Marketing teams routinely lose momentum because content ideas, deadlines, and performance signals live in different places. A content planning tool tightens that gap by turning scattered ideas into a repeatable pipeline, cutting duplication and missed opportunities. Industry practitioners note that better tooling reduces time spent on coordination and surfaces topics that actually move the needle for audiences and SEO.
Picture a small editorial team that stops firefighting and starts publishing with predictable cadence; traffic and conversions follow. Tools also make collaboration measurable, so editorial decisions rely on data rather than guesswork — a shift many social teams describe as transformational according to reviews of planning platforms and workflows.
- How a centralized calendar enforces consistency and reduces rework
- Ways automation routes briefs, assets, and publish tasks to the right contributors
- How to use workflow metrics to prioritize high-impact topics
- Simple governance patterns that keep evergreen content fresh
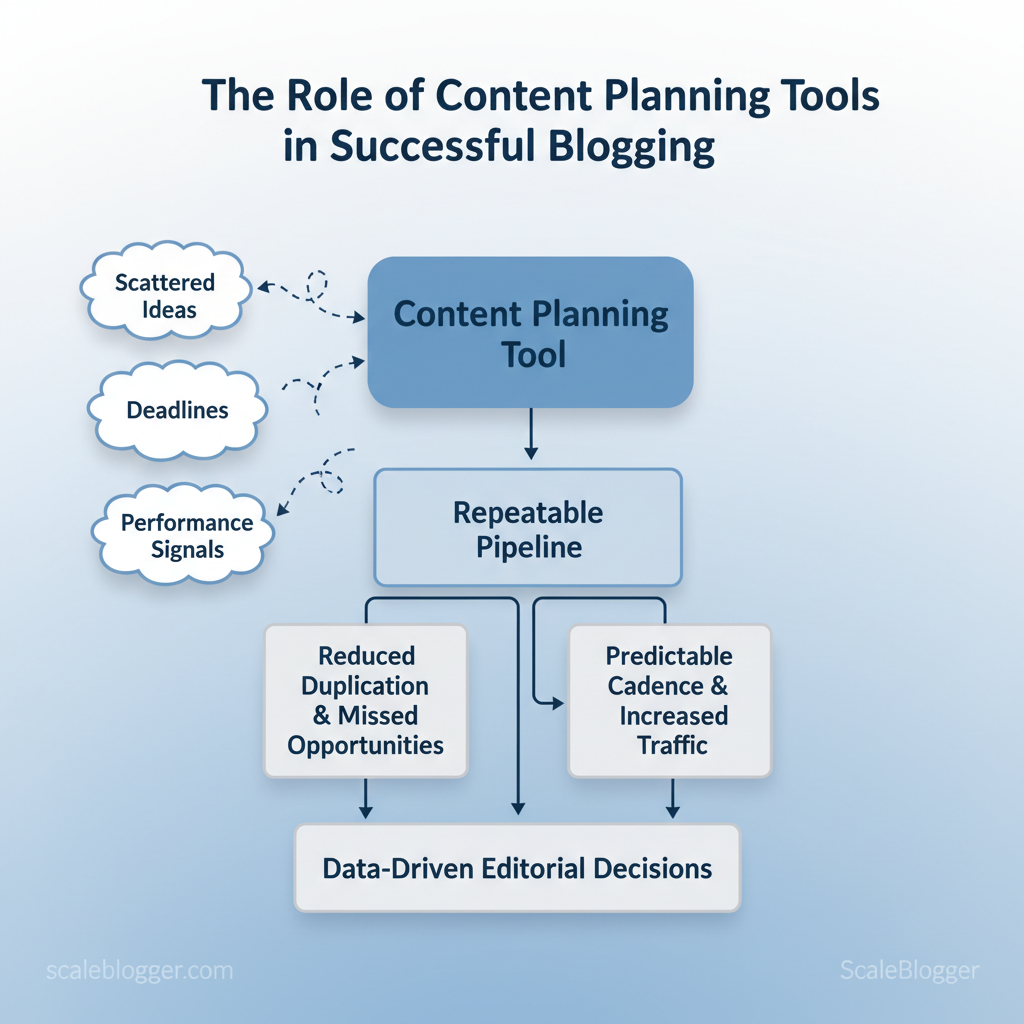
Why Content Planning Tools Matter
Start with the practical difference: content planning tools convert fragmented ideas and manual guesswork into a repeatable pipeline that scales. Teams using purpose-built planning systems move from firefight publishing to a predictable cadence that supports SEO growth, cross-team coordination, and measurable content reuse.
