Marketing teams waste hours each week reconciling calendars, approvals, and repetitive publishing tasks, and those inefficiencies blunt growth. A tightly designed content automation workflow removes manual friction, ensures consistency, and frees teams to focus on strategic creative work. Implementing automation successfully requires disciplined automation best practices and careful planning when integrating content tools across teams.
Effective automation reduces bottlenecks, prevents version confusion, and accelerates time-to-publish. Picture a content ops team that routes briefs, auto-assigns drafts, and publishes to multiple channels with a single approval — the result is faster campaigns and clearer performance tracking. Industry practitioners observe that starting with repeatable processes and measurable SLAs yields the fastest ROI from automation.
- What reliable trigger and approval patterns to standardize first
- How to design templates that scale without losing brand voice
- Ways to measure ROI from automated publishing and distribution
- Common pitfalls when connecting CMS, editorial, and analytics systems
- How to phase tool integrations to protect existing workflows
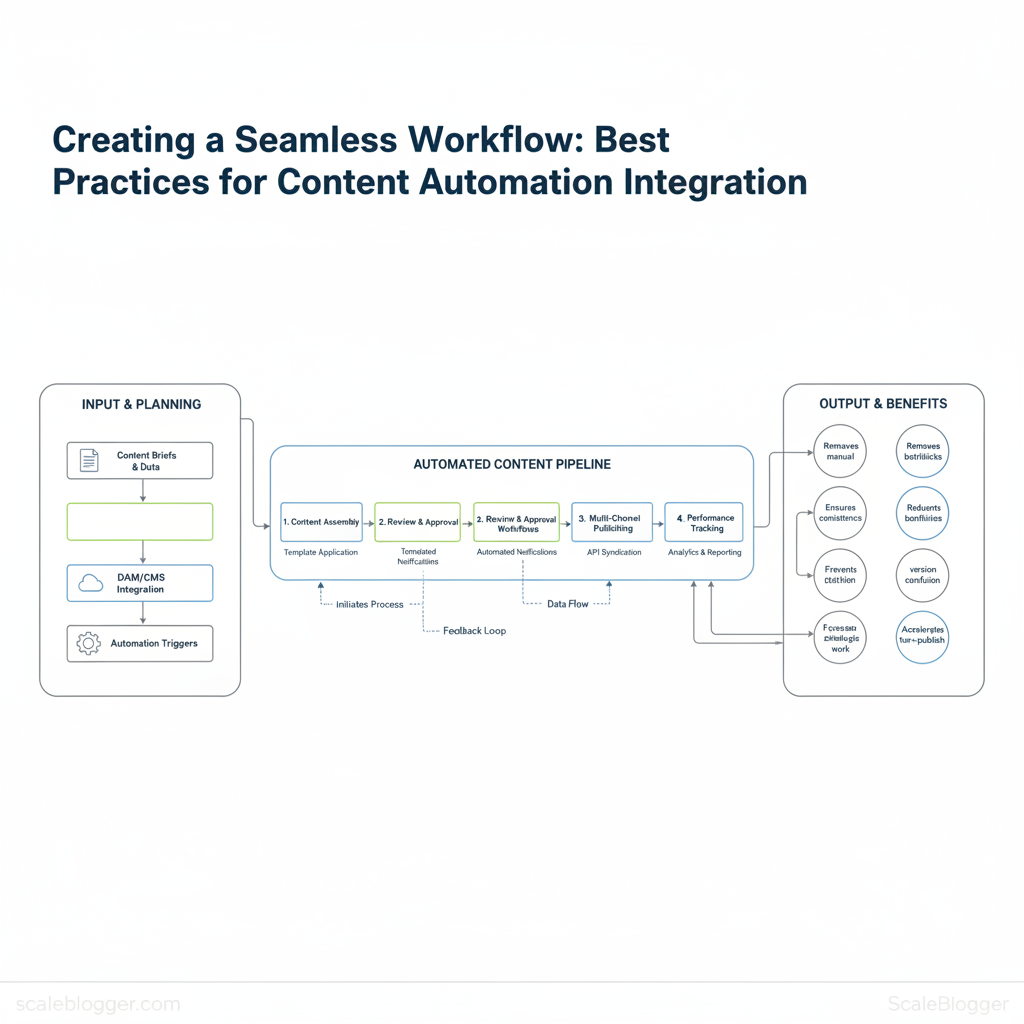
Plan your content automation strategy
Start by defining what automation must achieve for the business: faster cycle times, more consistent SEO performance, or predictable output volume. Map those goals directly to measurable KPIs, then design the content lifecycle so each handoff is either automated or a clear, low-friction manual checkpoint. The objective is to remove repetitive busywork without breaking ownership or quality controls.
