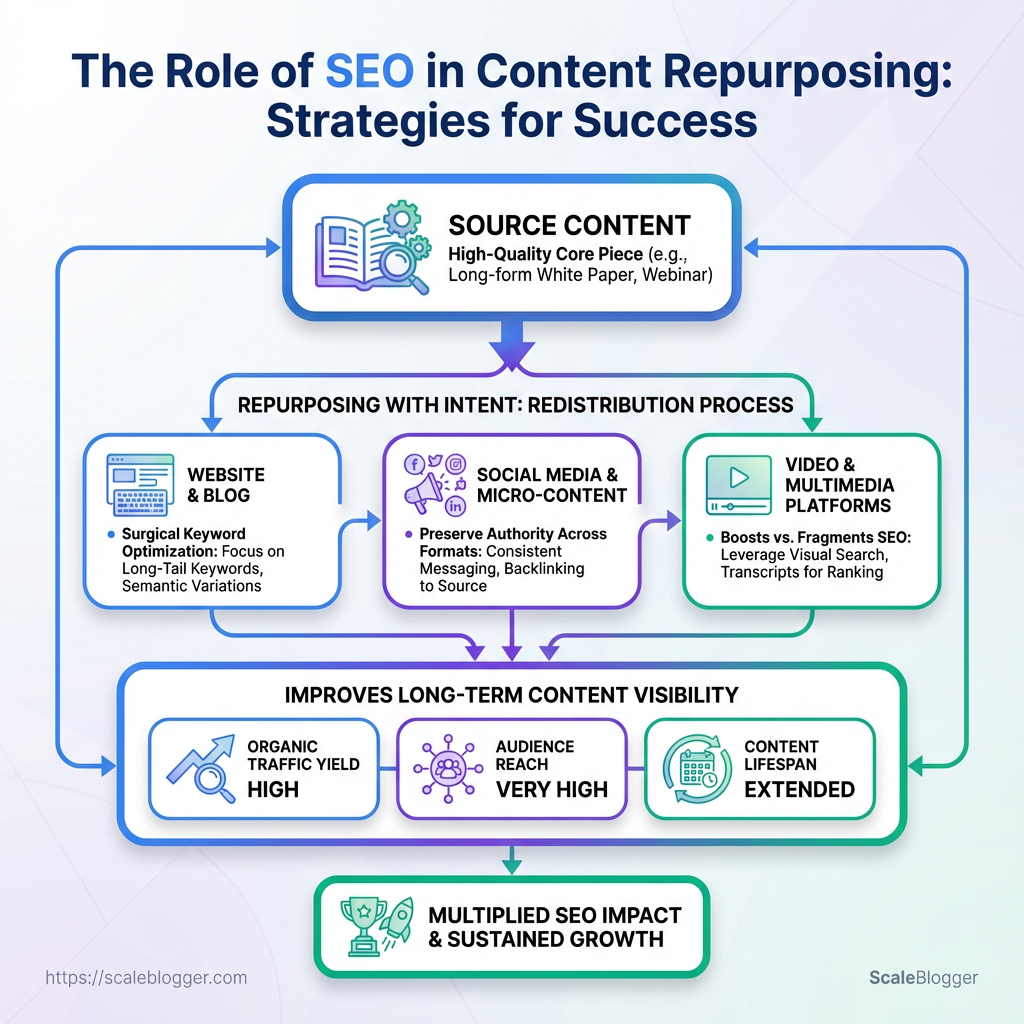
Repurposing a pillar blog into videos, newsletters, and social posts often feels like busywork until search traffic fizzles and results disappear. The real leak is rarely content quality; it’s the absence of deliberate SEO strategies that preserve authority across formats.
Treat repurposing as redistribution plus intent: map each asset to specific search intents, then apply surgical keyword optimization so fragments compete in search rather than cannibalize one another. Small decisions—title tweaks, metadata, canonical tags—determine whether a repurposed piece boosts or fragments your cumulative ranking.
When done right, repurposing multiplies audience reach without diluting rank signals, improving long-term content visibility across channels and queries. The following guidance focuses on practical moves that keep search engines and humans aligned during every reuse cycle.
