Too much content still fails if a single audience segment can’t access it. Organizations pour resources into video, interactive graphics, and long-form articles, then lose reach because design and distribution ignore real-world accessibility needs. This gap costs engagement, distorts measurement, and damages brand trust.
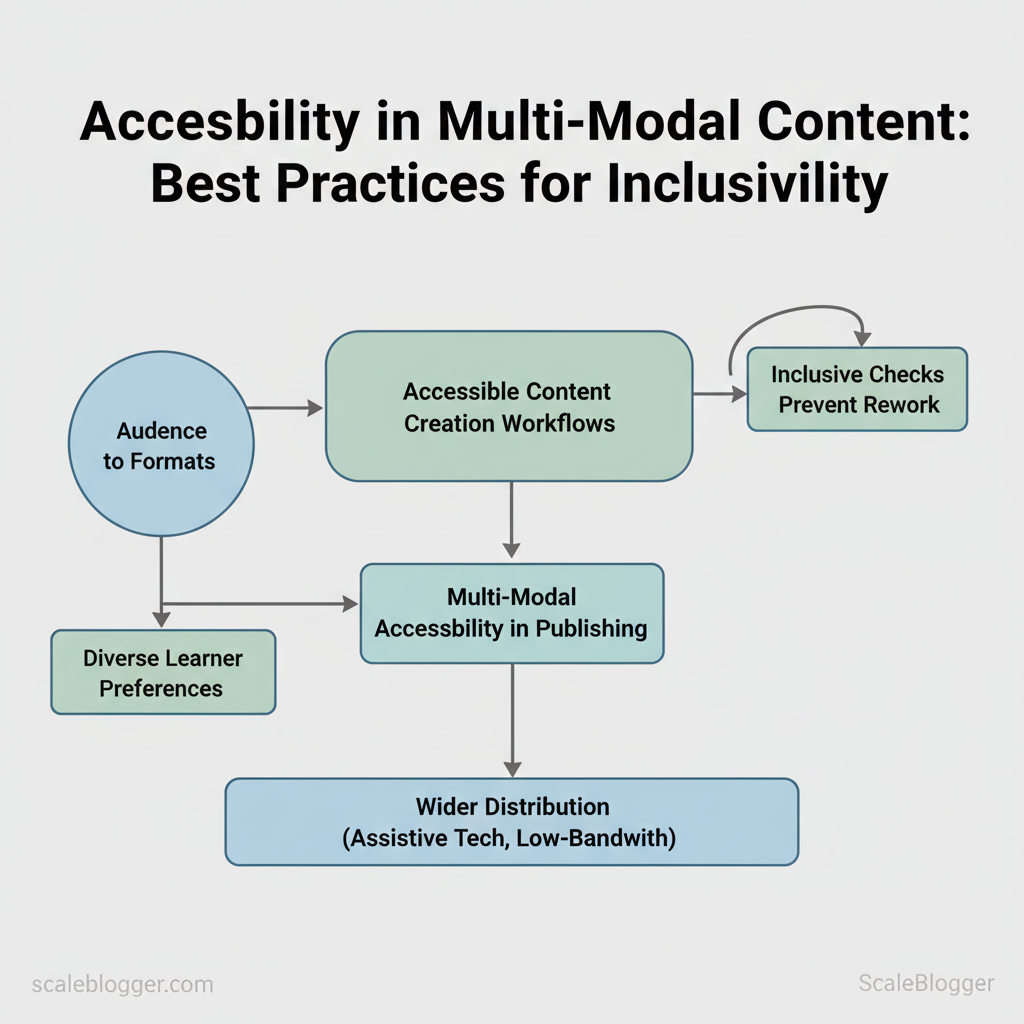
Early wins come from practical changes: prioritize accessible content creation workflows, map audiences to formats, and bake multi-modal accessibility into publishing pipelines. A clear set of inclusive checks prevents rework and unlocks wider distribution across assistive tech, low-bandwidth situations, and diverse learner preferences. Industry research shows teams that treat accessibility as a core publishing requirement avoid late-stage remediation and meet broader business goals faster.
