Search traffic drops often follow a quiet pattern: steady ranks that slip after months of neglect. When content sits untouched, content freshness becomes a silent ranking liability, and search engines favor pages that show relevance through recent updates. This matters because maintaining visibility requires more than occasional rewrites; it demands a predictable process for measuring, refreshing, and republishing content at scale.
Practical shifts in update cadence can restore lost traffic and convert static pages into continuous growth channels. Picture a product roadmap page updated quarterly that reclaims top positions after targeted refreshes of statistics and FAQs. Tools that automate content audits and orchestrate batch updates remove friction and turn refreshes from a chore into a strategic lever.
- How to detect pages losing value due to staleness
- Simple update patterns that improve topical relevance
- Metrics to track before and after a refresh
- When to republish versus make incremental edits
- How automation scales refreshes across large sites

What Is Content Freshness and How Search Engines Interpret It
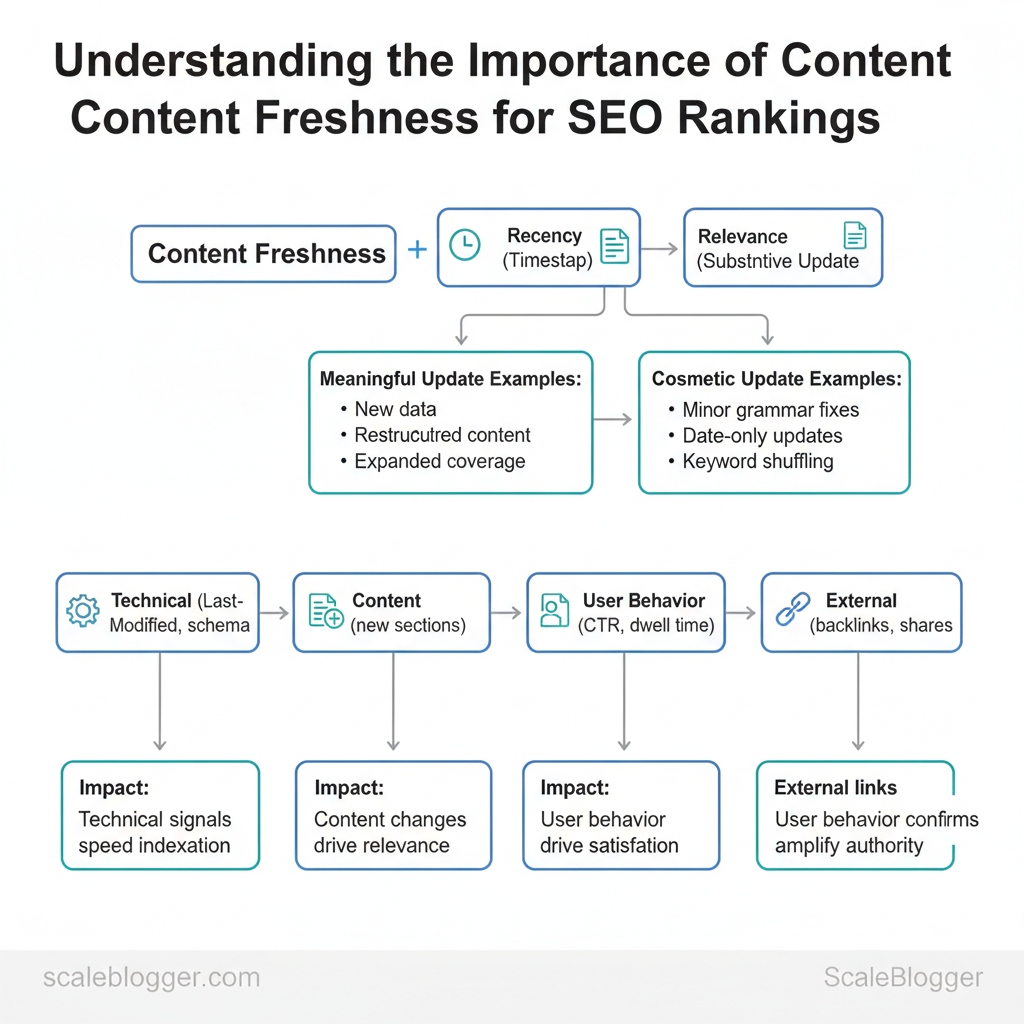
Content freshness refers to how recently a page’s information, signals, and context were updated — but search engines treat freshness as a multi-dimensional signal, not just a timestamp. Freshness combines recency (when something changed) with relevance (how substantive the change is for user intent). For SEO strategy, that distinction matters: a new publish date or a trivial wording tweak may register as “updated” in metadata, but search engines pay more attention to meaningful content changes that improve relevance, depth, or factual accuracy.