What You’ll Need (Prerequisites)
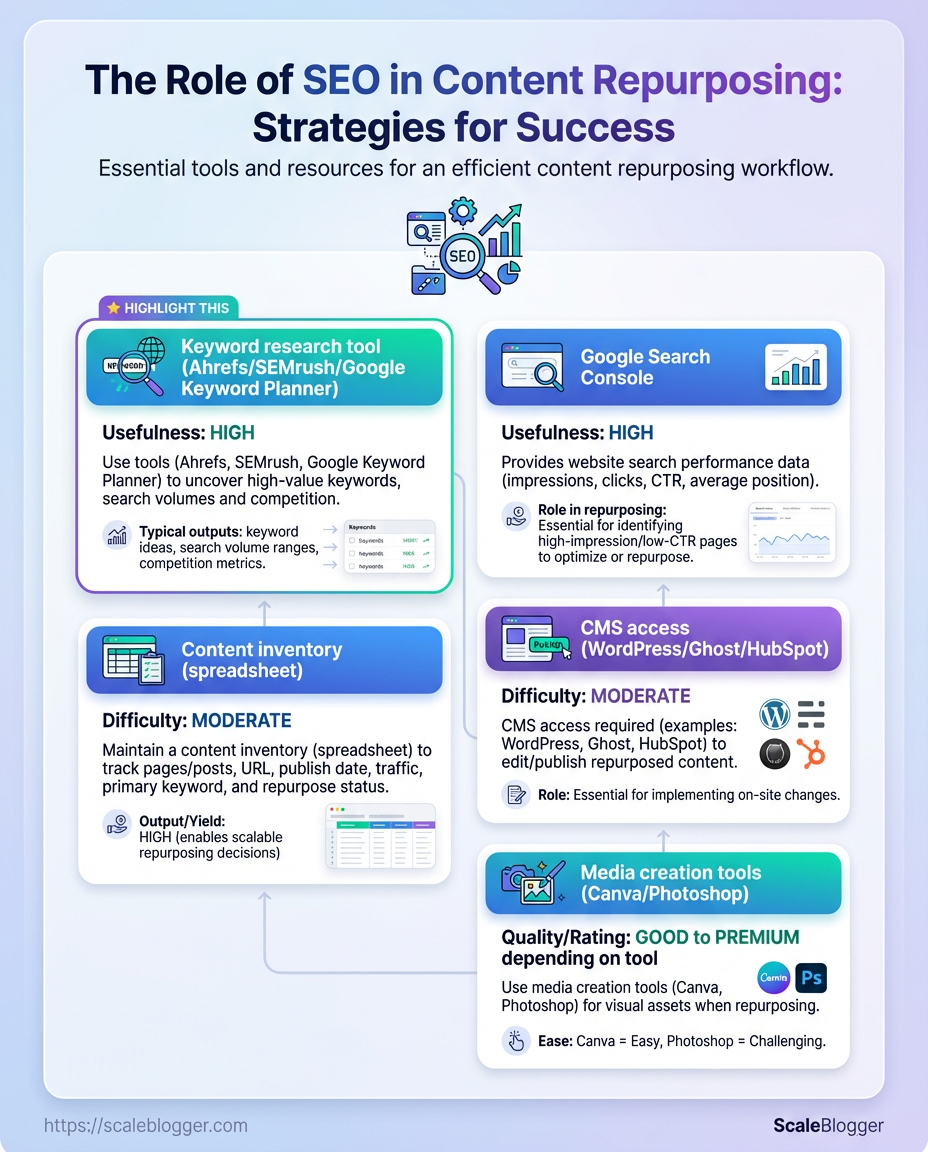
Start with the right access and a handful of reliable tools so the repurposing workflow doesn’t get bogged down. Expect to gather analytics access, set up a couple of SEO tools, confirm CMS editor permissions, and block out time for inventorying and tagging content. With these in place, converting long-form posts into high-value repurposed assets becomes predictable and repeatable.
- Analytics access: Read-only or editor access to Google Search Console and Google Analytics (or GA4) so performance signals can drive prioritization.
- Keyword research: A keyword tool for search intent and gap analysis—pick one that shows volume and difficulty.
- Content inventory: A spreadsheet or database containing URLs, publish dates, traffic, and target keywords.
- CMS permissions: Editor-level access in WordPress/Ghost/HubSpot to make on-page edits and publish new assets.
- Media tools: Basic design tools for thumbnails, headers, and social cuts.
Prerequisite: SEO tools (Google Search Console): Access to Google Search Console with the property verified and performance reports available.
Prerequisite: Keyword research tool: A subscription or free account to a keyword tool (examples include Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Google Keyword Planner) for volume and SERP features.
Prerequisite: Content inventory (spreadsheet): A list of existing posts with metrics—URL, title, traffic, backlinks, and conversion indicators.
Prerequisite: CMS/editor permissions: Editor or Admin rights in your CMS to update content, meta tags, and create campaign pages.
Prerequisite: Basic on-page SEO skills: Comfort editing title tags, meta descriptions, header hierarchy, and internal links.
Prerequisite: Media creation tools: Access to Canva, Photoshop, or equivalent for image resizing and simple edits.
Prerequisite: Time & difficulty estimate: Plan 4–8 hours for inventory + planning, then 1–3 hours per high-priority repurpose item; difficulty is moderate if you know CMS basics and basic SEO.
