Marketing teams drown in one-size-fits-all emails and generic landing pages while conversion opportunities slip away. Automated content personalization stops that leak by matching messages to intent, stage, and channel without scaling costs linearly with audience size.
When personalization is done right, engagement rises and wasted creative hours fall. Implementing `content targeting automation` across journeys enables timely, relevant touchpoints at scale, turning routine workflows into revenue-driving systems. Industry research shows organizations that treat personalization as an operating model, not a feature, capture outsized returns from existing channels.
- How to map user signals to personalized content blocks quickly
- Techniques for scaling personalization without exploding operations cost
- Where `automated content personalization` fits inside scalable marketing strategies
- Common pitfalls during rollout and how to avoid them
- Practical tools and processes to sustain content targeting automation over time
Understanding Personalization in Automated Content
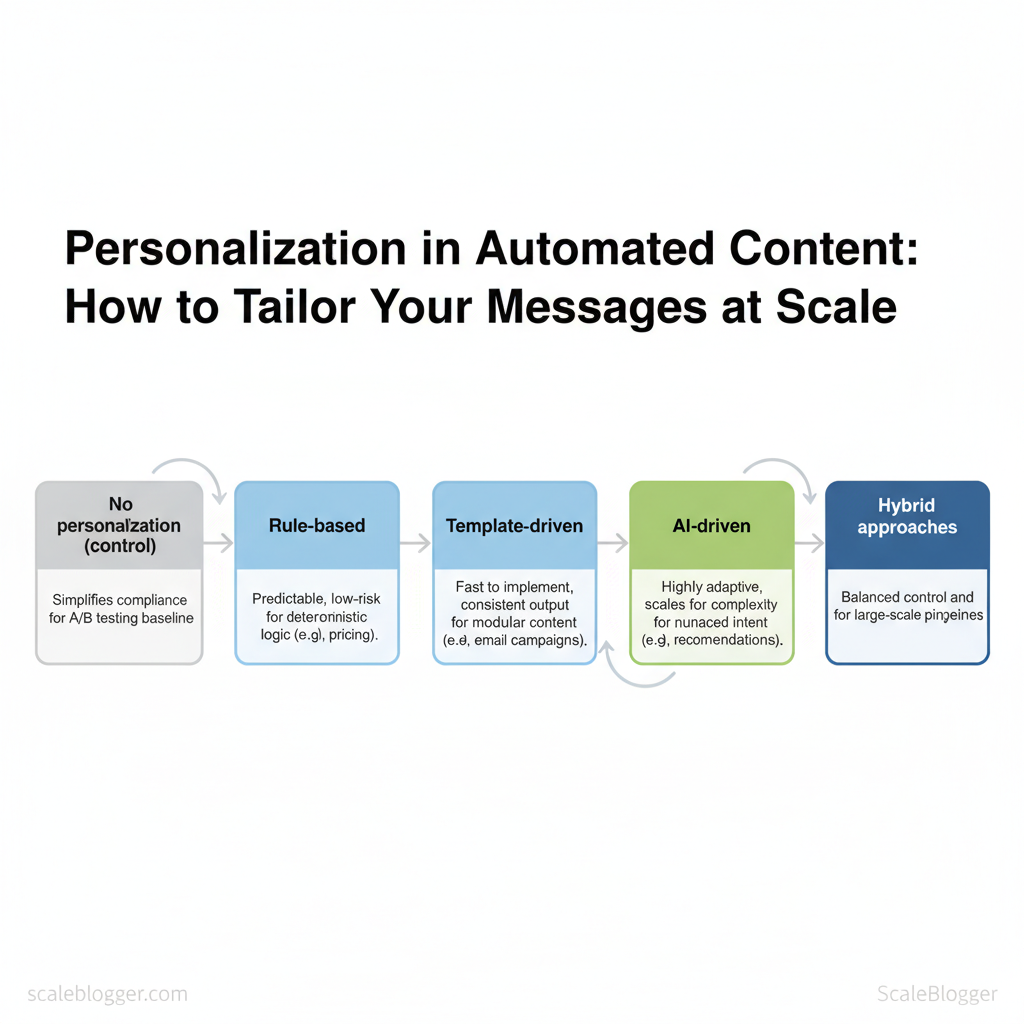
Personalization in automated content means tailoring messaging, structure, or recommendations to individual users or defined audience segments using rules, templates, or machine learning. At its simplest, personalization swaps a name or location into an email; at scale, it adapts topic focus, calls-to-action, and content depth based on behavior and intent signals. Choosing between rule-based, template-driven, and AI-driven approaches depends on precision needs, volume, and risk tolerance.
