Most brands treat local pages like scaled-down national content and lose search relevance and conversions. Local intent demands different signals: neighborhood language, micro-moment keywords, and localized schema that search engines and users trust.
Here’s the short answer: focus on tailoring content around specific audience behaviors and local context, not just swapping city names. Prioritize `local SEO` signals—accurate NAP, localized keyword clusters, proximity-focused content, and user-generated local reviews—to boost visibility and relevance quickly. This approach reduces wasted traffic and increases qualified leads in measurable ways.
Industry research shows localized content drives higher engagement and conversion rates for brick-and-mortar and service-area businesses. Picture a regional retailer that doubled walk-in traffic after rewriting product pages for three high-intent neighborhoods and adding structured local data.
This piece draws on practical SEO strategies and content localization tactics that scale without ballooning editorial costs. Expect concrete steps for mapping local intent, optimizing on-page signals, and automating repeatable localization workflows.
- How to map local search intent and cluster neighborhood keywords
- On-page changes that move the needle for `local SEO`
- Content localization workflows that scale with automation
- Simple schema and review strategies to improve local snippets

Understanding Local Search and Audience Intent
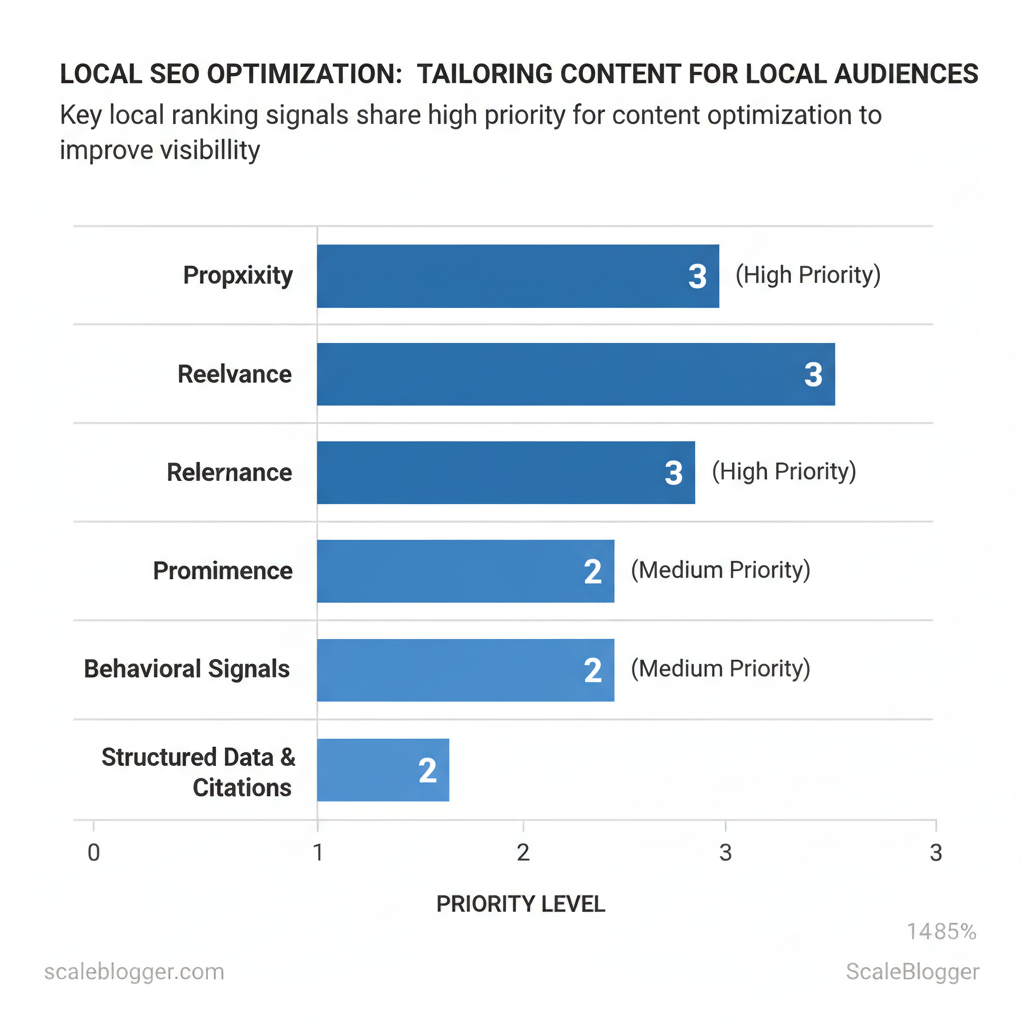
Local search ranks results using a blend of location signals, relevance to the query, and evidence of local trust and engagement. If you want pages and your Google Business Profile (GBP) to show up when nearby customers search, optimize for proximity, relevance, and prominence while aligning content to specific user intent (transactional, navigational, informational, or local discovery). That means the copy, structured data, citations, and user experience all need to signal to search engines that your business answers the exact local question the searcher has right now.