Quick reference mapping of required tools and their purpose in the repurposing workflow
| Tool/Resource | Purpose | Estimated Cost | Action to Take Before Starting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Performance signals, impressions, clicks, CTR | Free | Verify site property and grant access |
| Keyword research tool (Ahrefs/SEMrush/Google Keyword Planner) | Keyword volume, difficulty, SERP features | Ahrefs from $99/mo, SEMrush from $119.95/mo, Planner free | Create project and sync domain |
| Content inventory (spreadsheet) | Centralize URLs, metrics, tags | Free (Google Sheets) | Export URLs, traffic, and engagement data |
| CMS access (WordPress/Ghost/HubSpot) | Edit and publish repurposed assets | WordPress free; HubSpot CMS paid tiers | Ensure editor role and API keys if needed |
| Media creation tools (Canva/Photoshop) | Create images, thumbnails, social assets | Canva free/$12.99/mo Pro; Photoshop $20.99/mo | Prepare brand templates and asset folder |
This combo keeps the process efficient: analytics to pick winners, keywords to find opportunities, inventory to prioritize, CMS to execute, and media tools to finish polished assets. Consider automating parts of the inventory or tagging step—Scaleblogger.com offers systems that map these pieces into an AI-enabled pipeline if automation is desired.
Having these prerequisites sorted saves hours later and makes it obvious which posts will move the needle.
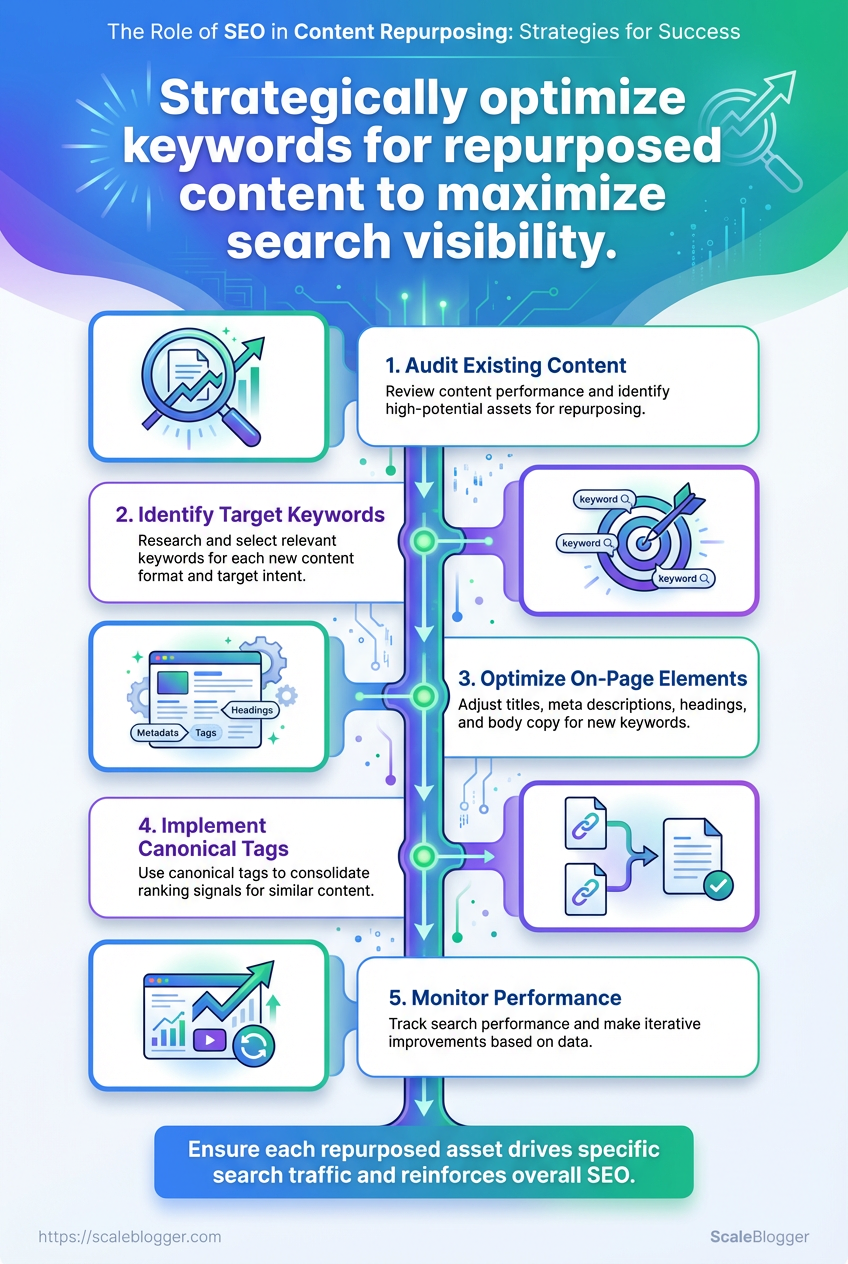
Step-by-Step Repurposing Workflow Overview
Start by treating repurposing as a production line: find ripe assets, extract searchable angles, craft format-specific outputs, optimize at publication, and measure impact. This keeps effort focused on pieces that already carry audience interest and SEO potential, instead of reworking everything at random.
- Audit content for targets.
- Run keyword opportunity analysis.
- Select repurposing formats.
- Create assets and apply on-page SEO optimization.
- Publish, track, iterate.