What to expect when you add personalization:
- Faster relevance: content reaches audiences with higher intent alignment.
- Higher conversion lift: targeted CTAs and content sequencing improve conversion rates.
- Increased complexity: personalization introduces data and governance requirements.
Primary KPIs and ROI signals to track
- Primary KPI — Engagement: page dwell time, scroll depth, and content interactions.
- Conversion metrics: micro-conversions (newsletter signups), macro-conversions (trial signups, purchases).
- Efficiency metrics: time-to-publish, content-per-author ratio, and cost-per-piece.
- Quality signals: bounce rate, user feedback, and editorial scorecards.
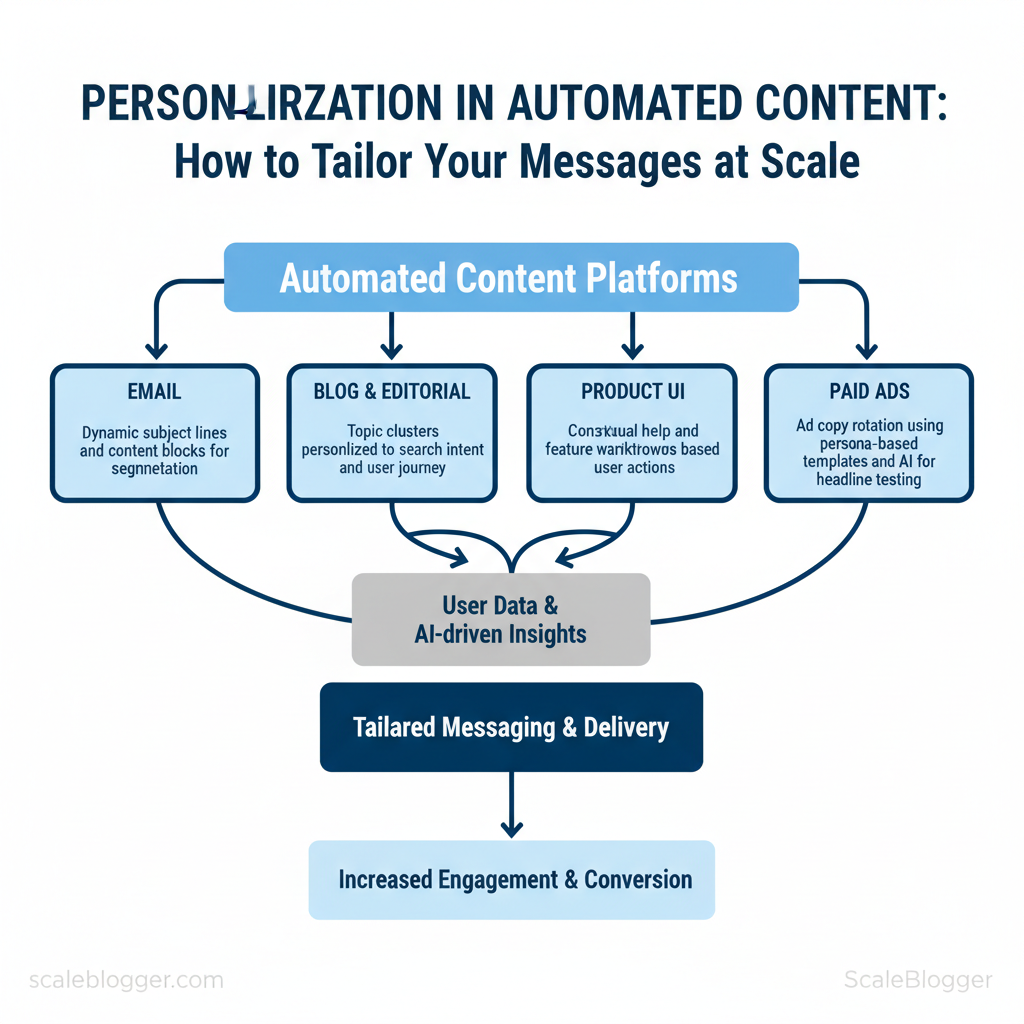
- Email: dynamic subject lines + content blocks for segmentation.
