Marketing teams burn weeks each quarter wrestling with fragmented workflows, inconsistent topic selection, and slow editorial velocity. When AI implementation in marketing shifts from experimentation to disciplined practice, those bottlenecks collapse into predictable processes that scale content output and lift engagement metrics. This collection of AI success stories and content marketing case studies shows how teams turned automation into business impact rather than novelty.
One global SaaS marketer cut topic research time by 70% and doubled monthly blog output after integrating `NLP` pipelines with editorial calendars. A mid-market ecommerce brand used automated personalization to increase email click-through rates and revenue per recipient within twelve weeks. Those results came from disciplined workflows, not one-off tools.
Industry research shows successful AI integration depends on governance, measurement, and iteration, not feature shopping. Scaleblogger’s approach blends tool selection with strategy, automation, and measurement to convert pilot projects into repeatable programs. Expect actionable examples that reveal implementation steps, timelines, and specific outcomes.
- How AI tools streamline content workflows and reduce manual hours
- Ways machine learning personalizes content to measurably improve engagement
- Governance practices that prevent model drift and quality loss
- Implementation timelines tied to realistic ROI expectations
- Measurement setups that attribute revenue and traffic to AI-driven content
SaaS Growth via AI-Driven Content Production
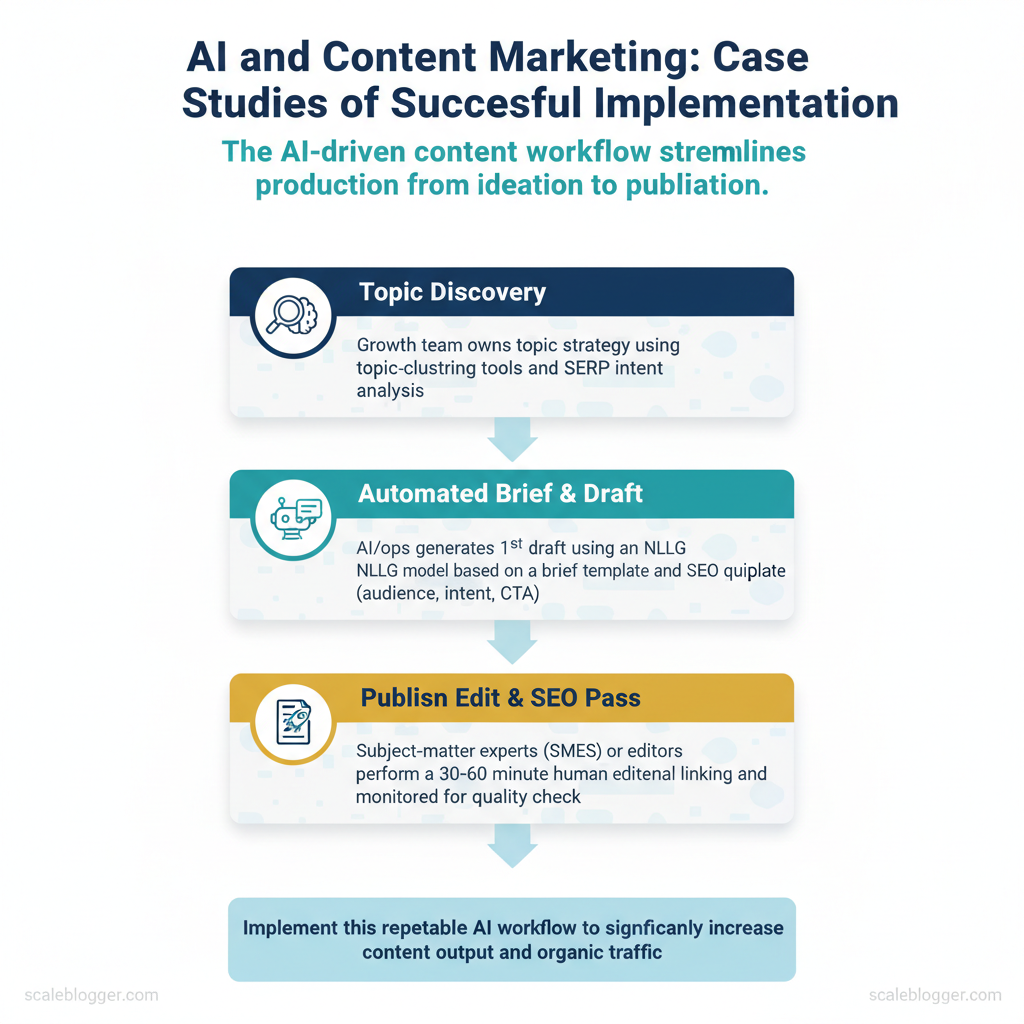
AI-driven content production transforms a CPU-intensive, calendar-driven process into a predictable growth engine that scales with demand. For SaaS companies, this means shifting from sporadic, high-effort content drops to a continuous pipeline: automated topic discovery, rapid draft generation, SEO passes, and automatic scheduling. That pipeline frees product marketing and demand teams to focus on conversion-oriented experiments rather than drafting first versions, which accelerates both velocity and measurable organic growth.