Why this sequence matters
Following the steps in that order saves time and increases reach. An audit narrows the universe to high-potential posts; keyword analysis converts attention into discoverability; format selection matches distribution; SEO optimization captures search traffic; tracking turns outcomes into repeatable processes.
Step-by-step process (practical notes)
Audit content: Use engagement and traffic data to rank posts by traction and strategic fit. Keyword opportunity analysis: Identify medium-competition keywords and long-tail phrases that map to each chosen post. Format selection: Opt for formats that multiply reach—short video, tweet threads, carousels, newsletters, and pillar updates. Asset creation & SEO optimization: Refresh headlines, add schema where relevant, optimize meta tags, and include internal links to topical clusters. Publish, track, iterate: Set measurement windows (30/60/90 days), compare against baseline KPIs, and A/B test thumbnails or hooks.
Practical tip: When automating parts of the pipeline, leverage AI tools for draft generation and scheduling—but keep a human review step for brand voice and factual accuracy. For teams scaling this, consider Scaleblogger.com for AI content automation and workflow orchestration.
Map each high-level step to expected duration and a quick KPI to track
| Step | Action | Estimated Time | KPI to Monitor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audit content | Identify top-performing posts by traffic & engagement | 1–3 days | Organic sessions change (%) |
| Keyword opportunity analysis | Map target keywords + search intent | 1–2 days per cluster | Ranking improvements (positions) |
| Format selection | Choose formats: video, carousel, thread | 0.5–1 day per asset | Reach (impressions) |
| Asset creation & SEO optimization | Produce assets and update on-page SEO | 1–5 days per asset | CTR, average position |
| Publish, track, iterate | Distribute and run experiments | Ongoing (30–90 days) | Conversions / traffic lift |
Brief analysis: Short audits and targeted keyword work shrink time-to-impact. Format choice drives distribution KPIs while the SEO step converts distribution into sustained organic traffic. Treat tracking as the feedback loop that prioritizes future repurposing.
This workflow turns single articles into a steady stream of discoverable assets, so a few focused hours now can produce compounding traffic for months.
Audit and Prioritize Existing Content
Start by treating the existing archive like a treasure map: some pages are buried gold, some are distractions. The goal of an SEO-focused audit is to find posts that already attract attention (impressions) but fail to convert that attention into clicks (CTR), then rank them by SEO potential and business relevance so work gets applied where it moves the needle fastest.
Impressions: The number of times a page appears in search results.
Clicks: How many users actually landed on the page from search.
CTR: Click-through rate, calculated as clicks / impressions.
Tools & materials
- Search Console export: Export
impressions,clicks,CTR,average positionfor the last 6–12 months. - Spreadsheet or BI tool: Use Google Sheets, Excel, or a simple dashboard to score pages.
- Content inventory template: Columns for URL, topic cluster, business priority, traffic metrics, and action recommendation.
- Optional automation: Consider Scaleblogger.com for automating exports and scoring if audits will be recurring.
- Export performance data from Search Console into a spreadsheet.
- Tag each URL with topical cluster, target keyword, and business relevance (high/medium/low).
- Calculate three quick signals:
impressions,CTR, andposition. Add a fourth: trend (improving/flat/declining). - Score SEO potential on a 1–10 scale using rules like: high impressions + low CTR = high potential; good position + low CTR = title/description rewrite candidate.
- Prioritize by combining SEO score and business relevance into a weighted rank.
- High-priority: High impressions, low CTR, high business relevance.
- Medium-priority: Moderate impressions or alignment with future campaigns.
- Low-priority: Low impressions and low business relevance — archive, consolidate, or ignore.
Practical examples: a how-to post with 50k impressions but 0.8% CTR often gets big lift from a title tweak and schema; a product comparison ranking in position 6 with steady impressions is a candidate for content expansion and internal linking.
Document every decision in the content inventory with one-line action items: rewrite title, add FAQ schema, merge with topic X, or retire. That makes execution fast and measurable. Do the audit this way once, and the next round becomes a performance-driven machine that keeps content visibility improving.
Keyword Optimization for Repurposed Assets
Start by treating repurposing like relaunching: extract the audience signals your original asset already sends, then map those signals to formats and queries that perform in each channel. That means pulling ranking keywords and impressions, spotting gaps versus competitors, and assigning a primary intent-driven keyword plus 2–3 supporting phrases to every repurposed asset.
Search Console export: CSV of current queries, clicks, impressions, CTR, and position.
Competitor list: 3–5 direct competitors or content leaders for your topic.
Keyword tool access: Any tool that shows volume and difficulty (estimates are fine).
- Extract current ranking keywords
- Export Search Console queries for the top-performing URL(s) you plan to repurpose.
- Filter to queries with impressions > 50 or average position < 20.
- Sort by clicks and CTR to prioritize intent and existing traction.
- Perform a gap analysis against competitors
- Collect competitor ranking keywords for the same topic cluster.
- Identify keywords competitors rank for in positions 1–10 where your asset is absent or below position 20.
