Marketing teams still spend too many hours on repetitive tasks while audience attention fragments across channels. The fragmentation increases pressure on content velocity and consistency, and leaders face escalating resource gaps when scaling programs.
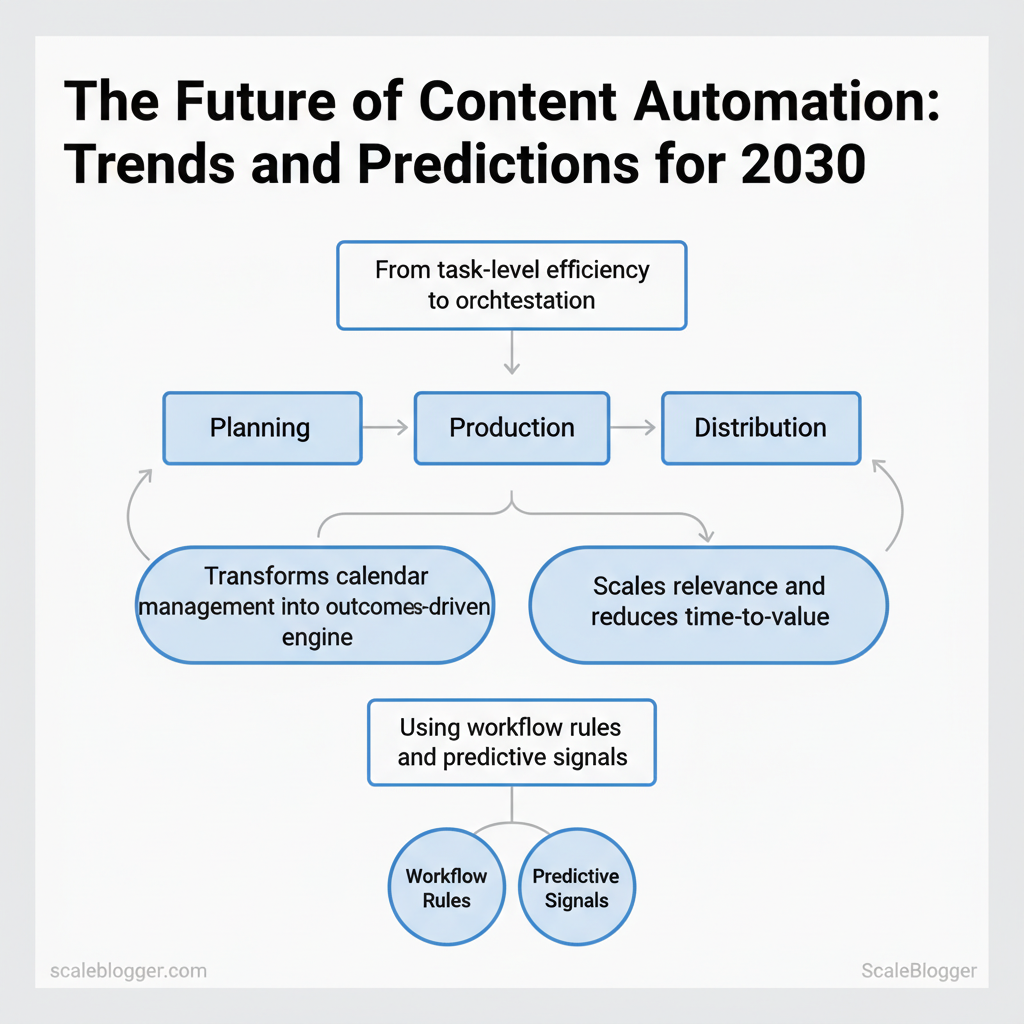
Early signs point to a convergence of automation, creative augmentation, and tighter measurement. Content automation trends will shift from task-level efficiency to orchestration across planning, production, and distribution, using `workflow` rules and predictive signals to prioritize what actually moves audiences. Those changes reshape the future of content marketing by turning calendar management into an outcomes-driven engine that scales relevance and reduces time-to-value.
