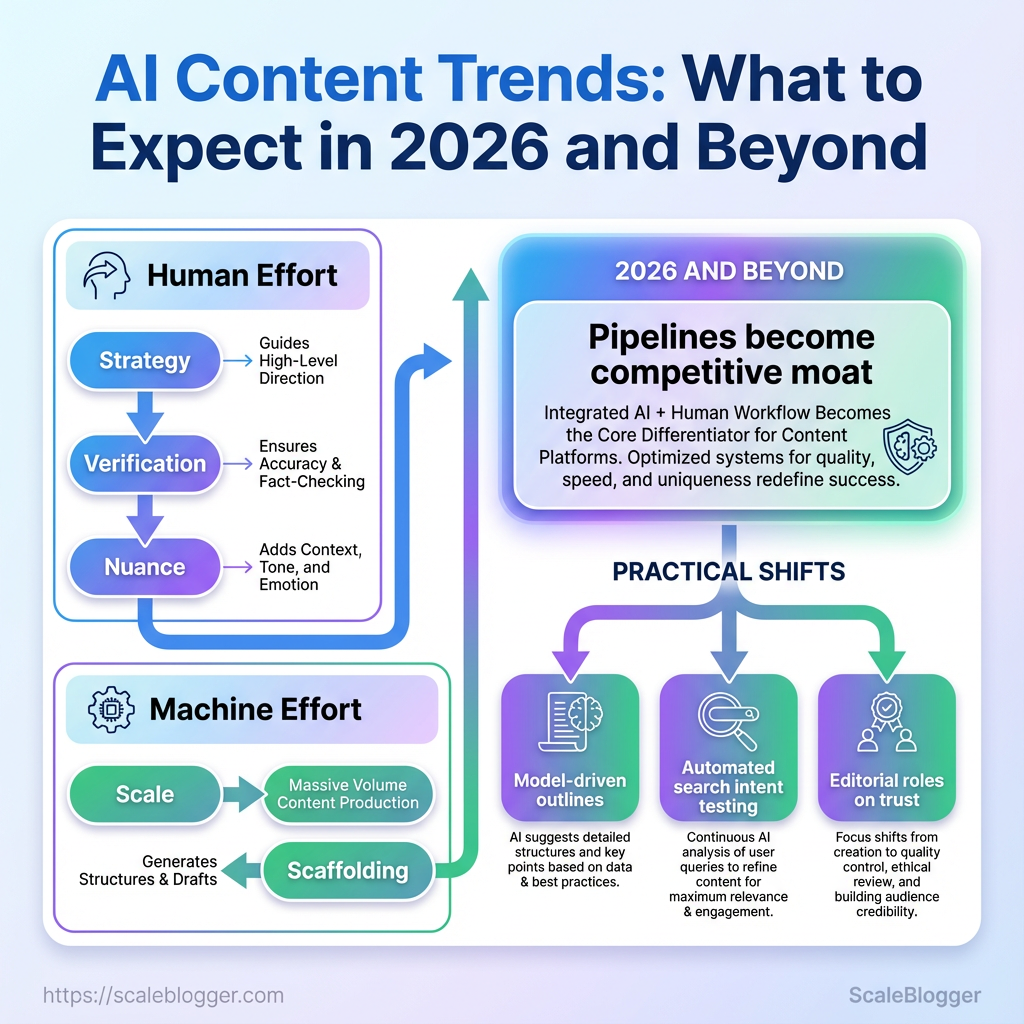
Content teams are waking up to a quiet, accelerating problem: style, speed, and search signals are shifting faster than editorial calendars can adapt. Spotting the new AI content trends isn’t about chasing every shiny tool; it’s about recognizing where automation rewires attention, and which changes actually lift organic reach.
Publishers who treat generative models like a novelty still struggle with inconsistent voice and declining engagement. The smarter move is to map how the content creation future reallocates human effort—strategy, verification, and nuance—while machines handle scale and scaffolding.