Picture a marketing team that repurposes the same script into captioned video, a summarized article, and an interactive transcript — engagement climbs while production time drops. That kind of inclusive content strategies thinking scales when paired with automation.
- How to apply accessibility checkpoints across audio, video, and text
- Practical checks that reduce remediation time and legal exposure
- Workflow patterns that enable consistent multi-modal accessibility at scale
- Tools and metrics to measure inclusive reach and engagement
What You’ll Need / Prerequisites
Start with a clear set of tools, skills, and permissions so content teams can produce accessible, search-optimized posts without last-minute blockers. For accessible content workflows, technical checks (captions, color contrast, screen-reader testing) and editorial skills (writing descriptive alt text, using semantic HTML) are both non-negotiable. Below are concrete prerequisites and how to get each one in place.
- Writing alt text: Team members must know how to write concise, descriptive alt text (≤125 characters) and when to use `aria-hidden`.
- Semantic markup: Editors need familiarity with `h1–h6`, `figure`/`figcaption`, and `aria-label` patterns.
- Caption quality control: Reviewers should verify speaker attribution and timestamps in captions for SEO and usability.
- Color awareness: Writers and designers must check contrast ratios (WCAG AA minimum 4.5:1 for normal text).
- Plugin installation sign-off: Request from IT or platform owner to add accessibility plugins.
- Budget approval: Typical paid tools require $8–$20/user/mo for transcription; include this in the quarterly budget request.
- Editorial policy update: Approve an accessibility checklist and include it in publishing SOPs.
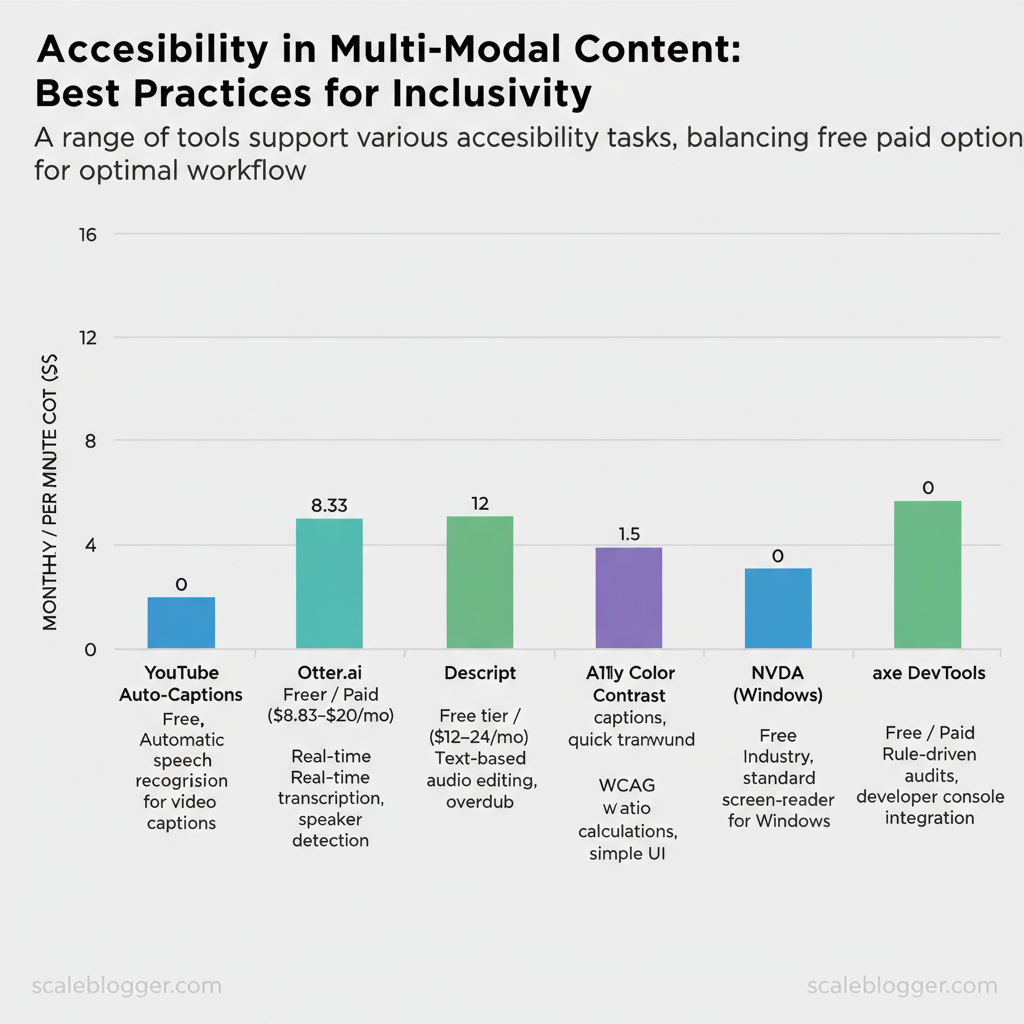
| Tool | Purpose | Free/Paid | Key feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| YouTube Auto-Captions | Auto-generate video captions | Free | Automatic speech recognition for uploaded videos |
| Otter.ai | Meeting/transcript generation | Free tier / Paid ($8.33–$20/mo) | Real-time transcription, speaker detection |
| Descript | Transcription + audio editing | Free tier / Paid ($12–$24/mo) | Text-based audio editing, overdub |
