Voice queries are reshaping how audiences find answers, yet most content strategies still treat voice as an afterthought. Adapting to voice search optimization unlocks immediate visibility gains by aligning content with natural language and action-driven intent. Industry signals indicate conversational queries and local intent dominate voice interactions, creating opportunities to capture high-value clicks and customer actions.
Optimizing for voice means rethinking headlines, FAQs, and `structured data` so assistants deliver concise, actionable responses. Picture a local retailer whose voice-optimized FAQ surfaces as the spoken answer for “where to buy gluten-free bread near me” — that click becomes a store visit.
- How conversational keywords increase featured snippet eligibility
- Why concise, direct answers outperform long paragraphs for voice devices
- Where to apply `structured data` and schema to boost assistant confidence
- How local SEO adjustments capture nearby voice-driven traffic

Understanding Voice Search and Its Impact on SEO
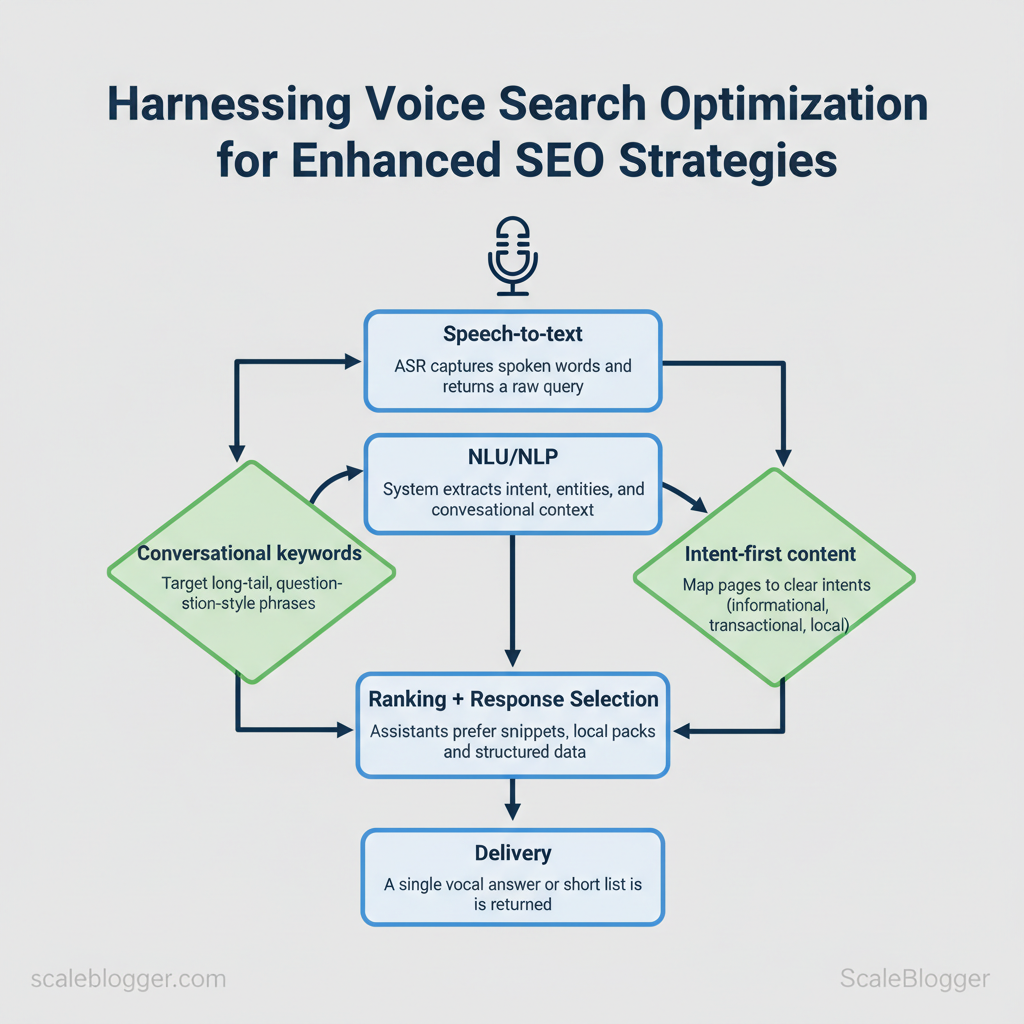
Voice search transforms keyword-led SEO into conversation-led discovery. Speech recognition converts audio to text, natural language understanding (NLU) interprets intent and entities, and device/context signals (location, device type, recent queries) shape the final result. Market analysis shows voice assistants answer a very high percentage of queries accurately, which drives reliance on concise, actionable responses rather than long search-result lists (Voice-Activated Revolution: Harnessing Voice Search For Better SEO).