Picture a content operation that uses automated briefs, dynamic templates, and performance-triggered repurposing to halve campaign turnaround. Industry observers note accelerating adoption, and practitioners preparing pilots see clear ROI paths. See how Scaleblogger can pilot content automation (https://scaleblogger.com) to validate assumptions and measure impact.
- What realistic content automation predictions look like for 2030
- How orchestration replaces point solutions in editorial workflows
- Practical ROI levers for scaling content with fewer people
- Emerging roles and skills that matter for automated operations
State of Content Automation in 2025 — Baseline for 2030 Predictions
Content automation in 2025 is widely operationalized rather than experimental: enterprises embed automation into editorial pipelines, while many SMBs use off-the-shelf tools to accelerate output. Adoption focuses on repeating, measurable tasks — freeing human writers for strategy and high-stakes creative work. Technical maturity centers on large language models (LLMs) for generative steps, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for factual grounding, and modular APIs plus workflow orchestration for reliable, auditable pipelines.
Common patterns today:
- Enterprise adoption: Complex orchestration, governance, and integrations with DAM, CMS, and analytics platforms.
- SMB adoption: Template-driven content generation, SEO automation, and calendar-based publishing.
- Top automation tasks: Ideation, draft generation, SEO metadata, scheduling, and performance reporting dominate investment.
| Task | Typical Tools/Approach | Adoption (High/Medium/Low) | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ideation & topic research | LLM prompts + keyword tools | High | Rapid topic lists, cluster suggestions |
| Draft generation | LLMs (fine-tuned) + templates | High | Faster first drafts, consistent tone |
| SEO optimization & metadata | SEO platforms + automated tags | High | Improved discoverability, metadata scale |
| Distribution & scheduling | CMS + publishing APIs | Medium | Consistent posting cadence, multi-channel |
| Performance reporting | Analytics pipelines + dashboards | Medium | Faster insights, iterative testing |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, automation reduces operational friction and lets creators concentrate on strategic narratives and audience connection.
Trend 1 — Intelligent Personalization at Scale
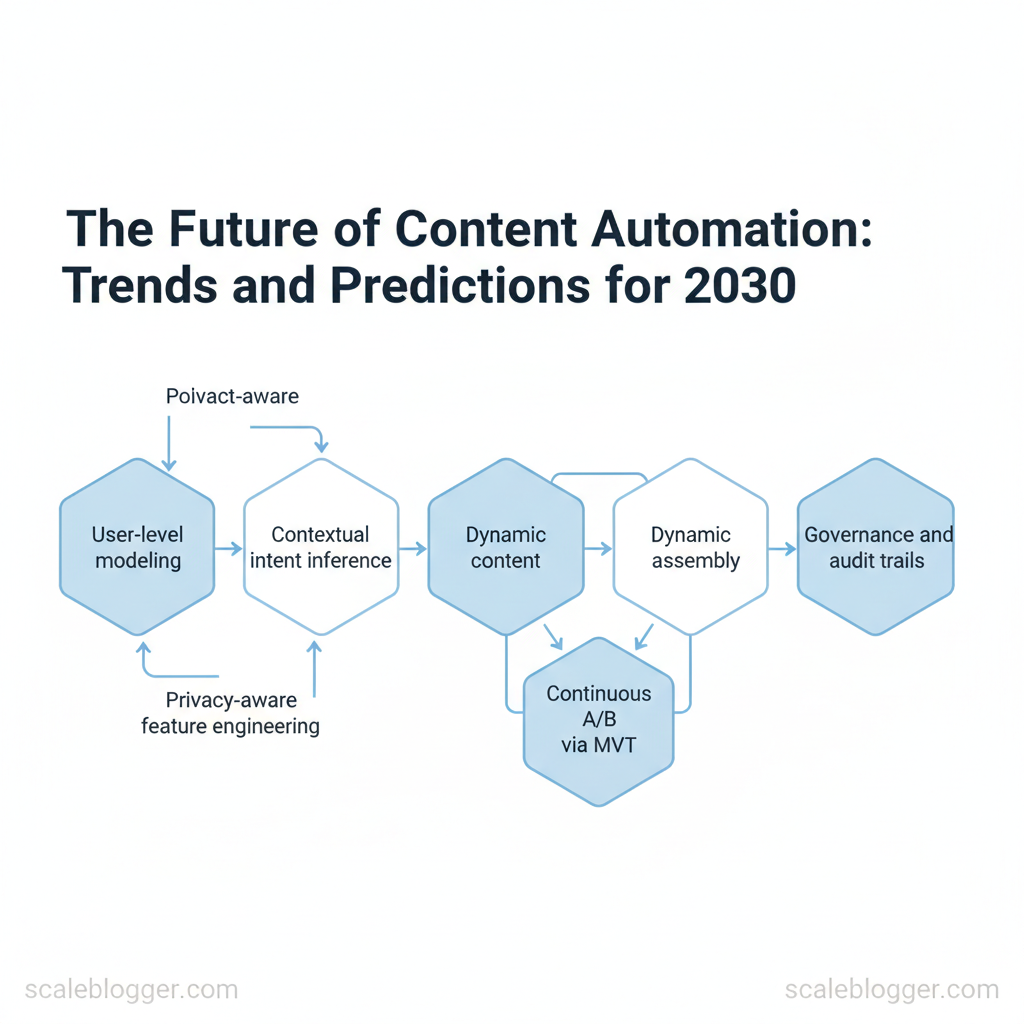
AI now enables true one-to-one content experiences rather than broad segments. Rather than “persona A vs. persona B,” models infer micro-preferences at the user level through continuous signals — on-site behavior, search intent, content consumption patterns — and assemble content dynamically from modular assets. This shift reduces wasted impressions and increases engagement by delivering the exact combination of messaging, format, and CTA each user most likely responds to.