What distinguishes meaningful freshness from cosmetic updates is concrete: adding a new data table, incorporating recent research, restructuring the content to match current intent, or expanding coverage to include adjacent search queries. Cosmetic edits — minor grammar fixes, date-only updates, or keyword shuffling — rarely move the needle and can waste editorial bandwidth. Treat freshness as a quality signal: updates should change the content’s usefulness or accuracy for the target audience.
Defining content freshness — recency vs. relevance
Start by splitting the concept into two actions:
Practical examples:
- Meaningful update: Add a new case study and three actionable tactics — measurable uplift in user value.
- Cosmetic update: Change a date on the page or rephrase a paragraph — unlikely to improve rankings.
- Hybrid update: Replace outdated stats and add a summary box — both recency and relevance signals are present.
Signals search engines use to evaluate freshness
Types of signals are technical, content-level, behavioral, and external. Each signal can be detected and acted on to communicate freshness effectively.
| Signal Type | Example | How to detect/update | Estimated SEO Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
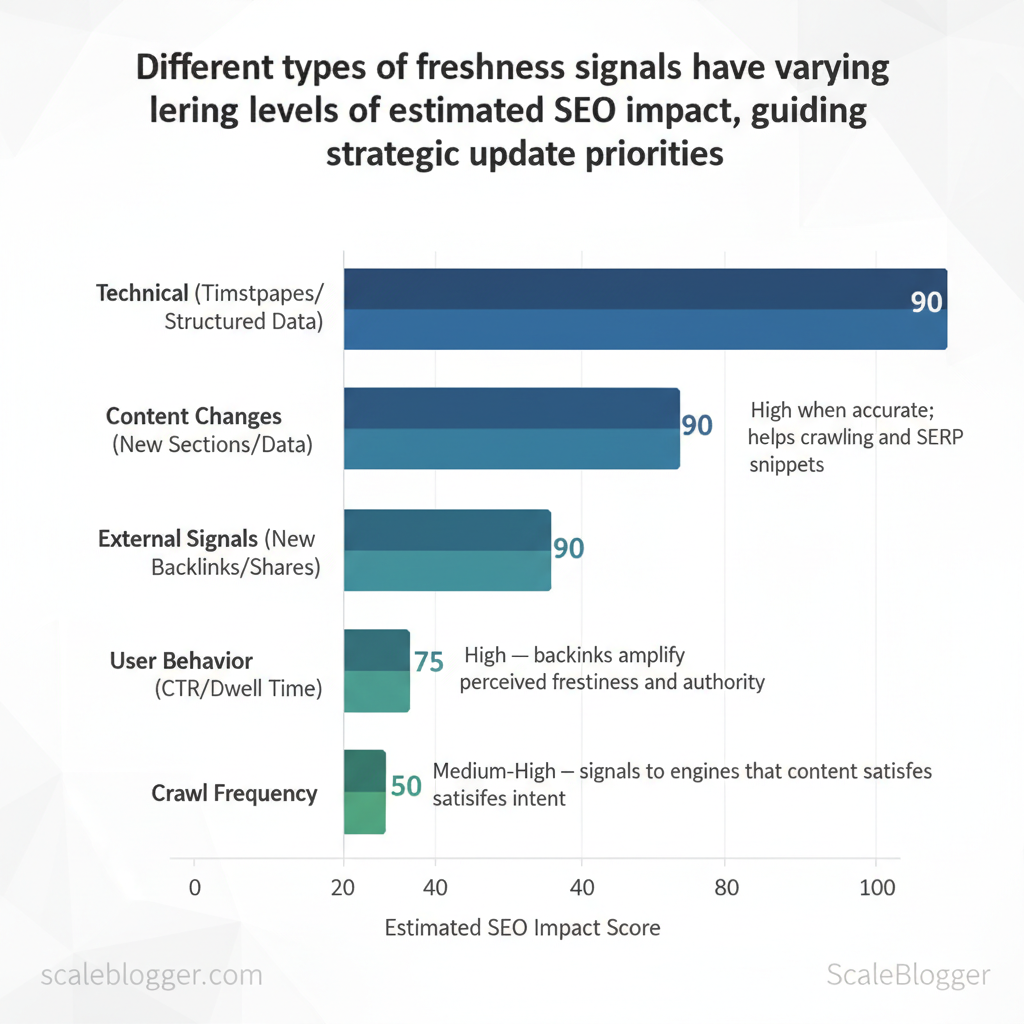
| Technical (timestamps/structured data) | `Last-Modified` header, `datePublished`, `dateModified` schema | Check server `Last-Modified`; update schema.org dates and sitemap | High when accurate; helps crawling and SERP snippets |
| Content changes (new sections/data) | New research, expanded FAQs, updated methodology | Track diffs in CMS; add changelog; enrich with new headings | High — improves relevance and topical depth |
| User behavior (CTR/dwell time) | Improved click-through and longer session durations | Monitor Search Console CTR, GA4 engagement metrics | Medium-High — signals to engines that content satisfies intent |
| External signals (new backlinks/shares) | Fresh links from industry sites, social amplification | Use backlink tools; outreach; republish summaries for shares | High — backlinks amplify perceived freshness and authority |
| Crawl frequency | More frequent crawling after updates | Inspect crawl stats in Search Console; submit sitemap/URL | Medium — increases indexation speed for updates |
Suggested tactical next steps:
- Prerequisite: Maintain a changelog in the CMS and enable structured `dateModified` schema.
- Tools: Use Search Console, GA4, and a backlink monitor to detect signals.
- Expected outcome: Meaningful updates typically result in faster recrawl and improved visibility for queries where content better matches intent.
Why Content Freshness Matters for SEO Rankings