Prerequisites
- Stakeholder alignment: executive sponsor and content owner identified.
- Data access: `GA4` and Google Search Console read access, CMS publishing logs.
- Baseline capture: export last 3 months of article-level metrics.
- Primary pilot KPIs: choose metrics that reflect impact, not effort.
- Baseline first: capture current state from `GA4`, Search Console, and CMS logs.
- Measurement cadence: weekly checks for process KPIs, biweekly for SEO signals.
- Low-risk automation candidates: auto-fill metadata, schedule publishing, generate first-draft outlines.
- High-value manual checkpoints: final edit, legal review, and topical accuracy checks.
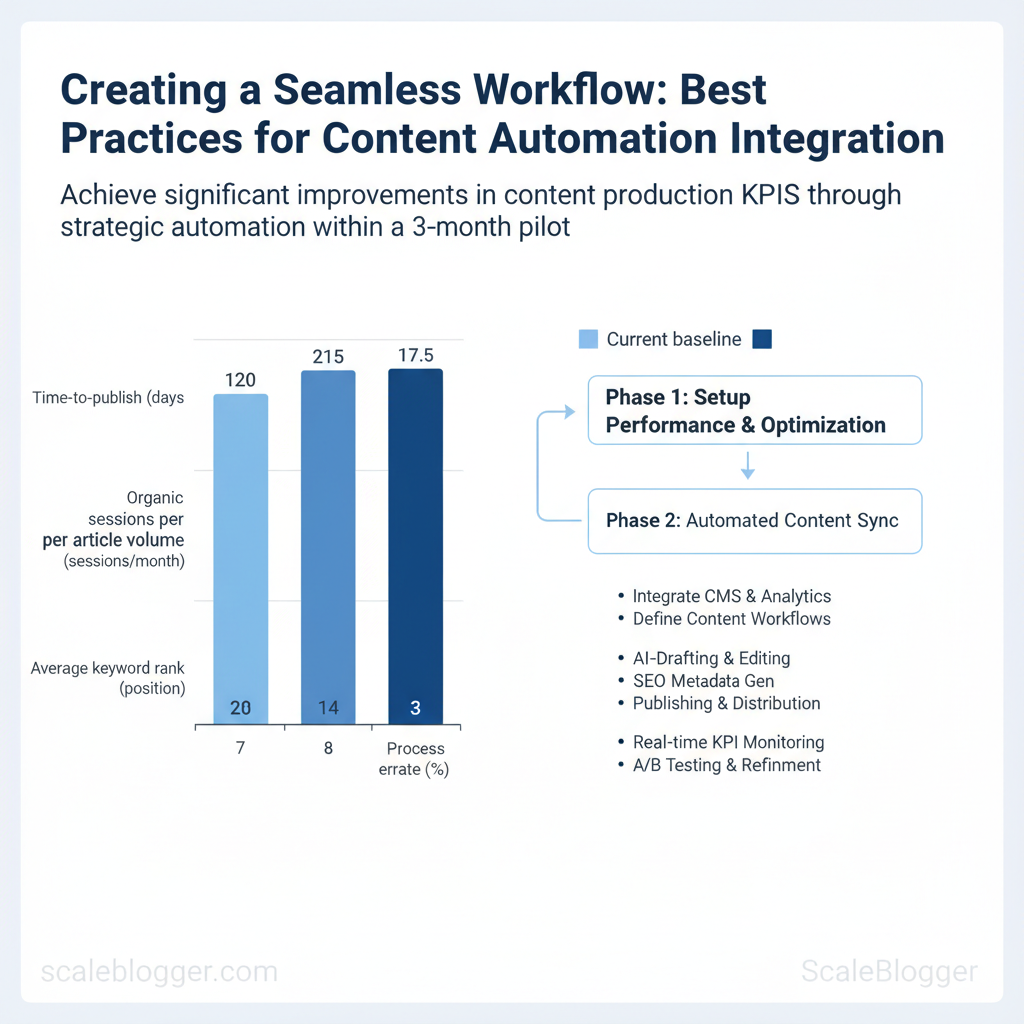
| KPI | Current baseline (example) | 3-month target | How to measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time-to-publish | 7 days average | 3–4 days | CMS publishing logs (avg time from brief to publish) |
| Organic sessions per article | 120 sessions/month | 180–250 sessions/month | GA4 article-level sessions |
| Content production volume | 8 published articles/month | 12–16 articles/month | CMS publishing counts |
| Average keyword rank | Position 28 (top query) | Improve to position 15–20 | Google Search Console (average position) |
| Process error rate (manual fixes) | 10% of publishes need fixes | ≤3% | CMS issue tracker / post-publish rollback logs |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented deliberately, the strategy reduces overhead and frees creators to focus on high-impact content.
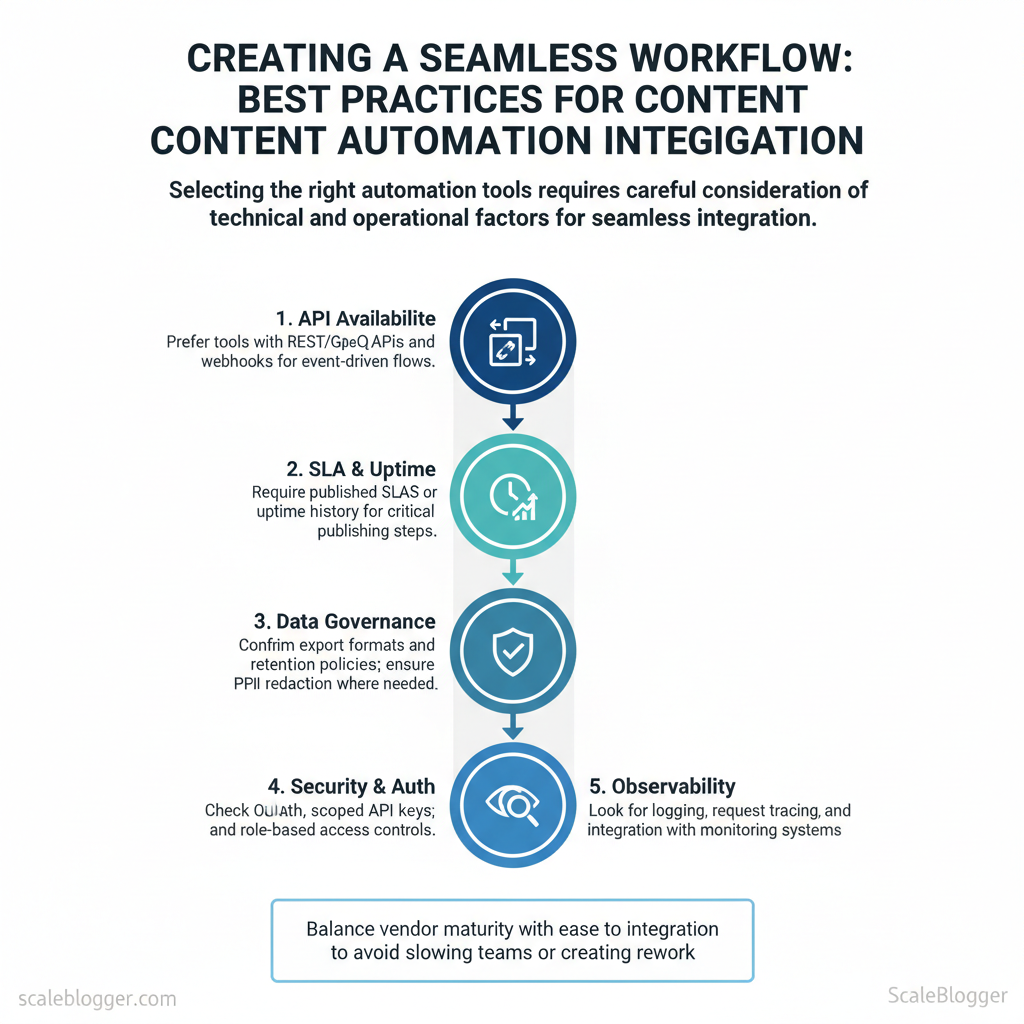