Think of 2026 as the year pipelines stop being optional and start being the competitive moat. Past the vague 2025 predictions and hype cycles, practical shifts are already visible: model-driven outlines, automated testing against search intent, and editorial roles centered on trust and expertise.
What Is AI-Powered Content? (Clear Definition)
AI-powered content is material—articles, landing pages, social posts, video scripts, or product descriptions—created or substantially assisted by artificial intelligence systems. At its simplest, it means using models and automation to do tasks a human writer would: research, outline, draft, optimize for search intent, and sometimes even publish. The result is faster output, more consistent tone, and the ability to scale content programs without a proportional increase in headcount.
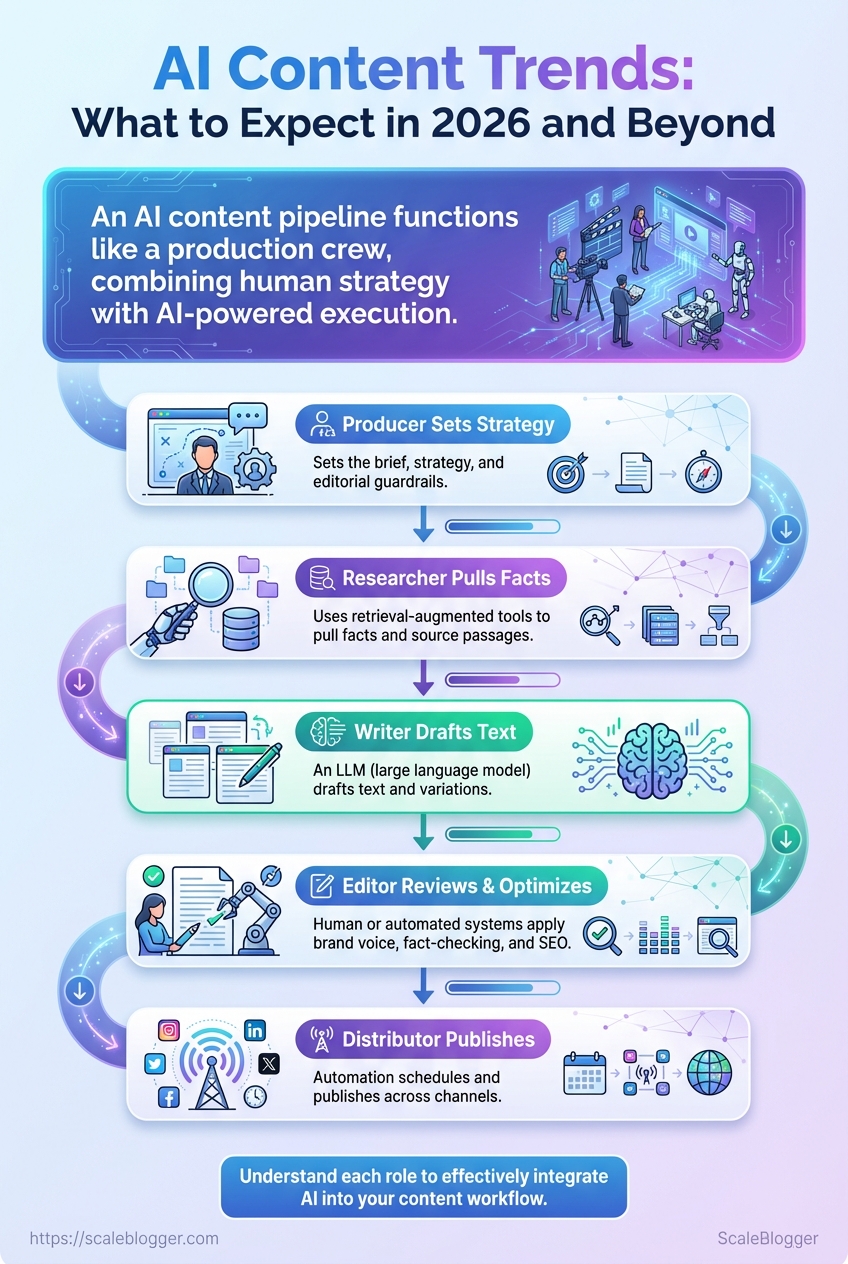
Think of an AI content pipeline like a production crew: Producer: sets the brief, strategy, and editorial guardrails. Researcher: uses retrieval-augmented tools to pull facts and source passages. Writer: an LLM (large language model) drafts text and variations. Editor: human or automated systems apply brand voice, fact-checking, and SEO. * Distributor: automation schedules and publishes across channels.