Prerequisites
- A documented content strategy or editorial brief
- Shared access to your CMS and analytics (GA4 or equivalent)
- A centralized place to capture ideas (spreadsheet or lightweight tool)
- Content calendar or planning platform (consider both enterprise and emerging tools)
- Keyword list and topic clusters exported from your SEO tool
- Performance dashboard (weekly reporting)
- Consistency and cadence: Maintain predictable publishing frequency and reduce missed cycles.
- Better SEO targeting: Map content to keyword clusters and avoid coverage gaps.
- Reduced duplicated effort: Single source of truth prevents multiple teams working similar topics.
- Faster approvals: Built-in workflows speed review and cut handoffs.
- Repurposing visibility: Track assets for reuse across channels.
Concrete examples and evidence
- Industry reviews note that planning platforms help social teams stay consistent and collaborate more efficiently; see the hands-on comparison in the SocialBee evaluation of content planning tools I tested 10+ content planning tools: Here’s what I recommend.
- Practical guides show how structured content plans reduce stress and improve outcomes when paired with a workflow; see The Ultimate Blog Content Plan: Better Content, Less Stress.
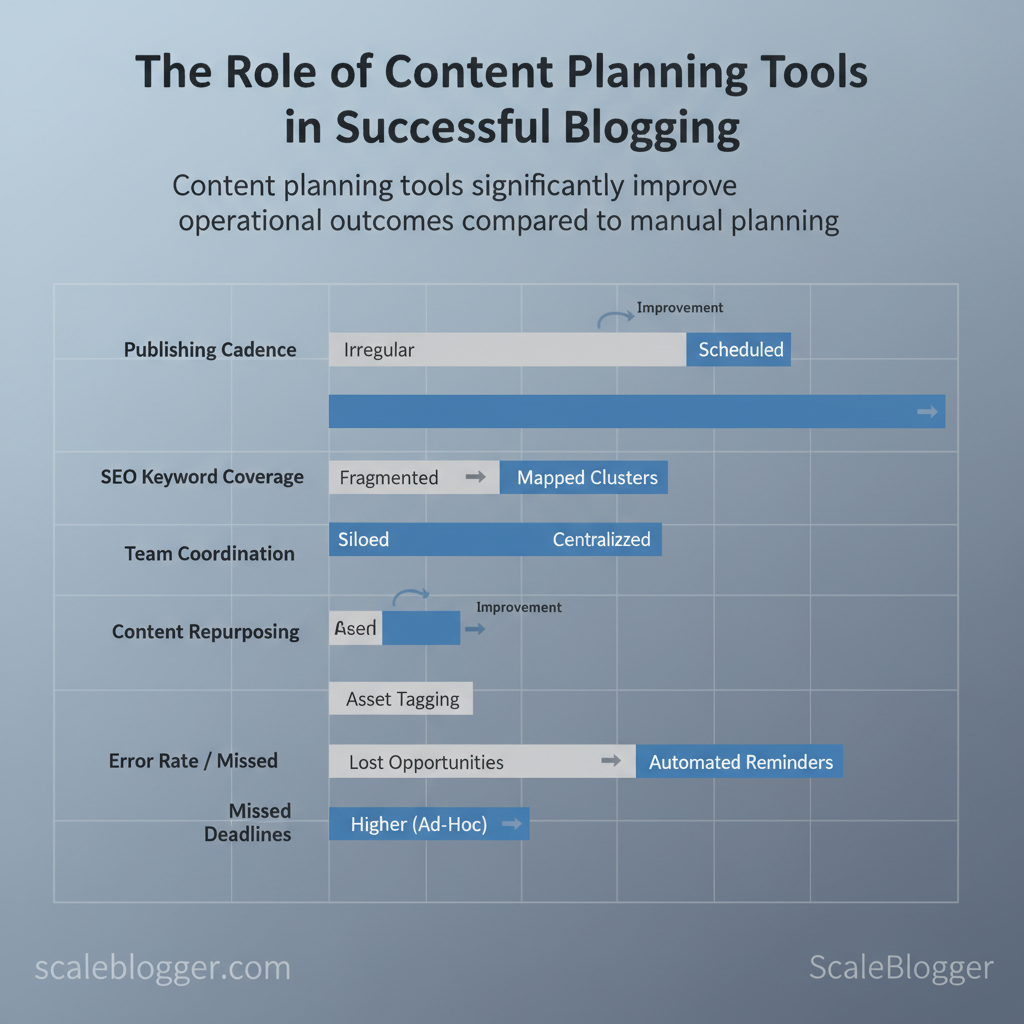
| Outcome | Manual/Ad-hoc Planning | Using Content Planning Tools | Impact (Time/Quality) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Publishing cadence | Irregular, reactive | Scheduled calendar with recurrence | Faster scheduling; fewer missed deadlines |
| SEO keyword coverage | Fragmented, opportunistic | Mapped to clusters and gaps | Improved topical coverage, fewer overlaps |