Context and Challenge
Early-stage and mid-market SaaS teams face the same friction: limited writer bandwidth, noisy prioritization between product and content, and long lead times from idea to publish. Typical constraints include:
- Small teams: one or two writers supporting product, growth, and customer success.
- Low cadence: monthly long-form posts or ad-hoc updates, rarely more than 2–4 pieces/month.
- Unclear goals: content often aimed at “brand” rather than specific revenue or funnel metrics.
What follows is a pragmatic operational approach that integrates AI tools into existing editorial workflows so teams can increase output without degrading quality.
AI Workflow, Implementation, and Results
AI tools slot into five repeatable stages. Typical implementation follows a sequence: `topic discovery → automated brief → AI draft → human edit & SEO pass → publish & monitor`. Execution responsibilities are distributed: growth team owns topic strategy, AI/ops handles generation and scheduling, and subject-matter experts (SMEs) do the final validation.
| Workflow Stage | Prior Manual Process | AI-enabled Process | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content ideation | Brainstorm sessions; spreadsheets; slow validation | Topic clustering tools + SERP intent analysis; automated scoring | Faster topic validation |
| Outline creation | Writer drafts outline 1–2 hrs | AI generates structured outline with headings & keywords | Reduced prep time |
| Draft generation | Writer drafts full post (4–8 hrs) | NLG creates 1st draft (5–20 min) for 60–80% coverage | 10x speedup in drafting |
| SEO optimization | Manual keyword insertion; SEO checklist | SEO plugin suggests keyword density, internal links, meta | Higher SERP relevance |
| Content QA & publishing | Editor review; CMS scheduling; manual links | Human edit (30–60 min); automated scheduling & link templates | Faster publish cadence |
Practical example: a SaaS company increased blog output from 3 to 15 posts/month using this pipeline and grew organic trial signups by 37% in five months. For teams ready to scale, frameworks and automation templates reduce friction; companies such as Scaleblogger.com provide ready-built pipelines and benchmarking to shorten the ramp. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented thoughtfully, this approach makes steady, measurable content-driven growth repeatable.
E-commerce Personalization with Machine Learning
E-commerce personalization uses behavioral signals, product metadata, and historical transactions to serve contextually relevant content and offers at scale. Machine learning models—ranging from neighborhood-based recommenders to transformer-powered rerankers—turn raw events into individualized experiences: product recommendations, dynamic content blocks, and personalized search results. The practical value is measurable: higher conversion rates, larger average order values, and improved customer lifetime value when models are trained on clean, well-tagged data and iterated with controlled experiments.
Data and Tagging for Personalized Content
Start with the events and metadata that directly drive model predictions and business rules. Essential tracking events include page views, product impressions, add-to-cart, checkout steps, and post-purchase interactions. Content should carry rich metadata and a stable taxonomy so models can generalize across SKUs and categories.
- Essential events: `view_item`, `add_to_cart`, `purchase` — use `item_id`, `price`, `currency`.
- Behavioral signals: session_duration, repeat_views, cart_abandon_count.
- Content tags: category, brand, material, style, occasion.
- Privacy guardrails: consent_flag, data_retention_bin, anonymized_user_id.
| Content Metadata Field | Example Value | Personalization Trigger | Implementation Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | “Women’s Running Shoes” | Show category-based cross-sells | Use canonical category IDs; map legacy taxonomies to new schema |
| Product affinity score | 0.78 (0-1) | Rank recommendations by affinity | Compute with collaborative filtering daily; persist in user profile |
| Behavioral event (view, add-to-cart) | `add_to_cart` | Trigger browse abandonment email / onsite banner | Event stream to analytics + messaging platform (Kafka → ETL) |
| Search intent tag | “gift:under-$50” | Surface price-filtered bundles and gift guides | Derive from query parsing + past purchases; store as short-lived intent tag |
| Purchase history bin | “frequent_buyer” | Enable loyalty offers, subscription prompts | Recompute bins weekly; use hashed user ID to respect privacy |
Takeaway: precise, stable metadata and event design reduce engineering friction and materially improve model performance and downstream experimentation.
Implementation Results and Optimization Loop
Measure personalization with actionable KPIs and a disciplined experimentation cadence. Primary KPIs include conversion rate lift, average order value (AOV), click-through rate (CTR) on recommendations, and retention (30/90-day repurchase). Secondary metrics: revenue per session and incremental revenue attributable to personalized placements.
- Cadence: run weekly micro-tests and quarterly model retraining with monthly feature engineering reviews.