| Rev | Human transcription & captions | Paid ($1.50/min for captions) | 99% accuracy human captions, quick turnaround |
| A11y Color Contrast Checker | Color contrast testing | Free | WCAG ratio calculations, simple UI |
| Colour Contrast Analyser | Desktop contrast tool | Free / Donation | Pixel sampling and ratio reporting |
| NVDA (Windows) | Screen-reader testing | Free | Industry-standard screen-reader for Windows |
| VoiceOver (macOS/iOS) | Screen-reader testing | Free (built-in) | System-level screen reader, mobile testing |
| WP Accessibility | CMS accessibility fixes (WordPress) | Free / Premium | Adds alt text helpers, skip links, role support |
| axe DevTools | Automated accessibility audits | Free / Paid | Rule-driven audits, developer console integration |
Understanding and provisioning these items up front removes bottlenecks during production and makes accessibility a routine part of publishing rather than an afterthought. When the team has the right tools, permissions, and basic skills in place, content moves faster and reaches more users without extra rework — and platforms like Scaleblogger can integrate into that workflow to automate repetitive steps.
Step-by-step Implementation: Planning Multi-Modal Accessible Content
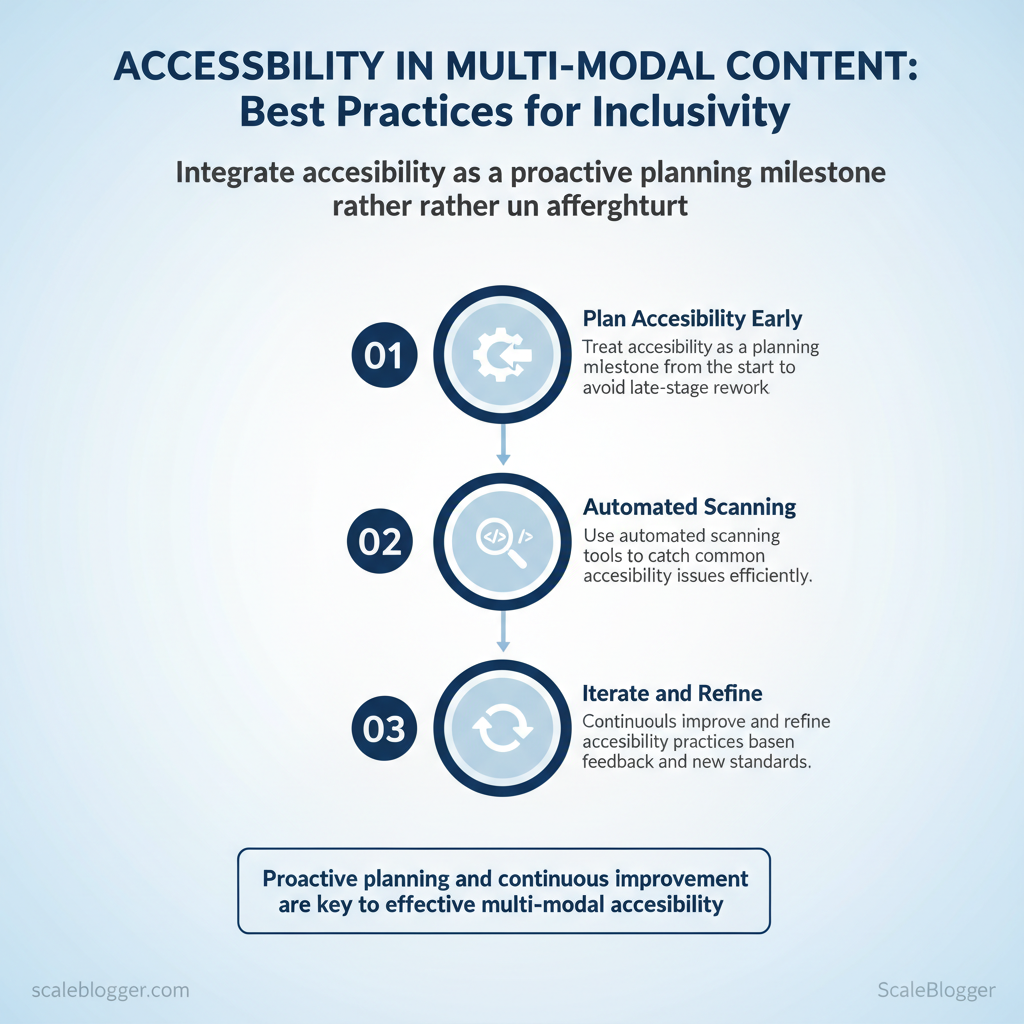
Start by treating accessibility as a planning milestone rather than an afterthought. Use automated scanning to find surface issues, then validate with hands-on checks (screen readers, keyboard-only navigation). Prioritize content by traffic and conversion lift, assign owners, and build a repeatable pipeline so accessibility work moves predictably through production and post-production.
| Content Type | Recommended Modalities | Persona Example | Priority (High/Med/Low) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Longform Article | Text, audio read-aloud, simplified summary | Older reader with low vision | High |
| Explainer Video | Captions (VTT), transcript, audio description | Deaf or hard-of-hearing learner | High |
| Podcast Episode | Transcript, chapter markers, show notes | Cognitive impairment, searchable text | Med |
| Infographic | Alt text, long description, downloadable PDF | Screen-reader user needing detail | Med |
| Social Short | Captions, image descriptions, plain-text post | Mobile users with captions off | Low |