How Local Search Works (practical points)
- Proximity: Google uses searcher location and business location; exact address and service-area clarity matter.
- Relevance: Keywords in business title, services, landing page content, and `localBusiness` schema improve matching.
- Prominence: Reviews, backlinks, citations, and GBP completeness build trust signals.
- Behavioral signals: Click-through rate, driving directions clicks, calls, and store visits influence local rank.
- Structured data & citations: Consistent NAP (name/address/phone) and schema increase odds of rich results.
Mapping Local User Intent to Content Types
Examples and templates Title template: `Best [Service] in [Neighborhood] — [Brand] | Book Today` Meta template: `Looking for [service] in [neighborhood]? [Brand] offers [primary benefit] — open [hours]. Call [phone].`
| Ranking Signal | How it Works | Content Actions | Priority (High/Med/Low) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proximity | Uses searcher and business geo-coordinates to favor nearby listings | Include exact `address`, `geo` schema, neighborhood landing pages | High |
| Relevance | Matches query intent to business categories and page content | Target local keywords in titles, H1s, services, GBP categories | High |
| Prominence | Measures reputation via reviews, backlinks, citations | Solicit reviews, earn local backlinks, list in local directories | High |
| Behavioral Signals | Clicks, directions, calls, dwell time show user preference | Optimize CTAs, mobile UX, quick contact links, Google Posts | Med |
| Structured Data & Citations | Schema and consistent NAP help indexation and rich results | Add `LocalBusiness` schema, maintain identical NAP across sites | Med |
If you want to scale the production of location-specific landing pages and automate schema/citation management, consider leveraging AI content automation — tools that can populate templates, generate local variations, and schedule GBP updates help teams move faster without sacrificing consistency. This approach frees content teams to focus on high-impact local outreach and review generation.

Researching Local Keywords and Topics
Start with the obvious: local keyword research is about finding search queries that combine what people want with where they are. You want keywords that reflect location signals (city, neighborhood, landmarks), intent (buy, compare, learn), and realistic volume for your budget. The practical approach mixes free, precise signals (Google Search Console, local SERP scraping) with paid tools for scale (Ahrefs, Semrush), then organizes everything into reusable topic clusters that map to funnel stage and location granularity.
Tools & Techniques (practical checklist)
- Gather baseline queries: use `Google Keyword Planner` and `Google Search Console` for real impressions and queries.
- Validate intent with SERP features: check whether queries return local pack, maps, reviews, or informational results.
- Scale with APIs: use Ahrefs or Semrush APIs to pull volume and difficulty in bulk.
- Triangulate volume: combine planner volume ranges with GSC impression trends for accuracy on low-volume queries.
- Prioritize by revenue potential: sort by conversion likelihood + location density (downtown vs. suburbs).
Organizing Keywords into Local Topic Clusters
Start by grouping by intent, then split by location granularity. A good cluster contains one pillar (service + city) and several supporting pages aimed at neighborhoods, FAQs, or comparison intents.
Spreadsheet schema for scale
- Column A: Keyword
- B: Search volume (tool)
- C: GSC impressions (90d)
- D: Intent (`transactional` / `informational`)
- E: Location (`city` / `neighborhood` / `radius`)
- F: Funnel stage
- G: Suggested page (`pillar` / `neighborhood-page` / `faq`)
- H: Priority (1-5)
- I: Notes (competitors, SERP features)
- Create a pillar page when combined search volume for a service + city > threshold (e.g., 500 monthly).