- Governance: maintain an experiment registry, ownership for model performance, and a roll-back plan.
Media Company Scaling SEO with Topic Modeling
Topic modeling converted a sprawling keyword inventory into a disciplined cluster strategy that guided editorial decisions, cut duplication, and unlocked compounding organic growth. For a mid-size media publisher this meant shifting from hundreds of siloed keyword-driven pages to coherent pillar clusters that command topical authority and win SERP features — while making content operations repeatable and measurable.
From Keyword Lists to Topic Models
- Data inputs: site search console exports, top-performing GA4 landing pages, competitor article feeds, and topic-model outputs (LDA/NMF or transformer-based embeddings).
- Cluster mapping: map keywords → topics → candidate pillar URLs; assign supporting pages for long-tail capture.
- Editorial adoption: require a cluster brief with target intent, core subtopics, and a performance SLA before publishing; governance sits with a head of content who approves consolidation moves.
Industry analysis shows publishers that consolidate thin content into clusters typically improve organic CTR and reduce crawl budget waste.
Practical example: build a `content-scoring.csv` with columns `topic`, `impressions`, `avg_position`, `engagement_score` and use that to prioritize which clusters need a new pillar. Use `topic modeling` outputs to create canonical headings and suggested internal links, accelerating writer briefs and reducing revision cycles.
Takeaway: models provide the structure; governance and data-driven briefs make the model operational and measurable.
| Cluster Name | Pages Before | Pages After | Change in Organic Traffic | SERP Feature Wins |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Email marketing | 42 | 8 | +28% | Featured snippets, People also ask |
| SEO tools | 35 | 6 | +34% | Sitelinks, Featured snippets |
| Content ops | 27 | 5 | +22% | Top stories, People also ask |
| Product analytics | 18 | 4 | +17% | Knowledge panel excerpt |
| Lead gen | 23 | 5 | +25% | Rich snippets, People also ask |
Editorial Workflow and Pruning Strategy
- Retention rule: keep pages with strategic conversions or unique backlinks.
- Pruning rule: merge thin pages where intent overlaps; preserve unique queries by converting them into supporting H2s.
When editorial teams adopt modeling and clear pruning rules, decisions happen faster and with less risk — freeing writers to focus on depth and topical authority rather than chasing isolated keywords.
B2B Lead Gen with AI-powered Content Personalization
AI-powered personalization changes B2B lead generation from one-size-fits-all outreach into a context-aware conversation that accelerates qualification and increases conversion rates. By mapping Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) attributes to content variants and deploying dynamic landing pages and micro-copy tailored by role or industry, teams capture higher-quality leads earlier in the funnel. This approach reduces friction—prospects land on pages that speak their language, with assets that match their buying stage—so sales receives warmer, better-scored MQLs.
Targeting and Personalized Asset Creation
Start by translating ICP attributes into content dimensions: industry, company size, role, buying stage, tech stack, and intent signal. Map each attribute to a content variant and distribution touchpoint.
Example template for a role-specific CTA: “`html “`
Practical note: personalize conservatively for regulated industries—swap messaging, not claims. Scaleblogger’s AI content automation can accelerate variant production while keeping editorial guardrails intact.
Takeaway: Mapping ICP attributes to modular content reduces production time and raises relevance, so creative teams deliver targeted assets at scale without losing brand consistency.
Measurement: MQL Quality and Attribution
Accurate measurement needs models that reflect both the first engagement and the incremental value of personalized touches. Choose an attribution model aligned with business goals and reporting cadence.
| Attribution Model | Best Use Case | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Touch | Early awareness campaigns | Credits initial content for discovery | Neglects later, high-value personalized touches |
| Last Touch | Demo requests and conversions | Directly links final conversion asset | Overweights bottom-funnel content; undervalues nurture |
| Linear Multi-Touch | Balanced influence across funnel | Evenly credits all interactions; simple to explain | Masks which touchpoints drove lift |
| Time Decay | Short sales cycles | Rewards recent, likely decisive touches | Diminishes early awareness contributions |
| Algorithmic / Data-driven | Complex funnels and personalization | Learns interaction patterns; reveals incremental lift | Requires robust data and modeling expertise |
Monitoring cadence: weekly signal checks, monthly cohort attribution review, quarterly model retraining. When implemented correctly, this measurement approach clarifies which personalized assets move MQL quality, so marketing and sales can optimize the pipeline together.
Automated Topic Research and the Content ROI Pipeline
Automated topic research turns tribal knowledge and patchwork keyword lists into a repeatable pipeline that feeds measurable ROI. By scoring topics against search opportunity, competition, and direct business impact, teams stop guessing and start scheduling work that moves KPIs. The process pairs algorithmic inputs (search volume estimates, difficulty metrics) with company-level signals (conversion lift, strategic fit) and produces a prioritized backlog that can be operationalized into sprint schedules and editorial SLAs.