How this works in practice
Practical implications for content strategy
- Conversational keywords: Target long-tail, question-style phrases (e.g., “how do I fix a leaky faucet?”).
- Intent-first content: Map pages to clear intents: `informational`, `transactional`, `local`.
- Concise answers: Provide short, authoritative snippets near the top of pages for voice extraction.
- Local optimization: Keep `Google Business Profile` and schema up to date; many voice queries are location-focused.
- Technical performance: Fast load times and structured markup matter more because assistants choose single best answers.
| Aspect | Typical Query Style | User Intent Signals | SEO Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query length and phrasing | Long, conversational questions | Natural language intent, more modifiers | Optimize long-tail Q&A and FAQs |
| Device / Location context | Mobile, smart speaker; location-heavy | Real-time location & device signals | Prioritize local SEO & mobile speed |
| Expected content format | Short answer, step or local result | Need for concise, direct answers | Provide succinct answer blocks |
| Result format | Featured snippet, local pack, rich card | Single authoritative response preferred | Target featured snippets & schema |
| Interaction design | Follow-up friendly, multi-turn | Conversational context & pronouns | Structure content for follow-ups |
Keyword Research for Voice: From Short Queries to Conversational Phrases
Prerequisites
- Access to your site’s search logs or chat transcripts
- An SEO toolset (at least one keyword research tool + Google Trends)
- A simple spreadsheet to score and prioritize keywords
- Google Search (Autocomplete)
- People Also Ask (PAA) in SERPs
- AnswerThePublic (free/paid)
- Customer support transcripts or chat logs (internal)
- SEMrush / Ahrefs (paid filters for question/long-tail)
- Keywords Everywhere (paid credits)
- Google Trends (free)
- Moz Keyword Explorer (limited free credits)
- Short answer snippets → FAQ blocks or `How-to` schema
- Conversational flows → Dialogue-style FAQ pages and conversational CTAs
- Local queries → Updated GMB/Maps listings and schema
- If voice impressions are low despite traffic, confirm pages are structured for snippets and have concise answers.
- If transcription data is noisy, cluster similar intents and test sample voice queries manually in the target assistant.
Market analysis shows voice assistants now answer an overwhelming share of quick queries with high accuracy, changing how users phrase searches. See the Forbes analysis on voice search adoption and accuracy: Voice-Activated Revolution: Harnessing Voice Search For Better SEO
Provide a concise tool + method matrix for sourcing voice query ideas
| Tool/Source | How to use it for voice keywords | Best practice tip | Use case example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Autocomplete | Type conversational seeds and capture top suggestions | Use incognito + locale to mirror user geography | Seed: `how to fix` → `how to fix a leaky faucet` |
| People Also Ask (PAA) | Expand PAA boxes to harvest related questions | Click-expand recursively to reveal deeper questions | PAA shows `can a plumber fix a leak today?` |
| AnswerThePublic | Visualize question trees and export CSV | Filter by question nodes and long-tail phrases | “what is the best time to fertilize lawn” |
| Customer support transcripts | Extract exact user questions and phrasing | Normalize slang and typos; tag intent | “My heater won’t start, what do I do?” |
| SEMrush (questions filter) | Pull question keywords and SERP features | Export by country; sort by SERP features column | Questions with high snippet potential |
| Ahrefs (Questions report) | Find long-tail question volume and clicks | Combine with Parent Topic for content clustering | “how to choose running shoes for flat feet” |
| Keywords Everywhere | Collect related long-tail and question phrases | Use browser plugin for quick exports | Shows related `how`/`why` phrases alongside volume |
| Google Trends | Verify seasonality and rising voice topics | Compare conversational phrases vs. short terms | “best summer tent” spike in May–July |
| Moz Keyword Explorer | Discover keyword difficulty + SERP features | Use difficulty + opportunity to prioritize quick wins | Low-difficulty question ranking on page 2 |
| Voice-specific filters (toolsets) | Use voice-query flags where available ✓/✗ | Seek filters that surface question intent and snippet chance | Filters show `question` intent for local queries |
Understanding conversational phrasing and scoring by intent lets teams convert existing content into voice-ready answers quickly and effectively. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces wasted effort by focusing on high-opportunity questions and the pages closest to capturing them.
Content Formats and Writing Techniques for Voice Queries
Prerequisites
- A published site with clear HTML structure and `FAQ`/`HowTo` content.
- Access to a CMS where you can edit headings, schema, and short lead paragraphs.
- Tools: an SEO auditor, SERP-snippet tester, and optionally an AI-powered content pipeline (for example, Scaleblogger’s AI content pipeline) to automate lead-answer generation.