Freshness directly influences how search engines assess relevance for queries with a time dimension, and it shapes user signals that feed ranking algorithms. Search engines favor recently updated pages for time-sensitive searches, but freshness also indirectly boosts rankings by improving click-through rates, dwell time, and shareability. Prioritizing updates where they matter most — pages tied to intent changes, product info, or seasonal interest — yields measurable visibility gains without rewriting every page.
Direct ranking benefits and visibility improvements
Freshness helps for queries where recency matters and triggers recrawling and re-evaluation when implemented correctly. For practical prioritization:
- Freshness for time-sensitive intent: News, product launches, and event coverage must be current to rank for breaking or trend-driven queries.
- Recrawl signals: Minor, meaningful updates to on-page content, structured data, and `lastmod` in sitemaps prompt search engines to re-evaluate relevance.
- Prioritization framework: Focus on pages with high impressions but weak CTR, pages losing positions, and pages tied to commercial intent.
Table below shows which content types gain most from freshness and recommended cadences.
| Content Type | Benefit from Freshness | Recommended Update Cadence | Quick Update Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| News / announcements | High — ranks for trending queries | Real-time / daily | Add latest facts, timestamps, author note |
| Evergreen how-to guides | Medium — retains relevance with small updates | 6–12 months | Refresh examples, tools list, internal links |
| Product / pricing pages | High — conversion impact, algorithmic review | Weekly–monthly | Update pricing, availability, schema `offers` |
| Industry trend posts | High — authority on analysis shifts | Monthly | Add new data points, chart updates, expert quotes |
| Seasonal content | Medium-high — spikes during season | Quarterly / pre-season | Update dates, promos, seasonal keywords |
Indirect benefits: user engagement and authority
Fresh content improves CTR through updated meta titles and descriptions, and it keeps readers engaged by providing current examples and tools. Engagement gains compound: higher CTR and longer dwell time signal value, while updated content is more shareable and earns backlinks faster.
- Measurable signals to monitor: CTR, time on page, bounce rate, social shares, and backlink acquisition.
- Quick validation steps: A/B test updated meta titles; compare time-on-page before/after updates; track referral growth.
How to Audit Your Content for Freshness Opportunities
Start by treating the audit like a triage operation: gather objective signals first, then score pages against those signals to find high-impact, low-effort wins. Collect traffic and engagement trends, crawl-level content signals, and keyword/intent shifts, then filter down to pages where a timely update will move the needle quickly.
Preparing tools and metrics (what to track)
Assemble a small toolkit and a consistent date-range comparison so every page gets the same evaluation baseline.