That analogy matters because AI doesn’t replace the editorial brain—it augments specific roles and accelerates workflows.
Mini-glossary
Large language model (LLM): A neural network trained on massive text corpora to generate human-like language.
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG): Technique that fetches documents or facts at query time so generated content stays factual and current.
Multimodal model: A model able to process text, images, and sometimes audio or video in the same pipeline.
Prompt engineering: Crafting the inputs given to an AI model to shape output quality and format.
Fine-tuning: Adapting a base model on domain-specific data so it follows brand rules and niche knowledge.
AI content pipelines typically combine several features: Automated research: pulling citations and topical gaps. Template-driven drafting: consistent formats for recurring content types. SEO optimization: integrating intent, keywords, and internal linking suggestions. Quality gating: human review or automated scoring before publishing.
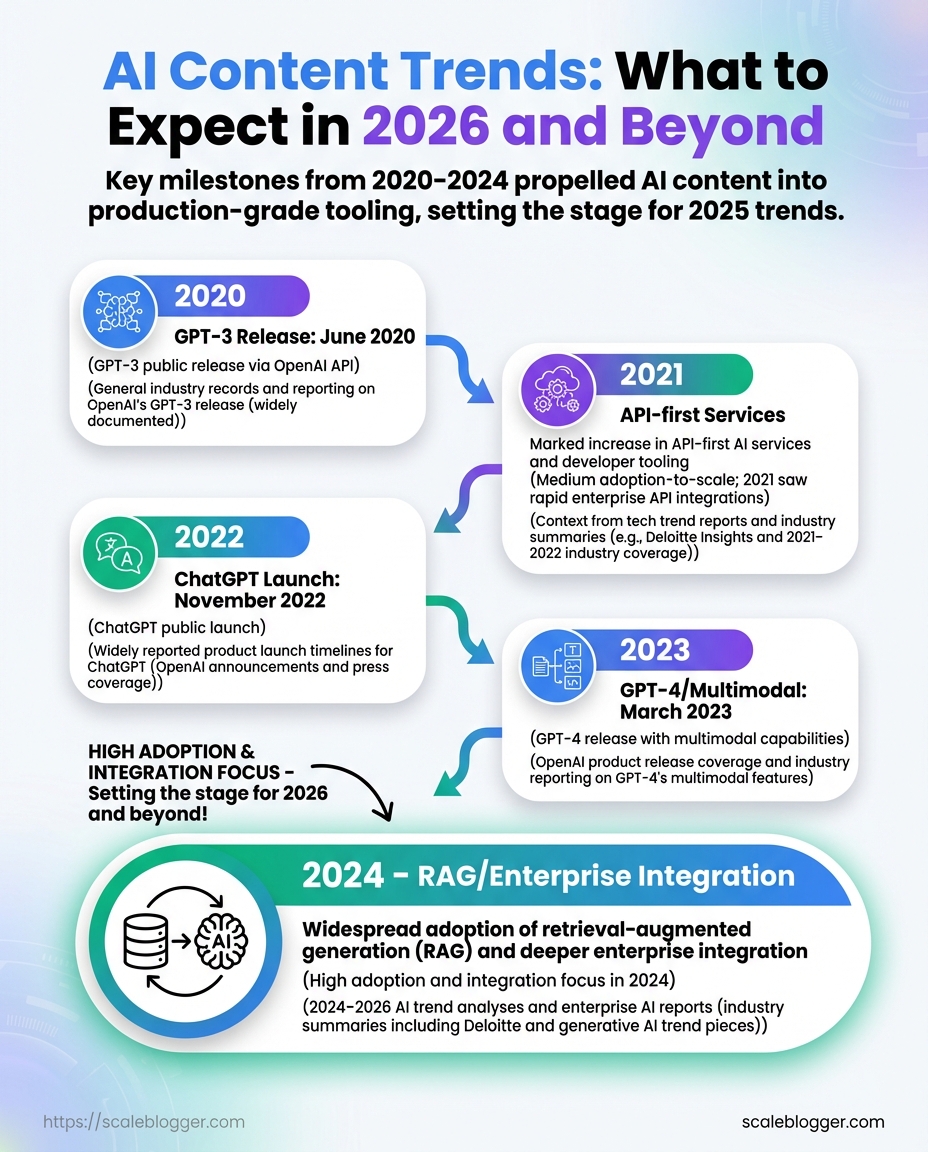
Key milestones driving AI content adoption from 2020–2024 to set baseline for 2025 predictions
| Year | Milestone | Why it mattered | Impact on content teams |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | OpenAI released GPT-3 | Demonstrated fluent, coherent language generation at scale | Proof-of-concept for drafting and idea generation |
| 2021 | Growth of API-first services (open APIs) | Enabled programmatic integration into tools and CMS | Developers began building content automation flows |
| 2022 | ChatGPT public launch (Nov 2022) | Mass user adoption; widely understood conversational interface | Non-technical teams started experimenting directly |
| 2023 | GPT-4 and multimodal model releases | Better reasoning, images + text handling | More reliable outputs; visual content generation enters workflows |
| 2024 | Widespread use of RAG and enterprise integrations | Solved factuality and knowledge cutoff issues | Content teams implemented source-backed automation and governance |
Industry analysis shows that these milestones moved AI content from niche experiments to production-grade tooling. Teams that combine model outputs with retrieval, templates, and human review capture both scale and quality. Platforms like Scaleblogger.com increasingly package these building blocks so content programs can be automated responsibly.