- Blog and editorial: topic clusters personalized to search intent and user journey.
- Product UI: contextual help and feature walkthroughs based on user actions.
- Paid ads: ad copy rotation using persona-based templates and AI for headline testing.
- Data minimization: store only what’s necessary and use hashed identifiers when possible.
- Consent and transparency: log consent and expose personalization choices to users.
- Fallback logic: ensure rule-based fallbacks if models return low-confidence outputs.
| Approach | How it works | Best use cases | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-based personalization | Deterministic `if/then` logic using known attributes | Pricing, legal messaging, billing flows | Predictable, low-risk, easy to audit | Scales poorly for nuanced intent |
| Template-driven personalization | Modular content templates with variable slots | Email campaigns, blog modules, landing pages | Fast to implement, consistent output | Limited creativity, repetitive tone |
| AI-driven personalization | Models infer intent from behavior, text, and signals | Content recommendation, dynamic article generation | Highly adaptive, scales for complexity | Requires data, monitoring, potential bias |
| Hybrid approaches | Rules enforce constraints; AI selects content | Large-scale editorial pipelines, product content | Balanced control and adaptability | More engineering and governance needed |
| No personalization (control) | Static content served to all users | A/B testing, baseline comparisons | Simplifies compliance, easy benchmark | Lower engagement potential |
Building a Scalable Personalization Framework
Start by treating personalization as a platform problem, not a one-off campaign. Prioritize first-party data collection, build a durable audience taxonomy, and create modular content components with decision logic that maps signals to content blocks. This prevents manual, brittle rules and makes personalization repeatable across channels. Practical implementation breaks down into three actions: design the data and identity layer, standardize reusable content templates, and encode decision logic as composable rules that teams can version and test.
Prerequisites
- Data sources available: first-party analytics, CRM exports, transaction logs.
- Identity layer plan: a strategy for deterministic + probabilistic matching.
- Governance: privacy policy aligned with GDPR/CCPA and a consent mechanism.
- CDP or unified data store (e.g., CDP, data warehouse)
- Templating engine supporting modular blocks (CMS with componentized templates)
- Rule engine / feature store for decision logic
- Tracking plan documented as `event_name`, `user_id`, `session_id`, `timestamp`
Creating Reusable Content Templates and Decision Logic
Industry analysis shows modular templates reduce production time and technical debt when teams reuse standardized blocks.
Tools, Platforms, and Integrations
A practical stack starts with three layers: content creation (AI + authoring), orchestration (CMS + workflow), and measurement (analytics + experimentation). Choose components to minimize handoffs and make automation the default path for repetitive work. Below are concrete selection criteria, integration patterns, and operational tips that accelerate a content program without creating brittle dependencies.
Stack Components and Selection Criteria
- Content generation — AI writing models with tone controls and templates.
- Authoring + CMS — headless CMS or CMS with API hooks to support automated publish flows.
- Workflow/orchestration — task engine or automation platform to manage approvals, metadata, and scheduling.
- SEO & analytics — keyword tools, rank trackers, GA4/BI for performance signals.
- Personalization & CDP — user segmentation and content-serving layer for personalized experiences.
- Integrations — webhooks, APIs, and middleware (e.g., Zapier, n8n) for connectivity.
Trade-offs by company size:
- Startups: prioritize speed and low cost; accept single-vendor lock-in for rapid iteration.
- SMBs: prioritize reliability and analytics; pay for integrations and mid-tier SLAs.
- Enterprises: prioritize security, governance, and multi-region support; higher cost but lower risk.
Integration Patterns and Practical Tips
Typical pitfalls and mitigations: Pitfall: Over-automating approvals → Mitigation:* keep human-in-loop for top 10% of strategic posts. Pitfall: Siloed analytics → Mitigation:* centralize events into a BI layer and map a shared taxonomy. Pitfall: Vendor lock-in → Mitigation:* enforce exportable metadata and an abstraction layer.
Monitoring and fallback strategies:
- Monitor: content publish success, API error rates, and model output quality.
- Fallback: queued retry logic, circuit breakers for third-party failures, and a safe-mode manual publish path.
