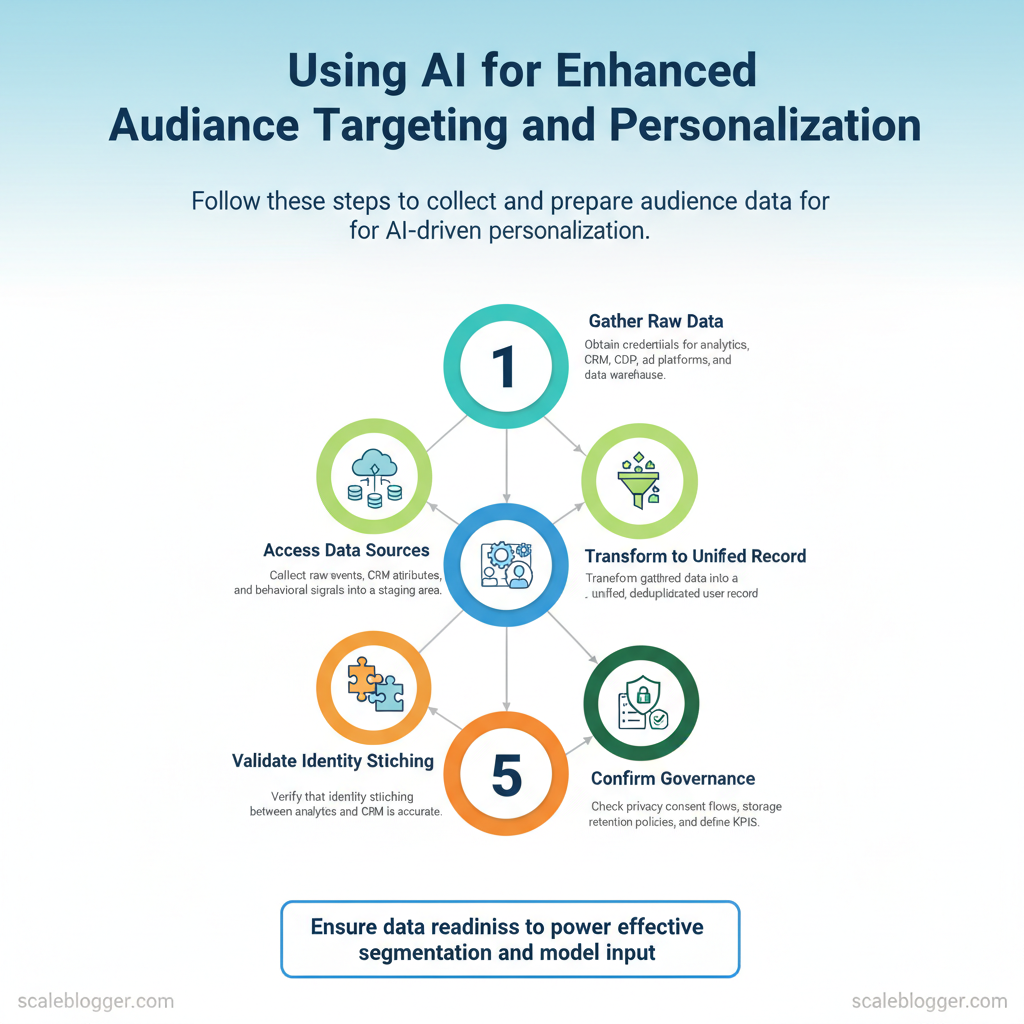
Step 1 — Collect and Prepare Audience Data
Start by treating audience data as the single source of truth for personalization and topic selection. Gather raw events, CRM attributes, and any behavioral signals into a staging area, then transform them into a unified, deduplicated user record ready for segmentation and model input.
Prerequisites
- Access: credentials to analytics, CRM, CDP, ad platforms, and data warehouse
- Compliance checklist: documented consent records and PII-handling rules
- Storage: S3, BigQuery, Snowflake, or a CDP for staging and unified profiles
- Data export tools: analytics export, CRM CSV/SQL, event streaming
- ETL: dbt, Apache Airflow, or an ELT service
- Enrichment: third-party enrichment API or in-house logic
- Quality checks: dedupe scripts, schema validators
Expected outcome: consolidated raw files that mirror source fidelity and retain original identifiers for reconciliation.