- Capture raw recordings with timecodes to ease captioning.
- Use templated fields for alt text and image long-descriptions.
- Start with automated transcription, then human-review for accuracy.
- Publish machine-readable transcripts and link them from the page.
- Provide audio descriptions for visually critical video segments.
| Format | Best for | Compatibility | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRT | Simple captions | Broad (YouTube, players) | Timecodes, no styling |
| VTT | Web captions with styling | HTML5 players, browsers | Supports `WebVTT` cues |
| TTML | Broadcast and DFXP workflows | Professional platforms | rich styling, complex |
| Plain HTML Transcript | SEO + accessibility | Any browser | Readable, searchable, linkable |
| Audio Description (separate file) | Detailed visual narration | Media players with AD support | Keeps core audio clean |
- Verify keyboard focus order, `skip to content` links, and semantic headings.
- Attach transcripts and captions prominently; don’t hide them behind menus.
- Track accessibility engagement metrics and schedule recurring audits.
- Use user feedback to refine templates and production checklists.
| Metric | Definition | How to Track | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transcript Downloads | Number of transcript file clicks | GA4 event on link | +10% q/q |
| Caption Toggle Use | Times captions are enabled | Player events | Baseline & trend |
| Screen-reader Page Visits | Pages visited via screen-reader user agents | Custom dimension, server logs | Increase engagement |
| Form Completion Rate | Conversions on accessible forms | GA4 conversion | Match site avg |
| Time on Page (accessible content) | Average time on accessible pages | GA4, filtered view | +5–15% vs baseline |
This plan creates repeatable steps teams can follow: audit, decide, build with accessibility in mind, finish with reviewed captions and transcripts, publish on verified templates, and measure results. For teams looking to automate parts of this pipeline, consider pairing content automation tools — including AI content automation from Scaleblogger.com — with manual QA to scale reliably. When implemented as part of the production rhythm, accessible multi-modal content reduces rework and improves reach.