| Team coordination | Email/DMs; siloed drafts | Centralized assignments & approval flows | Reduced rework; clearer ownership |
| Content repurposing | Lost opportunities | Asset tagging and reuse workflows | More cross-channel assets; higher ROI |
| Error rate / missed deadlines | Higher due to ad-hoc processes | Automated reminders and checklists | Lower error rate; consistent delivery quality |
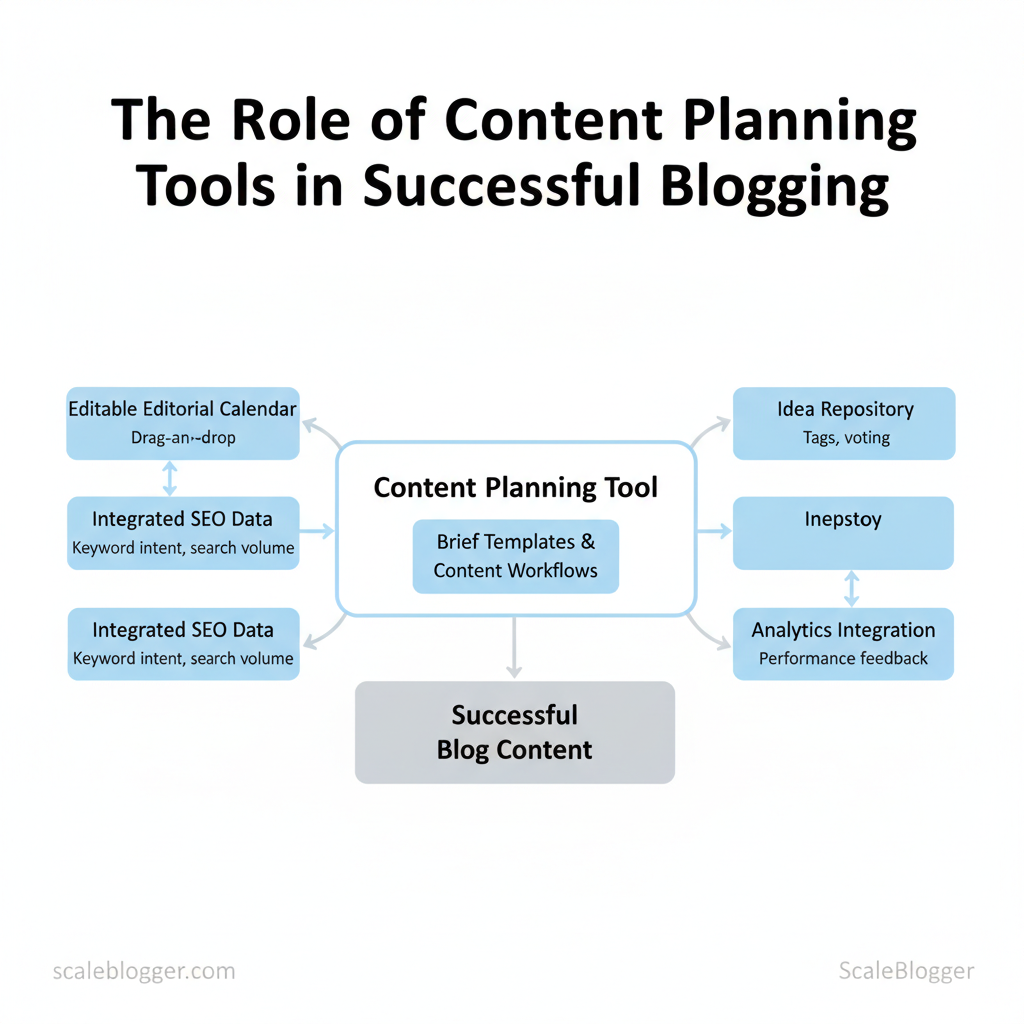
Core Features to Look For in a Planning Tool
Good planning tools remove friction so teams ship better work more often. Start by prioritizing a handful of features that directly affect velocity and quality: an editable editorial calendar that supports `drag-and-drop`, integrated SEO signals, reusable brief templates, and built-in analytics that close the loop between publication and performance. These features turn planning from a spreadsheet exercise into a repeatable system.
- Editorial calendar with `drag-and-drop` — Enables rapid rescheduling, visual cadence control, and conflict detection; critical when deadlines shift.
- Built-in or integrated SEO data — Keyword intent, search volume ranges, and SERP snapshots reduce guesswork during topic selection.
- Idea repository — Centralized backlog with tags and voting keeps ideas discoverable and prevents duplicate work.
- Analytics / reporting — Content-level metrics, trend views, and attribution to channels let teams optimize what actually moves the needle.