Choose tools & design integrations
Start by matching tools to the part of the content pipeline you actually need: authoring, review, optimization, scheduling, or delivery. Choose tools that expose stable APIs, support automation-friendly auth (OAuth or API keys with scoped access), and include monitoring hooks so failures don’t silently drop content. Balance vendor maturity with how easily the tool fits into your architecture—an overpowered CMS plugin can slow teams as much as an under-powered AI assistant can create rework.
Tool selection checklist
- API availability: Prefer tools with REST/GraphQL APIs and webhooks for event-driven flows.
- SLA & uptime: Require published SLAs or uptime history for critical publishing steps.
- Data governance: Confirm export formats and retention policies; ensure `PII` redaction where needed.
- Security & auth: Check OAuth, scoped API keys, and role-based access controls.
- Observability: Look for logging, request tracing, and integration with alerting (PagerDuty/Slack).
- Extensibility: Verify plugin SDKs, templating, or custom scripting support.
- Trialability: Run a technical proof-of-concept that writes, edits, and publishes a draft via the API.
Integration design patterns
- Event-driven integrations: Use webhooks or message queues (Kafka/SQS) to react to editorial events—ideal for near-real-time workflows.
- Scheduled integrations: Use cron-like jobs for batch tasks (SEO audits, backlog publishing) where immediate consistency isn’t required.