Numbered Checklist: Quick Implementation Steps
Get the first content automation pipeline running with a sequence you can execute in a single day. These steps prioritize momentum: define scope, generate outlines with AI, set simple quality gates, and publish with automated scheduling. Follow each numbered task, mark time and difficulty, and tick them off as you go.
Practical examples and templates
Troubleshooting tips
- If outlines feel generic, increase prompt specificity and add competitor URLs for style reference.
- If automated checks fail repeatedly, loosen thresholds temporarily and fix systemic prompt or template issues.
- If publish cadence stalls, reduce batch size to 2 posts/week and automate the rest.
- Scaleblogger.com provides AI-driven templates and scheduling that plug into this checklist if you want to accelerate setup.
- Consider building a simple dashboard to surface failing checks and weekly trends.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Accessibility failures usually reveal themselves through repeatable symptoms — missing alt text, focus getting trapped, or low contrast — and each symptom maps to quick diagnostics plus a durable fix. Start by reproducing the symptom, run an automated scan (`axe`, `Lighthouse`) and a keyboard-only walkthrough, then apply the immediate patch before scheduling the systemic change.
Common error messages and symptoms to look for:
- `”Image elements must have [alt] attribute”` — immediate fix: add `alt` or `role=”presentation”`.
- `”Focusable elements are not visible”` — immediate fix: ensure CSS `outline` or `box-shadow` for focus state.
- `”Color contrast ratio < 4.5:1"` — immediate fix: use accessible palette or `mix-blend-mode` changes.
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Immediate Fix | Long-term Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Captions out of sync | Transcoding or separate subtitle file timing | Re-sync .srt timestamps in editor | Use server-side timed-text pipeline |
| Images missing alt text | CMS allows empty alt fields | Add `alt` text immediately | Enforce required `alt` field in CMS |
| Keyboard traps on modal dialogs | Focus not managed on open/close | Add `focus()` and return focus on close | Use accessible modal component library |
| Low color contrast | Design palette with insufficient contrast | Adjust foreground/background colors | Adopt accessible design tokens |
| Embedded PDF inaccessible | PDFs lack tags/structure | Replace with HTML or provide tagged PDF | Convert source documents to tagged PDF workflow |
Scaleblogger’s AI content automation can help enforce alt-text and caption policies during content ingestion, accelerating remediation without adding manual overhead. Understanding these verification steps reduces rework and helps teams ship inclusive content faster.
Tips for Success / Pro Tips
Start by treating accessibility as an operational capability, not a checkbox. Implement automation for repeatable tasks, then layer human review where nuance matters. That combination reduces manual work while keeping content compliant and usable for real people.
Practical checklist (copy and adapt) “` – Alt text present: Y/N – Alt text quality: descriptive/functional – Captions present: Y/N – Transcript attached: Y/N – Color contrast: pass/fail – ARIA roles validated: Y/N “`
- Bold lead-in: Prioritize content types. Focus first on high-traffic pages and evergreen posts.
- Bold lead-in: Train editors. Run quarterly workshops on writing useful `alt` text and captioning standards.
- Bold lead-in: Measure impact. Correlate accessibility KPIs with engagement and SEO performance.
Market leaders recognize accessibility reduces friction and expands reach. For teams scaling content operations, consider integrating AI-powered pipelines to automate routine checks and preserve expert bandwidth—resources like `Scaleblogger.com` explain how to build topic clusters and automate publishing. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making accessibility a repeatable, measurable part of content production.
Measuring Impact and Reporting
Start by mapping measurable outcomes directly to stakeholder goals so reporting becomes a decision-making tool rather than ritual. Focus on three classes of metrics: business outcomes (traffic, conversions), content health (engagement, organic visibility), and process efficiency (time-to-publish, automation uptime). Reporting should answer: did the content move a business metric, and which parts of the pipeline caused the result?