- Flag high-intent gaps (transactional/comparative queries) and informational gaps you can answer quickly.
- Map primary and secondary keywords to each new asset
- For each repurposed format, assign one primary keyword (high intent, realistic difficulty) and 2–3 secondary keywords (supporting context and long-tail variants).
- Match format to intent: prioritize video for how-to/visual queries, article for research/deep-dive queries, social for discovery/short-form intent.
- Select based on intent and difficulty
- Search intent: Prefer keywords whose intent matches the asset’s goal (awareness, consideration, conversion).
- Difficulty trade-off: Favor mid-difficulty keywords with existing impression signals from your asset.
- Volume vs. ROI: A mid-volume query with strong conversion intent often outperforms high-volume, low-intent keywords.
Keyword options for repurposed formats (search volume vs. difficulty vs. intent fit)
| Keyword | Search Volume (est.) | Difficulty/Competition (est.) | Best Format (video/article/social) |
|---|---|---|---|
| long-tail keyword example: “how to optimize blog posts for search intent” | 800 | Medium | Article |
| mid-tail keyword example: “keyword optimization strategies” | 2,400 | Medium-High | Article/Video |
| head keyword example: “SEO strategies” | 12,000 | High | Video/Article |
| topic cluster keyword example: “content repurposing workflow” | 450 | Low-Medium | Article/Social |
| supporting keyword example: “optimize podcast for SEO” | 320 | Low | Video/Social |
Key insight: prioritize a mix—use one primary mid-tail keyword per asset for balance between competition and volume, and stitch in the long-tail/supporting queries throughout the format.
Practical example: a 1,500-word article mapped to “keyword optimization strategies” (primary) plus “how to optimize blog posts for search intent” and “content repurposing workflow” (secondaries) becomes the script outline for a 6-minute video and three short social posts.
Using this process keeps repurposed assets discoverable and aligned with real audience queries, so the work converts traffic into measurable engagement rather than just creating more content for content’s sake.
Scale your content workflow can automate the export, mapping, and scheduling steps if you want to speed the pipeline without losing precision.
Choose Repurposing Formats with SEO Impact
Match the repurposing format to what users are actually searching for and then bake SEO work into the asset. Pick formats that map to keyword intent (informational → long-form blog, navigational → branded video, commercial → comparison pages) and then add format-specific SEO actions: transcripts for videos, structured data for recipes/guides, and tightly optimized metadata for evergreen posts. That approach converts existing content into multiple discoverable entry points instead of scattering effort across low-impact outputs.
Format Selection Criteria & SEO Tactics
- Match to intent: Choose the format that aligns to dominant search intent for target keywords.
- SEO-first additions: Add transcripts,
FAQPageschema, and optimized title/meta combinations per format. - Distribution + backlinks: Favor formats that naturally earn embeds and links (long-form posts, infographics, video).
- Canonical control: Prevent duplicate-content problems by using
rel=canonicalor consolidating versions. - Measurement plan: Track impressions and clicks per format to reallocate effort to winners.
- Identify top-performing core asset URL for repurposing by traffic and backlinks.
- Map 3–5 target keywords to formats based on intent and SERP features.
- Implement format-specific SEO (transcripts, schema, canonical) before distribution.
Side-by-side comparison of repurposing formats and their SEO pros/cons
| Format | SEO Advantages | Best Use Case | Effort Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long-form blog post | Strong crawlability; easy to target multiple keywords; supports internal linking | Deep how-to, cornerstone content, topic clusters | Medium–High |
| Video (YouTube) | High visibility in blended SERPs; drives backlinks and embeds; watch time signals | Tutorials, product demos, interviews | High |
| Social carousel | Fast social traction; good for topical visibility and driving traffic to cornerstone post | Snippets, quick tips, visual summaries | Low–Medium |
| Podcast episode | Builds audience and backlinks; repurpose transcript into text for indexation | Thought leadership, interviews, industry commentary | Medium |
| Infographic | Highly linkable visual asset; great for outreach and earned links | Data-driven topics, process visualizations | Medium–High |
Key insight: Long-form posts and videos offer the richest SEO upside because they map to multiple search intents and earn links/embeds; infographics and podcasts excel at outreach and brand signals, while social carousels are best for amplification and quick traffic spikes.
Format-specific SEO checklist (examples) Long-form: Use descriptive H2s, internal links to cluster content, and schema Article or HowTo where applicable. Video: Include full transcript on the page, keyword-optimized title/description, and VideoObject schema. Podcast: Publish episode notes + full transcript, add Speakable or Podcast schema, link to show notes. Infographic: Add HTML alt text, host a crawlable landing page with embed code to capture backlinks. Social carousel: Link back to canonical long-form page and use structured captions for discoverability.*
Canonical & duplicate-content rules Always set rel=canonical on republished content that’s essentially the same as the original. Prefer hosting text-based repurposes (transcripts, summaries) on the canonical domain to capture search value. * When syndicating externally, request a link to the original and use noindex if full duplication is unavoidable.