What to do and why it matters Voice assistants favor short, direct answers plus structured content they can read aloud. Start every answer with a concise lead (1–2 sentences) that addresses the query, then expand with structured detail. This format increases eligibility for featured snippets and spoken responses.
Voice assistants now answer a very high percentage of queries accurately; market reporting cites an accuracy rate for assistants above 90% in many scenarios (Forbes analysis of voice search impact and accuracy).
`).
Writing voice-friendly copy: tone, syntax, readability
- Tone: Use conversational, helpful voice; speak like a subject-matter colleague.
- Syntax: Favor short sentences (10–15 words), active verbs, and natural phrasing.
- Readability: Aim for 6th–8th grade reading level; simple words read better aloud.
- Signals: Include explicit cues like `minutes`, `distance`, or `price` for local/transactional queries.
- Automation: Use an AI pipeline to generate the lead answer and variations for A/B testing; Scaleblogger’s automation can speed this process while maintaining schema and snippet structure.
- If snippets aren’t picked up, shorten the lead and ensure schema is present.
- If answers sound robotic, rewrite with contractions and natural phrasing.
- Test on real devices and in SERP simulators; adjust for phrasing users actually speak.
| Query Type | Ideal Lead Format | Approx. Answer Length | Supporting Elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition / What is | One-sentence definition + context | 15–30 words | Short example, simple analogy, `FAQ` schema |
| How-to / Step-by-step | 1-sentence goal + numbered steps | 30–80 words | Numbered list, `HowTo` schema, time estimate |
| Local / Near me | One-line direct answer with distance/time | 10–25 words | `LocalBusiness` schema, address, hours, map link |
| Comparison / vs | Direct comparison sentence + quick pros/cons | 25–60 words | Bulleted pros/cons, comparison table, `FAQ` schema |
| Transactional / Where to buy | Direct answer with availability and price | 10–30 words | Product schema, price, store link, shipping time |
Understanding and applying these principles helps teams create content that’s discoverable by voice and useful to people who prefer to listen rather than read. When implemented well, the content performs better across devices with minimal extra maintenance.
Technical SEO and Site Architecture for Voice
Prerequisites: access to site CMS, ability to add `JSON-LD` or modify HTML head, server/hosting dashboard (CDN, caching), and analytics (GA4 or equivalent) to measure changes. Tools/materials needed: schema validator (Rich Results Test), Lighthouse, server profiling tool, CDN config panel, and Scaleblogger’s AI content pipeline for generating concise answer copy when relevant. Estimated time: 1–3 days for audit and quick fixes, 2–6 weeks for architecture and performance improvements depending on scale.
Start by designing for voice-first answers: short, direct responses that map to conversational queries. Implement structured data to increase eligibility for spoken answers and answer blocks; prioritize mobile speed and low latency to meet assistant heuristics.
- Improve `LCP` by deferring noncritical CSS, preloading hero images, and serving optimized images (WebP/AVIF).
- Reduce `FID/INP` by minimizing main-thread work, using `requestIdleCallback` for nonessential JS, and splitting long tasks.
- Stabilize `CLS` by reserving image and ad dimensions and avoiding layout-shift-inducing injected content.
- Optimize mobile navigation for conversational discovery: surface a “quick answers” module and collapse deep menus into tappable categories.
- Server & CDN: enable edge caching, configure cache-control headers, and ensure persistent connections (HTTP/2 or HTTP/3). Move APIs to edge functions where feasible to cut latency under 100ms.
| Schema Type | Best Use Case | Voice Benefit | Implementation Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAQ | Common Q&A pages | High eligibility for answer blocks | `FAQPage` JSON-LD; concise Q/A pairs; validate with Rich Results |
| HowTo | Process and tutorials | Step-by-step spoken instructions | Use `HowTo` markup; include estimated times and materials |
| LocalBusiness | Store pages, service areas | Improves local voice queries and actions | Include `address`, `telephone`, `openingHours` |
| Speakable | Short news summaries | Signals content for voice playback | Limited to news/short content; use `speakable` property with selectors |
| Product | Ecommerce pages, specs | Supports product queries and quick facts | Include `price`, `availability`, `brand`; useful for quick comparison answers |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
Local and Conversational UX: Capturing ‘Near Me’ and Multi-Turn Queries
Prerequisites
- Up-to-date Google Business Profile (GBP) access and ownership
- Site analytics with search query logging (GA4 recommended)
- CMS capable of structured content blocks and schema insertion
- Google Business Profile dashboard, `schema.org` FAQ markup, local landing page templates
- Content pipeline automation (ScaleBlogger’s AI-powered content pipeline is an effective option alongside general CMS automation)
- Review management tool and mobile performance tester
Optimizing for Local Voice Queries and ‘Near Me’ Searches
- Consistent NAP: Ensure Name, Address, Phone are identical across GBP, site footer, and directories; mismatches reduce local ranking.