Practical report formats and cadence Weekly (1–2 pages): Operational KPIs, anomalies, fast actions.* Monthly (10–15 slides): Performance trends, top/bottom content, A/B results.* Quarterly (1 pager + appendix): Strategic outcomes, ROI, roadmap alignment.*
Example of a reporting rhythm:
A 90-day rollout and measurement timeline with milestones
| Week/Month | Milestone | Owner | Success Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1-2 | Accessibility audit (WCAG checklist) | Product Accessibility Lead | Audit report completed; top 10 issues identified |
| Week 3-4 | Fix top accessibility issues (keyboard, contrast) | Engineering Sprints | 70% of critical issues resolved |
| Month 2 | Implement content templates with accessible patterns | Content Ops Manager | Templates used in 80% new posts |
| Month 3 (weeks 9-10) | User testing with assistive tech | UX Researcher | 8-10 users tested; usability score ≥75% |
| Month 3 (week 12) | Reporting and handoff to ops | Head of Content | Accessibility metrics added to dashboard; monthly reporting live |
Troubleshooting tips: if dashboards show noise, tighten filters to page-level signals; if stakeholders ignore reports, reduce friction—send one highlighted action per report. Consider integrating `GA4` event exports and a content scoring framework from tools like Scaleblogger.com to automate scorecards and accelerate decisions. When reporting maps cleanly to goals, teams move faster and focus on the content that actually drives outcomes.
📥 Download: Multi-Modal Accessibility Checklist (PDF)
Advanced Topics: Legal, Internationalization, and Future-Proofing
Start by treating legal, internationalization, and future-proofing as integrated design constraints rather than afterthoughts. That means building workflows that enforce jurisdictional checks, localization pipelines, and modular content architecture from day one. Expect initial setup to take 2–6 weeks depending on content volume; ongoing maintenance becomes a small percentage of monthly operations once automated checks and human QA are in place.
- Actionable step: Add a `legal_review_required` flag in CMS metadata and route flagged items to counsel; time estimate 1–3 business days per item for review.
- Expected outcome: Reduced takedown risk and cleaner audit trails.
- Actionable step: Maintain a bilingual glossary and approved tone documents for translators; expected QA time 2–5 hours per long-form piece.
- Troubleshooting: If translations read literal, add example sentences in the glossary and require in-context screenshots for translators.
- Design for accessibility early: include alt text, semantic HTML, captions, and keyboard navigation checklists in briefs.
- Prepare for audio/voice and AR/VR: export structured content as `JSON-LD` and include short summaries for voice outputs.
- Modularize: separate facts, evergreen pillars, and date-stamped commentary so updates are surgical.
- Instrument: add performance and compliance webhooks to detect dips or legal flags automatically.
- Scale automation: tie `content_scoring` outputs to publishing rules so only high-scoring drafts auto-publish.
Understanding these principles reduces reactive work and keeps teams focused on creating valuable content while staying legally and culturally fit for global audiences. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making compliance and localization routine parts of the content lifecycle.
Conclusion
Putting accessibility at the center of content workflows turns wasted effort into amplified reach. After auditing assets, standardizing templates, and adding automated captioning and semantic markup, teams see clearer distribution paths and fewer compliance surprises. For example, teams that layered automated captions and short-form transcripts onto long videos extended view time and organic reach; editorial teams that introduced structured templates halved production rework. Expect an initial setup phase of 2–6 weeks, then steady time savings. Start by auditing your top three content formats, prioritize fixes that remove the biggest access barriers, and run a two-week pilot to measure uplift.
Questions about scale or integration are normal — it’s reasonable to ask whether this will disrupt existing pipelines or require new headcount. In practice, automation handles repetitive tasks while small process changes (a template and an approval gate) prevent bottlenecks. To streamline this process, platforms like Scaleblogger can orchestrate conversions, captioning, and CMS pushes so teams keep publishing velocity without losing accessibility. For teams ready to test automation, Learn how Scaleblogger automates accessible content workflows is a practical next step that demonstrates configuration options and expected outcomes.