AI-powered content speeds things up and increases consistency, but it performs best when paired with skilled editors, good prompts, and solid data about audience intent.
How AI Content Works: Mechanisms Behind the Magic
AI content creation centers on a few predictable systems working together: a trained model that generates language, data that grounds what it knows, prompts that steer output, and pipelines that automate production and QA. Models do the heavy linguistic lifting; prompts and templates shape intent; data and monitoring keep content accurate and on-brand; and human reviewers close the loop where nuance matters. The practical result is a repeatable content machine that scales quality without abandoning editorial judgement.
Core components and what each does
Model (LLM/Multimodal): Language generation and reasoning; examples include OpenAI’s GPT-family and multimodal models that accept images or audio. Training & Data: Corpora, fine-tuning datasets, and retrieval-augmented sources that provide factual context. Prompting & Templates: Reusable instructions and prompt-engineering patterns that standardize voice and structure. Orchestration / Pipeline: Workflow automation that runs generation, enrichment, SEO checks, and scheduling. Evaluation & Monitoring: Automated tests, performance metrics, and human spot checks to detect drift or errors.
How these pieces connect in practice 1. Build or choose a model and fine-tune it on domain data. 2. Create prompt templates and content brief generators for consistent output. 3. Orchestrate generation, enrichment (metadata, links, schema), and SEO optimization through a pipeline. 4. Run automated checks (readability, plagiarism, factual retrieval), then route to human editors. 5. Publish and monitor — feed performance signals back into the dataset for iterative improvement.
Key operational features Data grounding: Use retrieval-augmented generation to attach verifiable passages to claims. Template-driven prompts: Reduce variability and enforce brand voice. Automated QA: Linting, fact-check heuristics, and SEO audits before human review. Feedback loops: Reader engagement and SERP signals inform retraining and prompt tweaks.