Market data shows effective content planning bridges vision and execution; tools that centralize ideas, briefs, and performance reduce time-to-publish and increase ROI when used consistently. (See Tools and Strategies for Effective Content Planning: https://www.walkwithpic.com/blog/effective-content-planning-tools-strategies)
Nice-to-have features accelerate repeatability and reduce manual work:
- Automation for repetitive tasks (auto-scheduling, canonical tagging).
- CMS and analytics integrations (direct publish, GA4, Search Console).
- AI-assisted features (brief drafting, headline suggestions, content scoring) that speed first drafts and iterate headlines based on predicted CTR.
| Feature | Solo Creators | Small Teams (2-10) | Marketing Teams (10+) | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Editorial calendar | Essential ✓ `drag-and-drop` | Essential ✓ assignments, views | Essential ✓ enterprise workflows | Keeps cadence visible and reduces deadline conflicts |
| Idea repository | Helpful ✓ simple backlog | Important ✓ tagging, voting | Critical ✓ permissions, workflows | Prevents idea loss and aligns backlog with strategy |
| Keyword integration | Helpful ✓ basic suggestions | Important ✓ volume + difficulty | Critical ✓ SERP snapshots, integrations | Guides topic selection toward measurable demand |
| Brief templates | Important ✓ reusable templates | Essential ✓ approval flows | Essential ✓ custom templates by campaign | Standardizes handoffs and speeds brief creation |
| Analytics / reporting | Basic ✓ page metrics | Important ✓ custom reports | Essential ✓ attribution, dashboards | Turns outputs into optimizations and budget evidence |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead by making decisions at the team level.