Distribution and backlink play Outreach infographics to industry roundups. Embed videos into long-form posts and share transcripts to earn both clicks and text-indexed value. * Use social carousels to drive initial traffic and measure keyword movement.
For complex repurposing pipelines, consider automating transcript generation and schema insertion with an AI content pipeline—services like Scaleblogger.com can speed that work while preserving SEO controls. Pick the formats that fit search intent, add the SEO plumbing, and prioritize the ones that will win links and real traffic.
Optimize and Publish Repurposed Content
Start by treating repurposed pieces like new content: they must satisfy on-page signals and technical hygiene so search engines and readers find and trust them. Optimize titles and meta, apply appropriate structured data, decide whether to canonicalize or consolidate, and wire up internal links that pass topical authority. Do these well and repurposing becomes a traffic multiplier instead of duplicate-noise.
On-Page and Technical SEO Checklist
Title formula: Use Primary keyword — Benefit | Brand. Example: keyword optimization — practical checklist | Acme Blog Meta description formula: Use Actionable hook + 1–2 supporting phrases + CTA. Keep ~120–155 characters. Headings: Use H1 for the main topic; H2s reflect search intent subtopics; include semantic variants of target keywords. URL structure: Short, readable, keyword-rich. Prefer /topic/subtopic/ over query strings. Canonicalization: Use rel=canonical when the repurposed asset is a trimmed or format-variant version of a canonical piece. Structured data: Add JSON-LD for Article, FAQPage, and BreadcrumbList where relevant to enable rich results. Pagination & AMP: Ensure paginated series use rel="prev/next" or unified view; AMP pages must reference canonical desktop pages. Robots & sitemap: Confirm pages are crawlable, included in XML sitemap, and not accidentally blocked by robots.txt. Performance: Keep Largest Contentful Paint under ~2.5s; compress images and lazy-load non-critical media. Mobile UX: Responsive layout, tappable CTAs, readable font sizes.
Canonical vs. Consolidated publishing strategies
Canonical strategy: Use when repurposed content is a format-variant (e.g., transcript → blog post). Point the variant to the original with rel=canonical and ensure the canonical page is the best, full version.
Consolidated strategy: Merge similar assets into a single authoritative page when they target the same query. Redirect older fragments with 301s to the consolidated URL to preserve equity.
- Prepare the finalized content and validate metadata, schema, and canonical tags.
- Run a pre-publish QA: mobile viewport, core web vitals, schema validator, and link sanity.
- Schedule publish time and ensure XML sitemap and internal links are updated.
- Publish and monitor indexation via search console and server logs.
- Iterate based on performance signals (CTR, rankings, engagement).
- Internal linking: Add 3–5 contextual links from high-traffic pages to the repurposed asset, use descriptive anchor text, and consider a topical hub page to centralize authority.
Automation tools speed repetition at scale; consider AI content automation for pipeline scheduling and content-scoring if the workflow will be repeated across many assets. Getting optimization right before hitting publish saves time and prevents content fragmentation—so build that checklist into every republishing routine.
Distribute, Track, and Iterate
Start by treating distribution like the second half of content creation—the work that turns an asset into measurable outcomes. A steady publishing cadence plus disciplined tracking lets experiments surface clear winners and losers quickly. Promotion should be repeatable: publish, amplify, measure, then change one variable and repeat.
Promotion checklist
- Core publish: Publish asset with canonical tags and structured data where relevant.
- Social push: Share primary post + 3 tailored variants for different platforms.
- Email blast: Segment list and send one teaser, one follow-up, one long-form highlight.
- Repurpose: Turn the asset into 1 visual, 1 short video, 2 social cards.
- Community seeding: Post to niche forums or Slack groups with contextual commentary.
- Backlink outreach: Send personalized pitches to 10 high-fit domains.
UTM best practices
- Use consistent
utm_source,utm_medium,utm_campaignacross channels to avoid fragmenting data. - Include
utm_contentto differentiate creative variations or audience segments. - Keep values lowercase and use hyphens (e.g.,
utm_campaign=blog-repurpose-q1). - Store mapping of UTMs in a shared spreadsheet for repeatability.
- Example:
https://example.com/post?utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=repurpose_q1&utm_content=cardA
Recommended KPIs with measurement cadence and target thresholds
| KPI | Measurement Tool | Review Cadence | Target Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic traffic to repurposed asset | GA4 | Weekly | +20% vs baseline in 4 weeks |
| Impressions & CTR | Google Search Console | Weekly | CTR ≥ 3% on target queries |
| Time on page / engagement | GA4 / Session Replay | Biweekly | Avg time ≥ industry average (90s+) |
| Backlinks generated | Ahrefs / Moz / Majestic | Monthly | ≥ 3 quality backlinks in 60 days |
| Conversion rate | GA4 / CRM | Monthly | +15% conversion vs previous asset |
Key insight: Focus on relative lifts and consistent cadence. If impressions rise without CTR gains, prioritize title/meta experiments; if traffic increases but conversions lag, test page CTAs and offer clarity.