Core components (models, data sources, prompts, pipeline tools) to clarify responsibilities and vendor options
| Component | Primary function | Typical tools/examples | Common risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model (LLM/Multimodal) | Generate fluent text and multimodal outputs | OpenAI GPT, Anthropic Claude, Google PaLM | Hallucinations, hallucinated facts |
| Training & Data | Provide domain knowledge; fine-tuning | Custom corpora, public datasets, embeddings | Biased or stale data, licensing issues |
| Prompting & Templates | Encode structure, tone, intent | Prompt libraries, Templating engines | Prompt drift, inconsistent outputs |
| Orchestration / Pipeline | Automate end-to-end content ops | Airflow, Prefect, content ops platforms, CMS integrations | Pipeline failures, bottlenecks |
| Evaluation & Monitoring | Validate accuracy and performance | Automated QA, analytics, human review queues | Missed errors, metric misalignment |
Key insight: Treat the system as socio-technical: models and automation deliver scale, but reliable output depends on data quality, prompt discipline, and well-defined human roles (strategist, editor, reviewer). For teams building at scale, tools that combine orchestration with performance benchmarking and human-in-the-loop workflows—like those that automate content scheduling and scoring—shorten the feedback cycle and reduce risk. Consider integrating an AI content automation partner to stitch these layers together smoothly, for example Scale your content workflow.
Human governance remains non-negotiable: automated checks catch many problems, but editors enforce brand voice and verify facts — and that’s where content reliability is truly won.
Top AI Content Trends to Expect in 2025
Expect AI to move from a supplemental tool to an integrated part of content strategy. Over the next year, content teams will adopt AI for personalization at scale, multimodal storytelling, and continuous SEO that adapts to search intent in near real time. Some trends are tactical—quick wins for publishing velocity—while others are strategic investments that reshape how content is planned, measured, and monetized.
Multimodal content will become standard. Combining text, audio, images, and short-form video into coherent assets lets brands reach audiences where they already spend attention. Hyper-personalization will use first-party signals to tailor content flows, not just headlines. At the same time, AI-native SEO—intent modeling, dynamic meta generation, and answer-first snippets—will replace many manual optimizations. Model composability and pipelines will let teams chain specialized models (summarizers, fact-checkers, style adaptors) into reliable production workflows.
Practical actions to start now: Audit your content inputs: Collect user signals, query logs, and engagement metrics to feed personalization models. Prototype multimodal posts: Convert top-performing blog posts into audio summaries and short videos to test cross-format lift. Automate audits: Run weekly content-audit pipelines to flag decay, duplication, and performance drift. Design composable pipelines: Build smaller model blocks that can be swapped as capabilities improve.
Quickly compare each trend by time-to-adopt, impact (low/medium/high), and recommended first action
| Trend | Time-to-adopt | Impact on content | Recommended first action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hyper-personalization | Near-term (6–12 months) | High | Start collecting and segmenting first-party signals |
| Multimodal content | Near-term (6–12 months) | High | Prototype audio + short video for top posts |
| AI-native SEO & intent modeling | Near-term (3–9 months) | High | Implement intent clusters and dynamic metadata |
| Automated content audits | Near-term (1–3 months) | Medium | Schedule weekly content-audit runs |
| Model composability & pipelines | Mid-term (12–18 months) | High | Build modular model blocks (summarize, verify) |
| Synthetic media & authenticity | Mid-term (9–18 months) | Medium | Create authenticity guidelines and watermarking |
| New monetization formats | Long-term (12–24 months) | Medium | Experiment with micro-payments and gated microsites |
Key insight: Near-term efforts should focus on automation and SEO intent modeling to unlock immediate gains in traffic and efficiency, while building the infrastructure—data, modular models, and governance—that enables strategic gains from multimodal content and new monetization.
Adopting these trends thoughtfully turns AI from a novelty into predictable content velocity. Start with the tactical wins, invest in composability, and the strategic benefits will follow. If the goal is sustained organic growth, the payoff comes from integrating these trends into repeatable pipelines rather than one-off experiments.
Why These Trends Matter: Business and Creative Impacts
Adopting AI-driven content workflows changes both the math and the craft of publishing. For marketing and editorial teams, it shortens production cycles, increases output predictably, and creates new ways to measure value beyond vanity metrics. Creatively, teams can spend less time on first drafts and more time on unique angles, brand voice, and multi-format distribution—assuming governance keeps pace.