- Idempotency & retries: Implement idempotency keys for all write operations and exponential backoff + jitter on retries to avoid duplication and thundering herds.
- Observability: Emit structured events, retain request IDs, and wire errors to an incident channel for immediate triage.
Industry analysis shows that orchestrated automation reduces manual publish errors and accelerates time-to-live for high-value content.
| Tool category | Primary use | Strengths | Typical risks/cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMS automation plugins | In-editor templates, auto-tagging | Fast authoring, deep editorial UX | Tight CMS coupling, plugin conflicts |
| Workflow automation platforms (e.g., Zapier/Make) | Cross-app triggers & actions | Rapid prototyping, 3,000+ connectors | Rate limits, vendor lock-in on complex flows |
| AI content assistants | Drafting, rewriting, summaries | NLP generation, productivity gains | Hallucinations, content accuracy risk |
| SEO analytics connectors | Pull SEO metrics (GA4, Search Console) | Data-driven optimization, keyword signals | Data sampling, API quota limits |
| Publishing/CDN integrations | Deploy static content, cache invalidation | Fast delivery, global caching | Cache staleness, TLS/config complexity |
Build governance & content quality guardrails
Start by locking down the rules that let teams move fast without creating brand or legal risk. Standardize inputs, define approval gates based on risk, and automate routine checks so humans only touch exceptions. This reduces rework, keeps messaging consistent, and makes audits trivial.