- Run one experiment at a time.
- Keep test windows to 2–4 weeks depending on traffic volume.
- Use control pages when possible to measure true lift.
Iterative experiment examples
- Title/meta test: Swap headline, run for 2 weeks, measure CTR and organic clicks.
- CTA placement test: Move primary CTA above-the-fold vs end-of-post; measure conversion change.
- Promotion mix test: Shift ad spend from paid social to influencer seeding; measure cost-per-conversion.
Decision rules
- Scale winner: If a variant beats control on primary KPI by ≥15% with p-consistent trends, roll it site-wide.
- Kill fast: If no improvement after two full test cycles, revert changes and log learnings.
- Document everything: Store experiment hypothesis, duration, results, and next steps.
Automating scheduling and dashboards saves time; consider integrating an AI content pipeline like Scaleblogger.com for repeatable publishing and performance benchmarks. Keep experiments small, measurable, and frequent—this is how visibility turns into predictable growth.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When pages don’t rank or traffic stalls, the problem usually lives in one of four areas: duplicate/canonical signals, indexing and coverage, weak click-through rates from SERPs, or content that fails to match user intent. Fix each with focused diagnostics and surgical edits rather than broad rewrites.
Common Problems and Fixes
Canonical and duplicate content checks
- Symptom: Multiple URLs show the same content and none perform well.
- Fix: Verify canonical tags (
rel="canonical") point to the preferred URL and that server redirects are consistent. Check for URL parameter duplicates and strip or consolidate them withrobots.txtrules or parameter handling in Search Console. - Example: Two product pages differing only by tracking parameters should have a single canonical and 301-redirects from the variants.
Indexing and coverage troubleshooting
- Symptom: Pages missing from index or listed as “Crawled — currently not indexed.”
- Fix: Submit the URL in Google Search Console’s URL Inspection, check
robots.txtandnoindexmeta tags, validatesitemap.xmlinclusion, and ensure the page loads quickly and returns a 200. If thin content is the issue, enrich it and re-request indexing. - Step-by-step re-index request:
- Inspect the page in Google Search Console.
- Fix any
noindex, 4xx/5xx, or crawl-blocking issues. - Improve on-page substance (add unique data, examples, schema).
- Submit the URL for reindexing and monitor coverage reports.
Improving CTR with metadata and schema
- Symptom: Good impressions but low clicks from SERPs.
- Fix: Rewrite title tags for clarity and intent alignment, add emotional or utility-focused modifiers (e.g., “2026 guide”, “free checklist”), and tighten meta descriptions to a compelling one-line benefit. Implement relevant schema (
Article,FAQ,Product) to enable rich results that stand out. Usestructured datatesting tools to validate. - Example: Changing a bland title like “Marketing Tips” to “Marketing Tips for SaaS Startups — 7 Growth Hacks” lifts CTR by making the page’s audience explicit.
Content intent mismatch resolution
- Symptom: Page ranks but bounce rates are high and conversions are low.
- Fix: Reassess search intent for target keywords—informational, transactional, or navigational—and align content format accordingly. If users expect a how-to but find a long opinion piece, create a short practical guide or split the content into two pages. Use internal linking to route intent-appropriate visitors to conversion-focused pages.
Operational tips and quick wins
- Quick crawl check: Use
site:yourdomain.com keywordto spot duplicates. - Thin content triage: Merge similar posts or add unique case studies, data, or tooling screenshots.
- Monitoring cadence: Review Search Console and analytics weekly for new coverage issues.
For teams automating content pipelines, tools that enforce canonical rules and auto-populate schema can prevent many of these problems up front—Scaleblogger’s workflow automation is one option to consider for scaling those guardrails. Smooth indexing and intent alignment directly translate to better visibility and more useful traffic, so fix one small issue today and the payoff shows in steady improvements.
📥 Download: SEO Content Repurposing Checklist (PDF)
Tips for Success & Pro Tips
Start by treating SEO work like surgery: small, precise cuts now avoid larger operations later. Triage pages that already get clicks or impressions, then apply quick wins to lift CTR and visibility while building a pipeline of advanced tactics that compound over months.
Quick Wins Meta title tweak: Swap vague titles for benefit-driven ones (use numbers, action words, or year). Meta description refresh: Add a clear call-to-action and one keyword variant; keep under ~155 characters. Targeted internal links: Add 2–3 internal links from high-traffic posts to underperforming pages. Canonical fixes: Ensure duplicates point to a single canonical to stop rank-splitting.
Advanced Tactics Schema implementation: Add FAQ, HowTo, and VideoObject schema where applicable to capture SERP real estate. Content consolidation: Merge thin, overlapping posts into a definitive resource and 301 the rest. Media repurposing: Turn long posts into short videos and transcripts to capture new traffic channels. Automated monitoring: Set up scheduled reports that flag dips in clicks, impressions, and average position.