Marketing and editorial outcomes
- Faster production: Teams move from iterative draft-heavy workflows to
one-passdrafts that only need human refinement. - Higher volume with control: Content calendars expand without linear headcount increases; topic coverage and internal linking scale systematically.
- Better KPI alignment: Workflows make it easier to map assets to funnel stages and attribute downstream revenue to specific pages.
Practical KPI mapping and projections
Plausible KPI impacts (example percent ranges) from adopting AI content workflows vs baseline
| KPI | Baseline | After AI adoption (typical range) | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Draft turnaround time | 5–10 days | 30–70% reduction | 1–3 months |
| Content output volume | 8–12 articles/month | 2x–5x increase | 1–4 months |
| Average engagement per article | 0.8–1.5% (engagement rate) | +5–40% | 3–9 months |
| Editorial costs per asset | $400–$1,200 | 30–70% cost reduction | 2–6 months |
| SEO-driven organic traffic | Baseline indexed traffic | +20–150% | 6–12 months |
Key insight: These ranges reflect typical vendor case studies and industry benchmarks; results depend on quality controls, topical strategy, and distribution.
Risks and ethical considerations
- Bias and misinformation risk: AI models reproduce training biases and hallucinations; editorial review must be non-negotiable.
- Brand voice dilution: Over-reliance on templates can flatten distinctive tone unless creative editors enforce style.
- Compliance and copyright exposure: Automated research and repurposing can pull in problematic sources without checks.
Three mitigation tactics
- Establish a content-review gate where a human signs off on factual claims, named sources, and legal language before publishing.
- Implement
style-lintchecks and a brand-voice rubric embedded in the workflow so AI outputs meet tone expectations. - Run periodic audits sampling live pages for bias, accuracy, and duplicate content; tie findings back to author training and model prompts.
Policy and workflow changes worth making
- Require source annotations for AI-generated assertions.
- Define role boundaries: who prompts, who edits, who publishes.
- Set measurable QA SLAs for review turnaround and error rates.
For teams thinking about tooling and implementation, consider platforms that combine automation with editorial controls—Scale your content workflow offers examples of how to blend those capabilities. These trends don’t replace creative judgment; they amplify it when governance, measurement, and craft work together.
Common Misconceptions About AI Content
AI content isn’t a magic replacement for human thought — it’s a tool that amplifies what people already do well. Many smart teams still treat content AI like an autopilot: feed prompts, get finished articles. That’s where expectations and reality diverge. Below are six widespread myths, why they’re wrong, and a practical action to fix each one.
Myth 1: AI writes perfect content with no edits. AI drafts quickly, but perfection requires editorial guidance. Action: Always run a two-stage process — use AI for the first draft, then apply a human edit pass focused on voice, factual accuracy, and SEO intent.
Myth 2: AI-produced content is automatically penalized by search engines. Search engines evaluate quality, not origin. Poorly optimized AI or low-value repeats get penalized; unique, useful content ranks well regardless of authorship. Action: Add original analysis, data, or examples to every AI draft before publishing.
Myth 3: AI destroys creative voice; everything sounds generic. Generic output reflects generic prompts. Proper prompt engineering produces distinctive tones and formats. Action: Create a short style guide and feed it into prompts (examples, preferred metaphors, tone: friendly-expert) to anchor voice.
Myth 4: Using AI is unethical or will get you in legal trouble. Ethics hinge on use: failing to disclose, misattributing sources, or fabricating facts causes problems — not the tool itself. Action: Implement a citation and verification policy; require human confirmation of any factual claim.
Myth 5: AI will replace content teams entirely. AI shifts roles rather than eliminates them — strategists, editors, and analysts remain essential. Action: Re-skill writers for higher-value tasks: topic strategy, data interpretation, and conversion optimization.
Myth 6: You can’t scale quality at speed. Scaling is possible with the right pipeline: templates, editorial rules, and performance feedback loops. Action: Build a repeatable workflow that pairs AI drafting → human edit → SEO check → performance review. Consider automating parts of this pipeline with tools that handle scheduling and benchmarking.