Example unified schema: “`json { “user_id”: “uuid”, “email_hash”: “sha256”, “first_seen”: “2024-01-01T12:00:00Z”, “last_seen”: “2024-11-10T08:00:00Z”, “interest_topics”: [“ai-automation”,”seo”], “lifecycle_stage”: “active” } “`
Expected outcome: a repeatable mapping that prevents attribute sprawl and supports downstream joins.
- Match on primary IDs: prefer `user_id`; fallback to `email_hash` then persistent cookies
- Normalize values: lowercase strings, consistent date formats, canonical UTM keys
- Resolve conflicts: use last-touch or confidence-weighted merge rules
- Enrich: append industry, company size, or topic probabilities where missing
- Consent: attach `consent_status` and drop or mask PII when consent is absent
Market practice shows downstream models and segments fail faster from bad inputs than from imperfect features.
Practical tip: run a quick profiling job (count nulls, uniques, percent duplicates) after each transformation; aim for <5% critical-field nulls.
Integrate this prepared dataset into your content pipeline (manual or via platforms like `Scale your content workflow` at https://scalebloggercom) so content decisions derive from reliable, unified audience signals. Understanding and enforcing these steps lets teams generate targeted content faster and with lower risk.
Step 2 — Build AI Segments
Start by choosing a modeling approach that matches the business question and activation channel. Pick clustering when you need discovery and flexible groups; pick supervised models when you have labeled outcomes to predict; pick rule-based for immediate, transparent segments; and pick embedding similarity when semantic matching or content-to-user alignment matters. Use behavioral signals and content features together, validate quantitatively and qualitatively, then export segments in standard formats for real-world activation.
Prerequisites
- Data availability: user events, content metadata, engagement metrics
- Labeling budget: click/conversion labels for supervised tasks, or manual review time for clusters
- Activation targets: ad platform, email tool, CMS or personalization layer
- Feature store or DB (Postgres, BigQuery)
- Modeling stack (`scikit-learn`, `XGBoost`, `faiss` for embeddings)
- Export pipelines (CSV/JSON, API webhooks)
- Validation dashboard (sample lists, holdout A/B framework)
| Approach | Best use cases | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clustering (k-means, hierarchical) | Discovering personas, exploratory segmentation | Quick grouping, unsupervised, finds latent groups | Sensitive to scaling, needs feature tuning |
| Supervised classification (XGBoost, logistic) | Predicting conversions, churn risk | Predictive accuracy, interpretable features, scoring probability | Requires labeled outcomes, potential overfit |
| Rule-based / hybrid | Compliance segments, high-precision marketing lists | Transparent rules, fast to deploy, easy to audit | Hard to scale, brittle for complex behavior |
| Embedding-based similarity | Content personalization, semantic matching | Captures meaning, cross-language resilience, good for cold-start | Needs pre-trained models, compute for nearest-neighbor search |
Example export (CSV snippet) “`csv segment_id,user_id,score,source engaged_readers_v1,12345,0.82,supervised topic_ai_affin,67890,0.67,embedding “`
Warnings: avoid tiny segments (<0.1% of population) for paid activation; regularize features to avoid dominance by high-frequency events. When implemented correctly, this method produces operational segments that map directly to channels and measurable outcomes. Understanding these choices lets teams operationalize personalization without overcomplicating the stack.

Step 3 — Design Personalized Content Experiences
Prerequisites
- Audience segments defined: demographic, behavioral, and intent buckets exist.
- Tracking in place: first-party event data and identifiers available (`user_id`, `session_id`).
- Channel list finalized: blog, email, landing pages, paid social, and in-app messaging.
- Segmentation tool: CDP or analytics with audience exports.
- Template library: modular content blocks for each channel.
- Personalization engine: supports `tokens`, conditional logic, and fallbacks (can be a rules engine or an automated workflow).
- Testing and monitoring: A/B framework and performance tracker.
Create reusable content templates per channel
- Blog template: Headline (search intent) + Intro (hook for segment) + Key takeaways + CTA.
- Email template: Personalized subject + Benefit-led preview + Single CTA.
- Landing page template: Segment headline + Social proof + Prompt to act.
Implement personalization tokens and fallbacks
Handle users in multiple segments
- Priority rules: Explicit intent beats implicit — prioritize recent product-signup triggers over long-term demographic tags.
- Composite journeys: Combine templates with a primary and secondary path for overlap cases.
- Frequency caps: Limit messaging to avoid over-personalization fatigue.
Suggested assets to build: a segment-to-template matrix, a token reference sheet, and an overlap-priority table. Scaleblogger’s AI content automation can accelerate template generation and token mapping if automating at scale. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing relevance. When implemented cleanly, personalized experiences scale while keeping content creation efficient and measurable.