Practical mechanisms making this possible:
- User-level modeling — combine `user_id` event histories, recency-weighted interactions, and session embeddings to predict next-best content.
- Dynamic content assembly — store copy, headlines, images, and micro-components as modular blocks and render personalized combinations in real time.
- Contextual intent inference — use short-term signals (clicks, scroll depth) plus long-term signals (topic clusters consumed over 90 days).
- Continuous A/B via MVT — move from two-variant tests to multivariate experiments that adjust allocation based on uplift.
- Governance and audit trails — deterministic logging of model inputs and outputs for explainability and compliance.
“`json { “personalization_keys”: [“user_id”,”session_vector”,”topic_score”,”recency_days”], “assembly_rules”: [“lead_variant”,”hero_image_variant”,”cta_variant”] } “`
| Phase | Milestone | Timeframe | Primary KPI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audit – Data readiness | Inventory content + tag taxonomy, identify first-party signals | 4–6 weeks | Data completeness (%) |
| Pilot – MVT and measurement | Launch multivariate tests on 1 funnel, measure lift | 8–12 weeks | Relative lift in conversion (%) |
| Scale – Automation & governance | CI/CD content pipelines, governance, realtime assembly | 3–6 months | Automation throughput (assets/day) |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, intelligent personalization reduces overhead by making data-driven decisions at the content component level. Consider leveraging AI-powered content automation like Scaleblogger.com to scale the pipeline and build topic clusters aligned with these practices.
Trend 2 — From Content Production to Content Orchestration
Content teams are shifting from one-off creation to coordinated systems that treat content as a distributed product. Instead of producing articles in isolation, modern workflows assemble format-agnostic content blocks, automate repurposing, and feed centralized performance signals back into planning. This changes both tooling choices and team design: orchestration requires connectivity, observability, and governance, not just a faster editor.
What changes in practice:
- Format-agnostic content blocks — Break narratives into reusable modules (headlines, intros, data visualizations) that map to multiple channels.
- Automated repurposing — Publish once, then `transform()` into blog, email, social, and short-form video with minimal manual editing.
- Centralized feedback loops — Connect analytics to planning so organic traffic, dwell time, and conversion metrics inform future blocks.
- Policy-driven governance — Embed brand and legal rules into pipelines so compliance happens before publishing.