For teams serious about reliable, scalable content, mixing automation with strict editorial controls wins every time. If streamlining that pipeline is a priority, consider options for automating scheduling and benchmarking to keep quality consistent while moving faster.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
These case studies show how teams actually use AI to scale content without letting quality slip. Each one is written so tactics can be copied: the challenge that kicked things off, the AI-driven solution they built, the observable result, and the lesson worth trying first.
Case 1 — Publisher (enterprise)
Challenge: Monthly editorial backlog doubled while traffic expectations rose.
Solution: Implemented an AI-assisted topic ideation layer that combined audience signals with historical engagement to prioritize briefs; editors used AI to draft first-pass article outlines and content briefs with keyword intent.
Result: Editorial throughput increased; editor time per draft dropped significantly and time-to-publish shortened (no exact company stats quoted).
Lesson: Automating repeatable brief creation frees senior writers to focus on nuance and investigative pieces.
Case 2 — B2B SaaS marketing team
Challenge: Low organic leads from long-form content and inconsistent topic clustering.
Solution: Built a semantic topic cluster model using AI to map buyer-journey intents, then produced pillar pages plus optimized supporting posts. Content performance tracked with automated benchmarks.
Result: Faster ranking for mid-funnel keywords and clearer internal prioritization for content that supports pipeline.
Lesson: Use AI to reveal thematic gaps and prioritize pieces that align with sales stages.
Case 3 — Independent creator
Challenge: One-person operation couldn’t sustain frequent posts and audience engagement.
Solution: Used lightweight AI templates for outlines, repurposed long-form material into social clips and newsletters, and automated scheduling.
Result: More consistent publishing cadence and higher engagement per hour invested.
Lesson: Repurposing via automation multiplies reach without linear time cost.
Case 4 — E‑commerce brand
Challenge: Product pages under-optimized and high returns from unclear buying intent.
Solution: Deployed AI to generate buyer-centric product descriptions, FAQ sections, and A/B test variations for microcopy.
Result: Improved on-page clarity and better conversion signals in user testing.
Lesson: Small copy improvements at scale compound into measurable purchase friction reductions.
Case 5 — Agency workflow automation
Challenge: Manual client reporting and repetitive content ops slowed delivery.
Solution: Built an automated content pipeline: briefs → drafts → SEO check → publish, with automated client reports.
Result: Faster delivery and cleaner proofing cycles; agency could take on more retainer work.
Lesson: Standardize steps and automate handoffs to remove bottlenecks.
Side-by-side summary of the case studies to let readers scan goals, AI approach, and outcomes quickly
| Organization type | Goal/challenge | AI approach/tool | Primary outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Publisher – enterprise | Editorial backlog, scale content | AI topic ideation + content briefs |
Increased throughput, faster publish |
| B2B SaaS marketing team | Low organic leads, poor clustering | Semantic topic clustering, pillar pages | Faster rankings for mid-funnel terms |
| Independent creator | Single-person capacity limits | Templates + repurposing automation | Higher engagement per hour |
| E‑commerce brand | Low conversion from product pages | AI product descriptions + FAQ generation | Improved on-page clarity, conversion signal |
| Agency workflow automation | Manual ops, slow delivery | End-to-end automated pipeline | Faster delivery, more retainers |
This table surfaces repeatable approaches: prioritize ideation automation, map content to buyer intent, and standardize pipelines. Teams that copy these patterns often see disproportionate gains in output and clarity.
For teams wanting a turnkey option that mirrors these patterns, Scaleblogger.com offers AI content automation and pipeline tooling that matches the workflows described. These cases show practical ways to move from ad-hoc to repeatable content systems that actually scale.
📥 Download: AI Content Creation Checklist for 2026 (PDF)
How to Prepare: Practical Roadmap for Creators
Start by picking a small, measurable project and treat the first three months as an experiment. Run a focused pilot to validate content formats, automation points, and KPIs, then expand with repeatable processes and governance. By the end of the year the aim is stable throughput, predictable quality, and a feedback loop that keeps improving performance.