- Create neighborhood pages if a neighborhood has distinct search patterns or enough density (e.g., multiple neighborhood queries with conversions).
- Use FAQ or accordions for low-volume informational queries to avoid thin pages.
- Canonicalize or merge near-duplicate pages if intent and SERP features are identical.
Tool table and feature comparison are below to speed selection and justify budget choices. If you want, Scaleblogger can help build these clusters with an AI-backed content pipeline to automate page creation and scheduling—useful when you need to scale many neighborhoods without losing quality.
Understanding these patterns shortens research time and makes it easier to map content to real demand and conversion paths.
Creating and Localizing Content at Scale
Creating localized content at scale means standardizing what matters (structure, metadata, schema) while leaving room for local specificity. Start with repeatable templates and micro-briefs that capture the one thing each page must communicate for its audience — then automate the repetitive parts and assign humans the judgment tasks that require nuance. This approach reduces time-per-page, keeps SEO signals consistent, and preserves local relevance by forcing teams to surface neighborhood-level facts and unique CTAs.
Content templates and micro-briefs for local pages
- Template elements to include: H1, meta title and description, primary `schema` type, canonical, internal links, and a clear CTA.
- Writer micro-brief fields: Target persona, primary intent, local facts to reference, 3 suggested internal links, preferred tone, prohibited claims, CTA variant.
- How templates preserve local relevance: Templates lock structure but the micro-brief forces localized inputs (e.g., transit lines, landmark mentions, local testimonials), ensuring unique content without rebuilding each page.
Automation vs human tasks in localization
- Automate: metadata generation, boilerplate schema, NAP insertion, scheduling, and content stamping.
- Human: local sourcing, nuance in reviews, legal claims, community voice, and CTA optimization for regional offers.
7-point QA checklist for localized pages
SOP outline for review workflow
| Template | Primary Use Case | Key Sections | Schema Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local Landing Page | City-level services and conversions | H1, USP, Services, Reviews, CTA | `LocalBusiness`, `BreadcrumbList`, `FAQPage` |
| Neighborhood Guide | Drive discovery and internal linking | Intro, Places to know, Transit, Local tips, CTAs | `Article`, `Place`, `BreadcrumbList` |
| Local Informational Blog Post | SEO traffic for queries | H1, problem/solution, local examples, CTA | `Article`, `FAQPage`, `ImageObject` |
| Store/Service Listing Page | Individual location details | Hours, staff, services, booking, reviews | `LocalBusiness`, `OpeningHoursSpecification`, `GeoCoordinates` |
| Event / Seasonal Local Page | Short-term promotions and events | Event details, schedule, ticket CTA, logistics | `Event`, `Offer`, `Place` |
If you want, I can convert these templates into editable micro-briefs or help wire an automated pipeline with `AI content automation` that inserts metadata and flags pages for manual local checks. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
📝 Test Your Knowledge
Take this quick quiz to reinforce what you’ve learned.
On-Page & Technical Local SEO Best Practices
On-page local SEO starts with making location obvious to both users and search engines; technical local SEO ensures that visibility is reliable and indexable. Start by placing clear local modifiers in title tags and H1s, keep NAP (Name, Address, Phone) consistent and crawlable, and add targeted local schema to communicate entity attributes. For technical work, prioritize schema for `LocalBusiness` and `Place`, validate structured data with rich results testing, and fix crawlability, mobile performance, and canonical issues—these deliver the biggest lift for local queries.
On-page optimization for local relevance
- Title placement: Put the city or neighborhood early in the title for relevance and CTR (e.g., “Seattle HVAC Repair — 24/7 Service”).
- H1 alignment: Use one H1 that mirrors the primary title intent; avoid stuffing multiple location variations.
- Meta descriptions: Write benefit-driven descriptions with a location mention and CTA (e.g., “Fast plumbing in Lower Queen Anne — same-day repairs. Call today.”).