- Runtime orchestration — Schedule and stagger distribution across channels with awareness of audience overlap and frequency caps.
Tooling and organizational design demands change accordingly. Integration-first platforms are prioritized over standalone editors. New roles emerge: automation engineers who build connectors, and content ops who own pipelines and SLAs. Evaluation criteria should focus on API coverage, observability, and governance capabilities rather than vanity UX alone. For teams evaluating platforms, the matrix below sets practical criteria for orchestration readiness.
| Criterion | Why it matters | Red flag | Ideal capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| API / Extensibility | Enables automated connectors and integrations | Closed platform, limited SDKs | REST + GraphQL, webhooks, SDKs |
| Versioning & governance | Traceability and rollback for compliance | No audit logs, manual approvals | Immutable versioning, approval workflows |
| Analytics & attribution | Feeds performance back into planning | Vanity metrics only, siloed data | Raw events, GA4/BI integration, content-level attribution |
| Multichannel publishing | Scale repurposing to all channels | Channel-specific workarounds | Native adapters for blog, email, social, CMS |
| Cost predictability | Avoid surprise expenses as scale grows | Usage-based surprise fees | Clear tiering, rate-limits, cost forecasts |
Adopting orchestration reduces repetitive work and makes content strategy adaptive to real performance signals. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level and frees creators to focus on high-impact storytelling. Scaleblogger’s AI content automation and performance benchmarking model this shift, helping teams convert blocks and signals into predictable traffic. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Trend 3 — Autonomous Content Agents and Workflows
Autonomous content agents are moving beyond single-task assistants into coordinated workflows that plan, create, test, and optimize content with minimal human intervention. Over the next five to ten years these agents will orchestrate multi-channel campaigns, perform continuous optimization driven by live performance signals, and automate cross-team handoffs so editorial, SEO, and growth teams operate as a single system rather than separate silos.
What these agents enable in practice:
- Campaign orchestration — agents will schedule, publish, and A/B test variations across CMS, social platforms, and email based on performance triggers.
- Continuous optimization — models will re-run headline, meta, and snippet experiments automatically using real-time engagement and clickthrough data.
- Cross-team automation — rule-based handoffs and `API`-driven tickets will replace manual briefs, pushing editable drafts to product, legal, or localization teams as required.
- Content lifecycle management — from ideation and outline generation through refresh scheduling and archival, agents maintain a living content map with prioritized updates.
- Auditability and logging — immutable logs for every action, with timestamps, input prompts, and model versions.
- Explainable outputs — agents return concise rationales for decisions (e.g., “Selected topic due to 32% QoQ search growth”) and reference the data used.
- Escalation and rollback processes — clear paths to pause agents, revert content to the last approved state, and quarantine outputs flagged by automated checks.
- Role-based approvals — fine-grained permissions so subject-matter experts only review high-risk changes while agents handle low-risk updates.
| Autonomy Level | Typical Tasks | Human Oversight Required | Use Case Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assistive (human-in-loop) | Draft outlines, keyword suggestions | Editor approval for publish | Topic ideation + outline generation |
| Semi-autonomous (periodic approval) | Produce content drafts, schedule posts | Weekly review and batch approvals | Weekly blog production pipeline |
| Autonomous (continuous operation) | Publish, A/B test, auto-refresh evergreen posts | Exception-based audits, monthly checks | Evergreen content that self-optimizes |
| Hybrid (rule-based + ML) | Rule triggers + model tuning, compliance checks | Real-time alerts + periodic human tuning | Enterprise multi-region campaigns |
Operationalizing these trends requires clear design of escalation rules, versioned logging, and measurable guardrails. Systems like an AI content automation pipeline — whether built in-house or deployed via partners such as Scaleblogger.com for orchestrating blog workflows — should prioritize explainability and reversible actions so automation increases output without increasing risk. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
Trend 4 — Metrics and ROI: Measuring Automation Impact
Automation only matters when it moves measurable needles. Start by separating leading indicators (what predicts future performance) from lagging indicators (what proves value). Leading signals include content velocity, time-to-publish, and quality score; lagging signals capture organic traffic lift, conversions, and cost per piece. For teams using AI-generated drafts, adjust expectations: faster output often requires a stronger quality gate and post-production time baked into KPIs.