Industry analysis shows teams that instrument automation with observability lower incident time-to-repair.
| Company Size | Key Priorities | Must-have Features | Budget Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Startup | Speed to market, low overhead | API access, simple CMS, basic AI model | Pricing typically ranges $0–$150/mo; Free tiers common |
| Small‑Mid Business | Reliability, SEO growth | SEO analytics, scheduled publishing, GA4 integration | $150–$1,000/mo depending on seats and tools |
| Enterprise | Governance, security, scale | RBAC, audit logs, SSO, multi-region CDN | $2,000+/mo; annual contracts and enterprise SLAs |
| Agency/Consultancy | Multi-client management, reporting | Multi-tenant CMS, white-label reporting, content scoring | Per-client pricing or seat-based; $300–$2,000/client |
| In‑house experiment stack | Fast iteration, A/B testing | Feature flags, experiment platform, content variants | $50–$500/mo for lightweight setups; scale increases cost |
Practical next steps: implement one automation (publish + metadata + analytics) end-to-end, measure time saved, then expand. For robust, repeatable pipelines, combine a headless CMS, an orchestration layer, and continuous monitoring—this balances control with developer velocity and reduces time spent on repeatable tasks. Consider AI content automation from Scaleblogger.com as an option when standardizing pipelines and scoring content performance. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Operationalizing Personalization Workflows
Personalization must move from experiments to repeatable operations: build playbooks, automate decision points, and assign clear measurement standards so teams can scale without bottlenecks. Start with lightweight, prescriptive playbooks tied to content ops rules, then close the loop with testing and attribution that isolate personalization lift from seasonal or channel noise.
Playbooks and Content Operations
- Versioning: enforce semantic version tags for templates (`v1.0`, `v1.1`) and maintain changelog.
- Approvals: two-step approvals — content owner + legal for offers.
- Localization: centralize copy assets, use translation memory, and local QA.
- Rollback: keep immutable backups and quick rollback paths for live campaigns.
Testing, Measurement, and Attribution
– Testing methodologies: run phased A/B and multi-armed bandit tests; use holdout cohorts to measure incremental lift and avoid contamination from repeated exposure. – Attribution challenges & solutions: personalization often touches multiple touchpoints — use randomized control groups and incremental attribution models rather than last-touch. Combine server-side event tagging with client-side analytics and consolidate in a unified data layer. – Confidence thresholds & KPIs: adopt a minimum 95% confidence for primary revenue metrics, 90% for engagement signals. Track KPIs like activation rate, revenue per user, attach rate, lifetime value (LTV) lift, and cost per conversion.
This approach operationalizes personalization so teams can iterate quickly while preserving statistical rigor and localization fidelity. When implemented well, it reduces manual coordination and lets creators focus on content that actually moves metrics.
| Playbook | Trigger | Audience | Primary Content Block | KPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Welcome / Onboarding | Account creation | New users | 3-step walkthrough + tailored CTA | 7-day activation rate |
| Cart Abandonment | Cart idle 2 hours | Shoppers with items | Dynamic cart summary + 1-click checkout | Recovery rate, recovered revenue |
| Re-engagement | 30+ days inactivity | Dormant users | Personalized content list + incentive | Reactivation rate |
| Post-purchase Cross-sell | Order confirmation | Recent buyers | Product pairing + time-limited discount | Attach rate, AOV |
| Lead Nurture | MQL status | Sales prospects | Problem-aware sequence + case study | SQL conversion rate |
Privacy, Ethics, and Risk Management
Start by treating privacy, ethics, and risk management as design constraints rather than optional extras. Design consent and data flows so that collecting less data is the default, personalization is transparent, and humans retain final control over sensitive decisions. That approach preserves legal defensibility while keeping content personalization effective and auditable.
Compliance and consent best practices
- Consent capture patterns: Implement clear, contextual prompts at the point of data collection and avoid bundling unrelated purposes; prefer `explicit opt-in` for profiling and marketing.
- Data minimization principles: Collect only the attributes required for the feature being delivered; aggregate or hash identifiers where possible.
- Recordkeeping and audit readiness: Log consent timestamps, consent strings, source (web, mobile, third-party), and change history; store retention and deletion events alongside consent metadata.
Practical example: use a two-step newsletter flow — visible marketing opt-in on the signup form, then a `double opt-in` confirmation email that records timestamp and IP. That pattern balances conversion with compliance defensibility.
Ethical personalization and explainability
- Bias and fairness considerations: Monitor model outputs for demographic skews, evaluate personalization features across cohorts, and apply post-processing fairness adjustments where needed.