Create templates, style guides and approval gates
Automated QA: checks and monitoring Matrix of automated QA checks and recommended tooling or approach — automated content QA checklist
| QA check | Why it matters | Automation approach/tool | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEO metadata completeness | Ensures search discoverability | Screaming Frog crawl + CMS webhook to flag missing title/meta | Every publish + weekly site crawl |
| Broken links | Prevents UX/SEO penalties | Ahrefs Site Audit + internal link checker script | Daily |
| Readability score | Improves engagement and retention | Readability API (Flesch-Kincaid) + Editor plugin | On save |
| Duplicate content/plagiarism | Protects rankings and brand | Copyscape / Turnitin integration; `content-fingerprint` comparison | Pre-publish |
| Canonical and schema validation | Prevents indexation issues and rich result errors | Schema validator + Screaming Frog canonical report | Weekly |
Automated QA: checks and monitoring (continued)
- Set alert thresholds and escalation: Configure alerts for >5% broken links on a page, readability below target, or plagiarism score >5% and route to the content owner. Define a 24–72 hour SLA based on severity.
- Schedule manual audits: Run quarterly editorial audits that sample 10% of published posts, prioritize high-traffic pages, and reconcile automated findings with reader metrics.
- Example escalation path: Automated alert → content owner review (24h) → editor decision (48h) → legal (72h) for regulated content.
Implement automation safely (pilot to scale)
Start by treating automation as an experiment: run a tightly scoped pilot with measurable controls, then use documented wins to expand. A focused 6–8 week pilot reduces operational risk while proving ROI and surfacing integration issues early. Define which channels and content types are in-scope, pick a control group, and commit to specific, measurable outcomes so decisions are evidence-driven rather than anecdotal.
Pilot plan and success criteria
| Week | Milestone | Owner | Deliverable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Kickoff & tooling setup | Project Manager | Baseline metrics, access, runbooks |
| Week 2-3 | Content generation + control creation | Content Lead | 4 pilot pieces, 4 control pieces |
| Week 4 | QA and publish first batch | Editor & Dev | Published posts, publishing script |
| Week 5-6 | Measure early signals & iterate | SEO Specialist | Engagement report, 2 refinements |
| Week 7-8 | Final analysis & recommendation | Analytics Lead | Comparative report, scale decision |
Scale-up checklist and change management
- Document decisions: Capture runbooks, prompt templates, editorial rules, and exception policies.
- Train teams: Run role-specific sessions; create a short `how-we-publish.md` playbook.
- Appoint champions: Identify departmental owners to resolve issues and own outcomes.
- Roll out incrementally: Expand channel-by-channel, doubling cadence only after meeting thresholds.
- Monitor continuously: Set alerts on quality signals (plagiarism, readability, traffic drops).
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented incrementally, automation reduces overhead and lets creators focus on high-value strategy.
Measure impact and iterate
Begin by treating measurement as an operational process, not a one-off report. Build a dashboard that ties content activity to business outcomes, then use short- and long-term signals to prioritize experiments and update the content system. The immediate aim is to see whether automation is delivering time saved, traffic growth, and lead quality — and to convert those signals into repeatable improvements in templates, runbooks, and scheduling.
What to include in the dashboard and why
- Time saved per article: Track hours reclaimed by automation versus manual baseline to justify tooling and staffing changes.
- Publishing throughput: Monitor completed articles per week to spot bottlenecks in the pipeline.
- Organic traffic uplift: Measure page-level sessions and users to link content edits to traffic changes.
- Average rank improvement: Follow target keyword rank deltas over 30–90 days to capture SEO effect.
- Cost-per-lead (if tracked): Attribute content-driven leads through CRM to understand ROI.
| KPI | Definition | Data source | Refresh cadence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time saved per article | Average hours saved using automation vs manual process | CMS logs + team time-tracking | Weekly |
| Publishing throughput | Number of published posts meeting quality checklist | CMS logs (published status) | Daily |
| Organic traffic uplift | % increase in sessions from organic search vs baseline | Google Analytics 4 (GA4) | Daily |
| Average rank improvement | Median SERP position change for target keywords | Rank tracker (e.g., Ahrefs/SEMrush) | Weekly |
| Engagement rate | Avg. time on page + scroll depth combined metric | GA4 + page analytics | Weekly |
| Lead volume from content | Number of CRM-attributed leads originating from content pages | CRM (Salesforce/HubSpot) + UTM data | Daily |
| Cost-per-lead (content) | Content spend / attributed leads | Finance + CRM | Monthly |
| Conversion rate (content landing) | Leads / sessions on content landing pages | GA4 + CRM | Weekly |
Design experiments that produce decisive answers
Practical tips and common pitfalls
- Do: Refresh data frequently for operational KPIs and monthly for ROI metrics.