How to Evaluate and Select the Right Tool
Start by mapping who will use the tool and which workflows must be supported. Focus on the people doing the daily work—writers, editors, SEO, social—and the handoffs between them. The correct tool minimizes friction at those handoffs and surfaces the signals the team needs to move fast without rework.
- List all cost components: license fees, onboarding services, integration engineering, training hours, and change management.
- Translate time savings into dollars: multiply hours saved by fully-burdened hourly rate.
- Set payback period: target `6-12 months` for mid-market buys; longer for enterprise deals with heavy customization.
- Include soft ROI: improved SEO traffic, faster time-to-publish, and reduced churn in creators.
| Criteria | Weight (1-5) | Tool A (Asana) Score | Tool B (Trello) Score | Weighted Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core features fit | 5 | 4 | 3 | Tool A: 20, Tool B: 15 |
| Ease of use | 4 | 4 | 5 | Tool A: 16, Tool B: 20 |
| Integrations | 5 | 4 | 3 | Tool A: 20, Tool B: 15 |
| Cost | 3 | 3 | 5 | Tool A: 9, Tool B: 15 |
| Support & onboarding | 3 | 4 | 3 | Tool A: 12, Tool B: 9 |
| Pricing Model | Typical Cost Range | Pros | Cons | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per-seat monthly | $8–$99/user/mo | Predictable per-user features | Scales poorly with headcount | Growing teams |
| Flat/team monthly | $100–$1,000+/mo | Predictable team cost | Limited per-user controls | Small teams |
| Usage-based | $0.01–$0.50/action | Pay for what you use | Variable bills, hard to forecast | High-variance workflows |
| Enterprise / custom | $10k+/yr | Dedicated support, SLAs | Long contracts, higher TCO | Large orgs |
| Freemium / free tier | Free → limited | Low barrier to try | Lacks advanced features | Solo creators, trials |
Understanding these evaluation steps lets teams compare tools objectively, reduce rollout risk, and make procurement decisions that speed content velocity while protecting quality. When implemented correctly, this approach reduces overhead and keeps creators focused on high-impact work.
Practical Workflows: From Idea to Published Post
Prerequisites Editorial calendar* with prioritization rules Access to analytics* (GA4 or platform equivalent) Single-source brief template* stored in CMS or project tool
Tools / materials needed
- Content calendar (e.g., a shared Google Sheet or `Notion` board)
- SEO research (keyword tool, SERP checks)
- Collaboration platform (Slack, Asana, ClickUp)
- Scheduling/publishing tool (native CMS, or automation)
| Stage | Responsible Role | Typical Duration | Deliverable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Idea approval | Content Lead | 1–3 days | Approved topic list |
| Brief creation | Strategist / SEO | 1–2 days | Detailed brief & keywords |
| Drafting | Writer | 3–7 days | Draft (1–2k words) |
| Editing & SEO review | Editor / SEO Specialist | 2–4 days | Edited draft + SEO checklist |
| Publishing & promotion | Publisher / Growth | 1–3 days | Live post + promotion plan |
Operational notes for teams
- Roles: Writer owns first draft, Editor owns clarity and tone, SEO Specialist owns search intent and metadata, Publisher owns live checks and scheduling.
- SLAs: Set firm review windows (e.g., 48 hours for editing) and automated reminders.
- Recurring analytics: Weekly 30–60 minute review to adjust topics and repurpose top performers.
Measuring Impact and Iterating
Start by treating measurement as a product loop: instrument, measure, hypothesize, test, and repeat. Good instrumentation means dashboards that surface the primary KPIs—organic sessions, ranking for target keywords, leads generated—and a set of secondary KPIs that explain behavior (time on page, scroll depth, organic CTR). Build alerts so regressions trigger investigation before they compound.