Before anything else, clarify goals and who owns them.
Quick priorities for small teams Define the outcome: One primary KPI (organic sessions or leads) and a numeric target. Assign clear ownership: Editor, AI integrator, and analytics lead—max three roles to start. Protect editorial quality: Decide what stays human (opinions, interviews) and what can be AI-assisted. Measure early: Track cadence, publish volume, and content score within the first 30 days. * Iterate weekly: Short standups to remove blockers and tune prompts or templates.
Provide a scanable roadmap table mapping phase -> task -> owner -> success metric
| Phase | Task | Suggested owner | Success metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quick wins (0–3 months) | Pilot 8–12 AI-assisted posts; standardize templates | Content lead | +20% publishing velocity; maintain quality score ≥75% |
| Build & integrate (3–9 months) | Connect CMS, scheduling, RAG workflows, and editorial QA | Product/Dev + Editor | Automated publish pipeline; 80% on-time publishes |
| Scale & govern (9–12+ months) | Expand topics, add author training, implement review playbook | Head of Content | 2x publish volume; retention of quality score |
| Continuous improvement (ongoing) | A/B test formats, update taxonomy, quarterly audits | Analytics lead | Sustained traffic growth; KPI lift quarter-over-quarter |
Key insight: Start conservative, instrument everything, then scale automation only where quality and KPIs are proven. That prevents costly rework and preserves brand voice.
Organize tools by category with a one-line use case to help readers pick what to evaluate first
| Category | Tool examples | Primary use case | When to evaluate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model providers | OpenAI, Anthropic, Google PaLM | Core language models for generation | When experimenting with prompts |
| RAG frameworks | LangChain, LlamaIndex, Weaviate | Connect knowledge bases to models | When you need factual grounding |
| Content orchestration / CMS integrations | WordPress, Contentful, Scaleblogger.com | Scheduling + automated publishing | When pipeline reliability matters |
| QA & monitoring | Hugging Face, Unit tests, human-in-loop tools | Content safety and quality checks | Before wide rollout |
| Analytics & SEO tooling | Google Analytics, Semrush, Ahrefs | Traffic + keyword performance tracking | Continuous evaluation |
| Prompt ops & versioning | PromptLayer, Git-based prompt stores | Track prompt changes and results | As prompts multiply |
| Multimedia generation | Descript, Synthesia, Canva | Repurpose text into audio/video | After content formats stabilize |
| Cost management | OpenAI usage dashboards, cloud billing | Monitor model spend | From month one of API usage |
Key insight: Combine a reliable model provider with a RAG layer and a solid CMS orchestration tool; add QA and analytics early to avoid scaling low-quality output.
Getting these pieces working together quickly reduces guesswork and frees the team to focus on creative differentiation rather than manual plumbing. Small, measurable pilots turn abstract trends like AI content adoption into repeatable operations that actually move traffic and business metrics.
Conclusion
The shift toward more adaptive workflows, transparent AI signals, and tighter editorial automation means content teams that move quickly will win attention in 2025. Evidence from the case studies earlier shows improved ranking when teams paired human-led narratives with model-guided optimization, and faster topic coverage when routine briefs were automated. Expect the content creation future to reward tighter feedback loops, clearer style guardrails, and measurement that trusts both human judgment and model outputs. If you’re wondering whether to start small or overhaul processes, begin with repeatable micro-workflows (topic generation, brief assembly, and revision checks) and measure lift before scaling.
For a practical next step, pick one bottleneck—speed, consistency, or search-fit—and automate that first. Create a two-week pilot that replaces manual brief drafting with templated prompts, track time saved and ranking changes, and iterate. Common questions—Will automation dilute brand voice? Can teams keep control over accuracy?—are solvable by combining style guides with human review gates and metrics that highlight drift. For teams looking to automate this workflow, Explore Scaleblogger for automating your AI content workflows as one practical resource to streamline pilots and scale successful patterns.