- User transparency and control: Surface why a recommendation appeared (e.g., “Recommended because you read X”), and provide opt-outs for profile-based personalization.
- Human-in-the-loop review processes: Route high-impact or high-risk personalization decisions (financial offers, sensitive categories) to human reviewers before publishing.
| Consent Type | How it works | Typical use cases | Compliance risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implied consent | Consent inferred from user actions (continued site use) | Low-risk analytics, basic cookies | Moderate — not sufficient for profiling under `GDPR` |
| Explicit opt-in | User affirmatively agrees (checkbox, double opt-in) | Email marketing, targeted ads | Low when recorded correctly |
| Granular consent (per purpose) | Separate approvals per processing purpose | Personalization, behavioral profiling | Lower — best practice for complex uses |
| Opt-out mechanisms | Default on; user must request exclusion | Newsletter unsubscribe, remarketing lists | Higher — risky under `GDPR` if defaulted |
| Consent via third-party platforms | Consent captured by social/login providers | Social logins, platform-sourced profiles | Variable — depends on vendor practices and contracts |
Understanding and operationalizing these practices lets teams scale personalization without multiplying compliance debt. When policies, tooling, and human review are aligned, risk becomes manageable and predictable.
📥 Download: Personalization in Automated Content Checklist (PDF)
Scaling, Continuous Improvement, and Case Studies
Scaling personalization requires a clear maturity model, measurable KPIs, and a repeatable feedback loop so teams increase impact without ballooning costs. Start small with experiments, standardize what works, automate routine tasks, and expand governance and infrastructure as ROI solidifies. Below are practical stages, timelines, milestones, and resource estimates to plan a 12–24 month personalization scaling roadmap.
| Stage | Timeframe | Key Milestones | Resource Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | 1–3 months | Audience segmentation tests, 3 A/B tests, baseline KPIs set | 1 PM, 1 analyst, ~$5k tooling |
| Implement | 3–6 months | Content templates, personalization rules, CMS integrations | 1 PM, 2 devs, 1 analyst, ~$10–20k |
| Optimize | 6–12 months | Automated workflows, model tuning, performance dashboard | 1 product lead, 2 devs, 1 ML specialist, ~$25–50k |
| Enterprise | 12–18 months | Cross-channel orchestration, SLA, content ops playbook | 2 product leads, 4 devs, 2 analysts, ~$75–150k |
| Global Rollout | 18–24 months | Localization pipelines, governance, regional analytics | Org-wide stakeholders, regional leads, ~$150–300k+ |
Practical case studies and actionable steps make this tangible.
1) Case study — Niche B2B blog: what they did → measurable result
- Approach: Ran 6-week segmentation experiments combining intent signals and company size.
- Tactics: Built 3 dynamic templates, automated lead scoring, and rerouted high-intent traffic to sales pages.
- Result: 38% lift in qualified leads within 3 months.
- Approach: Implemented behavioral personalization on homepage and newsletters.
- Tactics: Used simple recency/frequency rules, automated content tagging, and weekly model retrains.
- Result: Engagement up 24% and churn down 12% in two quarters.
Conclusion
Automated content personalization converts passive traffic into engaged prospects by aligning messages with buyer intent, improving open and conversion rates, and reducing repetitive manual work. Teams that piloted rule-based personalization for onboarding emails saw open rates climb and trial-to-paid conversion improve within six weeks; a mid-market SaaS team that layered AI-driven topic selection onto that workflow doubled short-form content output without hiring additional writers. Expect initial setup to take a few weeks, ongoing tuning to be incremental, and early wins to appear in performance metrics rather than vanity counts. Common questions — “How fast will this scale?” and “How much engineering lift is required?” — resolve into trade-offs: faster gains from template-driven personalization, larger long-term returns from model-backed automation.
– Start small: prototype one high-value funnel (emails or landing pages) and measure lift. – Automate repeatable steps: free up creative time by offloading segmentation, drafting, and A/B orchestration. – Monitor and iterate: treat content automation as an optimization loop, not a one-off project.
For teams looking to streamline implementation and accelerate results, platforms like Explore Scaleblogger’s automation-first content solutions can be a practical next step. Book an internal pilot, map the first 30–60 day milestones, and prioritize quick, measurable experiments that prove the ROI of personalization.