Step 4 — Activate Personalization Across Channels
Personalization only works when data, identity, and delivery are tightly integrated; start by deciding where decisions run (server vs client) and follow through with reliable syncs, clear audience definitions, and robust QA. Make the architectural choice first, map identifiers consistently, then deploy audience definitions to each channel with monitoring hooks so personalization stays accurate at scale.
Choose server-side or client-side personalization
What to expect: server-side reduces flicker and data leakage; client-side improves perceived speed. Use both when user experience and data sensitivity differ by touchpoint.
Sync cadence and user ID mapping
Configure audiences per channel
- Channel-specific tuning: adjust thresholds by channel — what qualifies as “high intent” in email may be different for homepage banners.
- Propagation: export audience definitions to DSPs, ESPs, CMS, and in-app feature flags via the identity layer.
QA and monitoring after deploy
- Smoke tests: verify identity resolution and a sample of variant renders across devices.
- Realtime monitoring: track decision latency, error rates, and coverage % of identified users.
- Feedback loop: log delivered variants and short-term engagement to validate lift and feed back into models.
Industry analysis shows that systems with reliable identity mapping reduce personalization mismatch errors significantly.
Practical tools include feature-flag systems, data pipelines, and orchestration platforms; consider integrating an AI content automation pipeline like Scaleblogger.com when scaling content variations across channels. Getting these integration pieces right lets teams deploy personalized experiences quickly and keep them accurate as the audience evolves.
Step 5 — Test, Measure, and Iterate
Start by treating every change as an experiment: define a precise hypothesis, select the right metrics, and decide the sample size before touching creative or model parameters. A strong hypothesis looks like: “Personalized headings that include user intent segments will increase organic CTR by 10% within 6 weeks.” That clarity forces measurable design, prevents post-hoc rationalization, and speeds decision-making.
Practical templates and formulas “`text Minimum sample size (approx): n = (Zα/2 + Zβ)^2 * (p1(1-p1)+p2(1-p2)) / (p1-p2)^2 Lift calculation: Lift% = (Metric_treatment – Metric_control) / Metric_control * 100 “`
| Traffic Tier | Test cadence | Model retrain frequency | Content refresh frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low traffic (<100k monthly) | Every 8–12 weeks, pooled tests | Every 12–24 weeks, quarterly reviews | Every 24–36 weeks, evergreen updates |
| Medium traffic (100k–1M monthly) | Every 4–8 weeks, segmented A/B tests | Every 8–12 weeks, feature-level retrain | Every 12–24 weeks, performance-driven updates |
| High traffic (>1M monthly) | Continuous experiments, weekly rollouts | Every 4–8 weeks, retrain with fresh logs | Every 8–12 weeks, prioritized by ROI |
Operational tips and troubleshooting
- Instrumentation: ensure GA4, server logs, and experimentation platform are integrated before tests.
- Bias warning: avoid peeking—interim stops inflate false positives.
- When lift is small: combine microtests into meta-analysis or expand sample by time/segments.
- Scaling automation: use an AI content pipeline (for example, an AI content automation platform) to push prioritized updates once tests pass.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When personalization and automated matching fail to behave, start with data alignment: most failures trace back to mapping, consent blocks, or sync delays rather than model “mystery.” Diagnose problems systematically—verify identifiers, confirm data flows, and watch for signs of model drift—so fixes are surgical, repeatable, and measurable.
Practical checks and quick commands
- Quick mapping check: export sample keys and run `diff` or a small Python join.
- Consent check: search for `consent` or `gdpr` flags in the pipeline logs.
- Sync lag: inspect timestamps—if `last_updated` differs by >5 minutes, investigate ETL.
Normalize keys before join
df[’email_norm’] = df[’email’].str.lower().str.strip() “`When integrations are complex, automated pipelines like those provided by modern AI content automation platforms help reduce human error; tools that combine monitoring and retraining lower operational overhead. Understanding these checks and automating them quickly restores reliable personalization and consistent model performance.
📥 Download: AI Audience Targeting and Personalization Checklist (PDF)
Tips for Success & Pro Tips
Start by treating AI-driven content workflows as a product: focus on measurable improvements to quality, velocity, and relevance rather than automating everything at once. Begin with the highest-impact slice of work, build transparent model documentation, and enforce safety and privacy guardrails so teams can move fast with confidence.