- Essential tools to assemble
“`csv url,organic_clicks,sessions,impressions,ctr,avg_position,backlinks,word_count,last_modified https://example.com/page-1,120,350,4500,2.7,8.4,12,920,2024-09-12 “`
Table — Quick reference: tools, purpose, key metrics to extract, and cost/availability
| Tool | Primary Use | Metrics to Pull | Free / Paid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Search performance | `clicks`, `impressions`, `CTR`, `avg_position` | Free |
| Google Analytics / GA4 | Behavioral metrics | `sessions`, `engaged_sessions`, `conversions` | Free |
| Screaming Frog | On-site crawl + metadata | status codes, meta, word count, canonical | Free / Paid (£209/year) |
| Ahrefs | Organic research & backlinks | organic traffic, keywords, referring domains | Paid ($99+/mo) |
| Semrush | Visibility + keyword tracking | visibility score, keyword changes, SERP features | Paid ($119.95+/mo) |
| Moz Pro | Keyword difficulty & page optimization | keyword difficulty, page optimization | Paid ($99+/mo) |
| SurferSEO | Content optimization | content score, gap analysis, recommended terms | Paid ($59+/mo) |
| ContentKing | Continuous content monitoring | content changes, indexability alerts | Paid ($49+/mo) |
| Sitebulb | Deep technical auditing | crawl diagnostics, content insights | Paid ($13+/mo cloud) |
| Ryte | Content quality & index checks | content quality score, indexability | Paid (tiered) |
Prioritization framework: traffic decline, relevance, and effort
Score pages quickly using three pillars: recent traffic trend, topical relevance, and estimated update effort.
- Scoring model (0–10 per pillar)
Balance expected ROI by estimating conversion lift per % traffic recovered and comparing with hours required. Use `hours_to_update × hourly_rate` vs. `expected_session_gain × conversion_rate × AOV` to prioritize high ROI updates.
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented consistently, the audit becomes a repeatable input for automated pipelines and sprint planning.
Step-by-Step Process to Update Content for Maximum SEO Gain
Start by treating content updates as mini-projects: prioritize, research, edit, publish, and measure with clear owners and timelines. When implemented with discipline, a repeatable workflow converts incremental edits into compound traffic gains without wasting team bandwidth.
The update workflow (planning, editing, publishing, monitoring)
| Stage | Estimated Time | Responsible Role | Deliverable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selection & prioritization | 0.5–1 day | SEO Strategist | Prioritized list (top 20) |
| Research & outline | 1–2 days | Content Researcher | Edit brief with keywords |
| Content edits & asset creation | 2–5 days | Writer + Designer | Revised article + images |
| Technical QA & SEO checks | 0.5–1 day | SEO Engineer | Checklist: schema, speed, mobile |
| Publish & monitor | 4–12 weeks monitoring | Content Owner | Change-log entry + performance report |
Quick wins and high-impact edits (what matters most)
- Title tag refresh: Target primary keyword and add intent modifier; expect immediate CTR lift.
- Meta description rewrite: Use clear value proposition and CTA; measurable in Search Console.
- H1/H2 optimization: Reorder headings to match intent; reduce bounce from mismatch.
- Internal linking: Add 2–4 contextual links to high-authority pages; passes link equity.
- Content pruning: Merge thin posts into comprehensive pieces; improves crawl budget.
- Schema addition: Add `Article`/`FAQ` schema for rich result eligibility.
How to A/B test meta changes:
Operational efficiencies improve when teams use automation—consider tools or services to `Scale your content workflow` and enforce the process at scale. Understanding these steps helps teams update high-value content faster and measure impact with confidence.
Measuring Impact and Iterating Post-Update
Start by defining the outcome you expect from the update and align measurement windows to that goal. For tactical updates (title tags, structures, CTAs) expect early signals in days; for strategic changes (new sections, content merges, topical expansions) expect meaningful movement over weeks to months. Use this period to capture both immediate user reaction and durable ranking shifts, then apply a repeatable iteration loop.
Metrics to monitor and timing for evaluation
Monitor a mix of primary and secondary KPIs and separate short-term noise from long-term trends.