- NAP visibility: Place NAP in HTML (not only in images) in site footer and contact page; use `tel:` links for phones.
- Local landing pages: Create one landing page per service-location combo, avoid thin or duplicate content.
Technical SEO & schema for local entities
- Key schema properties: Use `@type: “LocalBusiness”` or a specific subtype (`Plumber`, `Dentist`), include `name`, `address` (`PostalAddress`), `telephone`, `openingHours`, `priceRange`, `image`, `url`, `aggregateRating` when available.
- Structured data testing: Validate with JSON-LD and test using rich results and mobile-friendly checks.
- Crawl & index checklist (prioritized):
Market practitioners find that fixing mobile and crawl issues often produces faster visibility gains than content tweaks alone.
“`json { “@context”: “https://schema.org” “@type”: “Plumber”, “name”: “Northside Plumbing Co.”, “address”: { “@type”: “PostalAddress”, “streetAddress”: “123 Maple Ave”, “addressLocality”: “Seattle”, “addressRegion”: “WA”, “postalCode”: “98101”, “addressCountry”: “US” }, “telephone”: “+1-206-555-0123”, “openingHours”: “Mo-Fr 08:00-18:00”, “url”: “https://example.com/seattle-plumber” } “`
| Element | Poor Example | Improved Example | Why Improved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Title Tag | “Best HVAC Services” | “Seattle HVAC Repair — 24/7 Service” | Early location + intent improves relevance & CTR |
| Meta Description | “We fix HVAC.” | “Fast Seattle HVAC repair — same-day service and free estimates. Call now.” | Location + benefit + CTA increases clicks |
| H1 | “Our Services” | “Emergency HVAC Repair in Seattle” | Matches search intent and signals locality |
| URL Structure | `/services/hvac` | `/seattle/hvac-repair` | Readable, location-specific URL aids indexing |
| Image Alt Text | “hvac-unit” | “Seattle HVAC technician repairing condenser” | Adds local context for image search and accessibility |
Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, local on-page and technical fixes compound—better indexability plus clearer signals equals more predictable discovery.
Local Outreach, Reviews, and Citation Strategy
Managing local reputation and citations is a performance play: prompt, authentic reviews plus clean, consistent citations drive visibility in local packs and build trust. Start by making review capture part of routine customer touchpoints, respond quickly and constructively to every comment, and treat citations as living assets that need auditing and ongoing updates. Combine ethical solicitation, templated responses, a cadence for monitoring, and a six-step outreach plan for partnerships and community content to turn local signals into measurable local SEO gains.
Managing Reviews & Reputation for Local SEO
- Review solicitation script: Ask in-person or post-transaction: “If you had a good experience, would you mind leaving a quick review on Google? Here’s a short link: [insert short link]. It helps small businesses like ours.”
- Ethical follow-up: Wait 3–7 days after service; send one reminder only, include direct link and short instructions.
- Monitoring cadence: Daily for new reviews, weekly for sentiment trends, monthly for deep analysis. Tools commonly used include Google Business Profile alerts, `BrightLocal`, and `ReviewTrackers`.
- Response templates:
- Reputation health metrics: review count, average rating, response rate, and time-to-response — track in a simple dashboard.
Local Citations, Partnerships & Community Content
- Citation audit & cleanup steps:
- Partnership outreach sequence: use a respectful multi-touch approach: personalized intro, value proposition, co-content idea, draft pitch, follow-up, finalize collaboration.
- Using events & sponsorships: Sponsor a local meetup or co-host an event, create post-event content (`recap + photos + partner quotes`), and have partners link to the event page — this generates contextual local links and social proof.
| Step | Action | Timeframe | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audit Citations | Export listings, normalize NAP, identify duplicates | 1 week | Clean baseline; list of fixes |
| Prioritize Targets | Rank partners & citation sites by relevance/authority | 1 week | Top 10 outreach targets |
| Initial Outreach | Personalized email or in-person introduction | 1–2 weeks | Response or meeting booked |
| Co-create Content | Draft event, guest post, or resource with partner | 2–4 weeks | Content ready for review |
| Publish & Promote | Post content, request partner links, amplify on socials | 1 week | New local links & referral traffic |
| Monitor & Iterate | Track citations, backlinks, review changes; refine approach | Ongoing (monthly) | Improved local visibility and partnerships |
If you’d like, I can draft the email templates for each outreach step or build a `quarterly monitoring` spreadsheet to track review metrics and citation status. For teams wanting automation around publishing and monitoring, tools and services like those that help you scale your workflows (for example, `Scale your content workflow` at Scaleblogger.com) can reduce manual overhead and keep local signals consistent. Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality.