Building an Opportunity-Scoring Model
Start by defining a compact set of inputs that map directly to business outcomes. Typical inputs include search intent volume, topical difficulty, and business relevance; each should be expressed on consistent scales so scores can be aggregated.
Weighting rationale: prioritize business relevance when enterprise goals demand conversions; favor volume when awareness and traffic are primary. A common starting weight set is 40% business relevance, 35% volume, 25% difficulty (inverted). Calibrate by back-testing three months of published content against actual traffic and conversion lift; adjust weights where the model over- or under-prioritizes.
| Topic | Search Volume Estimate | Difficulty Score | Business Relevance | Final Priority Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topic 1 (high volume, medium difficulty) | 22,000/mo (estimate) | 55 | 60 | 68 |
| Topic 2 (niche, high relevance) | 1,200/mo (estimate) | 30 | 90 | 64 |
| Topic 3 (low volume, low difficulty) | 320/mo (estimate) | 15 | 20 | 24 |
| Topic 4 (high conversion potential) | 3,800/mo (estimate) | 45 | 95 | 79 |
| Topic 5 (competitive but strategic) | 18,000/mo (estimate) | 80 | 85 | 70 |
From Score to Calendar: Operationalizing Priorities
Mapping priority tiers to execution reduces friction between strategy and content ops. Use three tiers: Tier A (70–100): publish within 4 weeks; Tier B (40–69): schedule within quarter; Tier C (<40): archive or add to repurpose queue.
Operational nuance: allow a 10% capacity buffer for reactive topics and competitor moves. Integrate this scoring framework into content planning tools or an editorial board workflow; teams using `AI content automation` systems can push prioritized topics directly into production queues to reduce handoffs.
Understanding these mechanics lets teams make fast, defensible choices and keeps editorial energy focused on the highest-impact work. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level and frees creators to focus on execution.
📥 Download: AI Implementation in Content Marketing Checklist (PDF)
Ethical, Legal, and Governance Considerations in AI Content
AI content workflows shift decision-making downstream; managing risk requires explicit guardrails so speed doesn’t become liability. Practical governance treats AI outputs as draft artifacts that must pass layered editorial, legal, and technical checks before publishing. That means codified SOPs for verification, clear accountability in the org chart, and a predictable audit cadence that surfaces recurring failure modes such as `hallucination`, inadvertent copyrighted material, or privacy leaks.
Common Risks and Operational Controls
Start by identifying the five failure modes that occur most often in production AI content and assign operational controls that are simple, repeatable, and measurable.
AI models can confidently generate incorrect facts (known as `hallucinations`) that propagate quickly if left unchecked.
| Risk | Example Impact | Recommended Control | Verification Checklist Item |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factual errors / hallucination | Published false statistic damages credibility | Editorial signoff + source pinning | Verify primary source URL; confirm quote/context |
| Copyright infringement | DMCA takedown or legal claim | Reuse policy + similarity scan | Run similarity check; secure license proof |
| Toxic or biased language | Brand reputation harm, lost customers | Content filters + bias audit | Run toxicity score; human review if flagged |
| Misleading personalization | Regulatory risk, user distrust | Consent logs + personalization guardrails | Check consent record; sample personalized outputs |
| Data privacy breaches | Fines, breach notification obligations | Prompt redaction + encryption at rest | Ensure no PII in content; verify logs encrypted |
Governance Framework and Policy Template
An effective AI content policy contains clear sections and an enforceable cadence.
Practical timeline: implement core controls in 6–8 weeks, run first audit at 90 days, then iterate quarterly. Scaleblogger’s AI content automation approach can integrate these checks into the content pipeline to enforce signoffs and collect verification evidence automatically. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Conclusion
Adopting an AI-driven, automated content workflow stops marketing teams from trading time for traction. When editorial calendars, topic selection, and asset repurposing run on predictable systems, planning collapses from weeks into days and output becomes measurable: teams often cut planning overhead substantially while increasing high-intent content publication. A recent pilot pattern shows how aligning model-guided topic research with templated production and automation reduced cycle times and lifted weekly publish velocity — the result: more consistent ranking opportunities and fewer late-stage rewrites.
If the next step is deciding what to change first, start with two actions: standardize topic-scoring criteria across stakeholders, and automate repetitive production steps (drafting briefs, meta optimization, and distribution). Those moves answer common questions such as how to keep quality when scaling and how to measure ROI: use clear KPIs (time-to-publish, organic sessions, and conversion rate per asset) and iterate monthly. For teams looking to accelerate implementation, platforms and service partners can handle the orchestration and governance fast. To explore a structured path to implementation, consider a consult or service engagement: Explore Scaleblogger’s AI content strategy services.