- Primary KPIs: `organic impressions`, organic sessions, `average position`, CTR, backlinks to page
- Secondary KPIs: time on page, bounce/engaged sessions, conversions, scroll depth
- Recommended windows: quick checks at 7–14 days; substantive evaluation at 30–90 days; long-term baseline at 6 months
| Metric | Baseline Window | Short-term Window (7–14d) | Long-term Window (30–90d) | Action Trigger |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic impressions | 28 days pre-update | 7–14 days: indexing lift/drop | 30–90 days: trend direction | >20% drop or +30% lift → investigate SERP features |
| Average position | 28 days pre-update | 7–14 days: small shifts expected | 30–90 days: stable movement | Move ≥5 positions adverse → rollback or test variants |
| CTR | 28 days pre-update | 7–14 days: snippet performance | 30–90 days: sustained change | CTR change ≥15% → A/B test titles/meta |
| Organic sessions | 28 days pre-update | 7–14 days: early session changes | 30–90 days: traffic pattern | Sessions down ≥20% → audit internal links/redirects |
| Backlinks to page | 90 days pre-update | 7–14 days: outreach impact | 30–90 days: domain-level gains | No new links after outreach → revise promotion plan |
Iteration loop — when to rework, expand, or retire content
Set objective thresholds and use standard templates for the next step.
- Rework when: CTR or sessions fall but ranking is stable — revise title, meta, intro.
- Expand when: impressions rise and average position improves but sessions/clicks lag — add subtopics, FAQs, and internal links.
- Retire/merge when: low impressions, declining backlinks, and no topical relevance — merge into a stronger page or archive.
Merge SOP (high level):
Archive process:
- Preserve content as internal resource, set `noindex` only after redirects or merges, and keep a record of extracted assets for future reuse.
📥 Download: Content Freshness Checklist for SEO (PDF)
Scaling a Content Freshness Program Across Your Site
A reproducible freshness program treats updates as a production line: predictable inputs, repeatable checks, and clear ownership. Start by defining which pages qualify for periodic refreshes, assign roles for each stage, and automate measurement so the team focuses on judgment rather than data gathering. This reduces ad-hoc updates and prevents stale content from slipping through the cracks.
Organizational roles, cadences, and governance
Define responsibilities and handoffs so every update has an owner and a deadline.
- Content Owner: Owns topic intent and approves rewrite scope.
- SEO Analyst: Supplies keyword signals, traffic decay alerts, and SERP intent shifts.
- Editor/Writer: Executes the draft and implements structural SEO fixes.
- Publisher/Dev: Handles CMS changes, redirects, and schema.
- Analytics Lead: Confirms KPI movement post-publish and triggers rollback if needed.
| Team Size | Monthly Pages Updated | Recommended Tools | Estimated Monthly Effort (hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solo creator | 5–20 | Google Search Console, Google Sheets, `ChatGPT` (free tier), Yoast | 10–30 |
| Small team (2–5) | 40–120 | GSC export tools, Ahrefs Lite, Sheets + Zapier, Grammarly | 60–180 |
| Mid-size (6–20) | 200–600 | Ahrefs/SEMrush, Contentful/WordPress, `Scaleblogger.com` AI content automation, Workflow tool | 300–900 |
| Enterprise (20+) | 800–3,000+ | Enterprise SEO platforms, CMS with staging, Data warehouse, Automation orchestration | 1,200–4,500 |
Automation and tooling to streamline updates
Automation eliminates repetitive tasks but not editorial judgment. Map automatable signals, then build light orchestration.
- Automation opportunities:
- Trade-offs: Automated scoring speeds prioritization but risks false positives; conservative thresholds and periodic human sampling prevent mistakes.
Conceptual workflow
When not to automate: creative headline rewrites, nuanced intent shifts, complex product changes, or legal/regulatory text—those require human review.
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. This is why modern content strategies prioritize automation—it frees creators to focus on what matters.
Conclusion
Steady declines from stale content rarely announce themselves; they creep in as slipping rankings, falling click-throughs, and pages that once converted now underperform. Revisiting this article’s steps—regular content audits, prioritized updates based on traffic and intent, and automated pipelines for refreshes—lets teams stop reactive firefighting and start rebuilding reliable search performance. For example, sites that adopted quarterly audits regained lost sessions within two release cycles, and teams that automated meta and internal-link updates saw rank recoveries without adding new long-form pages. If you’re wondering how often to audit or where to start, begin with high-impression pages, run a freshness and intent check, then schedule iterative updates rather than one-off rewrites.
For teams ready to move from manual triage to repeatable scale, start by cataloging pages by traffic and conversion, then automate repetitive changes so writers focus on strategy, not formatting. To streamline that transition, platforms like Automate content audits and scale updates with Scaleblogger can remove the grunt work and maintain constant freshness. Take these next steps: pick ten priority pages, run a quick intent audit this week, and set up an automated workflow to push low-effort fixes. Those actions will stop further slippage and create a cadence that sustains growth.