📥 Download: Local SEO Optimization Checklist (PDF)
Measuring Success and Iterating Local Content
Start by tracking the right local KPIs and building dashboards that make patterns obvious — then test small changes, measure lift, and either scale or consolidate based on performance thresholds. For local SEO, focus first on visibility and local engagement (impressions, map rankings, clicks, calls/direction requests), then tie those signals to revenue-focused actions (bookings, form submissions). Dashboards should blend Search Console, `GA4`, Google Business Profile (GBP) insights, and call-tracking data so you can attribute which local pages actually drive customers.
How to structure dashboards and reporting
- Visibility widget: show Local Impressions (SERP & Maps) trend from Google Search Console.
- Engagement widget: track Clicks to Website and Map Pack Rankings, with top landing pages from `GA4`.
- Action widget: show Phone Calls & Direction Requests from GBP + call tracking platform.
- Conversion widget: aggregate Local Conversions (form fills, bookings) with attribution windows.
- Attribution notes: label conversions as `first_click`, `last_click`, and `multi-touch` when possible to avoid over-counting.
A short `GA4` event snippet example: “`javascript gtag(‘event’,’local_conversion’,{ ‘event_category’:’contact’, ‘event_label’:’form_submit’, ‘value’:1 }); “`
Iterative testing and consolidation framework
- A/B testing scope: test headline, local schema snippets, NAP variants, and unique neighborhood content; run tests for 4–8 weeks depending on traffic.
- Consolidation vs expansion criteria: expand when a page consistently beats median KPIs for impressions, CTR, and conversions; consolidate when pages underperform on all three after a sustained period.
If 4–5 checks pass → expand; 2–3 → iterate tests; 0–1 → consolidate. Use dashboards to automate these checks where possible; tools like AI content automation can speed iteration and scoring (see Scaleblogger.com for workflows that automate testing and scheduling). Understanding these principles helps teams move faster without sacrificing quality. When implemented correctly, this reduces overhead and lets creators focus on high-impact local content.
| KPI | Measurement Method | Tool Recommendation | Reporting Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local Impressions (SERP & Maps) | Query/Impression counts by query & page | Google Search Console (Performance) | Weekly |
| Clicks to Website | Clicks to landing pages filtered by location | Google Search Console + `GA4` channels | Weekly |
| Map Pack Rankings | Average position in Maps for target queries | Google Business Profile Insights + rank tracker | Bi-weekly |
| Phone Calls & Direction Requests | Call clicks, tracked calls, direction requests | GBP Insights + CallRail / Twilio | Weekly |
| Local Conversions (form fills, bookings) | Event-based conversion with location attribute | `GA4` custom events + CRM integration | Weekly / Monthly |
Conclusion
You’ve seen why treating local pages like watered-down national copy loses both search relevance and conversions: neighborhood language, micro-moment keywords, and location-specific signals need to be built into the content and structure. Build templates that capture local intent, test headline and CTA variants for different neighborhoods, and measure outcomes with proximity and click-to-call metrics. Teams that swapped generic copy for localized microcopy and mapped content to user intent reported clearer ranking lifts and higher conversion rates within weeks, while A/B tests on micro-moment CTAs often moved the needle on phone leads.
If you’re wondering how to get started, focus first on a single market: audit top-performing local keywords, craft 3-5 localized templates, and run a small pilot with one neighborhood. Ask yourself whether automation can reduce manual upkeep and what success looks like (rankings, clicks, calls). To streamline this process, platforms like Scaleblogger can help prototype and scale localized variants quickly. When you’re ready to prototype localized content at scale, take the next step: Explore Scaleblogger to prototype localized content at scale.