- GBP completeness: Include hours, services, menu/pricing, and `special_hours` for holidays; keep hours updated in real time.
- Concise local landing pages: One page per neighborhood or service with clear address, service area, and 1–3 concise CTAs.
- FAQ with schema: Add `FAQ` and `LocalBusiness` schema to capture featured snippets and voice answers.
- Mobile-first performance: Prioritize sub-2s load on mobile to reduce abandonment for voice searchers.
Voice assistants answer a high percentage of queries with concise responses; optimizing for concise conversational keywords improves capture rates. (See Forbes on voice accuracy and adoption: https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2024/12/17/voice-activated-revolution-harnessing-voice-search-for-better-seo/)
| Task | Priority | Estimated Effort | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verify Google Business Profile | High | 1–2 hours | High local visibility, GBP features enabled |
| Add FAQ with schema | High | 2–4 hours/page | Increased featured snippet and voice answers |
| Create local landing pages | High | 4–8 hours/page | Better relevance for “near me” and local queries |
| Collect and respond to reviews | Medium | Ongoing | Trust signal; improves local ranking and CTR |
| Ensure mobile load times | High | 1–3 days | Lower abandonment; better voice conversion rates |
Understanding and implementing these patterns accelerates capture of local voice intent and makes follow-up flows feel seamless to users. When content anticipates the next question, conversational UX becomes a competitive advantage.
📥 Download: Voice Search Optimization Checklist (PDF)
Measuring Success and Scaling Voice Search Optimization
Prerequisites
- Access to Google Search Console and `GA4` property
- Rank-tracking or SEO platform with question/long-tail filters
- Local listings dashboard (Google Business Profile) and access to schema deployment
- Basic automation tooling (CMS access, CI/CD or tag manager)
- Google Search Console, Google Analytics (GA4)
- Rank tracker (SEMrush, Ahrefs, Rank Ranger)
- Local SEO tracker (BrightLocal, Yext)
- Automation: tag manager, CMS templates, deployment scripts
- Initial instrumentation: 4–8 hours
- Weekly reporting and triage: 1–3 hours
- SOP and template rollout: 1–2 weeks
| Tool | Voice-specific signals | Best for | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Featured snippet impressions, query-level clicks, `searchAppearance` flags | Organic performance, snippet tracking | Free; direct SERP signals |
| Google Analytics (GA4) | Events for voice-driven clicks, zero-click attribution, session behavior | Conversion tracing, engagement | Free; needs event tagging |
| SEMrush | Question-filter rank tracking, SERP feature detection | Keyword research, competitive gaps | Pricing from $129.95/mo |
| Ahrefs | Rank tracking with keyword intent, SERP feature alerts | Backlink + keyword intelligence | Pricing from $99/mo |
| Moz Pro | Keyword explorer with question suggestions, SERP feature reports | Mid-market SEO teams | Pricing from $99/mo |
| Rank Ranger | Custom voice/rich-feature tracking, historical SERP visualizations | Advanced rank reporting | Tiered pricing; agency features |
| BrightLocal | Local pack visibility, citation tracking, GBP metrics | Local SEO and voice-local visibility | Pricing from $29/mo |
| Yext | Listings syndication, voice-search-ready knowledge graph | Large-scale local listings | Custom pricing; enterprise focus |
| Alexa Skills Console | Skill impressions, utterance analytics | Amazon Alexa skill owners | Platform-specific metrics |
| Google Assistant Console | Action analytics, conversation paths | Google Assistant Actions | Platform-specific metrics |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented, this approach reduces manual churn and lets content teams focus on high-value creative work.
Conclusion
Voice-first queries are changing discovery: prioritize conversational keywords, structure answers for snippets, and automate scale so content stays timely and context-aware. Practical examples earlier showed content that answers multi-turn questions rising in visibility, and teams that mapped FAQ flows into short, precise answers saw faster ranking gains. Expect to audit existing pages, create concise voice-ready answers, and set up automation to publish variants — audit 10 priority pages this week, write 50–70 word canonical answers for each, and automate distribution to long-tail variants to capture voice intent at scale.
If questions linger — like how to measure voice traffic or which intents to prioritize — track conversational queries in search console and segment by query length and click-through behavior; prioritize informational, local, and how-to intents first. For hands-on implementation and to accelerate production, consider practical automation tools. As a next step, explore how to Scale voice-optimized content with AI automation to turn these tactics into repeatable workflows.