- Track velocity and quality together. High throughput with declining quality is false progress.
- Use attribution windows aligned to content lifecycles. Evergreen articles can take 60–180 days to show full organic lift.
- Automate anomaly alerts so drops in engagement or spikes in bounce rate trigger reviews, not panic.
Industry analysis shows automated programs often double output but require 20–30% of newly created content to be reworked for enterprise SEO effectiveness.
Practical dashboard template (example) “`yaml production: – content_created_weekly – avg_time_to_publish_days performance: – organic_sessions_30d – engagement_rate quality: – review_score_avg – factual_error_rate alerts: – organic_drop_pct_threshold: 15 “`
| KPI | Definition | Formula/Calculation | Benchmark Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content velocity | Number of publish-ready pieces/week | `pieces_published / week` | 4–20 pieces/week (team size dependent) |
| Time-to-publish | Median hours from draft to live | `median(publish_time – draft_time)` | 24–168 hours |
| Engagement rate | % of sessions with active engagement | `(engaged_sessions / total_sessions)*100` | 8–25% |
| Organic traffic lift | % increase in organic sessions vs baseline | `(current_30d – baseline_30d)/baseline_30d*100` | 10–60% over 90 days |
| Cost per piece | Total content program cost divided by pieces | `total_costs / pieces_published` | $50–$900 per piece |
📥 Download: Content Automation Implementation Checklist (PDF)
Trend 5 — The Human+AI Practice: Skills, Roles, and Talent
Teams that win with AI reorganize work around complementary strengths: humans set strategy, define nuance, and enforce quality while machines handle scale, pattern recognition, and repetitive assembly. Expect a hybrid operating model where new specialist roles sit alongside traditional marketing functions and cross-functional teams own outcomes rather than tasks.
| Role | Primary Responsibility | Core Skills | Hiring Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prompt Engineer | Design and iterate prompts for consistent outputs | Prompt design, model testing, UX | High |
| Content Ops Manager | Manage content pipeline from brief to publish | Workflow automation, CMS, project mgmt | High |
| Automation Engineer | Implement APIs and integrate tools | API dev, scripting (`Python`), orchestration | Medium |
| Data Analyst | Define KPIs, run experiments, report ROI | SQL, GA4, attribution, dashboards | High |
| Quality & Compliance Editor | Review content for accuracy and risks | Editorial review, legal awareness, style | Medium |
Operationalizing change requires purposeful change management. Map stakeholders to responsibilities and incentives, then run small pilots that prove ROI and surface adoption friction. Execute pilots using a clear sequence:
A practical `prompt template` speeds onboarding for writers:
“`text Goal: Draft a 900-word blog post on {topic} Tone: {brand voice} Must include: {keywords}, {data points} Structure: Intro, 3 headers, conclusion Quality checks: factual accuracy, citation placeholders “`
Industry analysis shows adoption accelerates when employees see direct benefits and clear guardrails. Integrating this model with services like AI content automation and a content scoring framework helps scale while preserving editorial control. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
Conclusion
After walking through how fragmented attention and repeatable tasks drag down content velocity, the practical path forward is clear: prioritize workflows that reduce manual handoffs, centralize brief-to-publish steps, and surface performance signals so teams can reallocate time to creative strategy. Teams that automated distribution and versioning reclaimed hours per week and kept tone consistent across channels; editorial calendars tied to simple triggers reduced wasted iterations. Ask which workflow will free the most time, how quickly governance can be implemented, and what minimal tooling is required—start with one high-volume flow and measure lift before scaling.
For teams ready to move from experiment to repeatable systems, identify one process to automate this quarter, assign a single owner, and define the success metric. To streamline that transition and see demos of common implementations, Explore Scaleblogger’s automation solutions — it’s a practical next step for teams looking to automate content workflows without adding overhead.