- Ask for rationales: require the model to output a `reasoning` field with sources and content pillars.
- Compare explanations: surface conflicting rationales in review so editors can correct model assumptions.
- Expected outcome: better alignment with search intent and fewer rewrites.
- Redaction rules: automatically redact PII with a preprocessing step using `pattern_matching`.
- Access controls: role-based publishing and review workflows for content flagged as “sensitive.”
- Expected outcome: reduced compliance risk and fewer post-publish takedowns.
- Versioned model cards: include model name, dataset summary, prompt templates, limitations, and recommended use cases.
- Runbook: step-by-step for retraining, rollback, and incident response.
- Expected outcome: faster onboarding and predictable troubleshooting.
- A/B micro-variants: test headline formulas, intro lengths, and semantic keywords in parallel.
- Feedback loop: log editor changes to train lightweight reranking models.
- Expected outcome: continuous lift in performance without large reworks.
Industry analysis shows teams that codify prompt templates and evaluation rubrics get faster, more consistent outcomes.
“`yaml model_card: model: “gpt-4x-content” version: “v1.2” intended_use: “SEO long-form blog drafts” limitations: [“may hallucinate facts”, “requires editor verification”] “`
Troubleshooting tips
- Issue: low factuality — retrain on verified corpora and require `citation` outputs.
- Issue: style drift — implement `style_guides` as weighted constraints in prompts.
- Issue: privacy flagging — add stricter regex for PII and audit last 30 publishes.
- Content scoring framework, editorial checklist, model card template, and a simple dashboard to visualize `draft_to_publish` time and revision counts. Consider linking operational workflows to platforms that automate scheduling and performance benchmarking—Scale your content workflow with AI content automation from Scaleblogger.com if integration and benchmarking accelerate execution.
Compliance, Privacy & Ethics
Start by treating personalization as a privilege, not a default. Personalization delivers measurable lift in relevance and engagement, but only when built on explicit consent, minimal data collection, and transparent controls. Practical, privacy-safe personalization follows simple principles: collect only what’s necessary, pseudonymize or hash identifiers, log every access, and give users clear, immediate control over opt-in and opt-out.
- Pseudonymize identifiers: replace direct PII with hashed or tokenized values to separate identity from behavior.
- Segregate purpose-built stores: keep personalization data in a separate datastore with stricter access controls and shorter retention.
- Maintain audit trails: log who accessed data, why, and when, with immutable timestamps.
- Expose transparency controls: provide a dashboard or simple links to view, edit, export, and delete personalized data.
Industry analysis shows users are more likely to keep personalization enabled when they understand the benefits and control the data used.
Technical implementation example — retention policy snippet: “`yaml retention_policy: personal_identifiers: 30 days behavioral_segments: 365 days access_logs: 730 days encryption: AES-256 hashing: SHA-256 “`
Practical checks and troubleshooting
- Consent mismatch: if users report unwanted personalization, verify consent token freshness and audit logs; refresh prompts if tokens expire.
- Segment bleed: when content appears mis-targeted, confirm pseudonym mapping and rule precedence in the targeting engine.
- Performance vs privacy: if removing PII reduces lift, test `contextual signals + anonymized segments` before reintroducing identifiers.
- Reduced legal friction: fewer data requests and simpler records for compliance audits.
- Higher opt-in quality: clearer value statements and controls improve long-term engagement.
- Lower breach risk: fewer direct PII fields reduce incident surface.
Conclusion
You now have a clear path away from broad, hope-driven campaigns toward content that actually reaches the right audience: prioritize tight audience segmentation, map content to specific intent, and automate distribution so relevance scales. Teams that moved from one-size-fits-all publishing to targeted personalization reduced wasted ad spend and saw steadier engagement; pilot programs that paired topic clusters with automated workflows produced predictable upticks in qualified leads. Ask how to begin, which metrics to track, and what tech to use — start by auditing top-performing pages, define two priority buyer journeys, and measure lift in engagement and conversion rather than vanity metrics.
Take three immediate actions to put this into motion: audit your content by buyer intent, create two automated content-to-audience workflows, and measure engagement and conversion lift over six weeks. To streamline this work, platforms like Scaleblogger services can help teams automate workflow creation and scale personalization without rebuilding systems. Those questions about resources and timeline are common: expect a 4–8 week pilot for measurable results and plan for iterative tuning afterward. Move from scattershot publishing to a repeatable, measurable system — the improvements in efficiency and reach compound quickly when the right processes are in place.