- Don’t: Draw conclusions from one-week traffic swings — SEO effects take time.
- Use: Automated alerts for throughput drops and sudden rank declines.
📥 Download: Content Automation Integration Checklist (PDF)
Case studies, common pitfalls & troubleshooting
Automation scaled two different teams fast: one increased monthly organic sessions by 42% while keeping quality stable; another accidentally published duplicate pages and lost rank for core keywords. Successful rollouts treat automation as a coordinated system—content generation, schema, publishing rules and analytics must be validated together. Failed rollouts treat automation as a single black box and skip triage and rollback strategies.
Mini case studies (success and failure) Success — Mid-market SaaS blog: The team implemented an AI-powered content pipeline, standardized templates, and `preflight` checks in the CMS. Results after 6 months: +42% organic sessions, 2.1x more indexed pages, and time-to-publish cut from 10 to 3 days. Why it worked: consistent templates, human-in-the-loop editing, and automated canonical/tagging rules prevented duplication. Failure — Publisher with aggressive scaling: Automation published hundreds of near-duplicate posts with slight title variations. Outcome: a visible drop in rankings for 12 core keywords and a 25% decrease in page-level impressions. Why it failed: missing deduplication rules, no canonical enforcement, and absent rollback process. Actionable lesson: enforce unique-title checks and require manual approval for template changes.
Troubleshooting checklist and escalation paths
| Problem | Symptom | Likely cause | Immediate remediation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duplicate/publishing multiple versions | Multiple slugs, duplicate titles in CMS | Missing dedupe rules, webhook retries | Disable webhook, run CMS dedupe, set canonical tags |
| Drop in organic traffic after automation | Sharp traffic fall, fewer impressions | Low-content quality, index bloat, wrong canonical | Rollback batch, audit top pages, submit updated sitemap |
| API failures or rate-limits | 429/5xx errors in logs, halted publishes | Exceeded API quotas, improper retry logic | Throttle requests, implement exponential backoff, contact API provider |
| Quality decline in content tone | Higher edit rejection, inconsistent voice | Poor prompt/templates, no human review | Pause generation, refine templates, require editor pass |
| Broken internal links after publish | 404s, orphaned pages, user flow breaks | Incorrect slug mapping, template bug | Repoint links, restore slugs, run site link audit |
Escalation paths: designate an incident lead, notify SEO and engineering, and only escalate to legal/PR if site-wide reputation risk exists. Use postmortems to convert failures into checklist items in the automation pipeline. When implemented correctly, these controls reduce firefighting and keep teams focused on strategy—Scale your content workflow by automating safeguards and human checks with tools like Scaleblogger.com when appropriate. Understanding these failure modes and having clear rollbacks ensures automation accelerates growth rather than creating risk.
Conclusion
After redesigning approval paths and automating repetitive publishing tasks, teams that standardized templates and set up automated review gates shipped content faster and cut publication errors. Pairing scheduled content feeds with simple integrations reduced calendar friction, and a pilot that routed drafts through an approval workflow saved several hours per week for a mid-sized SaaS marketing team. Those patterns show that consistency, automation, and clear ownership are the levers that actually move velocity and quality together.
– Standardize templates to reduce review cycles. – Automate approvals and publishing to reclaim hours each week. – Measure cycle time so improvements are visible and sustained.
For the next step, pick a small, high-impact workflow—one content type, one channel—and run a two-week pilot to prove time savings and error reduction. To streamline this process, platforms like Start a content automation pilot with Scaleblogger can help teams map workflows, automate handoffs, and measure outcomes without heavy engineering. If questions remain about scope or tooling, focus first on the single bottleneck that causes the most rework; resolving that will make the subsequent automations far easier to scale.