Prerequisites
- Access to `Google Analytics 4` and `Google Search Console`
- Tagging and UTM consistency across campaigns
- A lightweight experiment tracker (spreadsheet, Notion, or a simple database)
- Baseline dashboard (BI tool, GA4 Explorations, or native analytics)
- Organic sessions — trend and cohort breakdown by content type
- Average position for target keywords — focus on intent-matched phrases
- Organic CTR — SERP snippet effectiveness
- Conversion rate from blog — lead capture and downstream revenue attribution
| Metric | Good Threshold | Action if below threshold | Tool/Data source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic sessions | +10% MoM or steady growth curve | Audit recent content changes, distribution, and indexation; refresh top-performing posts | Google Analytics 4 |
| Average position for target keywords | ≤ 5 for priority keywords | Improve on-page SEO, add supporting content, build internal links | Google Search Console |
| Organic CTR | 3–8% (depends on SERP features) | Rewrite title/meta, test schema, run SERP intent review | Google Search Console, GA4 |
| Conversion rate from blog | 1–3% (lead form or CTA clicks) | A/B test CTAs, reduce friction, add contextual offers | GA4, tool native analytics |
Running content experiments and continuous improvement
Troubleshooting: if experiments show noise, extend the test window, segment by channel, or increase sample size. For dashboards, keep one canonical view for stakeholder alignment and one exploratory view for analysts.
Understanding these practices reduces churn and helps teams make faster, data-driven content decisions—freeing creators to focus on craft while automation handles the routine checks.
📥 Download: Content Planning Tool Implementation Checklist (PDF)
Adoption, Change Management, and Scaling
Start by treating adoption as a program, not a project. Successful rollout balances quick wins with governance that prevents drift as teams scale. Build a clear onboarding rhythm, standardized templates, and defined content ownership so teams can move fast while remaining accountable.
- Template standardization: Create a single source `template-library` with versioned filenames and a short manifest (e.g., `blog_post_v1_author_topic_date`). This prevents duplicate work and preserves SEO structure.
- Naming conventions: Use clear, consistent patterns for files, assets, and content IDs to enable automation and analytics.
- Assign content owners: Appoint owner, editor, and publisher for each content stream; define SLA for reviews (e.g., 48 hours).
- Review cadence: Weekly editorial triage, biweekly performance sync, quarterly governance review.
- Incremental automation: Automate publishing and basic QA checks first; add semantic checks later.
- Scale safeties: Limit write access to templates; log changes with `git` style or CMS revision notes.
- Governance playbook: Short, living doc with examples, roles, and escalation paths.
- Integration plan: Map integrations (analytics, CMS, scheduling) and test in a sandbox.
| Training Type | Frequency | Duration | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Live kickoff workshop | One-time + cohort repeats | 90–120 minutes | Rapid alignment, roles, hands-on setup |
| Recorded micro-tutorials | Evergreen; update quarterly | 3–7 minutes each | On-demand how-tos, new features |
| Office hours / Q&A | Weekly (first 90 days) then biweekly | 30–60 minutes | Troubleshooting, adoption barriers |
| Quarterly governance review | Quarterly | 60–90 minutes | Policy changes, metrics, roadmap |
Understanding these practices helps teams adopt tools faster without creating chaos. When governance and training are compact and repeatable, scaling becomes predictable and measurable. This is why modern content strategies prioritize automation and clear ownership—it frees creators to focus on value instead of process.
Bring the practical parts together: align topic selection with audience signals, centralize deadlines and assets, automate repetitive distribution, and measure content against specific business goals. Those steps reduce churn between ideation and execution, as teams that unify planning and publishing cut time-to-publish and improve topical consistency. If you wondered whether automation sacrifices quality, evidence and practitioner reports show the opposite when workflows preserve editorial review and audience-first briefs.
Start by piloting one content stream—pick a pillar topic, set a predictable cadence, and add a simple automation for publishing or reporting. Track engagement and iterate weekly. Remove redundant tools, document the workflow, and assign a single owner for each content lifecycle to keep momentum. For professional implementation or to scale faster, consider platforms that specialize in content strategy and automation; as WalkWithPic illustrates, planning tools change output and stress levels for the better. Next step: Explore Scaleblogger’s content strategy and automation services to translate these steps into a repeatable program.