Quick wins vs. advanced tactics — when to apply each and expected impact
| Tactic | When to Use | Estimated Effort | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meta title optimization | Pages with impressions but low CTR | Low (10–30 min/page) | Moderate CTR lift (5–30%) |
| Add FAQ schema | How-to or Q&A style content | Medium (30–90 min) | Higher SERP real estate, rich result visibility |
| Consolidate duplicated posts | Multiple thin posts on same topic | High (2–8 hrs + editing) | Strong authority signal, rank consolidation |
| Create video transcripts | Long-form posts or webinars | Medium (1–3 hrs) | Improves accessibility, keyword coverage |
| Automate performance reports | Sites with >100 pages | Medium (initial setup 2–6 hrs) | Faster reaction to drops, better prioritization |
Key insight: Quick metadata and internal-link fixes are low-effort, high-immediacy moves. Schema and consolidation take more work but deliver sustained ranking gains.
- Audit pages by impressions and CTR.
- Apply meta title + description changes to the top 20 pages.
- Implement schema on the 10 highest-opportunity pages.
- Consolidate overlapping posts and set up redirects.
- Automate weekly performance reports and alerts.
For teams ready to automate this workflow and scale content faster, consider tools that offer AI-powered SEO tools and content pipelines—Scaleblogger.com is one option that integrates automation with content scoring. Small, consistent wins compound: start with metadata and internal links this week, then build schema and consolidation into next quarter’s roadmap.
Measuring Success and Scaling the Process
Start by deciding which metrics actually prove that content is doing its job: traffic is just the beginning. Measure a mix of discovery (organic sessions, CTR), engagement (time on page, scroll depth), and business impact (leads, assisted conversions). Build a repeatable SOP that captures how those metrics are tracked, who owns each signal, and what triggers a scaling decision. The practical output should be a living document that teams follow when a piece of content hits performance thresholds and when it needs remediation or expansion.
SOP Template: components and how to fill them
Objective: Short statement tying content to a business metric (e.g., increase organic leads by 20% from topic cluster X).
Scope: Which content types, topics, and languages this SOP covers.
Success Metrics: List primary and secondary KPIs, using organic sessions, CTR, and revenue-attributed leads where possible.
Data Sources: Tools and dashboards (e.g., Google Analytics, Search Console, internal CRM).
Measurement Cadence: How often metrics are checked (daily for new posts, weekly for live content, monthly for audits).
Decision Rules: Specific thresholds that trigger actions (e.g., if CTR drops >15% vs. baseline, run headline test).
Action Steps: Concrete tasks for remediation, growth, or replication.
Owners: Who executes each step and who signs off.
Audit Log: Where changes and outcomes are recorded.
Assigning roles and responsibilities
- Content Owner: Owns topic strategy and sets objectives.
- Data Analyst: Pulls metrics and flags anomalies.
- Editor: Runs optimization/playback cycles.
- Automation Engineer: Builds scripts and integrations.
- Stakeholder: Signs off on scaling budget and priorities.
Automation opportunities to scale work
- Create
data pullsthat refresh performance dashboards nightly. - Automate low-risk content updates using templates and
bulk replacescripts. - Use scheduling APIs to enqueue replication across language or vertical variants.
- Wire alerts for KPI thresholds into Slack or email.
> Industry analysis shows content teams that automate metric collection cut reporting time by a large margin and scale output without proportionally increasing headcount.
Periodic audit schedule
- Weekly checks: New-post performance and urgent fixes.
- Monthly reviews: Topic-cluster performance and replication candidates.
- Quarterly audits: SOP effectiveness, tool integrations, and ROI.
Link workflows to a playbook that lists repeatable scaling patterns—identify winners, clone formats, automate distribution, and iterate. For teams looking to ramp faster, adopting AI-driven pipelines to score and prioritize content makes scaling predictable; see how to Scale your content workflow for frameworks and automation patterns that map directly to these SOPs.
These steps turn measurement from a reporting chore into an operational signal for scaling—so wins are replicated and underperformers are corrected before they waste budget.
This whole process comes down to three practical moves: audit what you already have, apply targeted keyword optimization as you repurpose, and measure distribution performance so you can iterate. If you followed the workflow—prioritizing high-traffic pillar posts, splitting them into video scripts and newsletter hooks, and optimizing titles/descriptions—you’ve already removed the busiest part of the work. Teams that used the audit-first approach saw clearer topic gaps and faster wins when they focused repurposing on pages with existing authority. If you’re wondering how to start, pick one pillar post, map three repurposed formats, and schedule two rounds of tracking in the first 30 days; if you’re asking what matters most, traffic trends and engagement per format are the signals to watch.
For teams looking to scale without burning hours on manual conversions, platforms that automate workflows can shave weeks off the cycle. To streamline this process, platforms like Explore Scaleblogger to automate and scale your content repurposing integrate keyword optimization and distribution steps so repurposed assets stay visible and discoverable. Next step: choose one post to repurpose this week, set up keyword-focused headlines for each format, and check performance after two weeks—small, consistent experiments beat one big overhaul.

